2011 SKODA ROOMSTER seats
[x] Cancel search: seatsPage 103 of 212

Safety
Passive Safety
Basic information
Driving the safe way Passive safety measures reduce the risk of injury in accident situa-
tions.
In this section you will find important information, tips and notes on the subject of
passive safety in your vehicle. We have combined everything here which you
should be familiar with, for example, regarding seat belts, airbags, child seats and
safety of children. Therefore, please follow especially the notes and warnings in
this section in your own interest and in the interest of your passengers. WARNING
● This chapter contains important information on how to use the vehicle for
the driver and his occupants. You will find further information on safety, which
concerns you and those travelling with you, in the following chapters of this
Owner's Manual.
● The complete on-board literature should always be in the vehicle. This ap-
plies in particular, if you rent out or sell the vehicle.
Safety equipment The safety equipment is part of the occupant protection and it can
reduce the risk of injuries in accident situations.
“Do not put at risk
” your safety and the safety of those travelling with you . In the
event of an accident, the safety equipment can reduce the risk of injuries.
The following list contains part of the safety equipment in your vehicle:
● three-point seat belts for all the seats;
● belt force limiters for front seats;
● belt tensioners for front seats; ●
seat belt height adjusters for front seats;
● front airbag for the driver and front passenger;
● side airbags;
● head airbags;
● anchoring points for child seat using the “ISOFIX” system;
● anchoring points for child seat using the “Top Tether” system;
● head restraints adjustable for height;
● adjustable steering column.
The specified safety equipment works together, in order to optimally protect you
and those travelling with you in accident situations. The safety equipment does
not protect you or the people travelling with you, if you or your occupants adopt
an incorrect seated position or the equipment is not correctly adjusted or used.
For this reason you will be provided with information on why these equipment
components are very important, how it protects you and the occupants, what
should be observed when using the equipment and how you and the people trav-
elling with you can make full use of the existing safety equipment. This Owner's
Manual contains important warning notes, which you and those travelling with
you should pay attention to in order to reduce a risk of injury.
Safety concerns everybody!
Before setting off The driver is always fully responsible for his occupants and for the
operating safety of the vehicle.
For your own safety and the safety of the people travelling with you, please pay
attention to the following points before setting off.
● Ensure that the lighting and the turn signal systems are functioning properly.
● Inspect the tyre inflation pressure.
● Ensure that all the windows offer a good visibility to the outside.
● Safely attach the items of luggage ⇒ page 55, Loading the luggage compart-
ment
. £ 101
Passive Safety Using the system Safety Driving Tips General Maintenance Breakdown assis-
tance Praktik Technical data
Page 104 of 212
●
Ensure that no objects can obstruct the pedal.
● Adjust the mirror, the front seat and the head restraint to match your body
size.
● Point out to your occupants that the head restraints must be adjusted to
match their body size.
● Protect the children in suitable child seats with correctly fastened seat belts
⇒ page 118, Transporting children safely .
● Adopt the correct seated position ⇒
page 102. Also inform your occupants to
adopt the correct seated position.
● Fasten the seat belt correctly. Also inform your occupants to properly fasten
the seat belts ⇒
page 107, How are seat belts correctly fastened?.
What influences the driving safety? The driving safety is primarily determined by the style of driving
and the personal behaviour of all the occupants.
The driver is fully responsible for himself and his occupants. If your driving safety
is effected, you place yourself and the oncoming traffic at risk.
Please refer to the following guidelines.
● Do not get distracted from concentrating on the traffic situation, e.g. by your
occupants or mobile phone calls.
● Never drive when your driving ability is impaired, e.g. through medication, alco-
hol, drugs.
● Keep to the traffic regulations and the permissible speed limit.
● Adjust the driving speed at all times to the road condition as well as to the
traffic and weather conditions.
● Take regular breaks on long journeys - at the latest every two hours. Correct seated position
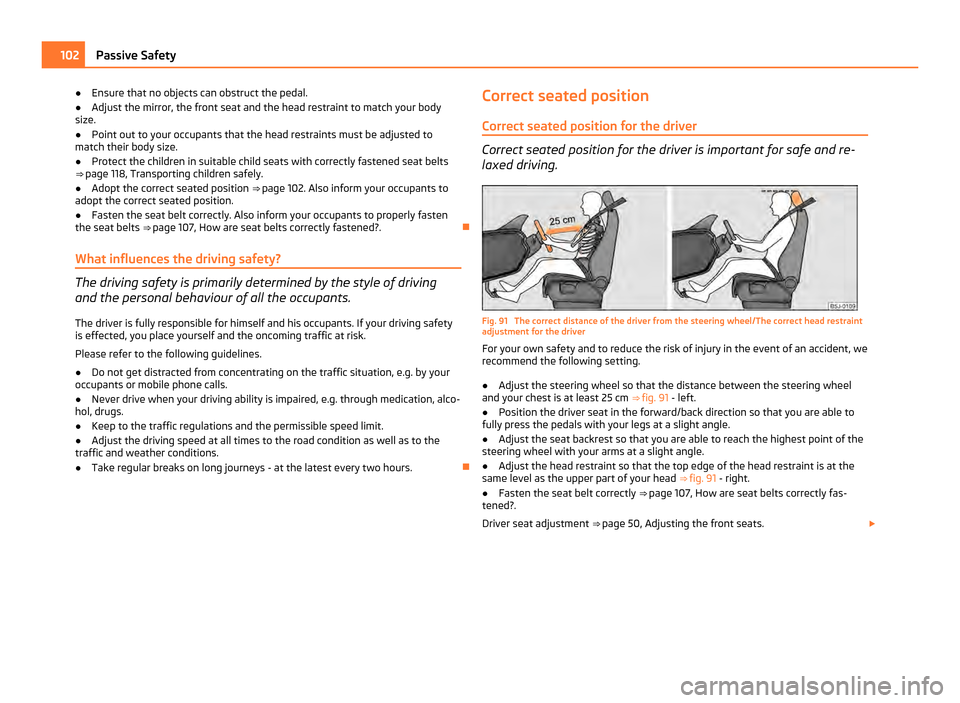
Correct seated position for the driver Correct seated position for the driver is important for safe and re-
laxed driving.
Fig. 91 The correct distance of the driver from the steering wheel/The correct head restraint
adjustment for the driver
For your own safety and to reduce the risk of injury in the event of an accident, we
recommend the following setting.
● Adjust the steering wheel so that the distance between the steering wheel
and your chest is at least 25 cm ⇒ fig. 91 - left.
● Position the driver seat in the forward/back direction so that you are able to
fully press the pedals with your legs at a slight angle.
● Adjust the seat backrest so that you are able to reach the highest point of the
steering wheel with your arms at a slight angle.
● Adjust the head restraint so that the top edge of the head restraint is at the
same level as the upper part of your head ⇒
fig. 91 - right.
● Fasten the seat belt correctly ⇒
page 107, How are seat belts correctly fas-
tened?.
Driver seat adjustment ⇒ page 50, Adjusting the front seats. £102
Passive Safety
Page 105 of 212
WARNING
● The front seats and the head restraints must always be adjusted to match
the body size of the seat occupant as well as the seat belts must always be
correctly fastened in order to provide an optimal protection for you and your
occupants.
● The driver must maintain a distance of at least 25 cm to the steering wheel
⇒ fig. 91. Not maintaining this minimum distance will mean that the airbag
system will not be able to properly protect you - hazard!
● When driving, hold the steering wheel with both hands firmly on the outer
edge in the 9 o'clock and 3 o'clock position. Never hold the steering wheel
firmly in the 12 o'clock position or in another way (e.g. in the middle of the
steering wheel or at the inner steering wheel edge). In such cases, injuries to
the arms, the hands and the head can occur when the driver airbag is de-
ployed.
● The seat backrests must not be angled too far back when driving other-
wise this will affect proper operation of the seat belts and of the airbag sys-
tem - risk of injury!
● Ensure that there are no objects in the footwell as any objects may get be-
hind the pedals during a driving or braking manoeuvre. You would then no
longer be able to operate the clutch, to brake or accelerate.
Correct seated position for the front passenger The front passenger must maintain a distance of at least 25 cm
from the dash panel so that the airbag offers him the greatest pos-
sible safety it is deployed.
For the safety of the front passenger and to reduce the risk of injury in the event
of an accident, we recommend the following setting.
● Adjust the front passenger seat as far as possible to the rear.
● Adjust the head restraint so that the top edge of the head restraint is at the
same level as the upper part of your head ⇒
fig. 91 - right.
● Fasten the seat belt correctly ⇒
page 107, How are seat belts correctly fas-
tened?.
In exceptional cases the front passenger airbag can be deactivated ⇒ page 116,
Deactivating airbags.
Adjusting the passenger seat ⇒ page 50, Adjusting the front seats. WARNING
● The front seats and the head restraints must always be adjusted to match
the body size of the seat occupant as well as the seat belts must always be
correctly fastened in order to provide an optimal protection for you and your
occupants.
● The front passenger must maintain a distance of at least 25 cm to the dash
panel. Not maintaining this minimum distance will mean that the airbag sys-
tem will not be able to properly protect you - hazard!
● Always keep your feet in the footwell when the car is being driven - never
place your feet on the instrument panel, out of the window or on the surfaces
of the seats. You will be exposed to increased risk of injury if it becomes nec-
essary to apply the brake or in the event of an accident. If an airbag is de-
ployed, you may suffer fatal injuries when adopting an incorrect seated posi-
tion!
● The seat backrests must not be angled too far back when driving other-
wise this will affect proper operation of the seat belts and of the airbag sys-
tem - risk of injury!
Correct seated position for the occupants on the rear seats Occupants on the rear seats must sit upright, keep the feet in the
footwell and must have their seat belts correctly fastened.
To reduce the risk of injury in the event of a sudden braking manoeuvre or an acci-
dent, the occupants on the rear seats must observe the following.
● Adjust the head restraints so that the top edge of the head restraints is at the
same level as the upper part of your head ⇒ fig. 91
- on the right.
● Fasten the seat belt correctly
⇒ page 107, How are seat belts correctly fas-
tened?.
● If you are transporting
⇒ page 118
, Transporting children safely children in the
vehicle, please use a suitable child restraint system. £ 103
Passive Safety Using the system Safety Driving Tips General Maintenance Breakdown assis-
tance Praktik Technical data
Page 106 of 212

WARNING
● The head restraints must always be adjusted to match the body size, in or-
der to offer an optimal protection for you and your occupants.
● Always keep your feet in the footwell when the car is being driven - never
put your feet out of the window or on the surfaces of the seats. You will be
exposed to increased risk of injury if it becomes necessary to apply the brake
or in the event of an accident. If the head airbag is deployed and when adopt-
ing an incorrect seated position, you are exposing yourself to an increased risk
of injury and in the event of an accident you may suffer fatal injuries!
● If the occupants on the rear seats are not sitting upright, the risk of injury
is increased due to incorrect routing of the seat belt.
● The seat backrests must not be angled too far back when driving other-
wise this will affect proper operation of the seat belts and of the airbag sys-
tem - risk of injury!
Examples of an incorrect seated position An incorrect seated position can lead to severe injuries or death for
the occupants.
Seat belts offer their optimum protection only if the webbing of the seat belts is
properly routed. Incorrect seated positions considerably reduce the protective
functions of the seat belts and therefore increase the risk of injury due to an in-
correct routing of the seat belt. The driver is fully responsible for himself and his
occupants, in particular for the children. Do not permit an occupant to adopt an
incorrect seated position when the car is moving.
The following list contains the examples of seated positions which are dangerous
for the occupants. This list is not complete, however, we want to direct your at-
tention to this subject.
Therefore, while the car is moving never:
● stand up in the vehicle;
● stand up on the seats;
● kneel on the seats;
● tilt the seat backrest fully to the back;
● lean against the dash panel;
● lie on the rear seat bench;
● only sit on the front area of the seat; ●
sit to the side;
● lean out of the window;
● put the feet out of the window;
● put the feet on the dash panel;
● put the feet on the seat upholstery;
● transport somebody in the footwell;
● have the seat belt not fastened when driving;
● occupy the luggage compartment. WARNING
● If the occupant adopts an incorrect seated position, he is exposed to life-
threatening injuries, in case he is hit by a deployed airbag.
● Before setting off, please adopt the correct seated position and do not
change this seated position while the car is moving. Also advise your occu-
pants to adopt the correct seated position and not to change this seated posi-
tion while the car is moving. 104
Passive Safety
Page 109 of 212

How are seat belts correctly fastened?
Fastening three-point seat belts Fasten your seat belt before starting!
Fig. 94 Routing of belt webbing over the shoulders and the lap belt/Routing of belt webbing
for an expectant mother
–
Correctly adjust the seat and the head restraint before fastening your seat
belt ⇒
page 102, Correct seated position.
– Slowly pull the belt webbing at the tongue of the lock over your chest and pel-
vis ⇒ .
– Insert the tongue of the lock into the seat belt buckle belonging to the seat
until it is heard to lock in place.
– Pull on the seat belt to check that it has also reliably engaged in the lock.
Each three-point seat belt is equipped with an inertia reel. This inertia reel offers
you complete freedom of movement if the belt is unreeled slowly. If the brakes
are applied suddenly, the inertia reel will block. The belts also block when the car
accelerates, when driving downhill and when cornering.
Expectant mothers must also wear the seat belt ⇒ . WARNING
● The shoulder part of the seat belt must never run across your neck but
must run approximately over the middle of the shoulder and fit snugly against
the chest. The lap part of the belt must run across the hip and must never be
routed across the stomach. It must always fit snugly ⇒
fig. 94 - left. Adjust the
belt webbing as required.
● The lap part of the belt should be positioned as low as possible at the pel-
vis of an expectant mother in order to avoid exerting any pressure on the low-
er abdomen ⇒ fig. 94 - right.
● Always ensure that the webbing of the seat belts is properly routed. Seat
belts which are not correctly adjusted can themselves cause injuries even in
minor accidents.
● A seat belt which is hanging too loose can result in injuries as your body is
moved forward by the kinetic energy produced in an accident and is then sud-
denly held firm by the belt.
● Only insert the lock tongue into the lock which is the correct one for your
seat. This will affect the protection which the belt offers and increase the risk
of an injury.
Seat belt height adjuster on the front seats Fig. 95 Front seat: Seat belt height ad-
juster
The seat belt height adjuster makes it possible for you to adapt the routing of the
front three-point seat belt in the area of the shoulder to match your body size.
– To adjust the belt height press the height adjuster and move it up or down
⇒ fig. 95 .
– Then pull firmly on the belt to ensure that the seat belt height adjuster has
correctly locked in place. £ 107
Seat belts Using the system Safety Driving Tips General Maintenance Breakdown assis-
tance Praktik Technical data
Page 110 of 212
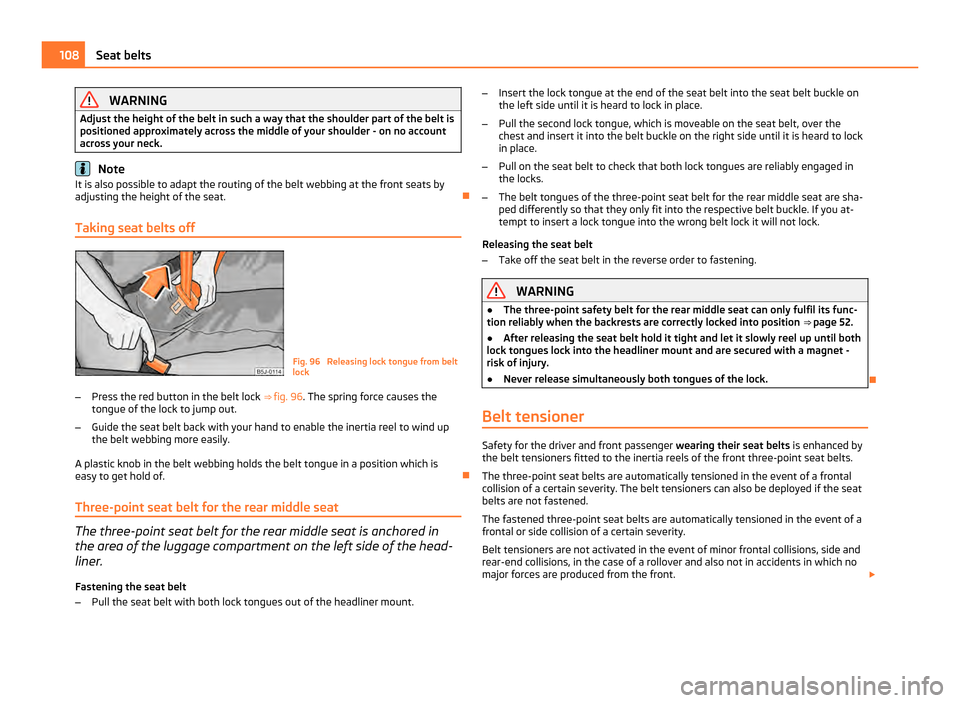
WARNING
Adjust the height of the belt in such a way that the shoulder part of the belt is
positioned approximately across the middle of your shoulder - on no account
across your neck. Note
It is also possible to adapt the routing of the belt webbing at the front seats by
adjusting the height of the seat.
Taking seat belts off Fig. 96 Releasing lock tongue from belt
lock
– Press the red button in the belt lock ⇒ fig. 96 . The spring force causes the
tongue of the lock to jump out.
– Guide the seat belt back with your hand to enable the inertia reel to wind up
the belt webbing more easily.
A plastic knob in the belt webbing holds the belt tongue in a position which is
easy to get hold of.
Three-point seat belt for the rear middle seat The three-point seat belt for the rear middle seat is anchored in
the area of the luggage compartment on the left side of the head-
liner.
Fastening the seat belt
– Pull the seat belt with both lock tongues out of the headliner mount. –
Insert the lock tongue at the end of the seat belt into the seat belt buckle on
the left side until it is heard to lock in place.
– Pull the second lock tongue, which is moveable on the seat belt, over the
chest and insert it into the belt buckle on the right side until it is heard to lock
in place.
– Pull on the seat belt to check that both lock tongues are reliably engaged in
the locks.
– The belt tongues of the three-point seat belt for the rear middle seat are sha-
ped differently so that they only fit into the respective belt buckle. If you at-
tempt to insert a lock tongue into the wrong belt lock it will not lock.
Releasing the seat belt
– Take off the seat belt in the reverse order to fastening. WARNING
● The three-point safety belt for the rear middle seat can only fulfil its func-
tion reliably when the backrests are correctly locked into position ⇒
page 52.
● After releasing the seat belt hold it tight and let it slowly reel up until both
lock tongues lock into the headliner mount and are secured with a magnet -
risk of injury.
● Never release simultaneously both tongues of the lock.
Belt tensioner Safety for the driver and front passenger
wearing their seat belts is enhanced by
the belt tensioners fitted to the inertia reels of the front three-point seat belts.
The three-point seat belts are automatically tensioned in the event of a frontal
collision of a certain severity. The belt tensioners can also be deployed if the seat
belts are not fastened.
The fastened three-point seat belts are automatically tensioned in the event of a
frontal or side collision of a certain severity.
Belt tensioners are not activated in the event of minor frontal collisions, side and
rear-end collisions, in the case of a rollover and also not in accidents in which no
major forces are produced from the front. £108
Seat belts
Page 112 of 212

Airbag system
Description of the airbag system General information on the airbag system The front airbag system is complementary to the three-point seat belts and offers
additional protection for the head and chest area of the driver and passenger in
the event of a frontal collision.
In the event of a side collision, the side airbags reduce the risk of injury to the oc-
cupants to the part of their body facing the side of the accident.
The airbag system is only functional after the ignition has been switched on.
The operational readiness of the airbag system is monitored electronically. The
airbag warning light comes on for a few seconds each time the ignition is switch-
ed on.
The airbag system (according to vehicle equipment) consists of:
● an electronic control unit;
● the front airbags for the driver and front passenger ⇒ page 111;
● the side airbags ⇒ page 113;
● head airbags ⇒ page 114;
● an airbag indicator light in the instrument cluster ⇒ page 26;
● a front passenger airbag switch ⇒ page 117;
● an indicator light for a switched off front seat passenger airbag in the middle
of the dash panel ⇒
page 117.
A fault in the airbag system exists if:
● the airbag indicator light does not light up when the ignition is switched on;
● the airbag indicator light does not go out after about 3 seconds after the igni-
tion is switched on;
● the airbag indicator light goes out and comes on again after the ignition is
switched on;
● the airbag indicator light comes on or flickers when driving;
● the airbag indicator light showing a switched-off front passenger airbag in the
middle of the dash panel flashes. WARNING
● To enable the occupants of a car to be protected with the greatest possi-
ble effect when the airbag is deployed, the front seats must be ⇒
page 102,
Correct seated position correctly adjusted to match the body size of the occu-
pant.
● If you do not fasten the seat belts when driving, lean too far forward or
adopt an incorrect seated position, you are exposing yourself to increased risk
of injury in the event of an accident.
● Have the airbag system checked immediately by a specialist garage if a
fault exists. Otherwise, there is a risk of the airbag not being activated in the
event of an accident.
● No modifications of any kind may be made to parts of the airbag system.
● It is prohibited to manipulate individual parts of the airbag system as this
might result in the airbag being deployed.
● The protective function of the airbag system is sufficient for only one acci-
dent. The airbag system must then be replaced if the airbag has been de-
ployed.
● The airbag system needs no maintenance during its working life.
● If you sell your car, please hand over the complete vehicle documentation
to the new owner. Please note that the documents relating to the possibility
of deactivating the front passenger airbag are also part of the vehicle docu-
ments!
● If the vehicle or individual parts of the airbag system are scrapped, it is es-
sential to observe the relevant safety precautions. The authorised
ŠKODA
Service Partners are familiar with these regulations.
● When disposing of vehicle or parts of the airbag system, it is important to
comply with the national legal requirements.
When are the airbags deployed? The airbag system is designed in such a way that the driver and front passenger
airbag are deployed in the event of a violent frontal collision
.
In the case of a violent side crash , the side airbag in the front seat and the head
airbag on the side on which the collision occurs are deployed. £110
Airbag system
Page 114 of 212
CAUTION
The dash panel must be replaced after the front passenger airbag has been de-
ployed.
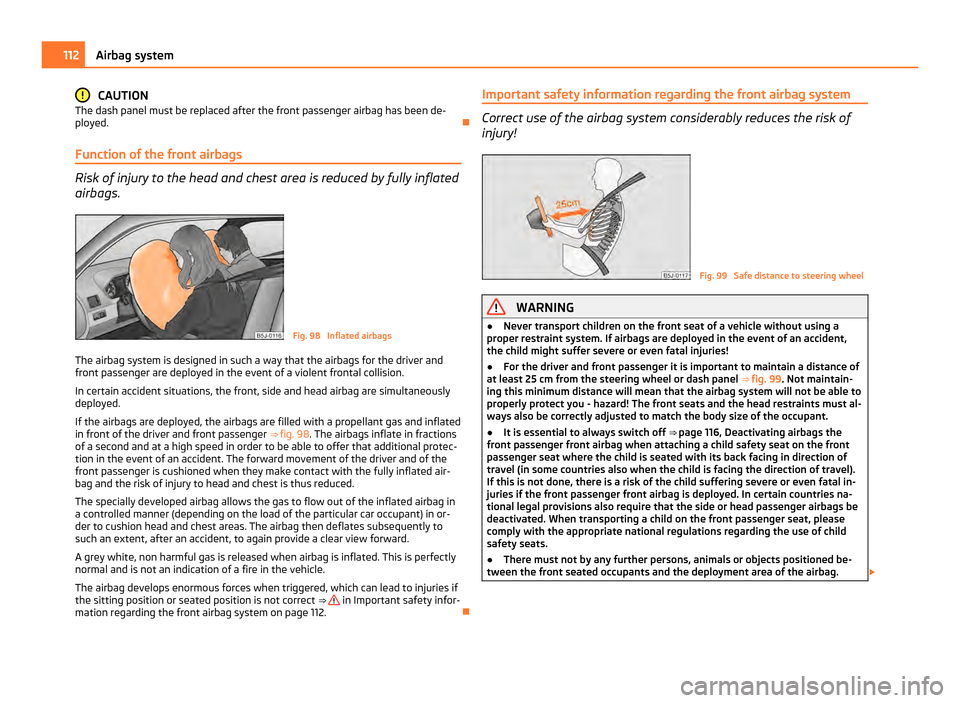
Function of the front airbags Risk of injury to the head and chest area is reduced by fully inflated
airbags.
Fig. 98 Inflated airbags
The airbag system is designed in such a way that the airbags for the driver and
front passenger are deployed in the event of a violent frontal collision.
In certain accident situations, the front, side and head airbag are simultaneously
deployed.
If the airbags are deployed, the airbags are filled with a propellant gas and inflated
in front of the driver and front passenger ⇒ fig. 98 . The airbags inflate in fractions
of a second and at a high speed in order to be able to offer that additional protec-
tion in the event of an accident. The forward movement of the driver and of the
front passenger is cushioned when they make contact with the fully inflated air-
bag and the risk of injury to head and chest is thus reduced.
The specially developed airbag allows the gas to flow out of the inflated airbag in
a controlled manner (depending on the load of the particular car occupant) in or-
der to cushion head and chest areas. The airbag then deflates subsequently to
such an extent, after an accident, to again provide a clear view forward.
A grey white, non harmful gas is released when airbag is inflated. This is perfectly
normal and is not an indication of a fire in the vehicle.
The airbag develops enormous forces when triggered, which can lead to injuries if
the sitting position or seated position is not correct ⇒ in Important safety infor-
mation regarding the front airbag system
on page 112. Important safety information regarding the front airbag system Correct use of the airbag system considerably reduces the risk of
injury! Fig. 99 Safe distance to steering wheel
WARNING
● Never transport children on the front seat of a vehicle without using a
proper restraint system. If airbags are deployed in the event of an accident,
the child might suffer severe or even fatal injuries!
● For the driver and front passenger it is important to maintain a distance of
at least 25
cm from the steering wheel or dash panel ⇒ fig. 99. Not maintain-
ing this minimum distance will mean that the airbag system will not be able to
properly protect you - hazard! The front seats and the head restraints must al-
ways also be correctly adjusted to match the body size of the occupant.
● It is essential to always switch off ⇒ page 116, Deactivating airbags
the
front passenger front airbag when attaching a child safety seat on the front
passenger seat where the child is seated with its back facing in direction of
travel (in some countries also when the child is facing the direction of travel).
If this is not done, there is a risk of the child suffering severe or even fatal in-
juries if the front passenger front airbag is deployed. In certain countries na-
tional legal provisions also require that the side or head passenger airbags be
deactivated. When transporting a child on the front passenger seat, please
comply with the appropriate national regulations regarding the use of child
safety seats.
● There must not by any further persons, animals or objects positioned be-
tween the front seated occupants and the deployment area of the airbag. £112
Airbag system