2011 FORD KUGA oil level
[x] Cancel search: oil levelPage 1796 of 2057

current value is reached. The PCM then
permanently connects the heating element to earth.
The catalyst monitor sensor is used by the PCM
to measure the oxygen content in the exhaust gas
in the TWC. If all the conditions for catalyst
diagnostics are met, based on this information the
PCM can check that the TWC is working
satisfactorily. The information is also used to
improve the air/fuel mixture adjustment.
The catalyst monitor sensor is similar in function
to an HO2S. The signal transmitted by the catalyst
monitor sensor changes sharply if the oxygen
content in the exhaust gas changes. For this
reason, catalyst monitor sensors are also called
"jump lambda sensors".
Fuel tank purging
The EVAP purge valve is only actuated by the PCM
if the coolant temperature is at least 60°C.
Actuation is done ground side by means of a PWM
signal. This makes it possible to have the full range
of opening widths, from fully closed to fully open.
The PCM determines from the operating conditions
when and how wide to open the EVAP tank purge
valve. If the EVAP purge valve is opened, the
engine sucks in ambient air through the activated
charcoal in the evaporative emission canister as
a result of the vacuum in the intake manifold. In
this way the adsorbed hydrocarbons are led to the
combustion chamber of the engine.
The EVAP tank purge valve is not actuated and
system cleaning is interrupted if the engine
switches to idle and/or a closed-loop control
process is initiated.
Power (battery voltage) is supplied via the
Powertrain Control Module relay in the BJB. The
solenoid coil resistance is between 17 and 24 ohms
at 20°C.
Engine speed control
The APP sensor provides the PCM with information
about the driver's request for acceleration.
The throttle control unit receives a corresponding
input signal from the PCM. An electric motor then
moves the throttle valve shaft by means of a set
of gears. The position of the throttle is continuously
recorded by the TP sensor. Information on throttle
position is processed and monitored by the PCM.
The TP sensor comprises two potentiometers.
These work in opposite ways to each other. In one
potentiometer, the resistance increases when the
throttle is opened, in the other it decreases. Thisallows the operation of the potentiometers to be
checked. The signal from the TP sensor is
amplified in the lower range (idle to a quarter open)
by the PCM to enable more precise control of the
throttle in this range. This is necessary because
the engine is very sensitive to changes in throttle
angle in this throttle opening range.
With the throttle valve position kept constant, the
ignition angle and the injected fuel quantity are
then varied to meet the torque demands.
Depending on the operating state of the engine, a
change in the position of the throttle flap may not
be necessary when the APP sensor changes.
If a fault develops in the throttle control unit, a
standby function is executed. This standby function
allows a slight opening of the throttle flap, so that
enough air passes through to allow limited engine
operation. For this purpose, there is a throttle flap
adjustment screw on the throttle housing. The
return spring closes the throttle flap until the stop
of the toothed segment touches the stop screw. In
this way a defined throttle flap gap is formed for
limp home mode.
The stop screw has a spring loaded pin, which
holds the throttle flap open for limp home mode.
In normal operating mode, this spring loaded pin
is pushed in by the force of the electric motor when
the throttle flap must be closed past the limp home
position (e.g. for idle speed control or overrun
shutoff).
Oil monitoring
The engine does not have an oil pressure
switch.
The oil level and oil quality are calculated.
Calculating the engine oil level
The oil level is determined by continuous
measurement of the capacitance (i.e. the ability to
store an electrical charge) between the two
capacitive elements of the engine oil
level/temperature/quality sensor. The different oil
levels cause the capacitance between the elements
to change. The data are recorded by the PCM and
converted into an oil level value. Temporary
fluctuations in oil level are automatically filtered out
by the PCM.
Calculating oil quality
The PCM calculates the oil quality from the oil level
measurement and the oil temperature measured
by the sensor, plus the engine speed and the
average fuel consumption. The driver is informed
about when an oil change is due.
G1021908en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14- 22
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
22
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1808 of 2057
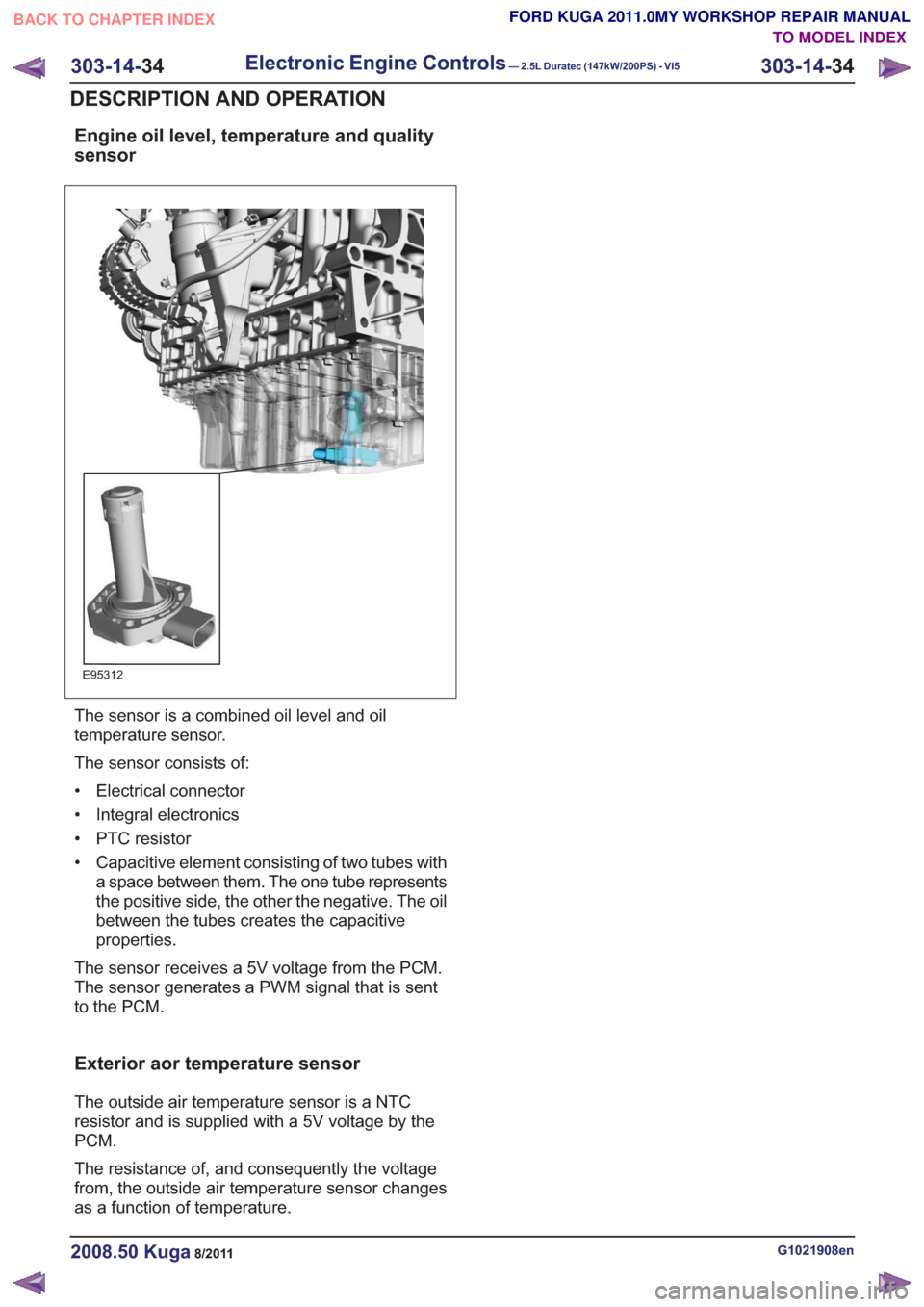
Engine oil level, temperature and quality
sensor
E95312
The sensor is a combined oil level and oil
temperature sensor.
The sensor consists of:
• Electrical connector
• Integral electronics
• PTC resistor
• Capacitive element consisting of two tubes witha space between them. The one tube represents
the positive side, the other the negative. The oil
between the tubes creates the capacitive
properties.
The sensor receives a 5V voltage from the PCM.
The sensor generates a PWM signal that is sent
to the PCM.
Exterior aor temperature sensor
The outside air temperature sensor is a NTC
resistor and is supplied with a 5V voltage by the
PCM.
The resistance of, and consequently the voltage
from, the outside air temperature sensor changes
as a function of temperature.
G1021908en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14- 34
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
34
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1823 of 2057

307-01-29
Automatic transmission, selector lever in position "D". ...................................................
307-01-29
Sport mode, selector lever in position "S" .......................................................................
307-01-29
Changing gear in select-shift mode........................................................................\
........
307-01-30
Selector lever from 'N' to 'R' position ........................................................................\
......
307-01-30
Self-test and Diagnosis ........................................................................\
...........................
307-01-30
Temperature controlled torque converter lockup ............................................................
307-01-30
Slip locking ........................................................................\
..............................................
307-01-30
Hill climbing ........................................................................\
.............................................
307-01-31
Downhill driving ........................................................................\
.......................................
307-01-31
Hill-hold function ........................................................................\
.....................................
307-01-31
Altitude correction ........................................................................\
...................................
307-01-31
Selector lever lock ........................................................................\
..................................
307-01-31
Shifting from P into another transmission range .............................................................
307-01-31
Shifting from N into another transmission range .............................................................
307-01-31
Power flow through the transmission ........................................................................\
......
307-01-31
Clutches and brakes ........................................................................\
...............................
307-01-33
Position P (park) ........................................................................\
.....................................
307-01-34
Position N (neutral) ........................................................................\
.................................
307-01-35
Position D, 1st gear........................................................................\
................................
307-01-36
Position D, 2nd gear ........................................................................\
...............................
307-01-37
Position D, 3rd gear ........................................................................\
................................
307-01-38
Position D, 4th gear ........................................................................\
................................
307-01-39
Position D, 5th gear ........................................................................\
................................
307-01-40
Position R (reverse) ........................................................................\
................................
307-01-41
Service instructions ........................................................................\
.................................
307-01-41
Towing procedure ........................................................................\
...................................
307-01-42
Reset adaptation data ........................................................................\
.............................
307-01-42
Limp home mode ........................................................................\
....................................
307-01-42
Component Description ........................................................................\
..............................
Tasks of the electronic components ........................................................................\
........
307-01-44
Input signals ........................................................................\
............................................
307-01-45
Output signals ........................................................................\
.........................................
Control valve assembly ........................................................................\
...........................
Shift solenoids S1 - S5 ........................................................................\
...........................
PWM-
solenoid valve – TCC (SLU) ........................................................................\
........
PWM solenoid valve – shift pressure (SLS) ...................................................................
PWM solenoid valve for main line pressure (SLT) ..........................................................
307-01-52
Installation position ........................................................................\
.................................
Operation ........................................................................\
................................................
Selector lever with integrated select-shift switch module ...............................................
Oil pump ........................................................................\
..................................................
Torque converter with TCC ........................................................................\
.....................
The TSS sensor ........................................................................\
......................................
The OSS sensor ........................................................................\
.....................................
The TFT sensor ........................................................................\
......................................
The TR sensor ........................................................................\
........................................
GENERAL PROCEDURES
T ransmission Fluid Level Check ........................................................................\
.................
307-01-63
T ransmission Fluid Drain and Refill ........................................................................\
............
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION 307-01-67
Halfshaft Seal LH ........................................................................\
........................................
307-01-68
Halfshaft Seal RH........................................................................\
.......................................
307-01-69
Main Control Valve Body ........................................................................\
............................
307-01-2
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 2
.
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
307-01-42
307-01-49
307-01-52 307-01-47
307-01-45
307-01-50
307-01-51
307-01-53
307-01-55
307-01-54
307-01-56
307-01-57
307-01-58
307-01-61 307-01-60
PAGE 2 OF 3 FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1882 of 2057
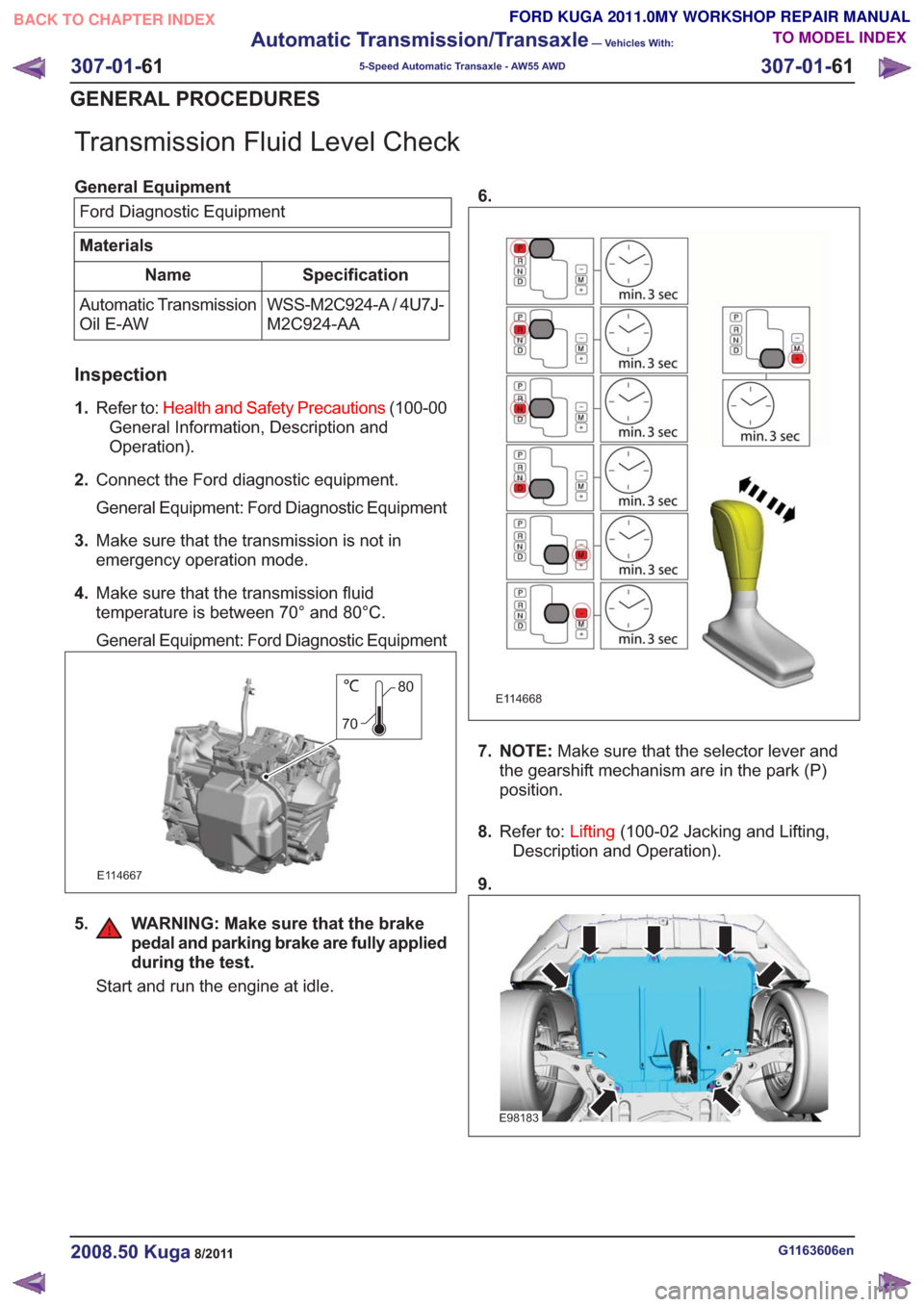
Transmission Fluid Level Check
General EquipmentFord Diagnostic Equipment
Materials
Specification
Name
WSS-M2C924-A / 4U7J-
M2C924-AA
Automatic Transmission
Oil E-AW
Inspection
1.
Refer to: Health and Safety Precautions (100-00
General Information, Description and
Operation).
2. Connect the Ford diagnostic equipment.
General Equipment: Ford Diagnostic Equipment
3. Make sure that the transmission is not in
emergency operation mode.
4. Make sure that the transmission fluid
temperature is between 70° and 80°C.
General Equipment: Ford Diagnostic Equipment
80
70
E114667
5. WARNING: Make sure that the brake pedal and parking brake are fully applied
during the test.
Start and run the engine at idle. 6.
E114668
7. NOTE:
Make sure that the selector lever and
the gearshift mechanism are in the park (P)
position.
8. Refer to: Lifting(100-02 Jacking and Lifting,
Description and Operation).
9.
E98183
G1163606en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01- 61
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 61
GENERAL PROCEDURES
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1883 of 2057
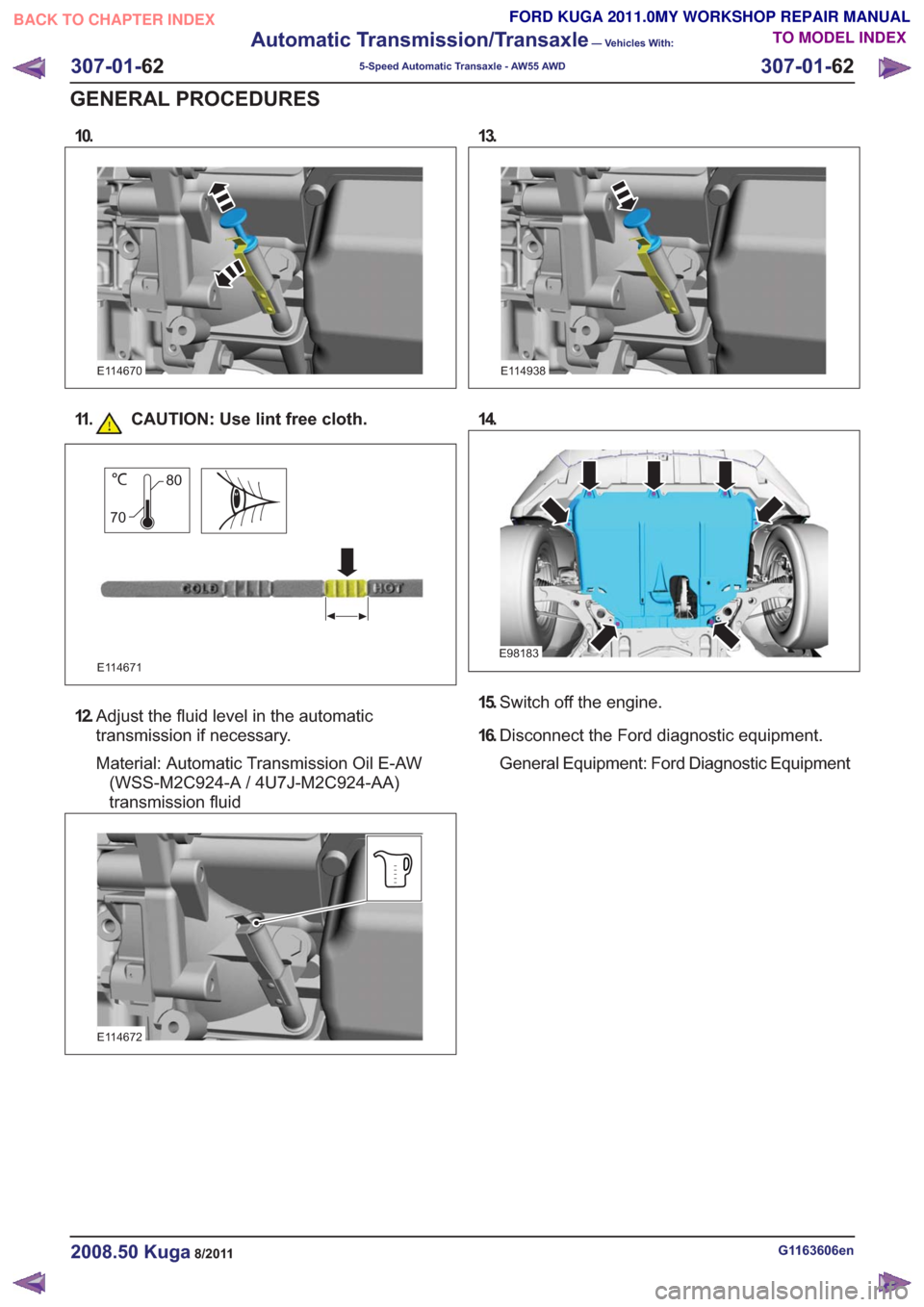
10.
E114670
11. CAUTION: Use lint free cloth.
E114671
80
70
12. Adjust the fluid level in the automatic
transmission if necessary.
Material: Automatic Transmission Oil E-AW
(WSS-M2C924-A / 4U7J-M2C924-AA)
transmission fluid
E114672
13.
E114938
14.
E98183
15. Switch off the engine.
16. Disconnect the Ford diagnostic equipment.
General Equipment: Ford Diagnostic Equipment
G1163606en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01- 62
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 62
GENERAL PROCEDURES
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1951 of 2057

Transfer Case Fluid Level Check
MaterialsSpecification
Name
8U7J-19G518-BA
Rear Axle Oil SAE 75W-
90
Inspection
1. Refer to: Health and Safety Precautions (100-00
General Information, Description and
Operation).
2.
E139436
3. Material: Rear Axle Oil SAE 75W-90
(8U7J-19G518-BA) transmission fluid
•
• Correct the rear axle oil level if neccessary.
• 20ml~1mm
0mm0mm
E114595
4. NOTE:
Make sure that a new component is
installed.
Torque: 34
Nm
E139434
G1164988en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-07- 9
Transfer Case
— Vehicles With: 5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55
AWD/6-Speed Automatic Transaxle - 6DCT450
307-07- 9
GENERAL PROCEDURES
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL