2011 FORD KUGA open
[x] Cancel search: openPage 1677 of 2057
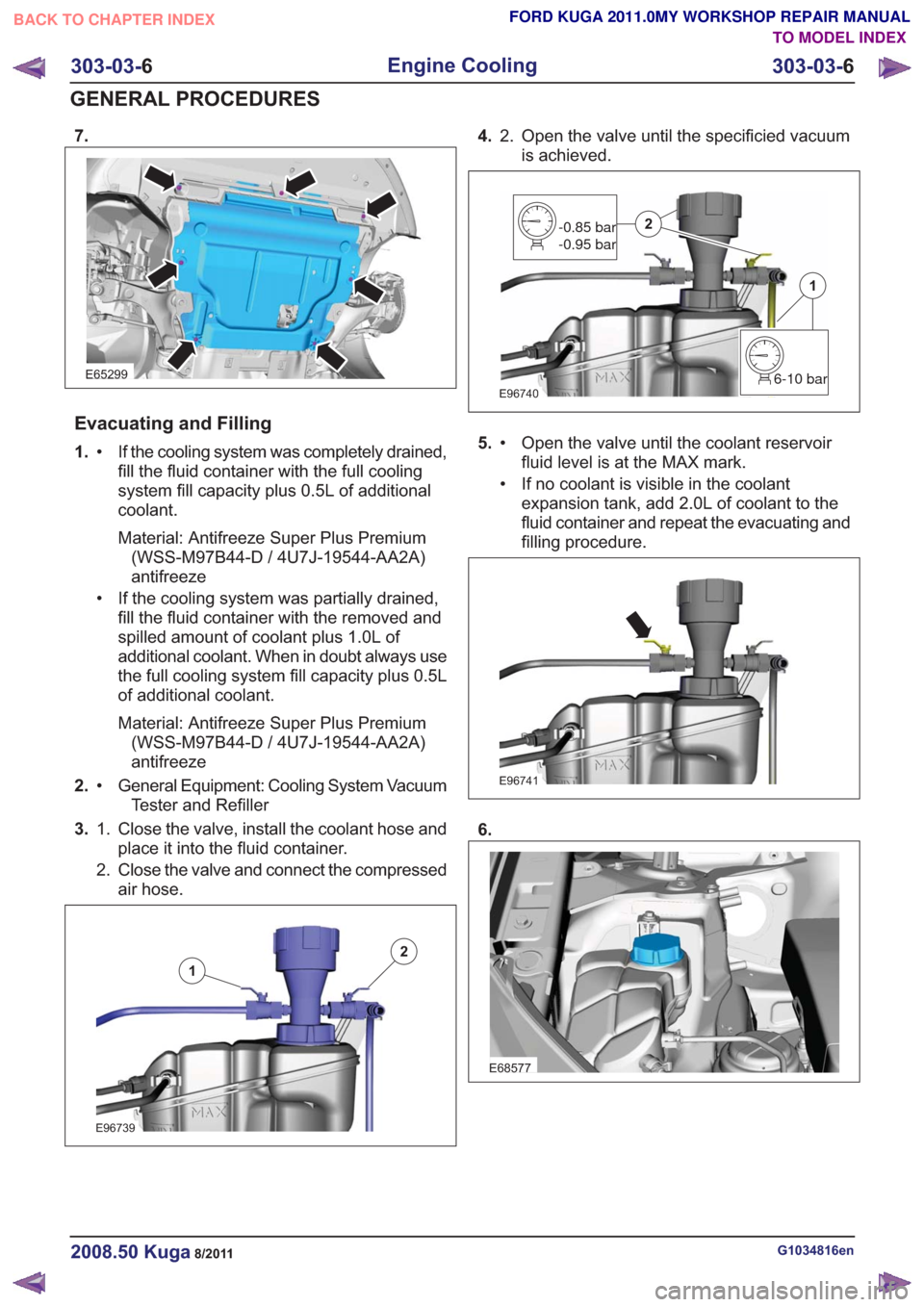
7.
E65299
Evacuating and Filling
1.If the cooling system was completely drained,
fill the fluid container with the full cooling
•
system fill capacity plus 0.5L of additional
coolant.
Material: Antifreeze Super Plus Premium(WSS-M97B44-D / 4U7J-19544-AA2A)
antifreeze
• If the cooling system was partially drained, fill the fluid container with the removed and
spilled amount of coolant plus 1.0L of
additional coolant. When in doubt always use
the full cooling system fill capacity plus 0.5L
of additional coolant.
Material: Antifreeze Super Plus Premium(WSS-M97B44-D / 4U7J-19544-AA2A)
antifreeze
2. General Equipment: Cooling System Vacuum
Tester and Refiller
•
3. Close the valve, install the coolant hose and
place it into the fluid container.
1.
2. Close the valve and connect the compressed
air hose.
E96739
1
2
4. Open the valve until the specificied vacuum
is achieved.
2.
E967406-10 bar
1
-0.85 bar
-0.95 bar2
5.
Open the valve until the coolant reservoir
fluid level is at the MAX mark.
•
• If no coolant is visible in the coolant
expansion tank, add 2.0L of coolant to the
fluid container and repeat the evacuating and
filling procedure.
E96741
6.
E68577
G1034816en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-03- 6
Engine Cooling
303-03- 6
GENERAL PROCEDURES
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1722 of 2057

Description
Item
PWM (pulse width modulation) signal
Comments:from PCM (powertrain control module)
5
Atmospheric pressure
6
Turbocharger boost pressure.
7
from air filter
8
Intake air
9Description
Item
Recirculated air valveRefertoComponentDescription:(page
7)
10
Vacuum line, recirculated air valve
11
to intake manifold
12
Throttle plate
13
Compressor
14
Turbine
15
System Operation
Turbocharger(s)
The TC consists of a turbine and a compressor.
The turbine is driven by the exhaust gas flow. A
common shaft drives the compressor and this then
compresses the intake air.
Turbocharger boost pressure control
E98942
1
2
3
4
Description
Item
Atmospheric pressure
1
Turbocharger boost pressure.
2
Wastegate control valve
3
Pilot pressure
4
The size of the TC is designed to produce a charge
effect even at medium engine speeds and lower
exhaust gas flows. This means that, when the engine speed is high and there is a large amount
of exhaust gas, either the boost pressure of the
TC will become too high or its speed will be too
high. The TC must therefore be regulated. The
best regulation is achieved by an electronically
controlled wastegate control valve. The wastegate
control valve controls the pressure on the
membrane in the boost pressure regulator.
The wastegate control valve is actuated by the
PCM with a PWM signal according to a map. The
boost pressure is applied to the wastegate control
valve via the pressure line from the compressor.
This pressure is passed to the boost pressure
regulator via the wastegate control valve. This
opens the bypass valve using a linkage. This
channels a portion of the exhaust gases around
the turbine. If the wastegate control valve is
actuated by the PCM, a bypass is opened in the
wastegate control valve. This causes the pressure
which can act on the membrane in the boost
pressure regulator to be reduced. This occurs until
the boost pressure has reached a set value. By
actuation with a PWM signal, it is also possible to
partially open or close the wastegate control valve.
This results in a constant boost pressure and
therefore high torque over a wide range of engine
speeds.
Because the PCM calculates the boost pressure
using the signal from the boost pressure sensor
and the IAT (intake air temperature) sensor, the
atmospheric pressure and the temperature are
automatically compensated for. Because of this
compensation, the engine power is not noticeably
affected by variations in atmospheric temperature
or pressure.
G1032426en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-04B-
6
Fuel Charging and Controls - Turbocharger
—
2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5
303-04B- 6
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1723 of 2057
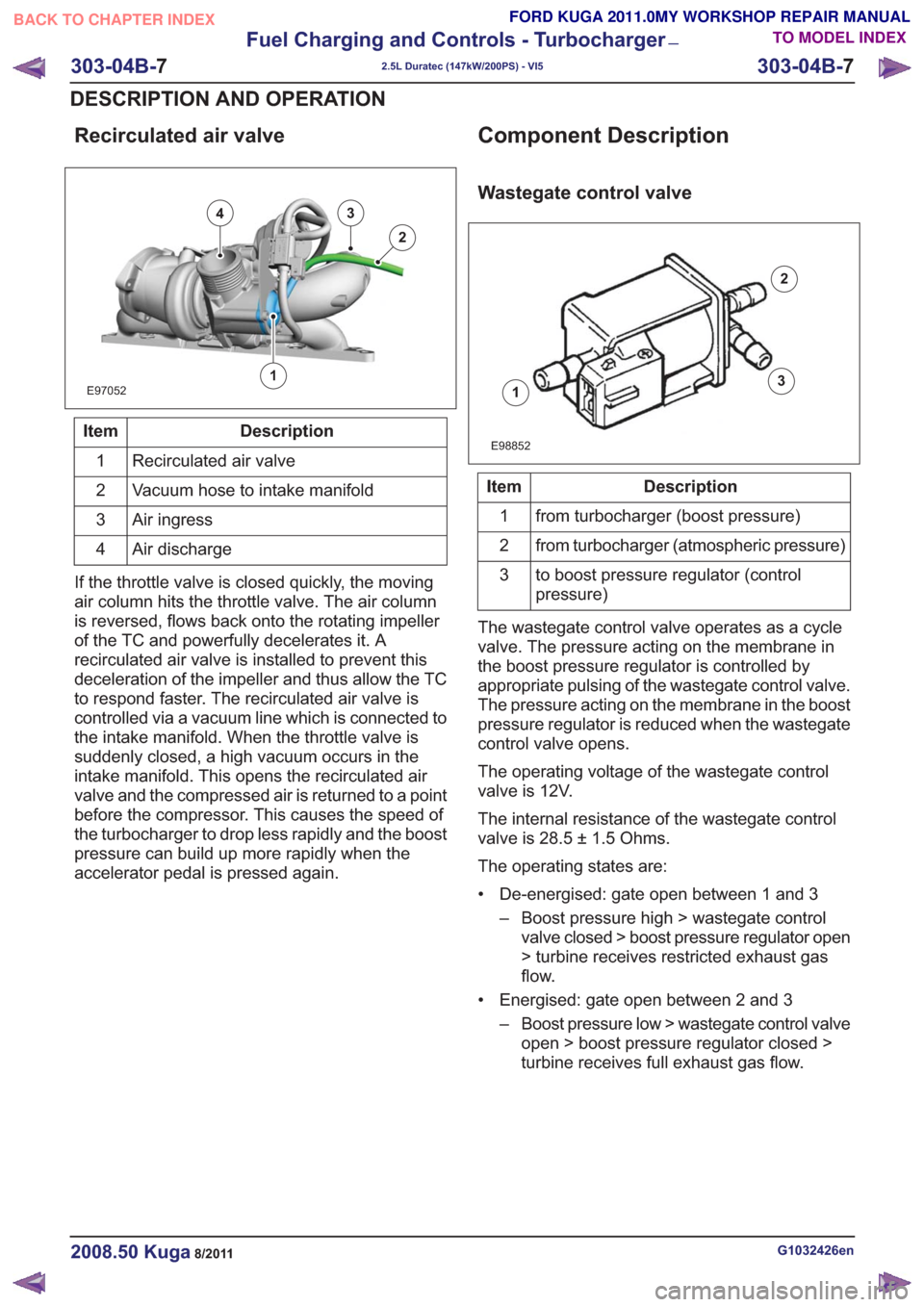
Recirculated air valve
E97052
43
2
1
Description
Item
Recirculated air valve
1
Vacuum hose to intake manifold
2
Air ingress
3
Air discharge
4
If the throttle valve is closed quickly, the moving
air column hits the throttle valve. The air column
is reversed, flows back onto the rotating impeller
of the TC and powerfully decelerates it. A
recirculated air valve is installed to prevent this
deceleration of the impeller and thus allow the TC
to respond faster. The recirculated air valve is
controlled via a vacuum line which is connected to
the intake manifold. When the throttle valve is
suddenly closed, a high vacuum occurs in the
intake manifold. This opens the recirculated air
valve and the compressed air is returned to a point
before the compressor. This causes the speed of
the turbocharger to drop less rapidly and the boost
pressure can build up more rapidly when the
accelerator pedal is pressed again.
Component Description
Wastegate control valve
1
2
3
E98852
Description
Item
from turbocharger (boost pressure)
1
from turbocharger (atmospheric pressure)
2
to boost pressure regulator (control
pressure)
3
The wastegate control valve operates as a cycle
valve. The pressure acting on the membrane in
the boost pressure regulator is controlled by
appropriate pulsing of the wastegate control valve.
The pressure acting on the membrane in the boost
pressure regulator is reduced when the wastegate
control valve opens.
The operating voltage of the wastegate control
valve is 12V.
The internal resistance of the wastegate control
valve is 28.5 ± 1.5 Ohms.
The operating states are:
• De-energised: gate open between 1 and 3 – Boost pressure high > wastegate controlvalve closed > boost pressure regulator open
> turbine receives restricted exhaust gas
flow.
• Energised: gate open between 2 and 3 – Boost pressure low > wastegate control valveopen > boost pressure regulator closed >
turbine receives full exhaust gas flow.
G1032426en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-04B- 7
Fuel Charging and Controls - Turbocharger
—
2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5
303-04B- 7
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1724 of 2057

Recirculated air valve
E98940
The recirculated air valve is a vacuum-controlled
spring/membrane valve. If vacuum is applied to
the recirculated air valve, the piston is pulled in
against the spring pressure and a bypass bore is
opened.
As the vacuum decreases, the spring pressure
prevails and the piston re-closes the bypass bore.
G1032426en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-04B-8
Fuel Charging and Controls - Turbocharger
—
2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5
303-04B- 8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1734 of 2057

Accessory Drive
Inspection and Verification
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of mechanicaldamage.
Visual Inspection Chart
Mechanical
– Damaged or contaminated accessory drive belt or air conditioning (A/C) compressor belt
– Damaged or contaminated pulley(s)
– Incorrect accessory drive belt or A/C compressor belt
– Incorrect fitment of the accessory drive belt or A/C compressor belt
– Accessory drive belt tensioner
– Accessory drive belt idler pulley
– Generator
– A/C compressor
– A/C compressor belt tensioner
– Pulley(s)
– Loose hardware
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible)
before proceeding to the next step.
Accessory Drive Belt Concerns
CAUTION: Do not lubricate the accessory
drive belt, accessory drive belt tensioner(s)
or idler pulley(s) as potential damage to
the accessory drive belt material
construction, accessory drive belt
tensioner damping mechanism, accessory
drive belt tensioner pulley bearing and idler
pulley(s) bearing may occur.
NOTE: All the diagnosis and testing information
contained within this procedure can be used for
the accessory drive belt and the A/C compressor
belt.
Cracking
Accessory drive belts are made from rubber which
hardens with time and can develop cracks. As the
accessory drive belt runs on the back of some of
the pulleys, the cracks are opened up. Small cracks
are not considered to be a failure of the accessory drive belt. Only if the crack is deep enough to reach
the bottom of the groove to expose the cord or any
chunks are found to be missing from the accessory
drive belt, is the accessory drive belt condition
considered to be unacceptable.
1. Check the accessory drive belt for cracks. If the
damage exceeds the acceptable limit, install a
new accessory drive belt.
REFER to: Accessory Drive Belt (303-05
Accessory Drive - 2.5L Duratec
(147kW/200PS) - VI5, Removal and
Installation).
and/or
REFER to: Air Conditioning (A/C) Compressor
Belt (303-05 Accessory Drive - 2.5L Duratec
(147kW/200PS) - VI5, Removal and
Installation).
Chunking
Chunking describes the condition where long
lengths of rubber become detached from the ribs
of the accessory drive belt. This is considered to
be a failure of the accessory drive belt.
MPZ9632071
2. Check the accessory drive belt for damage. If any chunks are found to be missing, install a
new accessory drive belt.
REFER to: Accessory Drive Belt (303-05
Accessory Drive - 2.5L Duratec
(147kW/200PS) - VI5, Removal and
Installation).
and/or
REFER to: Air Conditioning (A/C) Compressor
Belt (303-05 Accessory Drive - 2.5L Duratec
(147kW/200PS) - VI5, Removal and
Installation).
G1183443en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-05- 4
Accessory Drive— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-05-
4
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1791 of 2057

• Starting process
• Engine running– Fuel supply to the engine including lambdacontrol
– Ignition setting including knock control
– Idle speed control
– Boost pressure control
– Valve timing via the camshaft adjuster for the intake and exhaust camshafts (including
internal exhaust gas recirculation)
• Refrigerant compressor (activation, deactivation and delivery)
• EVAP purge valve
• Charging system
Fuel is supplied to the engine via a sequential
multi-point injection system. Ignition is performed
by a distributor-less ignition system with one
ignition coil unit for each cylinder.
The PCM optimizes engine power and emissions
at all times by processing the sensor signals and
information received via the CAN databus and
using these for open or closed loop control of the
different variables.
The PCM contains part of the PATS (passive
anti-theft system).
The PCM is supplied with battery voltage via a fuse
in the BJB (battery junction box). This power supply
is needed to ensure that saved data is not lost
when the engine is switched off.
For other power supply requirements, the PCM
switches on a relay in the BJB which is responsible
for supplying power to the PCM and to some
sensors and actuators. Each of these are protected
by fuses in the BJB.
To guarantee optimum engine running at all times,
the PCM has several adaptive (self-learning)
functions. These adapt the output signals to
changing circumstances, such as wear or system
faults.
In some cases a faulty signal is replaced with a
substitute value or limited. A substitute value can
be calculated from other signals or it can be
predefined by the PCM. The substitute value allows
the vehicle to keep on running without the emission
values changing unduly. Depending on the signal
failure, the PCM operates in emergency mode. In
this mode, the engine power and/or the engine
speed is reduced to prevent further damage.
Depending on the faulty signal, a fault code is
stored in the error memory of the PCM. These can be read out using IDS (Integrated Diagnostic
System) via the DLC.
The PCM processes and evaluates the signals
from the sensors. The following sensors send
signals to the PCM:
• CMP sensors
• CKP sensor
• MAF sensor
•KS
• ECT sensor
• TP sensor
• APP sensor
• Broadband HO2S
• Catalyst monitor sensor
• MAPT sensor
• Air conditioning (A/C) pressure sensor
• Alternator
• Fuel temperature and fuel pressure sensor
• Engine oil level, temperature and quality sensor
• Outside air temperature sensor
The following components receive signals from the
PCM:
• Powertrain Control Module relay
• A/C clutch relay
• injectors
• Direct ignition coils
• Cooling fan module
• Throttle control unit
• Camshaft adjuster solenoid valve
• Starter Relay
• EVAP purge valve
• Alternator
• Heating element - broadband HO2S
• Catalyst monitor sensor heating element
• FPDM
• Wastegate control valve
• Air conditioning compressor
The PCM receives the following signals via the
CAN databus:
• APP
•CPP
• BPP
• Vehicle speed.
• Refrigerant compressor request
• PAT S
G1021908en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14-
17
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
17
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1795 of 2057

actuated) or opened (actuated). Each cylinder has
its own injector. The injection is accurately dosed
and takes place at a time determined by the PCM.
Injection takes place immediately in front of the
intake valves of the cylinder. The injectors are
actuated ground side via end-stages integrated
into the PCM and using the signal calculated by
the engine management system. Power is supplied
via the Powertrain Control Module relay in the BJB.
The injected fuel quantity depends on the opening
time, the fuel pressure and the diameter of the
nozzle holes.
The fuel metering is determined via open or
closed-loop control.
The open control loop differs from the closed
control loop in that the lambda control is
deactivated.
The PCM switches from closed to open-loop control
if the HO2S cools down to below 600°C or fails, as
well as when accelerating, coasting and at full load.
Regulation of injected fuel quantity via the PCM
involves:
• controlling the fuel pump,
• calculating the required quantity of fuel forengine starting,
• observance of the desired air/fuel ratio,
• calculating air mass,
• and calculating the fuel quantity for the different operating states and corresponding fuel
adjustment measures.
Open loop control
Open loop control is used primarily for fuel
injection, as long as the signals of the HO2S are
not involved in the calculation of the PCM.
The two most important reasons that make it
absolutely essential to run the engine without
lambda control (open-loop control) are the following
operating conditions:
• Cold engine (starting, warm-up phase)
• Full-load operation (WOT (wide open throttle))
Under these operating conditions the engine needs
a rich air/fuel mixture with lambda values below λ
= 1 in order to achieve optimum running or
optimum performance.
It is possible to keep this unregulated range very
small by using a broadband HO2S.
Closed-loop control
Closed loop control ensures strict control of
exhaust emissions in conjunction with the TWC (three-way catalytic converter) and economical fuel
consumption. With closed loop control, the signals
from the HO2S are analyzed by the PCM and the
engine always runs in the optimum range of λ = 1.
In addition to the normal HO2S, the signal from the
monitoring sensor for the catalytic converter is also
included in the control. The lambda control is
optimized on the basis of this data.
Certain factors such as wear, component
tolerances or more minor defects such as air leaks
in the intake system are compensated for by
lambda control. If the deviation occurs for a longer
period of time, this is recorded by the adaptive
(self-learning) function of lambda control. In this
instance, the entire map is shifted by the
corresponding amount, to enable control to
commence once again from the virtual baseline.
These adaptive settings are stored in the PCM and
are also used in open-loop control conditions.
If the adaptive value is too high or too low, an error
is stored in the fault memory of the PCM.
Oxygen sensor (HO2S) and catalyst monitor
sensor
A broadband HO2S is used as the HO2S. The
HO2S is located in front of the TWC. The catalyst
monitor sensor is located in the center of the TWC
so that it can detect any deterioration in the
cleaning performance of the TWC more quickly.
The HO2S measures the residual amount of
oxygen in the exhaust before the TWC.
The catalyst monitor sensor measures the amount
of oxygen in the exhaust gas after or in the TWC.
Both the HO2S and the catalyst monitor sensor
transmit these data to the PCM.
The broadband HO2S works at temperatures of
between 650°C and 900 °C. If the temperature
rises above 1000°C, the oxygen sensor will be
irreparably damaged.
To reach optimum operating temperature as quickly
as possible, an electrically-heated oxygen sensor
is installed. The heating also serves to maintain a
suitable operating temperature while coasting, for
example, when no hot gases are flowing past the
oxygen sensor.
The heating element in the HO2S is a PTC
(positive temperature coefficient) resistor. The
heating element is supplied with battery voltage as
soon as the Powertrain Control Module relay
engages. The HO2S is earthed via the PCM. As
the heating current is high when the element is
cold, it is limited via PWM in the PCM until a certain
G1021908en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14-
21
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
21
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1796 of 2057

current value is reached. The PCM then
permanently connects the heating element to earth.
The catalyst monitor sensor is used by the PCM
to measure the oxygen content in the exhaust gas
in the TWC. If all the conditions for catalyst
diagnostics are met, based on this information the
PCM can check that the TWC is working
satisfactorily. The information is also used to
improve the air/fuel mixture adjustment.
The catalyst monitor sensor is similar in function
to an HO2S. The signal transmitted by the catalyst
monitor sensor changes sharply if the oxygen
content in the exhaust gas changes. For this
reason, catalyst monitor sensors are also called
"jump lambda sensors".
Fuel tank purging
The EVAP purge valve is only actuated by the PCM
if the coolant temperature is at least 60°C.
Actuation is done ground side by means of a PWM
signal. This makes it possible to have the full range
of opening widths, from fully closed to fully open.
The PCM determines from the operating conditions
when and how wide to open the EVAP tank purge
valve. If the EVAP purge valve is opened, the
engine sucks in ambient air through the activated
charcoal in the evaporative emission canister as
a result of the vacuum in the intake manifold. In
this way the adsorbed hydrocarbons are led to the
combustion chamber of the engine.
The EVAP tank purge valve is not actuated and
system cleaning is interrupted if the engine
switches to idle and/or a closed-loop control
process is initiated.
Power (battery voltage) is supplied via the
Powertrain Control Module relay in the BJB. The
solenoid coil resistance is between 17 and 24 ohms
at 20°C.
Engine speed control
The APP sensor provides the PCM with information
about the driver's request for acceleration.
The throttle control unit receives a corresponding
input signal from the PCM. An electric motor then
moves the throttle valve shaft by means of a set
of gears. The position of the throttle is continuously
recorded by the TP sensor. Information on throttle
position is processed and monitored by the PCM.
The TP sensor comprises two potentiometers.
These work in opposite ways to each other. In one
potentiometer, the resistance increases when the
throttle is opened, in the other it decreases. Thisallows the operation of the potentiometers to be
checked. The signal from the TP sensor is
amplified in the lower range (idle to a quarter open)
by the PCM to enable more precise control of the
throttle in this range. This is necessary because
the engine is very sensitive to changes in throttle
angle in this throttle opening range.
With the throttle valve position kept constant, the
ignition angle and the injected fuel quantity are
then varied to meet the torque demands.
Depending on the operating state of the engine, a
change in the position of the throttle flap may not
be necessary when the APP sensor changes.
If a fault develops in the throttle control unit, a
standby function is executed. This standby function
allows a slight opening of the throttle flap, so that
enough air passes through to allow limited engine
operation. For this purpose, there is a throttle flap
adjustment screw on the throttle housing. The
return spring closes the throttle flap until the stop
of the toothed segment touches the stop screw. In
this way a defined throttle flap gap is formed for
limp home mode.
The stop screw has a spring loaded pin, which
holds the throttle flap open for limp home mode.
In normal operating mode, this spring loaded pin
is pushed in by the force of the electric motor when
the throttle flap must be closed past the limp home
position (e.g. for idle speed control or overrun
shutoff).
Oil monitoring
The engine does not have an oil pressure
switch.
The oil level and oil quality are calculated.
Calculating the engine oil level
The oil level is determined by continuous
measurement of the capacitance (i.e. the ability to
store an electrical charge) between the two
capacitive elements of the engine oil
level/temperature/quality sensor. The different oil
levels cause the capacitance between the elements
to change. The data are recorded by the PCM and
converted into an oil level value. Temporary
fluctuations in oil level are automatically filtered out
by the PCM.
Calculating oil quality
The PCM calculates the oil quality from the oil level
measurement and the oil temperature measured
by the sensor, plus the engine speed and the
average fuel consumption. The driver is informed
about when an oil change is due.
G1021908en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14- 22
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
22
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL