2011 RENAULT SCENIC fuel
[x] Cancel search: fuelPage 8 of 329

13B-8
MR-372-J84-13B050$078.mif
V17
DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – Cleanliness guidelines
Siemens Injection
SID301 and 304
Vdiag No.: 44-45-48-49-4D-4C
Program No.: B1 and B2
13B
Check that you have hermetically resealable plastic bags for storing removed parts. Parts stored in this way will be
less susceptible to the risk of contamination. The bags are to be used once only, and discarded after use.
Use lint-free cleaning cloths (cloth part number 77 11 211 707). Using normal cloth or paper is prohibited. They are
not lint-free and could contaminate the fuel circuit. Each cloth should only be used once.
Use fresh cleaning agent for each operation (used cleaning agent is contaminated). Pour it into an uncontaminated
container.
For each operation, use a clean brush in good condition (the brush must not shed its bristles).
Use a brush and cleaning agent to clean the unions to be opened.
Blast compressed air over the cleaned parts (tools, workbench, the parts, unions and injection system zones).
Check that no bristles remain.
Wash your hands before and during the operation if necessary.
When wearing leather protective gloves cover them with latex gloves to prevent contamination.
III - INSTRUCTIONS TO BE FOLLOWED DURING THE OPERATION
As soon as the circuit is open, all openings must be plugged to prevent impurities from entering the system. The
plugs to be used are available from the Parts Department. The plugs must not be reused under any circumstances.
Seal the pouch shut, even if it has to be opened shortly afterwards. Ambient air carries contamination.
All components removed from the injection system must be stored in a hermetically sealed plastic bag once they
have been plugged.
Using a brush, cleaning agent, air gun, sponge or normal cloth is strictly prohibited once the circuit has been
opened. These items could allow contamination to enter the system.
A new component replacing an old one must not be removed from its packaging until it is to be fitted to the vehicle.
Page 9 of 329

13B-9
MR-372-J84-13B050$117.mif
V17
13B
DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – List and location of components
High pressure pump:
The high pressure pump is located upstream of the common rail.
Rail pressure sensor:
The sensor is fitted to the common rail.
Rail pressure regulator:
The regulator is fitted on the high pressure pump.
Fuel flow regulator:
The regulator is fitted on the high pressure pump.
Piezoelectric injectors:
The injectors are fitted on the cylinder head after the common rail.
Vacuum pump:
The vacuum pump is fitted at the end of the camshaft.
Control solenoid valve:
The solenoid valve is located on the turbocharger.
Turbocharger:
The turbocharger is located after the exhaust manifold.
Intake air pressure sensor:
The sensor is integrated into the injection computer.
Turbocharger pressure sensor:
The turbocharger pressure sensor is located on the air circuit between the turbocharger and the damper valve.
Air mass flow meter:
The air mass flow meter is located at the air circuit inlet and integrates the air temperature sensor.
EGR valve:
The EGR valve is located between the inlet manifold and the exhaust manifold.
EGR position sensor:
The sensor is integrated into the EGR valve.
Damper valve:
The damper valve is located before the inlet manifold (Vdiag 44, 45, 48, 49 and 4D only).
Particle filter:
The filter is located on the exhaust pipe after the catalytic converter.
TDC sensor:
The sensor is located on the flywheel.
Camshaft sensor:
The sensor is located at the end of the camshaft.
Electric coolant pump:
The electric coolant pump is located between the heating elements and the turbocharger (only on vehicles equipped
with a particle filter).
Refrigerant pressure sensor:
The sensor is located on the coolant circuit.
MR-372-J84-13B050$117.mif
Siemens Injection
SID301 and 304
Vdiag No.: 44-45-48-49-4D-4C
Program No.: B1 and B2
Page 10 of 329

13B-10
MR-372-J84-13B050$117.mif
V17
Siemens Injection
SID301 and 304
Vdiag No.: 44-45-48-49-4D-4C
Program No.: B1 and B2DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – List and location of components13B
Heating elements:
The heating elements are located in the cooling circuit before the additional coolant pump which cools the
turbocharger (Vdiag 45, 49 and 4D only).
