2011 FORD KUGA Index
[x] Cancel search: IndexPage 1429 of 2057

HCU to check for sudden actuation of the brakes.
With the brake pedal pressed, the ABS module
triggers emergency braking if the rate of increase
of hydraulic pressure exceeds the predetermined
limit.
If the brake pedal is pressed so hard that the ABS
becomes active on the front wheels then the ABS
control unit increases the pressure to the rear
wheel brakes up to the ABS intervention threshold.
EBA operation continues until the driver releases
the brake pedal sufficiently for the hydraulic
pressure in the HCU to drop below a threshold
value stored in the ABS module.
Trailer stability control:If the vehicle is ordered
with a trailer coupling then the Trailer Stability
Control function is integrated in the ESP. The ESP
detects snaking when driving with a trailer and
reduces the speed of the vehicle and trailer through
adapted braking and, if necessary, by also reducing
the engine output until the snaking movement of
the trailer is corrected.
Roll-over protection: The ESP dynamically
determines the tipping tendency of the vehicle and
works in conjunction with the EBA system to
prevent the vehicle from tipping over during
dynamic maneuvers like lane changing or while
negotiating bends.
Emergency brake light: The emergency brake
light automatically switches on the hazard flasher
system to warn drivers of other vehicles that
emergency braking is being initiated. Based on a
defined delay value, the ABS/ESP module sends
a signal to the generic electronic module (GEM)
via the CAN data bus. The GEM activates the
hazard flasher system, that then flashes 7 times.
Prerequisites for activation of the emergency brake
light are:
• The speed is higher than 50 km/h.
• The brake pedal is being actuated.
• The deceleration is greater than 9 m/s².
To prevent activation on snow or ice, for example,
the following prerequisites must be met:
• The speed is higher than 50 km/h.
• The brake pedal is being actuated.
• ABS regulation takes place.
• The deceleration is greater than 6 m/s².
Tire pressure monitoring system: The tire
pressure monitoring system used in the Kuga is
able to detect loss of air in a tire at an early stage
and warn the driver. Because it can only compare
the behaviour of the tyres with each other, it is not possible to draw conclusions about the absolute
tyre pressure. It is also not possible to monitor the
spare tyre pressure. In order for the system to
operate correctly, the tyre pressures must be
regularly checked and corrected and the system
subsequently initialised (see below).
The tire pressure monitoring system used here,
depending on the equipment level, is built into the
anti-lock braking system (ABS) as an extra function
and therefore does not have its own sensors.
The ABS module measures the loss of pressure
in the tyres by calculation using the wheel speed
sensors of the ABS system. If a tyre loses
pressure, its diameter decreases and the speed of
the wheel therefore increases. If the ABS module
detects such a loss in pressure, it sends a signal
to the instrument cluster via the CAN bus and a
warning message is displayed in the message
centre. The warning threshold depends among
other things on the dimension of the tyres being
used, the vehicle operating conditions and the
status at the last initialisation. Since neither the
absolute tyre pressure nor the position of the tyre
is known, the pressure of all the tyres must be
checked and the system re-initialised after a tyre
pressure warning. If necessary, the cause of the
loss of pressure must be investigated.
Regular tyre pressure checks are still necessary.
The system must be initialised after a tyre is
changed, winter or summer tyres fitted, the
pressures corrected or adjusted to suit the vehicle
load. This can be done by the driver using the
driver information system. For further information,
see: Owner’s Manual.
Component Description
Opto-electronic steering wheel rotation
sensor
E80158
G1001304en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-09B-
11
Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist
206-09B- 11
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1430 of 2057

The opto-electronic steering wheel rotation sensors
use light barriers for contactless scanning of a
segment disk which is connected fixedly to the
steering shaft.
E54014
1
23
4
Description
Item
Segment disk
1
Photoelectric barrier
2
Electronics
3
Electrical connection
4
Use is made of opto-electronic types of sensors
with relative and absolute steering angle sensing.
For relative steering angle sensing, changes in the
steering angle are measured exclusively by the
sensor and transmitted to the ABS/ESP module.
With the aid of other vehicle status signals (e.g.
wheel speed sensors) the module calculates the
straight ahead position of the steering. For absolute
steering angle sensing, the sensor transmits a
specific signal to the module for each steering
angle position (in relation to one turn of the steering
wheel). The straight ahead position of the steering
is therefore defined in the sensor. On an absolute
steering angle sensor, several photoelectric barrier
modules are distributed around the segment disk
at varying distances. The gaps between segments
of the segment disk are also unequal. For each specific steering angle there is therefore a specific
switch status of all photoelectric barriers.
ABS/ESP module or hydraulic control unit
(HCU)
E97648
1
2
3
Description
Item
ABS Pump Motor
1
Valve block (with low-pressure
accumulators)
2
ABS module
3
The HCU comprises the ABS module, the valve
block (with low-pressure accumulators) and the
ABS pump.
The valve block combines all of the brake pressure
control valves in one unit. Depending on the
system, either simple changeover valves or
proportioning valves (e.g. on EBD (electronic brake
force distribution) systems) are installed. The
low-pressure accumulators store the brake fluid
that is returned from the wheel brakes during the
pressure reduction phase until it is drawn back into
the system by the ABS pump.
The ABS pump is designed as a dual piston pump.
This means that two separate pump elements
assure an increase in brake pressure during control
interventions. A direct current motor drives the
pump pistons via an eccentric shaft.
The ABS/ESP module monitors the input signals
of all sensors and actuates the electro-magnetic
brake pressure valves and the ABS pump as
required. For reasons of safety, the module is of
the redundant type, whereby processing of the
signals is carried out via two separate processors
that also monitor each other.
G1001304en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-09B- 12
Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist
206-09B- 12
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1431 of 2057

ESP switch
E99006
Stability assist can be deactivated via the menu in
the instrument cluster. The stability assist functions
are deactivated when the Set switch is actuated.
The ABS control module makes the stability assist
functions available once more when the Set switch
is actuated again. The stability assist function is
automatically reactivated when the ignition is
switched on.
The electronic EBA is a constant function and will
remain active even if the ESP has been switched
off.
Combined yaw rate sensor and lateral
acceleration sensor / longitudinal
acceleration sensor
E96822
The heart of the combined yaw rate sensor and
lateral acceleration sensor/longitudinal acceleration
sensor is a small, double-sided tuning fork made
of a piezo crystal (A). The exciter side of this tuning
fork is set to a resonance of 11 kHz with the aid of
an alternating current. The measuring side of the
tuning fork features a resonance frequency of 11.33
kHz and therefore does not vibrate (B). Since,
under influence of an external accelerating force,
a vibrating mass reacts slower than a comparable
mass that is not vibrating, the tuning fork twists
within itself with rotational movement being
imparted on the sensor (C). This rotation results
in a change in the charge distribution in the Piezo
element, which is subsequently picked up and
converted into an electronic signal by electronics
integrated into the sensor. This electronic signal is
then sent to the ESP module. The ESP module
evaluates these data and takes into account the
other input data (vehicle speed, wheel speed)
before deciding whether the ESP function is
required.
G1001304en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-09B-13
Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist
206-09B- 13
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1432 of 2057

E53340
1
2
3
Description
Item
Tuning fork exciter
1
Suspension
2
Measuring side
3
Due to the special way in which it works. the
combined yaw rate sensor and lateral acceleration
sensor/longitudinal acceleration sensor must be
installed the right way up in the designated location
specified by the manufacturer. Any slight deviation
in the installation position and/or installation
location could lead to impaired functionality and
thereby possible failure of the stability assist.
Front wheel sensor
E96823
Active sensors are used to determine the rotational
speeds of the wheels at the hub. After the ignition
is switched on, the ABS module supplies the
sensors with power. The sensors work in
accordance with the Hall effect principle and
G1001304en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-09B- 14
Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist
206-09B- 14
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1433 of 2057
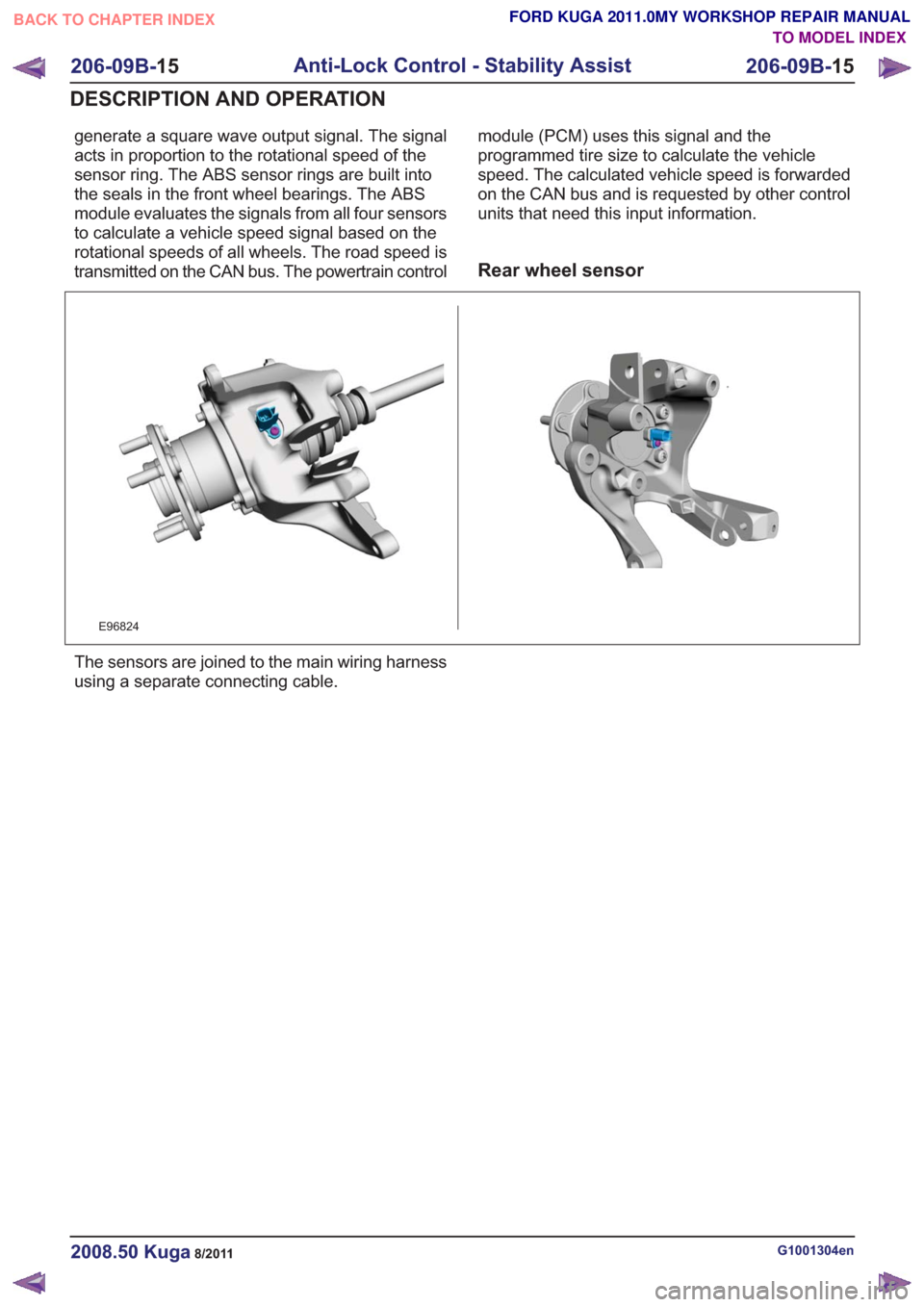
generate a square wave output signal. The signal
acts in proportion to the rotational speed of the
sensor ring. The ABS sensor rings are built into
the seals in the front wheel bearings. The ABS
module evaluates the signals from all four sensors
to calculate a vehicle speed signal based on the
rotational speeds of all wheels. The road speed is
transmitted on the CAN bus. The powertrain controlmodule (PCM) uses this signal and the
programmed tire size to calculate the vehicle
speed. The calculated vehicle speed is forwarded
on the CAN bus and is requested by other control
units that need this input information.
Rear wheel sensor
E96824
The sensors are joined to the main wiring harness
using a separate connecting cable.
G1001304en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-09B-
15
Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist
206-09B- 15
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1434 of 2057

Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU)
Removal
NOTE:Removal steps in this procedure may
contain installation details.
1. Refer to: Brake System Health and Safety
Precautions (100-00 General Information,
Description and Operation).
2. Refer to: Battery(414-01 Battery, Mounting and
Cables, Removal and Installation).
3. Torque: 12
Nm
E100290
4. Connect one end of a suitable piece of clear
plastic pipe to the brake caliper bleed nipple
1.
and place the other end into a suitable
container.
2. Loosen the bleed nipple.
3. Depress the brake pedal until all the brake fluid is drained from the brake fluid reservoir.
4. Tighten the bleed nipple.
5. Repeat the draining procedure on the opposite side brake caliper.
E86914
Left-hand drive vehicles
5. NOTE: Make sure that the seal is correctly
located.
Torque: 18
Nm
E69767
Right-hand drive vehicles
6.
E66148
7. Torque: 18Nm
G1001225en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-09B- 16
Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist
206-09B- 16
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1435 of 2057
E101093
All vehicles
8. NOTE:Make sure that the seal is correctly
located.
2. Torque: 18
Nm
3. Torque: 9Nm
G1001225en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-09B- 17
Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist
206-09B- 17
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1436 of 2057
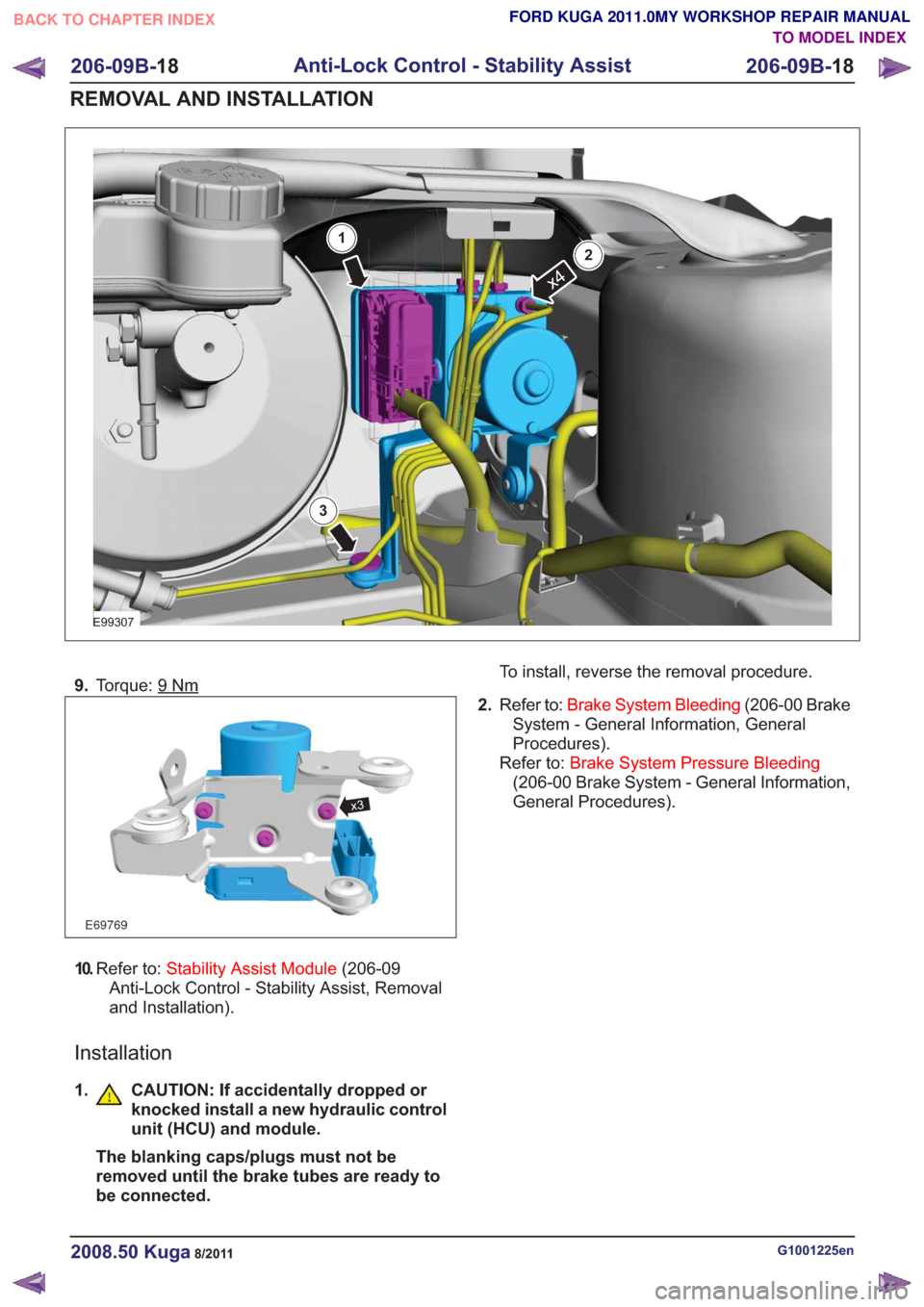
E99307
x4
1
2
3
9.Torque: 9Nm
E69769
x3
10.Refer to: Stability Assist Module (206-09
Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist, Removal
and Installation).
Installation
1. CAUTION: If accidentally dropped or knocked install a new hydraulic control
unit (HCU) and module.
The blanking caps/plugs must not be
removed until the brake tubes are ready to
be connected. To install, reverse the removal procedure.
2. Refer to: Brake System Bleeding (206-00 Brake
System - General Information, General
Procedures).
Refer to: Brake System Pressure Bleeding
(206-00 Brake System - General Information,
General Procedures).
G1001225en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
206-09B- 18
Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist
206-09B- 18
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL