2011 FORD KUGA instrument cluster
[x] Cancel search: instrument clusterPage 1424 of 2057
Vehicles with ESP are equipped with an
opto-electronic steering wheel rotation sensor as
an integral part of the clockspring.
The following must be taken into account when
removing/installing or replacing the opto-electronic
steering wheel rotation sensor:
• If installing a new clockspring, remove theclockspring locking screw.
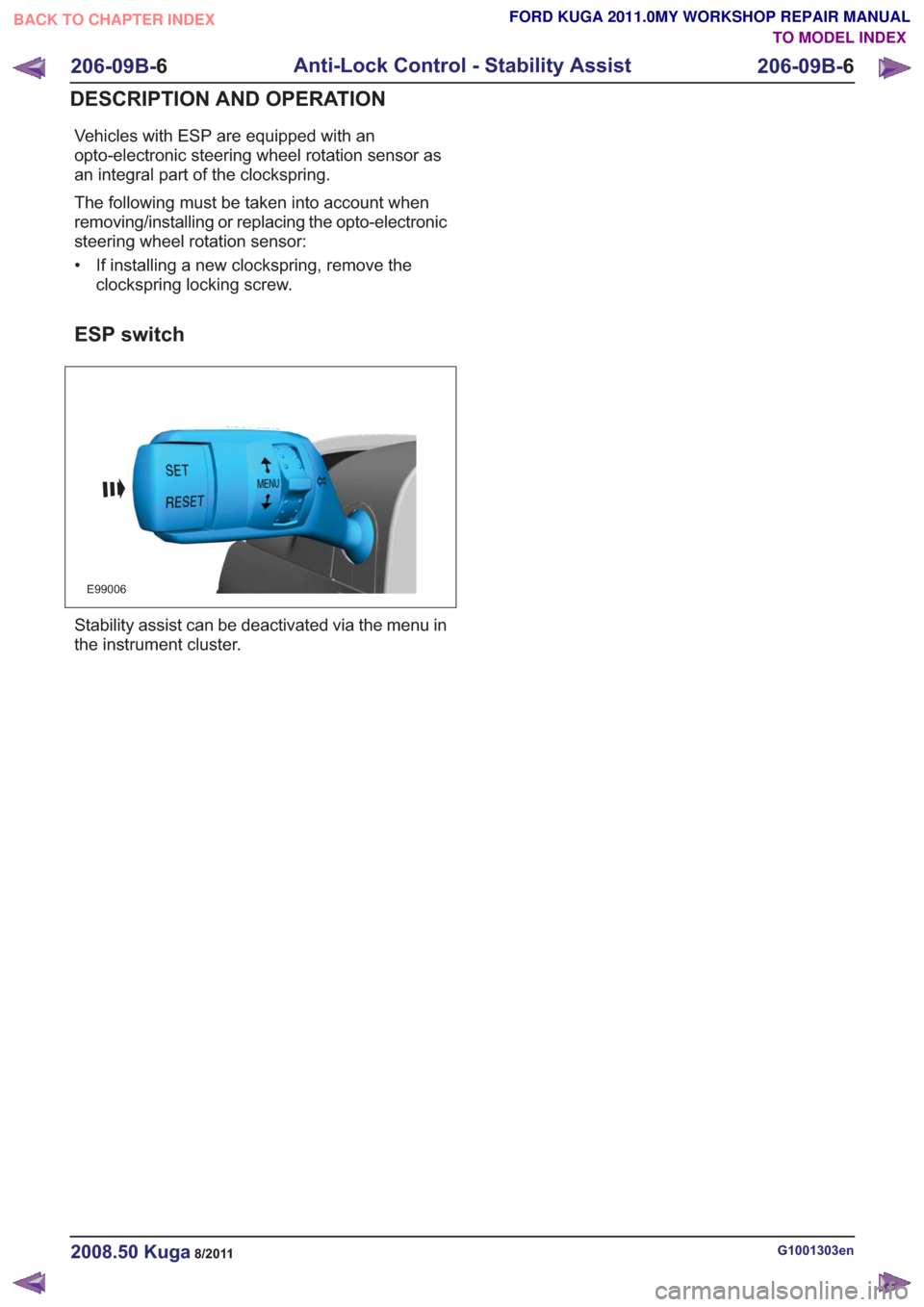
ESP switch
E99006
Stability assist can be deactivated via the menu in
the instrument cluster.
G1001303en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-09B- 6
Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist
206-09B- 6
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1428 of 2057

Description
Item
Battery
1
Battery junction box (BJB) in the engine
compartment
2
Generic electronic module (GEM)
3
Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
4
Instrument cluster
5
Data link connector (DLC)
6
Steering Wheel Rotation Sensor
7
ABS/ESP module or hydraulic control unit
(HCU)
8Description
Item
Combined yaw rate sensor and lateral
acceleration sensor / longitudinal
acceleration sensor
9
Front wheel sensor
10
Rear wheel sensor
11
Rear wheel sensor
12
Front wheel sensor
13
ESP switch
14
Rear brakes
15
Front brake
16
The ABS monitors the different wheel speeds of
the vehicle with the aid of wheel speed sensors.
Using the data from all of the wheel speed sensors,
the ABS module calculates the so-called reference
speed, which is a measure of the actual road
speed. The ABS module compares the individual
circumferential wheel speeds with this reference
speed when the driver initiates braking. If one or
more of the circumferential wheel speeds deviates
too far from the reference speed, this means that
slip at the affected wheels is so great that steering
stability of the vehicle is no longer ensured. The
ABS module actuates electro-mechanical valves
which influence the brake pressure at the relevant
wheels.
Like the traction control system (TCS), the ESP
system uses a large proportion of the ABS
components. In addition, there are sensors which
pick up the steering angle, the acceleration forces
acting on the vehicle and the yaw rate or yaw
moment. The sensors transmit these signals to the
combined ABS/ESP module. Using the wheel
speed and steering angle data, the ABS/ESP
module calculates the direction of travel planned
by the driver and determines the corresponding
speed-dependent lateral acceleration and yaw
moment. These values are compared with those
actual measured. If the actual lateral acceleration
and the yaw moment deviate excessively from the
target values (unstable driving characteristics), the
ABS/ESP module actuates individual brakes
selectively via the HCU (hydraulic control unit). In
addition, the engine speed is reduced by
intervention in the engine management system.
How the system works for understeer: In the
event of understeer, brake intervention occurs at
the wheels on the inside of the curve. The rear
wheel is braked heavily, so that a high amount of slip is caused. In this way, the cornering force of
the rear axle is heavily reduced and the centrifugal
force that now becomes effective turns the rear of
the vehicle back into the curve. The front wheel is
not braked as hard. The braking force that is
transmitted via the front wheel to the road surface
generates a torque with the aid of the lever arm
(vertical tire force to the vehicle's centre of gravity),
which supports the yaw moment of the vehicle.
Both measures together result in the vehicle
reverting back to the curved path intended by the
driver.
How the system works for oversteer:
In the
event of oversteer the wheels on the outside of the
curve are braked. This time, the front wheel is
subjected to a high level of slip so that the
cornering force at the front axle is reduced. The
rear wheel is not braked as heavily and, together
with the effective lever arm, results in a reduction
in the vehicle yaw moment. Both measures
together result in the vehicle being stabilized and
reverting back to the curved path intended by the
driver.
If ESP control occurs, possible ABS interventions
will be overridden as the ESP works at higher slip
rates than the ABS.
Emergency brake assist (EBA): The emergency
brake assist helps drivers in emergency braking
situations by automatically applying the brakes with
the maximum possible braking force.
If the brake pedal is pressed very suddenly, the
ABS module increases the hydraulic pressure to
all of the brakes until the threshold for ABS
intervention is reached. This applies the maximum
braking effort for the available traction. The ABS
control unit monitors inputs from the brake pedal
switch and from the pressure sensor within the
G1001304en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-09B- 10
Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist
206-09B- 10
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1429 of 2057

HCU to check for sudden actuation of the brakes.
With the brake pedal pressed, the ABS module
triggers emergency braking if the rate of increase
of hydraulic pressure exceeds the predetermined
limit.
If the brake pedal is pressed so hard that the ABS
becomes active on the front wheels then the ABS
control unit increases the pressure to the rear
wheel brakes up to the ABS intervention threshold.
EBA operation continues until the driver releases
the brake pedal sufficiently for the hydraulic
pressure in the HCU to drop below a threshold
value stored in the ABS module.
Trailer stability control:If the vehicle is ordered
with a trailer coupling then the Trailer Stability
Control function is integrated in the ESP. The ESP
detects snaking when driving with a trailer and
reduces the speed of the vehicle and trailer through
adapted braking and, if necessary, by also reducing
the engine output until the snaking movement of
the trailer is corrected.