Coolant temperature sensor:
The sensor is located on the cylinder head near the engine water chamber.
Air temperature sensor:
The air temperature sensor is located at the air circuit inlet, integrated into the air flowmeter.
Turbocharging pressure sensor solenoid valve:
The solenoid valve is located on the turbocharger.
Catalytic converter:
The catalytic converter is located upstream of the exhaust system and downstream of the turbocharger.
Fuel temperature sensor:
The sensor is located near the injection pump and injector return.
Catalytic converter downstream temperature sensor:
The sensor is located after the catalytic converter.
Turbine upstream temperature sensor:
This sensor is located between the exhaust pipe and the turbocharger.
Cruise control/speed limiter on/off switch:
This switch is located in the passenger compartment to the left of the steering wheel near the lighting dimmer.
Water in diesel fuel sensor (optional):
This sensor is located in the diesel filter.
Fan unit relay:
The relay is located on the cooling radiator.
Accelerator potentiometer:
The potentiometer is located on the accelerator pedal.
Brake pedal switch:
The switch is located on the brake pedal.
Clutch pedal switch:
The switch is located on the clutch pedal.
Heater plugs:
The heater plugs are located on the cylinder head.
Particle filter injector:
The injector is located between the particle filter injector fuel pump and the exhaust pipe. (Vdiag 45, 49 and 4D only)
Electric fuel pump:
The pump is located between the tank and the particle filter injector fuel filter. (Vdiag 45, 49 and 4D only)
Page 12 of 329
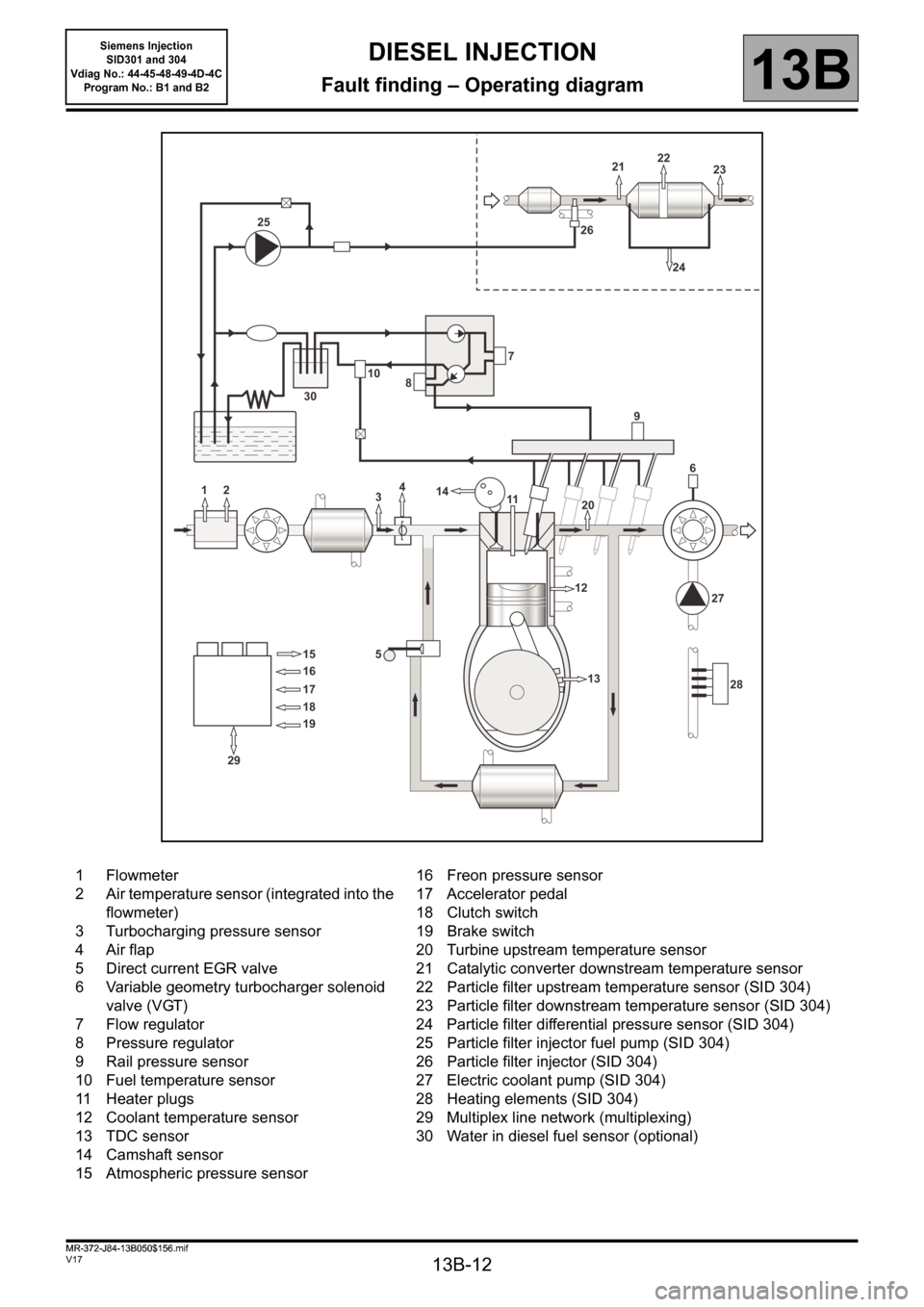
13B-12
MR-372-J84-13B050$156.mif
V17
13B
DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – Operating diagram
1 Flowmeter
2 Air temperature sensor (integrated into the
flowmeter)
3 Turbocharging pressure sensor
4 Air flap
5 Direct current EGR valve
6 Variable geometry turbocharger solenoid
valve (VGT)
7 Flow regulator
8 Pressure regulator
9 Rail pressure sensor
10 Fuel temperature sensor
11 Heater plugs
12 Coolant temperature sensor
13 TDC sensor
14 Camshaft sensor
15 Atmospheric pressure sensor16 Freon pressure sensor
17 Accelerator pedal
18 Clutch switch
19 Brake switch
20 Turbine upstream temperature sensor
21 Catalytic converter downstream temperature sensor
22 Particle filter upstream temperature sensor (SID 304)
23 Particle filter downstream temperature sensor (SID 304)
24 Particle filter differential pressure sensor (SID 304)
25 Particle filter injector fuel pump (SID 304)
26 Particle filter injector (SID 304)
27 Electric coolant pump (SID 304)
28 Heating elements (SID 304)
29 Multiplex line network (multiplexing)
30 Water in diesel fuel sensor (optional)
MR-372-J84-13B050$156.mif
Siemens Injection
SID301 and 304
Vdiag No.: 44-45-48-49-4D-4C
Program No.: B1 and B2
Page 13 of 329

13B-13
MR-372-J84-13B050$195.mif
V17
13B
DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – Function
SYSTEM FLOWCHART
The high pressure injection system is designed to deliver a precise quantity of diesel fuel to the engine at a set
moment.
The Siemens VDO piezo Common Rail system used on the K9K Step 2 engine is a second generation Common Rail
injection system. Fuel pressure in the rail can reach a maximum of 1650 bar.
The Siemens VDO piezo Common Rail system uses injectors which are controlled by piezoelectric actuators.
The fuel is pressurised by means of a high pressure pump then sent to a rail which supplies the four injectors.
The system includes two subsystems, which have different fuel pressure levels:
●the low pressure system which includes the tank, diesel fuel filter, internal fuel transfer pump and injector
return pipes,
●the high pressure system which includes the high pressure pump, rail, injectors and high pressure pipes.
There are a number of sensors and regulating actuators for controlling and monitoring the entire system.
It is fitted with a 112- track (or 128- track for Kangoo II) SIEMENS computer (SID 301 and SID 304).
The system comprises:
– a priming bulb,
– a diesel filter,
– a high pressure pump (HPP) with a fuel pressure solenoid valve (PCV), a fuel flow solenoid valve (VCV) and an
internal fuel transfer pump (ITP, low pressure pump),
– an injector rail,
– a rail pressure sensor,
– four piezoelectric injectors,
– a fuel temperature sensor,
– a coolant temperature sensor,
– a camshaft sensor,
– a TDC sensor,
– a turbocharger pressure sensor,
– an exhaust gas recirculation solenoid valve with integrated position sensor (EGR),
– an accelerator pedal potentiometer,
– an atmospheric pressure sensor integrated into the injection computer,
– an air mass flowmeter with integrated air temperature sensor,
– an air damper valve (Vdiag 44, 45, 48, 49 and 4D only),
– a temperature sensor upstream of the turbine,
– an antipollution system:
●a temperature sensor upstream of the particle filter (Vdiag 45, 49, 4D only),
●a temperature sensor downstream of the particle filter (Vdiag 45, 49, 4D only),
●a particle filter differential pressure sensor (Vdiag 45, 49, 4D only),
●a particle filter injector (Vdiag 45, 49, 4D only),
●a particle filter (Vdiag 45, 49, 4D only),
– a temperature sensor downstream of the catalytic converter,
– an electric fuel pump,
– an electric coolant pump (Vdiag 45, 49, 4D only),
– four heating elements and their control unit (Vdiag 45, 49, 4D only),
– four heater plugs,
– a water in the fuel detection sensor (optional).
MR-372-J84-13B050$195.mif
Siemens Injection
SID301 and 304
Vdiag No.: 44-45-48-49-4D-4C
Program No.: B1 and B2
Page 14 of 329

13B-14
MR-372-J84-13B050$195.mif
V17
DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – Function
Siemens Injection
SID301 and 304
Vdiag No.: 44-45-48-49-4D-4C
Program No.: B1 and B2
13B
FUEL SUPPLY
High pressure pump
The high pressure pump consists of the following components:
– Internal fuel transfer pump (ITP):
The pump is a rotary pump with vanes which sucks the fuel from the tank through the fuel filter and supplies the high
pressure pump with fuel.
– Fuel flow solenoid valve (VCV):
The solenoid valve regulates the flow of fuel entering the high pressure pump and enables an optimum quantity of
fuel to be pressurised according to the operating phase; this improves the efficiency of the high pressure pump
and the engine.
– High-pressure pump (HPP):
The pump is a 3-piston radial pump which generates the required pressure in the rail.
– Fuel pressure solenoid valve (PCV):
The solenoid valve regulates the output pressure of the high pressure pump.
Piezoelectric injectors
The piezoelectric injectors enable rapid, precise metering of the quantity of fuel injected, with excellent injection
process repetitiveness.
The piezoelectric actuator operates like a condenser. To control the injector, the computer sends, at the correct time,
a quantity of energy which is sufficient to enable the actuator to deform and the injector to open.
During the injection period, the piezoelectric actuator stores this energy.
At the end of the injection period, the computer recovers the energy sent at the start of the control operation.
The piezoelectric actuator discharges and returns to its original shape. The injector closes.
To improve efficiency, the energy stored by the piezoelectric actuator is reused, reducing the energy required for the
next injection.
WARNING:
The injector voltage is very high (much higher than that of conventional injectors).
This voltage can be as much as 150 V.
Page 15 of 329

13B-15
MR-372-J84-13B050$195.mif
V17
Siemens Injection
SID301 and 304
Vdiag No.: 44-45-48-49-4D-4C
Program No.: B1 and B2DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – Function13B
Engine synchronisation
One of the determining factors for fuel injection control is knowing the position of each of the pistons in their
respective cylinders at all times.
The angular position is measured using a TDC sensor triggered by machined teeth on the flywheel. The flywheel
has 60 teeth, with 2 teeth missing which forms a notch which is used as a reference point for the 1
st cylinder.
A second sensor (Hall-effect), excited by a machined tooth on the camshaft, and turning at half the engine speed,
provides information on the progress of the injection cycle. When the piston of cylinder 1 is at top dead centre (TDC),
either at the end of the compression stroke or at the end of the exhaust stroke, the camshaft sensor enables
a distinction to be made between these two states.
By comparing the signals from these two sensors, the computer is able to provide all of its systems with
synchronisation parameters, namely: the angular position of the flywheel, engine speed, the number of the active
injector and the progress of the injection cycle.
The module supplies the system with the rotation speed signal.
The camshaft sensor is only used when starting the engine. As soon as the engine is running by itself (not being
cranked by the starter), the signal provided by the TDC sensor is sufficient. A camshaft sensor fault, when the
engine is running, does not prevent the engine from operating correctly.
Quantity of fuel injected and control of start of injection
The parameters for controlling injection are, for each cylinder, the quantity to be injected and the start of injection.
These parameters are calculated by the injection computer using the following information:
– Engine speed.
– Accelerator pedal position.
– Turbocharging air pressure.
– Coolant temperature.
– Air temperature.
– Fuel temperature.
–Air flow.
– Pressure of fuel in the rail.
Page 17 of 329

13B-17
MR-372-J84-13B050$195.mif
V17
Siemens Injection
SID301 and 304
Vdiag No.: 44-45-48-49-4D-4C
Program No.: B1 and B2DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – Function13B
AIR SUPPLY
Measurement of the fresh air flow
The flow of fresh air entering the engine is measured by a flow sensor (ratiometric hot-wire sensor).
A fresh air temperature sensor is integrated into the air flowmeter.
EGR valve control
The EGR (exhaust gas recirculation) system consists of a direct current EGR valve fitted with a valve position
sensor. The EGR valve is controlled in a closed-loop via the position sensor. Up to a certain rate, exhaust gas
recirculation enables nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions to be reduced significantly.
Turbocharger control
The turbocharger system consists of a solenoid valve connected to the vacuum pump circuit, which controls the
vanes via a diaphragm to create an overpressure or a vacuum in the fresh air inlet circuit (the overpressure can
reach 2.6 bar).
Damper valve control (for Vdiag 44, 45, 48, 49 and 4D only)
By default the valve is open when in the rest position and is actuated only when the engine is switched off; this has
a damping effect and helps to stop the engine.
It also controls the flow of fresh air during regeneration.
IDLE SPEED MANAGEMENT
The injection computer regulates the idle speed according to the idle speed setpoint which it calculates.
The idle speed setpoint is dependent on:
– the coolant temperature,
– the emission control programs,
– air conditioning requirements,
– the gear ratio engaged (automatic or sequential gearbox),
– the electrical consumers,
– battery voltage.
ENGINE TORQUE MANAGEMENT
The torque structure is the system which translates the driver's request into a torque supplied by the engine. Certain
functions such as the electronic stability program (ESP), the automatic gearbox (BVA) or the sequential gearbox
(BVR), if fitted to the vehicle, use this information.
Each inter-system (ESP, automatic gearbox, sequential gearbox) sends the injection computer a torque request via
the multiplex network.
The injection computer arbitrates between the inter-system torque requests and the driver request (depressing the
accelerator pedal or setting the cruise control/speed limiter function). The result of the arbitration gives the torque
setpoint.
From this torque set point, the computer determines the quantity of fuel to be injected (injection duration and number
of injection processes) and the amount of air required (turbocharging pressure and EGR valve rate) so that the
engine is able to provide the torque required in the best possible conditions (in terms of smooth running
performance, pollutant emissions, etc.).