Page 943 of 1082
10-12
5. SYSTEM OPERATION
1) Block Diagram of ABS HECU
Page 944 of 1082

10-134890-00
2) Basic Theory of ABS Function
To give you a better understanding of the tasks and functions of ABS, we will first look at the physics
principles.
(1) Stopping distance
The stopping distance depends on the vehicle weight and initial speed when braking starts. This also
applies for vehicle with ABS, where ABS always tries to set an optimum brake force on each wheel. As
great forces are exerted between the tires and the carriageway when braking, even with ABS the wheels
may scream and rubber is left on the road. With an ABS skid mark one may be able to clearly recognize
the tire profile. The skid mark of an ABS vehicle does not however leave any hint of the speed of the
vehicle in the case of an accident, as it can only be clearly drawn at the start of braking.
(2) Brake force on a wheel
The maximum possible brake force on a wheel depends on the wheel load and the adhesion coefficient
between tire and carriageway. With a low adhesion coefficient the brake force, which can be obtained is
very low. You are bound to know the result already from driving on winter roads. With a high adhesion
coefficient on a dry road, the brake force, which can be obtained, is considerably higher. The brake
force, which can be obtained, can be calculated from below formula:
Maximum brake force ▶
FBmax = wheel load FR x coefficient of frictionMh
The braking process cannot be described sufficiently
accurately with the brake forces calculated. The
values calculated only apply if the wheel is not locked.
In the case of a locking wheel, the static friction turns
into lower sliding friction, with the result that the
stopping distance is increased. This loss of friction is
termed "slip" in specialist literature.
Page 945 of 1082
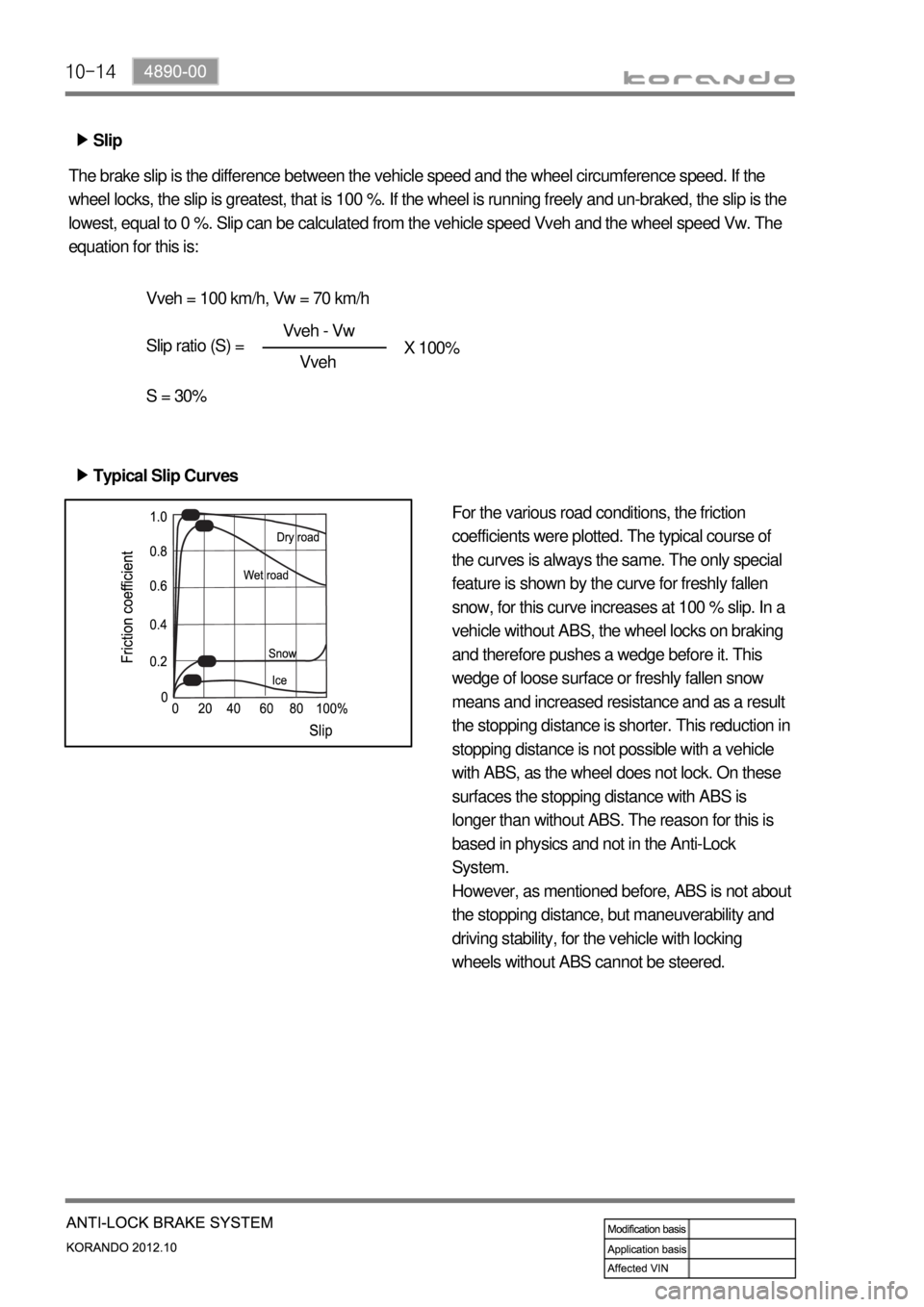
10-14
Slip ▶
The brake slip is the difference between the vehicle speed and the wheel circumference speed. If the
wheel locks, the slip is greatest, that is 100 %. If the wheel is running freely and un-braked, the slip is the
lowest, equal to 0 %. Slip can be calculated from the vehicle speed Vveh and the wheel speed Vw. The
equation for this is:
Vveh = 100 km/h, Vw = 70 km/h
Slip ratio (S) =
For the various road conditions, the friction
coefficients were plotted. The typical course of
the curves is always the same. The only special
feature is shown by the curve for freshly fallen
snow, for this curve increases at 100 % slip. In a
vehicle without ABS, the wheel locks on braking
and therefore pushes a wedge before it. This
wedge of loose surface or freshly fallen snow
means and increased resistance and as a result
the stopping distance is shorter. This reduction in
stopping distance is not possible with a vehicle
with ABS, as the wheel does not lock. On these
surfaces the stopping distance with ABS is
longer than without ABS. The reason for this is
based in physics and not in the Anti-Lock
System.
However, as mentioned before, ABS is not about
the stopping distance, but maneuverability and
driving stability, for the vehicle with locking
wheels without ABS cannot be steered. Typical Slip Curves ▶Vveh - Vw
VvehX 100%
S = 30%
Page 946 of 1082

10-154890-00
KAMM circle ▶
Before we go into the Kamm circle, you should
know that a tire offers a maximum of 100 %
transmissibility. It is all the same for the tire
whether we require 100 % in the direction of
braking or in the direction of the acting lateral
force, e.g. when driving round curves. If we drive
into a curve too fast and the tire requires 100 %
transmissibility as cornering force, the tire cannot
transmit any additional brake force. In spite of the
ABS the car is carried out of the curve. The
relationship between brake force B and cornering
force S is shown very clearly in the Kamm circle. I
f
we put a vehicle wheel in this circle, the
relationship becomes even clearer. In this
relationship: as long as the acting forces and the
resulting force remain within the circle, the vehicle
is stable to drive. If a force exceeds the circle, the
vehicle leaves the road.
Brake force
When depressing the brake pedal the brake force
increases to the maximum, then the brake force
decreases until the wheel locks.
Cornering force
The cornering force is a maximum when the
wheel is turning freely with zero slip. When
braking the cornering force falls to zero if the
wheel locks (slip 100 %).
ABS operating range
The operating range starts just before the
maximum brake force and ends in maximum, for
the unstable range then begins, in which no
further modulation is possible. The ABS controls
the regulation of the brake pressure so that the
brake force only becomes great enough for a
sufficient proportion of cornering force to remain.
With ABS we remain in the Kamm circle as long
as the car is driving sensibly. We will leave driving
physics with these statements and turn to the
braking systems with and without ABS. -
-
- Brake and cornering force ▶
Page 947 of 1082
10-16
3) Basic ABS Control
Operation of ABS control unit ▶
Applications of the ABS control unit The signals
produced by the wheel sensors are evaluated in
the electronic control unit. From the information
received, the control unit must first compute the
following variables:
Wheel speed
Reference speed
Deceleration
Slip -
-
-
-
Reference speed ▶
The reference speed is the mean, I.e. average speed of all wheel speeds determined by simple
approximation.
Simplified ABS control ▶
If, during braking, one wheel speed deviates from the reference speed, the ABS control unit attempts to
correct that wheel speed by modulating the brake pressure until it again matches the reference speed.
When all four wheels tend to lock, all four wheels speeds suddenly deviate from the previously
determined reference speed. In that case, the control cycle is initiated again in order to again correct the
wheel speed by modulating the brake pressure.
Page 951 of 1082
10-20
2) DUMP (ABS is working) Mode
Even when the hydraulic pressure on each circuit is constant, the wheel can be locked as the wheel
speed decreases. This is when the ABS HECU detects the wheel speed and the vehicle speed and
gives the optimized braking without locking the wheels. In order to prevent the hydraulic pressure from
increasing, the inlet valve will be closed, the outlet valve will be opened and the oil will flow into the low
pressure chamber. In addition, the ABS HECU operates the pump to circulate the oil in the low pressure
chamber to the master cylinder. This may make the driver to feel the brake pedal vibration and some
noises.
Solenoid valve Valve Open/Close Pump motor
Inlet valve - Normal open (NO) valve Close
ON
Outlet valve - Normal close (NC) valve Open
Page 952 of 1082
10-214890-00
3) HOLD (ABS is working) Mode
As hydraulic pressure on each wheel increases, the wheel tends to lock. In order to prevent the wheel
from locking, the hydraulic valve modulator operates the inlet valve control solenoid to stop increasing
the hydraulic pressure by closing the inlet valve. At this moment, the outlet valve is closed. This
procedure helps the wheel to maintain a constant hydraulic pressure.
Solenoid valve Valve Open/Close Pump motor
Inlet valve - Normal open (NO) valve Close
OFF
Outlet valve - Normal close (NC) valve Close
Page 953 of 1082
10-22
4) RISE (ABS is working) Mode
As the wheel speed increases, the inlet valve opens and the wheel's pressure increases due to the
master cylinder pressure. In addition, the pump circulates the oil in the low pressure chamber to the
wheel. As the hydraulic pressure to the wheel increases, the wheel speed will reduce. This operation
continues repetitively until there are no signs that the ABS HECU tends to lock the wheels. Since the
ABS hydraulic pressure control process takes place repeatedly for a short time, there may be some
vibration and noises at the brake pedal.
Solenoid valve Valve Open/Close Pump motor
Inlet valve - Normal open (NO) valve Open
ON
Outlet valve - Normal close (NC) valve Close