Page 308 of 1082
15-32
c. Input/Output for oxygen sensor
Page 309 of 1082
15-330000-00
d. Oxygen sensor control
The wide band oxygen sensor uses ZnO2. It produces the voltage by movement of oxygen ions when
there is oxygen concentration difference between exhaust gas and atmosphere.
If a certain voltage is applied to the sensor, the movement of oxygen ions occurs regardless of the
oxygen density. The current generated through this flow of ions, is called pumping current (IP), and the
oxygen sensor measures this value.
Page 310 of 1082
15-34
Coolant temp.
sensor
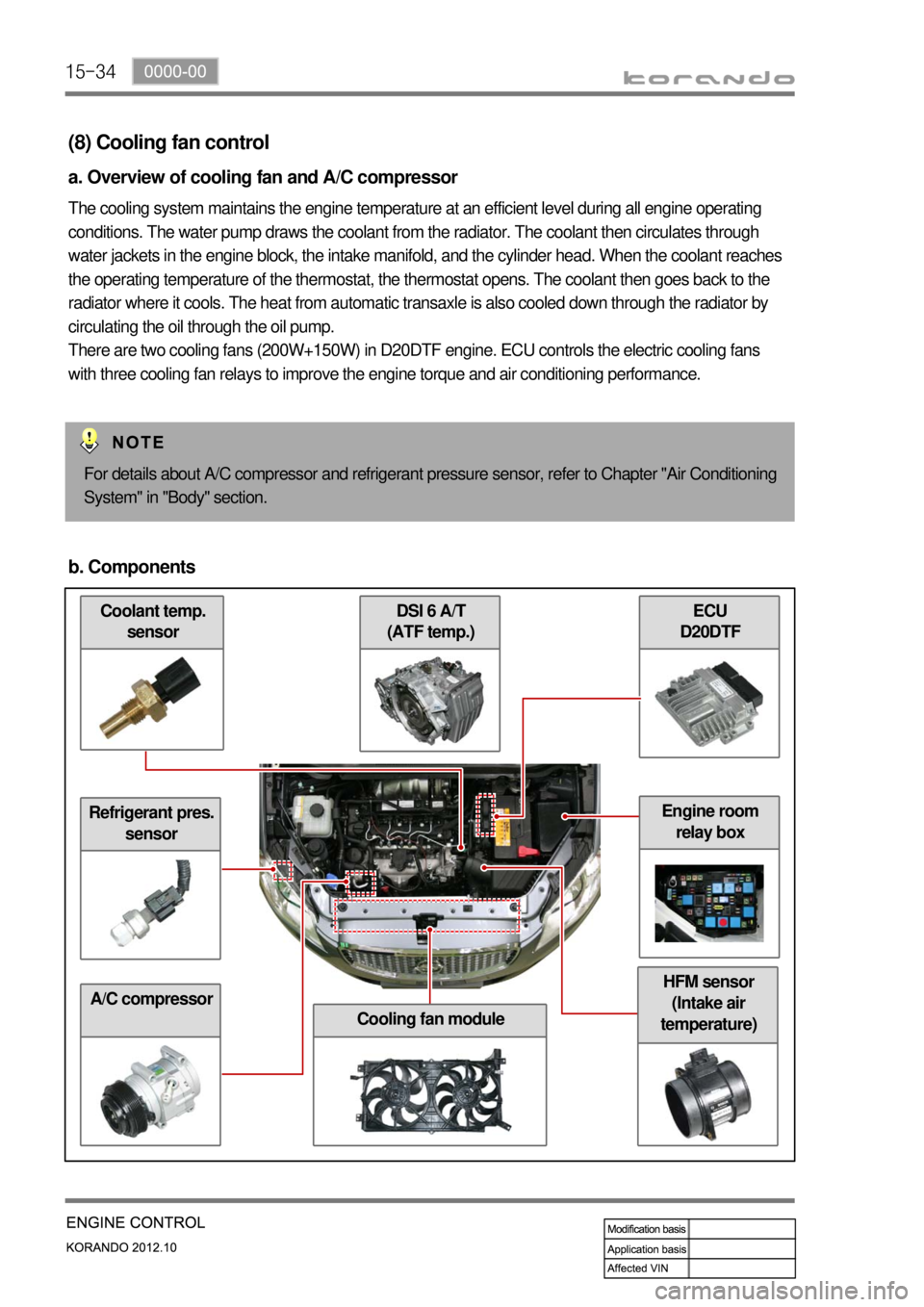
(8) Cooling fan control
a. Overview of cooling fan and A/C compressor
The cooling system maintains the engine temperature at an efficient level during all engine operating
conditions. The water pump draws the coolant from the radiator. The coolant then circulates through
water jackets in the engine block, the intake manifold, and the cylinder head. When the coolant reaches
the operating temperature of the thermostat, the thermostat opens. The coolant then goes back to the
radiator where it cools. The heat from automatic transaxle is also cooled down through the radiator by
circulating the oil through the oil pump.
There are two cooling fans (200W+150W) in D20DTF engine. ECU controls the electric cooling fans
with three cooling fan relays to improve the engine torque and air conditioning performance.
For details about A/C compressor and refrigerant pressure sensor, refer to Chapter "Air Conditioning
System" in "Body" section.
b. Components
Refrigerant pres.
sensor
A/C compressor
ECU
D20DTF DSI 6 A/T
(ATF temp.)
Cooling fan module
HFM sensor
(Intake air
temperature)
Engine room
relay box
Page 312 of 1082

15-36
d. Cooling fan and A/C compressor control
Conditions for cooling fan ▶
The cooling fan module controls the cooling fan relay, high speed relay and low speed relay. The cooling
fan is controlled by the series and parallel circuits.
A/C switch Cooling fanCoolant temperature Refrigerant pressure
A/C
compressor
OFF OFF Coolant temp. < 90℃-
LO 90℃ ≤ Coolant temp.
< 105℃-
HI105℃ ≤ Coolant temp-
ONLO
Coolant temp. < 105℃Refrigerant pressure <
18 bar
ON HI18 bar ≤ Refrigerant
pressure
HI105℃ ≤ Coolant temp.
< 115℃-
HI115℃ ≤ Coolant temp. - OFF (cut)
A/C compressor OFF conditions ▶
Coolant temperature: below -20℃ or over
115℃
Approx. 4 seconds after starting the engine
Engine rpm: below 650 rpm or over 4500 rpm
When abrupt acceleration
Refrigerant pressure:
* OFF below 2.0 kg/㎠, then ON over 2.4 kg/㎠
* OFF over 30 kg/㎠, then ON below 21.4 kg/㎠ -
-
-
-
-
The output voltage from refrigerant pressure sensor is 1.7 V to 3.5 V when the refrigerant pressure is 10
to 24 kgf/㎠ with A/C "ON".Output voltage according to refrigerant pressure ▶
Cooling fan control according to ATF temperature ▶
ATF temperature Cooling fan Remark
Over 100˚CHigh speed -
Page 313 of 1082
15-370000-00
HFM
(Intake air temp.)Coolant temp.
sensor
(9) PTC heater control
a. Overview
The supplementary electrical heater is installed in DI engine equipped vehicle as a basic equipment. The
PTC system is operated according to two temperature values measured at the coolant temperature
sensor and HFM sensor. This device is mounted in the heater air outlet and increase the temperature of
air to the passenger compartment. Because PTC system is heated by electrical power, high capacity
alternator is required. PTC does not operate during engine cranking, while the battery voltage is lower
than 11 V or during preheating process of glow plugs.
b. Components
PTC heater
D20DTF
ECU
Engine room relay box
A: PTC 1 (changeable)
B: PTC 2,3 (not changeable)
Page 315 of 1082
15-390000-00
d. Control conditions
Operation Operating condition PTC Heater
HI
(PTC2)- Coolant temperature < 15℃
PTC HI ON
LO
(PTC1)- Coolant temperature 15℃ ≤ 65℃, intake air
temperature ≤ -10℃
- Coolant temperature 15℃ < 65 to 60℃, intake air
temperature <-10℃ to 0℃
- Coolant temperature 15℃ ≤ 60℃, intake air
temperature ≤ 0℃ to 5℃PTC LO ON
Stop- A/C blower switch OFF
- Defective ambient air temperature sensor
(including open or short circuit)
- Engine cranking
- Low battery voltage (below 11V)
- During pre-glow process (glow indicator ON)
Operation diagram for PTC heater LO (step 2) ▶
Page 320 of 1082
15-44
Front temp. sensor
(11) CDPF control
a. Overview
As the solution for environmental regulations and PM Particle Material) of diesel engine, the low emission
vehicle is getting popular. This vehicle is equipped with an extra filter to collect the soot and burn it again
so that the amount of PM in the exhaust gas passed through the DOC (Diesel Oxidation Catalyst) is
reduced. The CDPF (Catalyst & Diesel Particulate Filter) is an integrated filter including DOC (Diesel
Oxidation Catalyst) and DPF (Diesel Particulate Filter).
For details, refer to Chapter "CDPF".
b. Components
Rear temp. sensorCDPF (DOC+DPF)
Throttle valveD20DTF ECUDifferential pres.
sensorOxygen sensor
Page 322 of 1082

15-46
Rear temp. sensor:
Measure DPF
temp.DPF performs
recycling
(combustion)
process at 600C,
and rear
temperature sensor
monitors the
temperature of DPF.
Differential pressure
sensor measures the
pressure difference
between pre-CDPF
and post-CDPF (If
PM has been
accumulated, the
measured value is
over the specified
value).Diff. pres. sensor:
Measure
pressure between
front side and
rear side of CDPF
Injector: Control
post injection
Front temp.
sensor: Measure
DOC temp.DOC performs
oxidation and
reduction process at
300~500˚C, and
front temperature
sensor monitors the
temperature of
DOC.
Electronic
throttle body:
Control intake ai
r
mass
ECU (DCM 3.7)
d. Operation process
When the differential pressure sensor detects the pressure difference between the front and the rear
side of CDPF, the sensor sends signal indicating the soot is accumulated and the post injection is
performed to raise the temperature of exhaust gas. The amount of fuel injected is determined according
to the temperature of exhaust gas detected by the rear temperature sensor. If the temperature is below
600°C, the amount of fuel injected is increased to raise the tem
perature. If the temperature is over
600°C, the amount of fuel injected is decreased or not controlled. When the engine is running in
low load range, the amount of post injection and the amount of intake air are controlled. It is to raise the
temperature by increasing the amount of fuel while decreasing the amount of intake air.
T-MAP sensor
Intake air
mass
Exceed PM
limitBooster
pressure/
temperaturePost injection
Control intake air
mass