Roll-over protection: The ESP dynamically
determines the tipping tendency of the vehicle and
works in conjunction with the EBA system to
prevent the vehicle from tipping over during
dynamic maneuvers like lane changing or while
negotiating bends.
Emergency brake light: The emergency brake
light automatically switches on the hazard flasher
system to warn drivers of other vehicles that
emergency braking is being initiated. Based on a
defined delay value, the ABS/ESP module sends
a signal to the generic electronic module (GEM)
via the CAN data bus. The GEM activates the
hazard flasher system, that then flashes 7 times.
Prerequisites for activation of the emergency brake
light are:
• The speed is higher than 50 km/h.
• The brake pedal is being actuated.
• The deceleration is greater than 9 m/s².
To prevent activation on snow or ice, for example,
the following prerequisites must be met:
• The speed is higher than 50 km/h.
• The brake pedal is being actuated.
• ABS regulation takes place.
• The deceleration is greater than 6 m/s².
Tire pressure monitoring system: The tire
pressure monitoring system used in the Kuga is
able to detect loss of air in a tire at an early stage
and warn the driver. Because it can only compare
the behaviour of the tyres with each other, it is not possible to draw conclusions about the absolute
tyre pressure. It is also not possible to monitor the
spare tyre pressure. In order for the system to
operate correctly, the tyre pressures must be
regularly checked and corrected and the system
subsequently initialised (see below).
The tire pressure monitoring system used here,
depending on the equipment level, is built into the
anti-lock braking system (ABS) as an extra function
and therefore does not have its own sensors.
The ABS module measures the loss of pressure
in the tyres by calculation using the wheel speed
sensors of the ABS system. If a tyre loses
pressure, its diameter decreases and the speed of
the wheel therefore increases. If the ABS module
detects such a loss in pressure, it sends a signal
to the instrument cluster via the CAN bus and a
warning message is displayed in the message
centre. The warning threshold depends among
other things on the dimension of the tyres being
used, the vehicle operating conditions and the
status at the last initialisation. Since neither the
absolute tyre pressure nor the position of the tyre
is known, the pressure of all the tyres must be
checked and the system re-initialised after a tyre
pressure warning. If necessary, the cause of the
loss of pressure must be investigated.
Regular tyre pressure checks are still necessary.
The system must be initialised after a tyre is
changed, winter or summer tyres fitted, the
pressures corrected or adjusted to suit the vehicle
load. This can be done by the driver using the
driver information system. For further information,
see: Owner’s Manual.
Component Description
Opto-electronic steering wheel rotation
sensor
E80158
G1001304en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-09B-
11
Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist
206-09B- 11
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1431 of 2057

ESP switch
E99006
Stability assist can be deactivated via the menu in
the instrument cluster. The stability assist functions
are deactivated when the Set switch is actuated.
The ABS control module makes the stability assist
functions available once more when the Set switch
is actuated again. The stability assist function is
automatically reactivated when the ignition is
switched on.
The electronic EBA is a constant function and will
remain active even if the ESP has been switched
off.
Combined yaw rate sensor and lateral
acceleration sensor / longitudinal
acceleration sensor
E96822
The heart of the combined yaw rate sensor and
lateral acceleration sensor/longitudinal acceleration
sensor is a small, double-sided tuning fork made
of a piezo crystal (A). The exciter side of this tuning
fork is set to a resonance of 11 kHz with the aid of
an alternating current. The measuring side of the
tuning fork features a resonance frequency of 11.33
kHz and therefore does not vibrate (B). Since,
under influence of an external accelerating force,
a vibrating mass reacts slower than a comparable
mass that is not vibrating, the tuning fork twists
within itself with rotational movement being
imparted on the sensor (C). This rotation results
in a change in the charge distribution in the Piezo
element, which is subsequently picked up and
converted into an electronic signal by electronics
integrated into the sensor. This electronic signal is
then sent to the ESP module. The ESP module
evaluates these data and takes into account the
other input data (vehicle speed, wheel speed)
before deciding whether the ESP function is
required.
G1001304en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-09B-13
Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist
206-09B- 13
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1834 of 2057
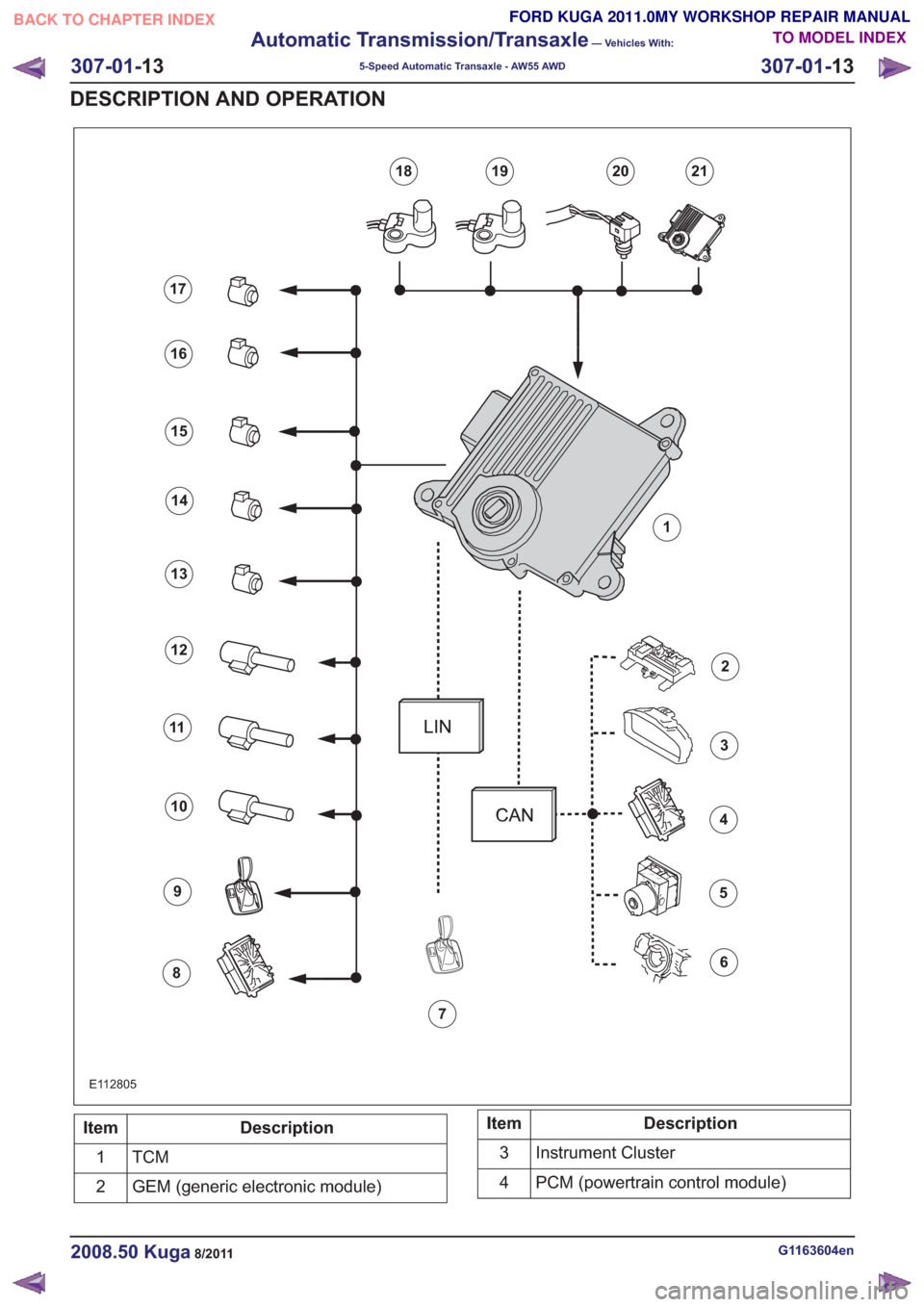
E112805
59
13
2
6
10
14
3
7
11
15
4
8
12
16
17
19202118
1
Description
Item
TCM1
GEM (generic electronic module)
2Description
Item
Instrument Cluster
3
PCM (powertrain control module)
4
G1163604en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01- 13
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 13
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1851 of 2057

select-shift switch module transmits a downshift
signal to the TCM.
If you move the gear selector lever backwards (+),
an upshift signal is transmitted to the TCM. In the
instrument cluster, the symbol when the selector
lever is in the 'S' position changes from 'D' to the
current gear, for example 3.
The TCM transmits a signal to the select-shift
switch module to switch on the light emitting diode
for 'S' and to switch off all other light emitting
diodes. The TCM decides whether the shift process
is possible.
If the shift process is permitted, then the various
valves are activated according to the intended
combination for each gear.
In certain situations however, the TCM determines
the gear shifting. The following applies:
• If the vehicle is stationary, only 1st, 2nd and 3rdgears can be selected. 4th gear can be selected
at speeds over 30 km/h and 5th gear at speeds
over 40 km/h.
• The kickdown function is only available in the automatic transmission range 'D'
• Automatic gear changes into the next higher or next lower gear occur at fixed vehicle speeds
and fixed engine speeds
• The permitted engine speed for manual change down agree with that for the kickdown change
up, i.e. an engine speed of approximately 6000
rpm.
• If the temperature inside the transmission rises too high, the TCM takes control of the shift
decisions in order to select a gear in which
activation of torque converter lockup at the
current speed is possible
• Torque converter lockup is possible in 3rd, 4th and 5th gear. (1st and 2nd gears do not have
torque converter lockup)
The signal that specifies the position of the lever
to the select-shift switch module is generated as
follows in the selector lever position 'S': there is a
Hall sensor at the printed circuit board for the
module for each of the three selector lever
positions. A permanent magnet on the cover in the
selector lever affects the output signals to the
control module from the sensors. The control
module recognizes the position of the lever by the
differences in the signal properties.Selector lever from 'N' to 'R' position
The TCM only permits shifting to reverse gear if
the vehicle speed is less than 4.35 mph.
If the vehicle speed is greater than 7 km/h (approx.
4.35 mph), the clutch (C2) and the multi-plate brake
(B3) are not activated and the gearshift is thus
prevented.
Self-test and Diagnosis
The TCM monitors all the transaxle sensors and
electronic components including the PCM. If a fault
occurs, the driver is informed via a warning
indicator and a text message in the instrument
cluster. Faults are stored as DTCs in the fault
memory of the TCM and can be read out and
cleared using the IDS.
Temperature controlled torque converter
lockup
If heavy load and high ambient temperatures cause
an abnormal rise in the transmission temperature,
torque converter lockup is activated as often as
possible (temperature controlled lockup).
This reduces the slip and the heat developed in
the transmission. When the temperature drops
below +20 °C, torque converter lockup is not used.
Slip locking
When changing gear this function makes it possible
for the gears to engage more smoothly with
reduced vibration and less noise. In this mode, the
torque converter clutch is activated but not fully
locked.
The following conditions must be met for the
function to activate:
• Gear selector lever in position D or S.
• Gear 3, 4 or 5.
• The transmission input speed is 1100 rpm or more and the throttle plate opening 20 - 35%.
• The transmission fluid temperature is 40 - 120 °C.
Hill climbing
The TCM can change the shift pattern slightly when
driving uphill to avoid changing gear too often.
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01- 30
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 30
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1863 of 2057

Reset adaptation data
Adaptation values are stored in the software of the
TCM:
• Adaptation should be reset after an internalcomponent has been exchanged or the whole
transmission has been changed.
The adaptation of the transmission is reset via IDS.
Limp home mode
The TCM software contains functions which take
control of the transmission if serious faults occur.
The fault characteristic decides which strategies
are to be used.
The vehicle remains capable of restricted
operation.
The TCM strategy differentiates between four emergency modes adapted to the fault situation:
Gear
Position
Mode
4th
D, S+
Emergency 1
2nd
S-
Reverse
Reverse
3rd
D, S+
Emergency 2
2nd
S-
Reverse
Reverse
4th
D, S+
Emergency 3 (*)
2nd
S-
Reverse
Reverse
4th
D, S+, S-
Emergency 4
Reverse
Reverse
(*) As for Emergency 1 mode, the second gear will however be shifted using other solenoid valves.
Different measures are implemented, depending
on the current gear position and driving situation
when the fault occurs:
• When a fault occurs, the TCM makes it possible
for the vehicle to maintain restricted operation.
The distance travelled should be kept as short
as possible.
• Torque limitation is activated in order to protect the transaxle components.
• When the engine is restarted (ignition switched off for approx. 15 seconds), the transaxle is no
longer in limp home mode. There is no longer
a fault indication on the instrument cluster, and
the MIL (malfunction indicator lamp) is off.
However, the fault remains stored in the TCM.
If the fault is still present, limp home mode is
reactivated.
• If limp home mode is reactivated after the ignition is switched on, the option exists in select-shift mode to pull away in 2nd gear. This
is the case unless the transaxle is in emergency
mode 4. Only 4th gear and the reverse gear are
available in this mode.
Component Description
Tasks of the electronic components
The following overview summarizes the input and
output signals from the transmission control
module.
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01-
42
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 42
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1864 of 2057
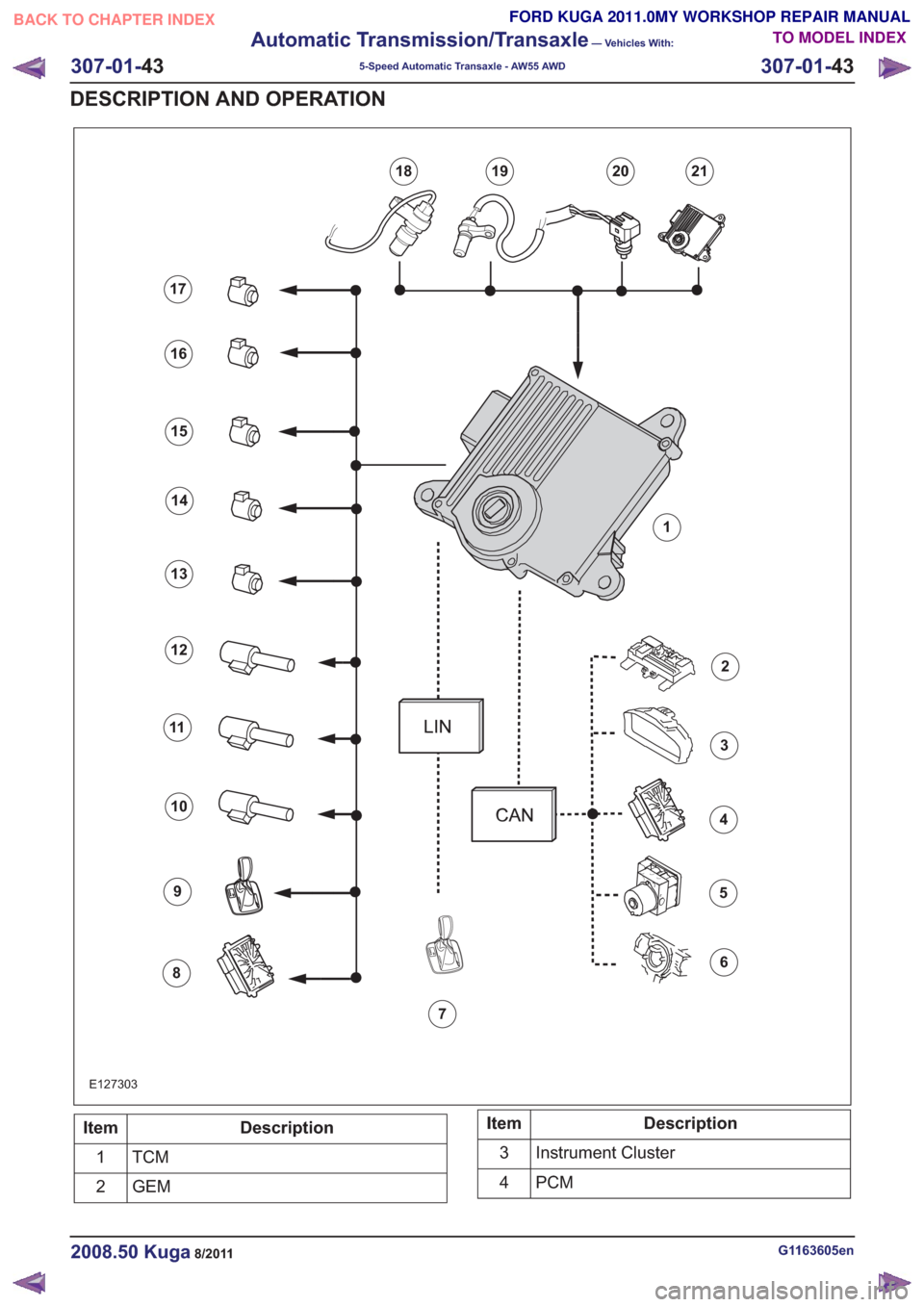
E127303
59
13
2
6
10
14
3
7
11
15
4
8
12
16
17
19202118
1
Description
Item
TCM1
GEM
2Description
Item
Instrument Cluster
3
PCM
4
G1163605en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01- 43
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 43
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL