2011 FORD KUGA gem module
[x] Cancel search: gem modulePage 1849 of 2057
21
22 20 19
15 14 13
161718 12
876
9
10
11 5
3
42121
22 20 19
15 14 13
161718 12
876
9
10
11 5
3
421
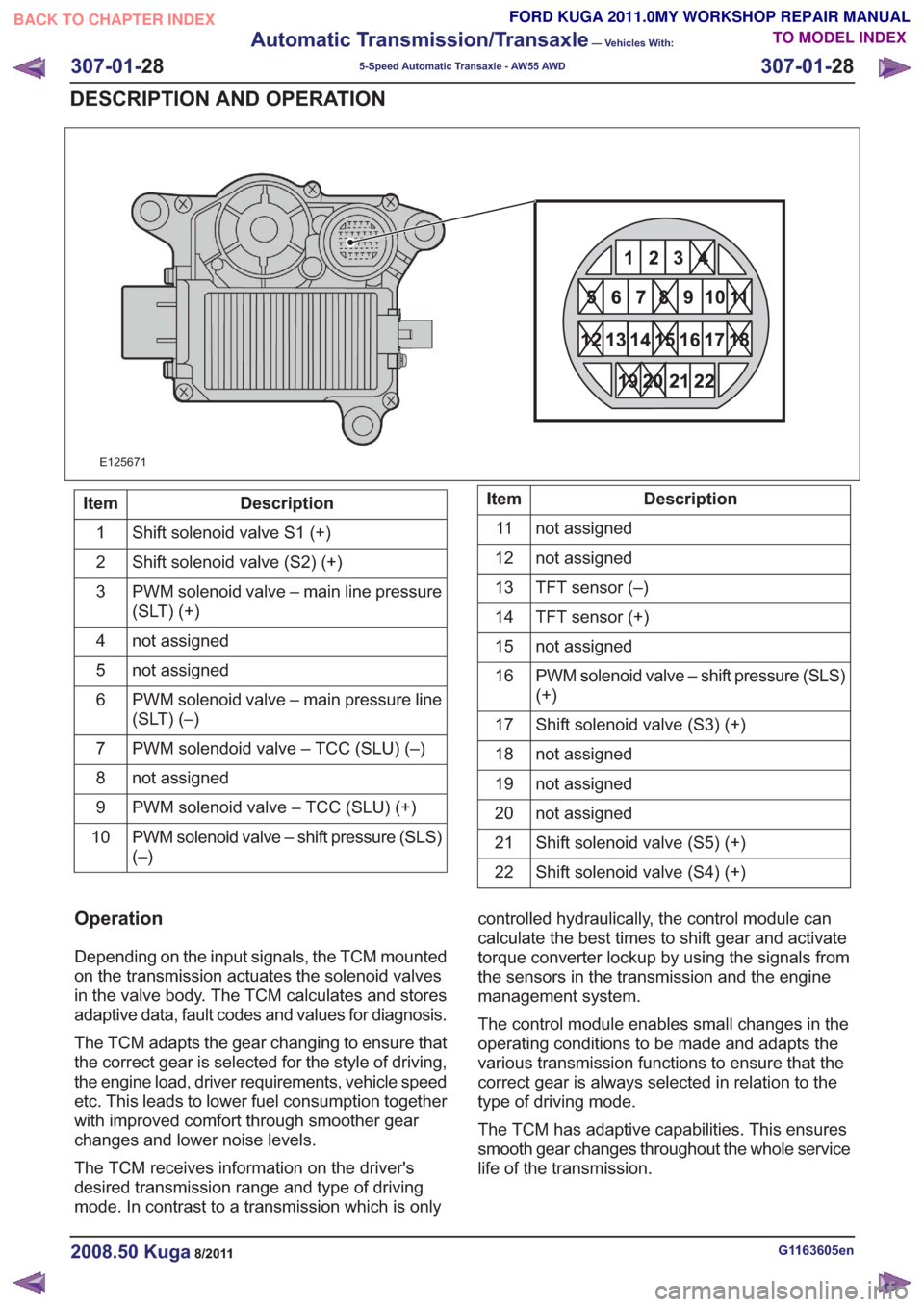
E125671
Description
Item
Shift solenoid valve S1 (+)
1
Shift solenoid valve (S2) (+)
2
PWM solenoid valve – main line pressure
(SLT) (+)
3
not assigned
4
not assigned
5
PWM solenoid valve – main pressure line
(SLT) (–)
6
PWM solendoid valve – TCC (SLU) (–)
7
not assigned
8
PWM solenoid valve – TCC (SLU) (+)
9
PWM solenoid valve – shift pressure (SLS)
(–)
10Description
Item
not assigned
11
not assigned
12
TFT sensor (–)
13
TFT sensor (+)
14
not assigned
15
PWM solenoid valve – shift pressure (SLS)
(+)
16
Shift solenoid valve (S3) (+)
17
not assigned
18
not assigned
19
not assigned
20
Shift solenoid valve (S5) (+)
21
Shift solenoid valve (S4) (+)
22
Operation
Depending on the input signals, the TCM mounted
on the transmission actuates the solenoid valves
in the valve body. The TCM calculates and stores
adaptive data, fault codes and values for diagnosis.
The TCM adapts the gear changing to ensure that
the correct gear is selected for the style of driving,
the engine load, driver requirements, vehicle speed
etc. This leads to lower fuel consumption together
with improved comfort through smoother gear
changes and lower noise levels.
The TCM receives information on the driver's
desired transmission range and type of driving
mode. In contrast to a transmission which is only controlled hydraulically, the control module can
calculate the best times to shift gear and activate
torque converter lockup by using the signals from
the sensors in the transmission and the engine
management system.
The control module enables small changes in the
operating conditions to be made and adapts the
various transmission functions to ensure that the
correct gear is always selected in relation to the
type of driving mode.
The TCM has adaptive capabilities. This ensures
smooth gear changes throughout the whole service
life of the transmission.
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01-
28
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 28
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1850 of 2057

To exactly determine the activation points of the
gear shifts and torque converter lockup on the
basis of the type of driving mode chosen, the TCM
receives the following information:
• Selected transmission range (TR sensor)
• Selected driving mode (normal/sport/select-shift)
• Transmission input shaft speed (TSS sensor)
• Transmission output shaft speed (OSS sensor)
• Transmission fluid temperature (TFT sensor)
• The engine speed and the torque as well as thethrottle plate opening - from the PCM via the
CAN databus
• Actuation of accelerator – from the PCM via the CAN databus
• The coolant temperature – from the PCM via the CAN databus
• Road speed – from the ABS module via the CAN databus
• Actuation of brake pedal – from the PCM via the CAN databus
Gearshift control
Adaptation
The TCM monitors every shift operation in all
driving conditions to make even and smooth gear
shifts possible. This is done by the control module,
which either lowers or increases the hydraulic line
pressure during gearshifts.
The changed pressure values are stored in the
control module memory after the engine is switched
off and retrieved during engine starting. This
improves the shift comfort and extends the service
life.
Full adaptability occurs when the following criteria
are met:
• Throttle plate opening is constant.
• Transmission fluid temperature between 65 °Cand 110 °C.
Shifting from 'P' to another transmission
range
To be able to move the selector lever from 'P' into
another transmission range, the ignition must be
switched on and the brake pedal pressed (stoplamp
switch on). The TCM detects the position of the
brake pedal via the CAN data bus and the engaged
transmission range from the TR sensor. Based on this information, the TCM transmits a
signal to the select-shift switch module. This
activates the brake shift interlock actuator in the
selector lever assembly.
When the brake shift interlock actuator is activated,
the locking pin is retracted so that another
transmission range can be selected.
The brake shift interlock actuator is deactivated
when the ignition is switched off. It is mechanically
locked when the gear selector lever is in 'P'.
Automatic transmission, selector lever in
position "D".
The TCM adapts the shift points to match the
driving conditions. Normally the TCM is in adaptive
mode and gear changes take place adapted to the
driving conditions. If special driving conditions are
detected, the TCM switches to predefined
characteristics.
When driving with normal acceleration, the TCM
uses a preset shift program which is optimized for
economical driving.
This shift program is suitable for "normal" driving
and delivers early upward changes and torque
converter lockup. Furthermore, the transmission
fluid pressure is adapted to make smooth
engagement of the gears possible.
Sport mode, selector lever in position "S"
The transmission switches from automatic
operation into sport mode. In this mode the TCM
switches to another set of characteristic curves.
These characteristic curves for control of the gear
changes are adapted to sporting calculations (e.g.
gear change at higher engine speed).
In the sport mode shift program the shift points are
set so that good performance is offered. Changing
down occurs at lower engine speeds.
Manual gear changes (select-shift mode) can be
made in sport mode by moving the selector lever
in the (+) or (-) direction.
Changing gear in select-shift mode
If you move the selector lever to 'S', the automatic
transaxle remains hydraulically in 'D' position. If
you move the gear selector lever forwards (-), the
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01-
29
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 29
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1866 of 2057

Output signals
Hard wired
• Item 8: PCM– Start inhibitor. Supplies the PCM with a signalthat indicates whether the engine can be
started or not.
• Item 9: Selector lever module (select-shift module)
– Controls the solenoid switch in the selectorlever unit.
• Position 10: PWM solenoid valve – shift pressure (SLS)
– Matches the line pressure to a shift pressureand is activated for certain gears.
• Position 11: PWM solenoid valve – main line pressure (SLT)
– Adjusts the linear line pressure for gearchanges without jolts.
• Position 12: PWM- solenoid valve – TCC (SLU) – Matches the line pressure to a torqueconverter lock-up pressure. Is also used for
certain gearshifts.
• Items 13 - 17: Shift solenoids S1 – S5 – The TCM checks which gear is engaged asthe solenoids become active in different
patterns.
Via the LIN data bus
• Item 7: Selector lever module (select-shift module)
– The TCM transmits a signal to the selectorlever module which activates the LED (light
emitting diode) in the selector mechanism
assembly according to the selector lever
position. Via the CAN data bus
• Item 2: GEM
– The selector lever module transmits a signalvia the TCM, which indicates that the selector
lever is locked in position P. The GEM uses
this information to control the ignition switch
key inhibit function.
– The TCM transmits a signal via the GEM to activate the back-up lamps.
• Item 3: Instrument Cluster – Current selector lever position. Used toindicate the selector lever position in the
instrument cluster.
– Check the warning lamps via the GEM. In the event of a fault, the general warning lamp
lights.
– Text messages in the instrument cluster via the GEM. The driver receives various
malfunction messages from the TCM.
– The TCM transmits signals on the CAN data bus to the PCM so that the MIL lights up in
the event of emissions-related faults.
• Item 4: PCM – Transmission fluid temperature, used tocompensate for increased loads at low fluid
temperatures.
– Gear selected, used by the engine so that it can compensate for different loads.
– Torque converter lockup, used by the engine so that it can compensate for different loads.
– Next gear planned by the TCM, used by the engine to compensate for different loads.
– Requirement for a reduced engine torque during gear shifts, the engine reduces the
engine torque during gear shifts.
– Torque limiting requirement, the engine limits the engine torque according to the gear
engaged.
• Item 5: ABS module – Current gear, used to transmit a signal, notfor shift control.
– Vehicle speed, used as reserve.
Control valve assembly
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01- 45
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 45
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 2006 of 2057
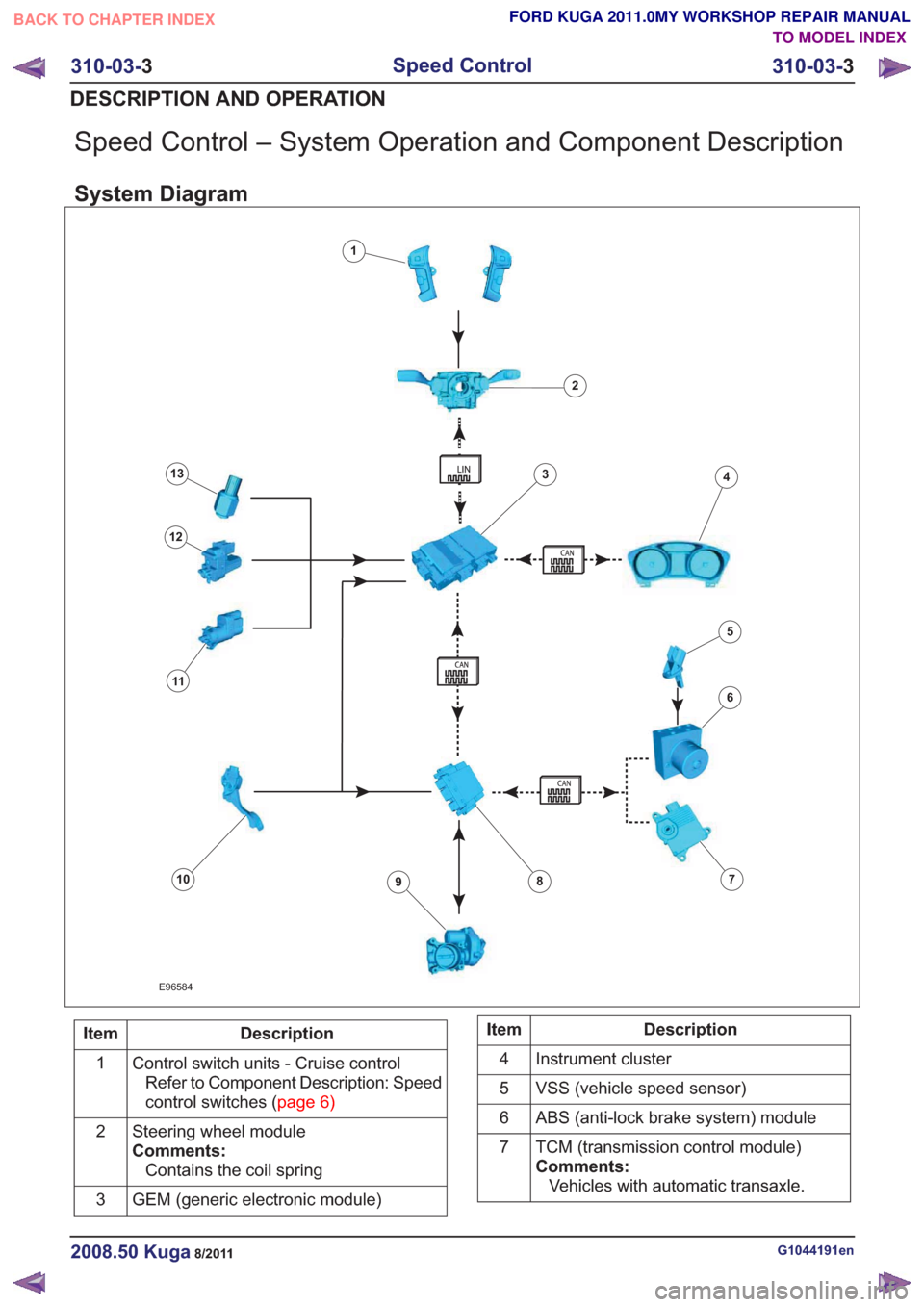
Speed Control – System Operation and Component Description
System Diagram
E96584
1
2
34
6
78910
11
12
13
5
Description
Item
Control switch units - Cruise controlRefer to Component Description: Speed
controlswitches(page6)
1
Steering wheel module
Comments:Contains the coil spring
2
GEM (generic electronic module)
3Description
Item
Instrument cluster
4
VSS (vehicle speed sensor)
5
ABS (anti-lock brake system) module
6
TCM (transmission control module)
Comments:Vehicles with automatic transaxle.
7
G1044191en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
310-03-
3
Speed Control
310-03- 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 2007 of 2057

Description
Item
PCM
8
Throttle body
Comments:Contains the TP (throttle position) sensor
9
The APP (accelerator pedal position)
sensor.
10Description
Item
CPP (clutch pedal position) switch
Comments:Vehicles with manual transaxle.
11
BPP (brake pedal position) switch
12
Reverse gear solenoid
Comments:Vehicles with manual transaxle.
13
System Operation
Speed Control
Cruise control is integrated into PCM and
intervenes in engine management to automatically
keep to the target speed selected by the driver.
When the system is active, the vehicle can be
accelerated or decelerated without the accelerator
pedal being pressed. Cruise control is operated
using the control switch units on the steering wheel.
The PCM controls the throttle to achieve this. The
ABS module supplies the VSS signal for this.
On vehicles with automatic transmission, the TCM
receives a notification via the CAN (controller area
network) bus that cruise control is active. The TCM
then controls the transmission based on special
engine maps.
Cruise control recognizes three operating modes:
• "OFF": Control is switched off.
• "STANDBY": Control is switched on but not
active. The speed of the vehicle is not regulated
by the cruise control.
• "ACTIVE": Control is switched on and active. Cruise control adjusts the vehicle speed to the
stored or desired target speed.
Every time the engine is started, cruise control is
in the "OFF" mode. In this mode, only the "ON"
button is operable.
Cruise control is initially set to "STANDBY" mode
when the "ON" button is pressed. The green cruise
control indicator lamp in the instrument cluster
lights up. There is no target speed saved.
Cruise control can only be set to "STANDBY" mode
under the following conditions:
• Engine speed is between idle speed and maximum permissible speed. Cruise control can only be changed into "ACTIVE"
mode under the following conditions:
• 2nd - 6th gear engaged.
• Engine speed between idle speed and maximum
permissible speed.
• Vehicle speed at least 40 km/h.
Pressing the "SET+" or "SET-" button activates
cruise control ("ACTIVE" mode). The green "Cruise
control" indicator lamp in the instrument cluster
lights up. The current vehicle speed is saved as
the target.
In "ACTIVE" mode the "OFF", "SET+", "SET-" and
"RES" buttons are active. If the "RES" button is
pressed again, control is suspended. The "RES"
button has a dual function and is used to resume
and suspend the cruise control.
Tapping the "SET+" button (for less than 640 ms)
increases the target speed by 1 km/h at a time.
Holding down the "SET+" button (for longer than
640 ms) increases the target speed until the button
is released. If the button is not released, cruise
control accelerates the vehicle up to the maximum
permissible vehicle speed (200 km/h) or up to the
vehicle's maximum speed (whichever speed is
lower). Tapping the "SET-" button (for less than
640 ms) reduces the target speed by 1 km/h at a
time. When the the "SET-" button is held down, the
control reduces the target speed until the button is
released. If the "SET-" button is held down until
the minimum speed of 40 km/h is reached, cruise
control switches to "STANDBY" mode.
Cruise control is put into "STANDBY" mode when
the "RES" button is pressed. Control to the stored
target speed can be started again by pressing the
"RES" button again. If the "SET+" or "SET-" button
is pressed while the "RES" function is being
performed (control to saved target speed), cruise
G1044191en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
310-03- 4
Speed Control
310-03- 4
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 2008 of 2057

control saves the current speed as the target
speed.
Cruise control goes into STANDBY mode in the
following situations:
• Operation of the brake pedal
• Operation of the clutch pedal
• Operation of the parking brake
• If the driver operates the accelerator pedal andthe saved target speed is subsequently
exceeded for more than 5 minutes.
• Pressing any cruise control button for more than 2 minutes
• Intervention by the traction control or electronic stability program (for longer than 40 ms)
• Shifting of the gear selector lever to the "N" position (vehicles with automatic transmission
only)
• Minimum speed falls below 40 km/h.
• Occurrence of particular DTC (diagnostic trouble code)
• faulty signal from the backup lamp switch
Cruise control is switched off when the "OFF"
button is pressed.
If the accelerator pedal is pressed down, the
vehicle speed increases. As soon as the pedal is
released, the speed falls to the saved target value. The following components supply the signals
needed by the cruise control:
• The APP sensor.
– The APP sensor identifies the currentposition of the accelerator pedal and sends
a PWM (pulse width modulation) signal to
the PCM and an analog DC (direct current)
signal to the GEM.
– If one or both of the APP sensors fails, a fault is stored in the PCM fault memory and cruise
control cannot be activated.
• BPP switch – The BPP switch tells the PCM whether thevehicle is being braked. In its rest state the
switch is closed and sends an earth signal
to the GEM. This signal is sent via the CAN
to the PCM.
– The brake light switch is likewise connected to the GEM and is opened in the rest state.
When the vehicle is braked, the brake light
switch sends a signal to the GEM. This
compares the signals from the BPP switch
and the brake light switch. If a discrepancy
occurs, a fault is stored in the error memory
of the GEM. Cruise control cannot be
activated.
• CPP switch – The CPP switch sends a ground signal to theGEM as soon as the clutch is operated. This
signal is passed on by the GEM via the CAN
bus to the PCM. This then supplies the signal
to the cruise control.
– If the CPP switch is incorrectly installed or set, cruise control cannot be activated.
• Wheel speed sensors – The wheel speed sensors record the speedof all the wheels. The recorded speed values
are sent to the ABS module via a hard-wired
connection. The ABS module calculates a
vehicle speed signal (VS signal) from the
speed values and the wheel diameter. This
vehicle speed signal is transferred via the
CAN bus to the PCM and supplied to the
cruise control. If the vehicle speed signal is
faulty, cruise control cannot be activated.
G1044191en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
310-03- 5
Speed Control
310-03- 5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 2014 of 2057

Climate Control System
Refer to Wiring Diagrams Section 412-00, for
schematic and connector information.
Special Tool(s) / General EquipmentTerminal Probe Kit
418-S035
29011A
Digital Multimeter (compatible with K-type
thermocouple)
The Ford approved diagnostic tool
Refrigerant center
Thermometer - Fluke 80 PK-8 (FSE number 260
4102 001 07)
Inspection and Checking
NOTE:The electronic automatic temperature
control (EATC) module is integrated into the air
conditioning control assembly.
1. VERIFY customer concern.
2. Visually CHECK for any obvious mechanical or electrical damage.
NOTE: Ensure correct locking of the wiring harness
connector.
Visual Inspection
Electrical
Mechanical
• Fuses
• Wiring harness
• Connector
• Refrigerant lines
• Condenser core
• Coolant level
• Drive belt
• A/C compressor
3. RECTIFY any obvious causes for a concern found during the visual inspection before
performing any further tests. CHECK the
operation of the system.
4. If the concern is still present after the visual inspection, perform fault diagnosis on the
electronic engine management, the charging
system, the generic electronic module (GEM)
and the instrument cluster (vehicles with EATC:
read out the EATC fault memory as well) using the Ford approved diagnostic tool and RECTIFY
the fault(s) displayed in accordance with the
fault description. CHECK the operation of the
system.
5. For vehicles with no stored fault(s), PROCEED in accordance with the Symptom Chart
according to the fault symptom.
6. Following checking or elimination of the fault(s) and after completion of operations, the fault
memories of all vehicle modules must be READ
OUT and any stored faults must be DELETED.
Refrigerant Circuit - Quick Check
WARNING: The air conditioning system is
filled with refrigerant R134a. Observe
"Health and Safety Precautions". For
further information
REFER to: Air Conditioning (A/C) System
Recovery, Evacuation and Charging
(412-00 Climate Control System - General
Information, General Procedures).
Refrigerant circuit check
WARNING: Under certain circumstances,
refrigerant lines and A/C components may
be extremely hot or cold. Exercising care,
touch the refrigerant lines or A/C
components in order to check this. Failure
to follow these instructions may result in
personal injury.
When the A/C system is operating, the following
conditions should apply:
• The refrigerant line from the refrigerant compressor to the condenser must be hot.
• The refrigerant line from the A/C condenser to the fixed orifice tube must be warm, but not so
hot as the refrigerant line mentioned above.
• Determine the difference in temperature upstream and downstream of the A/C condenser
by measuring the temperatures at the refrigerant
lines. The temperature difference should be
more than 20° C, depending on the ambient
temperature. If the temperature difference is
less, check the condenser for contamination or
damage to the fins as well as operation of the
radiator fans.
G1055878en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
412-00- 3
Climate Control System - General Information
412-00- 3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 2015 of 2057

• The refrigerant line between the fixed orificetube and the evaporator must be cold from the
point where the fixed orifice tube is installed.
Depending on the weather, the refrigerant line
may also have ice on its surface.
• The refrigerant line between the evaporator and the A/C compressor including the dehydrator
must be cold.
Evaporator outlet line temperature test
To test the power of the A/C system, the
temperature at the evaporator outlet line must be
measured. To do this, the following preconditions
must be met:
• Open all windows.
• Set the air distribution to the defrost/dashboardposition and open all the ventilation nozzles.
• DO NOT switch on recirculated air.
• Select lowest blower switch setting.
• Select lowest temperature setting.
NOTE: The temperature measurement cannot be
done with a thermometer which makes no contact.
The surface reflection from the metal line may
cause incorrect readings.
Connect the temperature sensor (Fluke 80 PK-8)
to the outlet line of the evaporator. Locate the
temperature sensor as close as possible to the
evaporator. Connect the temperature sensor to the
multimeter.
Start the engine and allow it to run at idle speed
for several minutes.
Switch on the A/C.
After three minutes, measure the surface
temperature of the evaporator outlet line.
If the temperature measured is 4° C or lower, the
A/C system is OK. If the temperature is higher, the
A/C system may be under-filled. For further
information, refer to
REFER to: Air Conditioning (A/C) System
Recovery, Evacuation and Charging (412-00
Climate Control System - General Information,
General Procedures).
Frequent faults and their causes
If the cooling power of the A/C system is not
adequate, make certain that the temperature
control flap(s) is/are operating correctly. • No or poor cooling performance:
– Blockage or narrowing of a refrigerant line orin the dehydrator. The location of the
blockage or narrowing can easily be located
by temperature comparisons at the
refrigerant lines and the dehydrator. The
blockage or restriction is located at the point
where the temperature difference is
identified. Note: A temperature difference
in the area of the fixed orifice tube is
normal. If the location of the blockage or
narrowing is found, check the corresponding
component and renew as applicable.
• Sudden drop in cooling performance (after the air conditioning has been switched off for
approx. 5 minutes, the cooling performance
returns to normal):
– The cause is an iced-up fixed orifice tubebecause of moisture in the refrigerant circuit.
In order to ensure that moisture is completely
removed from the refrigerant circuit, the
dehydrator should be renewed and the
evacuation time should be extended to 2-3
hours. For further information
REFER to: Air Conditioning (A/C) System
Recovery, Evacuation and Charging
(412-00 Climate Control System - General
Information, General Procedures).
Sequence of A/C Request Signal
NOTE: The electronic automatic temperature
control (EATC) module is integrated into the air
conditioning control assembly.
NOTE: The generic electronic module (GEM) is
an integral part of the central junction box (CJB).
After actuating the A/C ON/OFF switch integrated
into the A/C control assembly, an A/C request
signal is sent from the A/C control assembly
(vehicles with EATC: EATC module) to the GEM.
From there, the signal is sent to the instrument
cluster via the MS-CAN bus. A gateway is installed
in the instrument cluster, which establishes the
connection between the MS-CAN bus and the
HS-CAN bus.
After the signal has been converted in the gateway,
it is relayed to the powertrain control module (PCM)
via the HS-CAN bus. Once all the required
parameters have been met, the PCM switches on
the refrigerant compressor and thus the A/C system
via the A/C clutch relay.
G1055878en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
412-00- 4
Climate Control System - General Information
412-00- 4
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL