Page 304 of 828
14-16
4) Fuel Injection During CDPF Regeneration
Page 308 of 828
15-50000-00
Fuel rail pressure
sensorEGR valveFuel temperature
sensor
Electric throttle bodyKnock sensor
(2 ea)
Coolant temperature
sensor
T-MAP sensorD20DTR ECU
E-VGT actuator
Water sensorGCU (Preglow control
unit)
E-EGR bypass valve
Page 310 of 828
15-70000-00
Fuel rail pressure
sensor
(2) Components for ECU Input
CAN
- ABS & ESP
- GCU
- Instrument
cluster
- TCUSwirl valve position
sensor
Differential
pressure sensorE-EGR valve
position sensorCamshaft position
sensorCoolant
temperature senso
r
Exhaust gas
temperature senso
r
HFM sensorOxygen sensorT-MAP sensor
Crankshaft position
sensor
Accelerator pedal
sensorThrottle position
sensorKnock sensor
-Auto cruise switch
- Rear right wheel
speed (without ABS)
- Refrigerant pressure
sensor
- Clutch pedal signal
- Blower switch signal
- Brake pedal signal
Water sensor
Page 312 of 828

15-90000-00
2) ECU Control
(1) Function
a. ECU Function
ECU receives and analyzes signals from various sensors and then modifies those signals into
permissible voltage levels and analyzes to control respective actuators.
ECU microprocessor calculates injection period and injection timing proper for engine piston
speed and crankshaft angle based on input data and stored specific map to control the engine
power and emission gas.
Output signal of the ECU microprocessor drives pressure control valve to control the rail pressure
and activates injector solenoid valve to control the fuel injection period and injection timing; so
controls various actuators in response to engine changes. Auxiliary function of ECU has adopted
to reduce emission gas, improve fuel economy and enhance safety, comforts and conveniences.
For example, there are EGR, booster pressure control, autocruise (export only) and immobilizer
and adopted CAN communication to exchange data among electrical systems (automatic T/M
and brake system) in the vehicle fluently. And Scanner can be used to diagnose vehicle status
and defectives.
<00760097008c00990088009b00900095008e0047009b008c00940097008c00990088009b009c0099008c0047009900880095008e008c00470096008d0047006c006a007c00470090009a0047009500960099009400880093009300a000470054005b005700
47009b009600470052005f005c00b6006a004700880095008b> protected from factors like oil,
water and electromagnetism and there should be no mechanical shocks.
To control the fuel volume precisely under repeated injections, high current should be applied
instantly so there is injector drive circuit in the ECU to generate necessary current during injector
drive stages.
Current control circuit divides current applying time (injection time) into full-in-current-phase and
hold-current-phase and then the injectors should work very correctly under every working
condition.
b. Control Function
Controls by operating stages
To make optimum combustion under every operating stage, ECU should calculate proper
injection volume in each stage by considering various factors.
Starting injection volume control
During initial starting, injecting fuel volume will be calculated by function of temperature and
engine cranking speed. Starting injection continues from when the ignition switch is turned to
ignition position to till the engine reaches to allowable minimum speed.
Driving mode control
If the vehicle runs normally, fuel injection volume will be calculated by accelerator pedal travel
and engine rpm and the drive map will be used to match the drivers inputs with optimum
engine power. -
-
-
Page 313 of 828
15-10
(2) Fuel injection control
a. Multi injection
Fuel injection process consists of 3 steps: Main Injection, Pilot Injection, Post Injection
InjectionFunction
MainProduces engine power
Pilot 1Reduces PM by injecting
before main injection.AfterPM control
Pilot 2Reduces NOx and noise by
shortening main injection delay
due to flammability Post 1Reduces PM by enabling fuel
activation.
PreControls NOx emission level,
Combustion noise and
Stable idle Post 2Activates CDPF by increasing
exhaust gas temperature and
supplying reduction material
Pilot injection ▶
Multi injection ▶
Page 314 of 828
15-110000-00
b. Pilot Injection
Injection before main injection. Consists of 1st and 2nd pilot injection, and Pre-injection
Inject a small amount of fuel before main injection to make the combustion smooth. Also, called
as preliminary injection or ignition injection. This helps to reduce Nox, engine noise and vibration,
and to stabilize the idling.
The injected fuel volume is changed and stopped according to the coolant temperature and
intake air volume.
Pilot injection is much earlier than main injection due to higher engine rpm
Too small injection volume (insufficient injection pressure, insufficient fuel injection volume
in main injection, engine braking)
System failure (fuel system, engine control system) -
-
-
Pilot injection
Main injection
Combustion pressure with pilot injection
Combustion pressure without pilot injection 1.
2.
1a.
2b. Stop conditions
Combustion pressure characteristic curve for pilot injection ▶
Page 315 of 828
15-12
c. Main Injection
The power of the vehicle is determined by the main fuel injection volume.
Main injection calculates the fuel volume based on pilot injection. The calculation uses the value
for accelerator pedal position, engine rpm, coolant temperature, intake air temperature, boost
pressure, boost temperature and atmospheric pressure etc.
d. Post Injection
Injection after main injection. Consists of After injection, Post 1, Post 2 injection.
Post injection reduces PM and smoke from exhaust gas. No actual output is generated during
these injections, instead, fuel is injected to the unburned gas after main injection to enable fuel
activation. The PM amount in the emission and smoke can be reduced through these processes.
Only up to 5 types of injections can be performed within 1 cycle. If these 7 injections are all
performed, fuel economy and emission performance becomes poor.
Page 316 of 828
15-130000-00
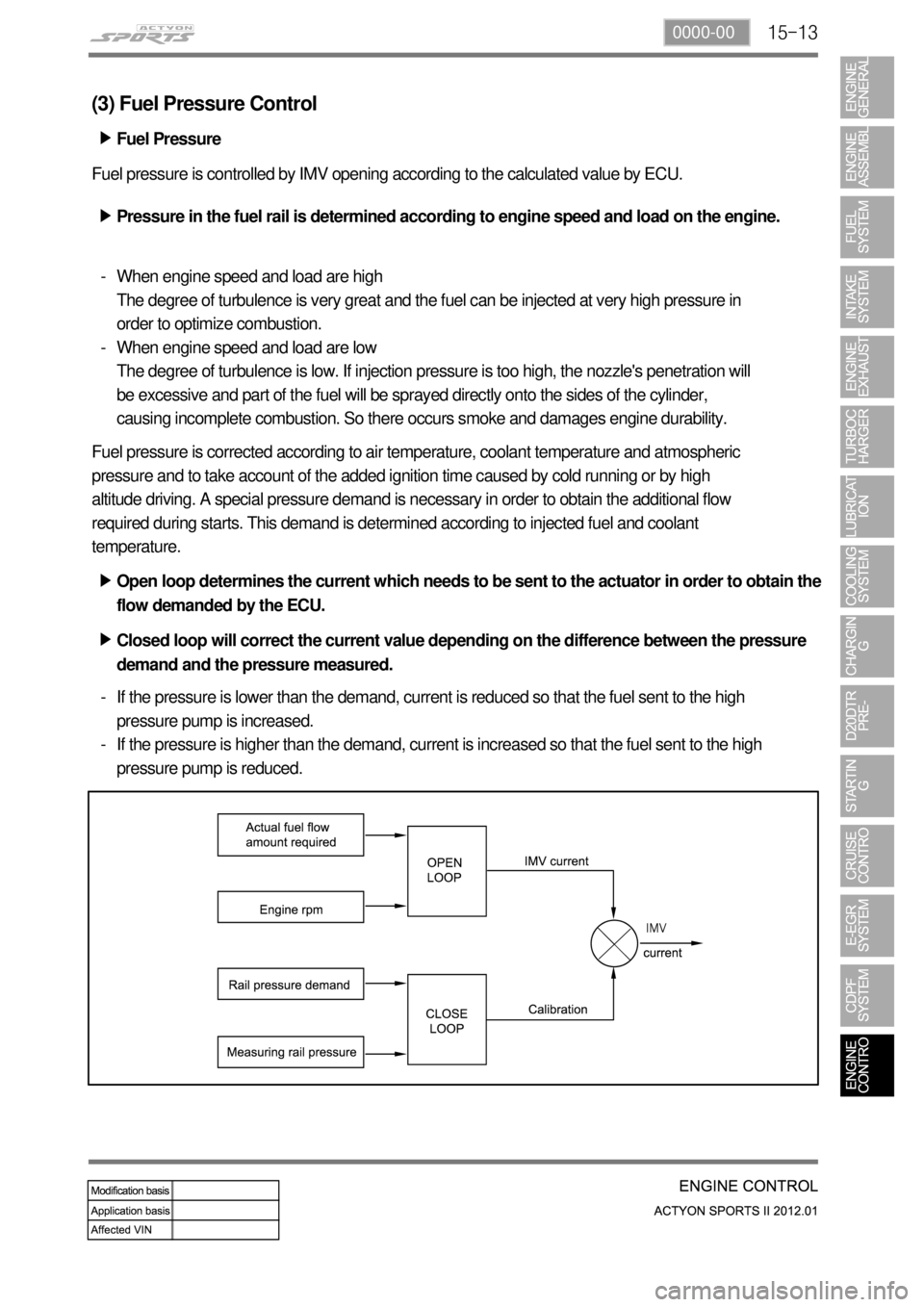
(3) Fuel Pressure Control
Fuel pressure is controlled by IMV opening according to the calculated value by ECU.
Pressure in the fuel rail is determined according to engine speed and load on the engine. ▶
When engine speed and load are high
The degree of turbulence is very great and the fuel can be injected at very high pressure in
order to optimize combustion.
When engine speed and load are low
The degree of turbulence is low. If injection pressure is too high, the nozzle's penetration will
be excessive and part of the fuel will be sprayed directly onto the sides of the cylinder,
causing incomplete combustion. So there occurs smoke and damages engine durability. -
-
Fuel pressure is corrected according to air temperature, coolant temperature and atmospheric
pressure and to take account of the added ignition time caused by cold running or by high
altitude driving. A special pressure demand is necessary in order to obtain the additional flow
required during starts. This demand is determined according to injected fuel and coolant
temperature.
Open loop determines the current which needs to be sent to the actuator in order to obtain the
flow demanded by the ECU. ▶
Closed loop will correct the current value depending on the difference between the pressure
demand and the pressure measured. ▶
If the pressure is lower than the demand, current is reduced so that the fuel sent to the high
pressure pump is increased.
If the pressure is higher than the demand, current is increased so that the fuel sent to the high
pressure pump is reduced. -
-Fuel Pressure ▶