2011 FORD KUGA Battery
[x] Cancel search: BatteryPage 1796 of 2057

current value is reached. The PCM then
permanently connects the heating element to earth.
The catalyst monitor sensor is used by the PCM
to measure the oxygen content in the exhaust gas
in the TWC. If all the conditions for catalyst
diagnostics are met, based on this information the
PCM can check that the TWC is working
satisfactorily. The information is also used to
improve the air/fuel mixture adjustment.
The catalyst monitor sensor is similar in function
to an HO2S. The signal transmitted by the catalyst
monitor sensor changes sharply if the oxygen
content in the exhaust gas changes. For this
reason, catalyst monitor sensors are also called
"jump lambda sensors".
Fuel tank purging
The EVAP purge valve is only actuated by the PCM
if the coolant temperature is at least 60°C.
Actuation is done ground side by means of a PWM
signal. This makes it possible to have the full range
of opening widths, from fully closed to fully open.
The PCM determines from the operating conditions
when and how wide to open the EVAP tank purge
valve. If the EVAP purge valve is opened, the
engine sucks in ambient air through the activated
charcoal in the evaporative emission canister as
a result of the vacuum in the intake manifold. In
this way the adsorbed hydrocarbons are led to the
combustion chamber of the engine.
The EVAP tank purge valve is not actuated and
system cleaning is interrupted if the engine
switches to idle and/or a closed-loop control
process is initiated.
Power (battery voltage) is supplied via the
Powertrain Control Module relay in the BJB. The
solenoid coil resistance is between 17 and 24 ohms
at 20°C.
Engine speed control
The APP sensor provides the PCM with information
about the driver's request for acceleration.
The throttle control unit receives a corresponding
input signal from the PCM. An electric motor then
moves the throttle valve shaft by means of a set
of gears. The position of the throttle is continuously
recorded by the TP sensor. Information on throttle
position is processed and monitored by the PCM.
The TP sensor comprises two potentiometers.
These work in opposite ways to each other. In one
potentiometer, the resistance increases when the
throttle is opened, in the other it decreases. Thisallows the operation of the potentiometers to be
checked. The signal from the TP sensor is
amplified in the lower range (idle to a quarter open)
by the PCM to enable more precise control of the
throttle in this range. This is necessary because
the engine is very sensitive to changes in throttle
angle in this throttle opening range.
With the throttle valve position kept constant, the
ignition angle and the injected fuel quantity are
then varied to meet the torque demands.
Depending on the operating state of the engine, a
change in the position of the throttle flap may not
be necessary when the APP sensor changes.
If a fault develops in the throttle control unit, a
standby function is executed. This standby function
allows a slight opening of the throttle flap, so that
enough air passes through to allow limited engine
operation. For this purpose, there is a throttle flap
adjustment screw on the throttle housing. The
return spring closes the throttle flap until the stop
of the toothed segment touches the stop screw. In
this way a defined throttle flap gap is formed for
limp home mode.
The stop screw has a spring loaded pin, which
holds the throttle flap open for limp home mode.
In normal operating mode, this spring loaded pin
is pushed in by the force of the electric motor when
the throttle flap must be closed past the limp home
position (e.g. for idle speed control or overrun
shutoff).
Oil monitoring
The engine does not have an oil pressure
switch.
The oil level and oil quality are calculated.
Calculating the engine oil level
The oil level is determined by continuous
measurement of the capacitance (i.e. the ability to
store an electrical charge) between the two
capacitive elements of the engine oil
level/temperature/quality sensor. The different oil
levels cause the capacitance between the elements
to change. The data are recorded by the PCM and
converted into an oil level value. Temporary
fluctuations in oil level are automatically filtered out
by the PCM.
Calculating oil quality
The PCM calculates the oil quality from the oil level
measurement and the oil temperature measured
by the sensor, plus the engine speed and the
average fuel consumption. The driver is informed
about when an oil change is due.
G1021908en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14- 22
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
22
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1798 of 2057
Starting process
The PCM enables the starting process when a key
providing a valid code is read via the PATS.
Refer to:Starting System (303-06 Starting System
- 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5, Description
and Operation).
Alternator control (Smart Charge)
The vehicle is fitted with a Smart Charging charge
system.
In this system, the charge voltage is regulated by
the PCM.
Refer to: Generator (414-02 Generator and
Regulator, Description and Operation).
Component Description
PCM
E73522
A voltage transformer integrated into the PCM
provides various components of the PCM and
sensors on the engine with a 5 volt supply.
Functions which work at battery voltage, such as
the injectors, are controlled via internal power end
stages or, like the ignition coils, via external power
end stages in the ignition coils themselves.
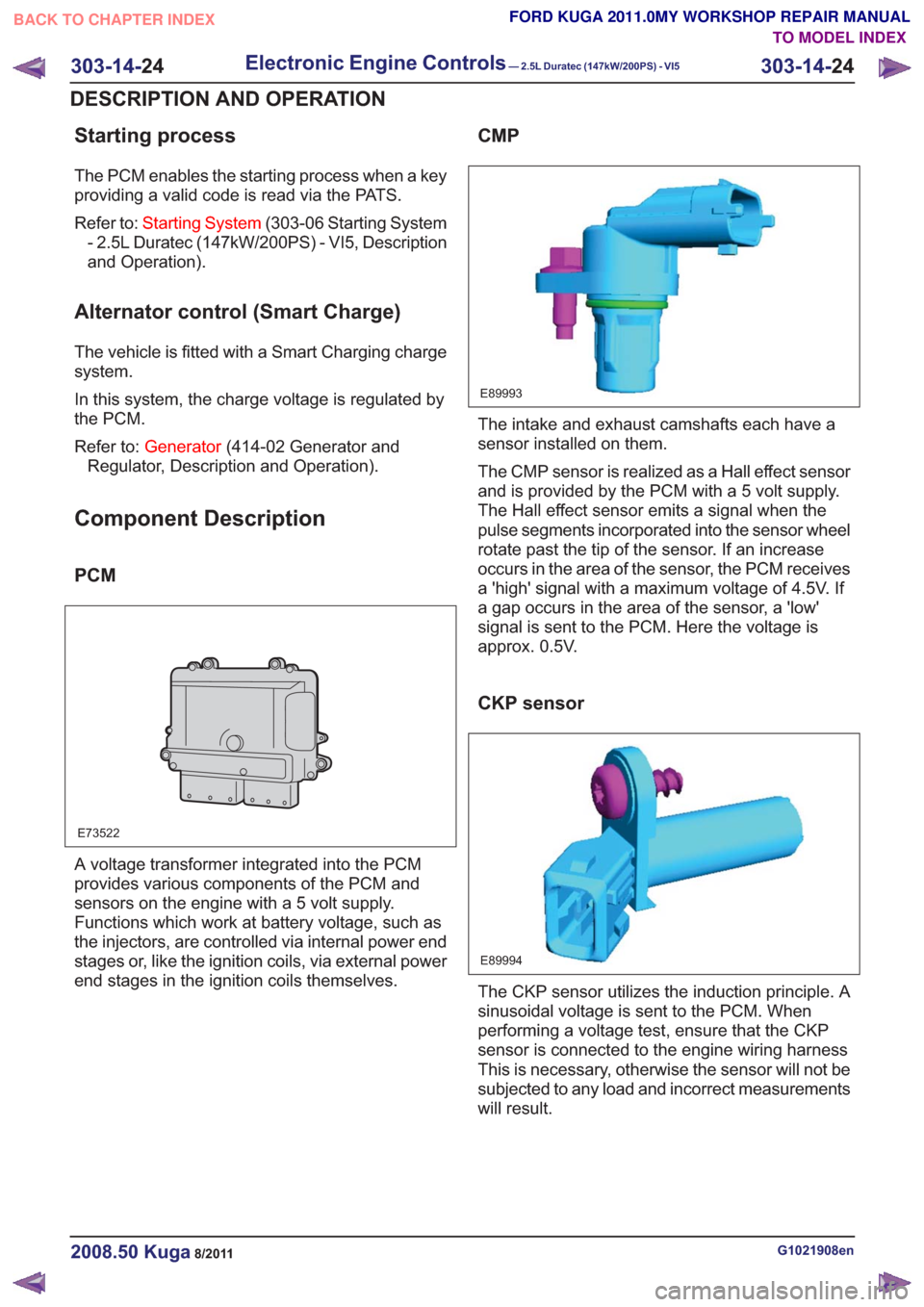
CMP
E89993
The intake and exhaust camshafts each have a
sensor installed on them.
The CMP sensor is realized as a Hall effect sensor
and is provided by the PCM with a 5 volt supply.
The Hall effect sensor emits a signal when the
pulse segments incorporated into the sensor wheel
rotate past the tip of the sensor. If an increase
occurs in the area of the sensor, the PCM receives
a 'high' signal with a maximum voltage of 4.5V. If
a gap occurs in the area of the sensor, a 'low'
signal is sent to the PCM. Here the voltage is
approx. 0.5V.
CKP sensor
E89994
The CKP sensor utilizes the induction principle. A
sinusoidal voltage is sent to the PCM. When
performing a voltage test, ensure that the CKP
sensor is connected to the engine wiring harness
This is necessary, otherwise the sensor will not be
subjected to any load and incorrect measurements
will result.
G1021908en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14- 24
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
24
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1805 of 2057

E74168
1
23456
Description
Item
Stop screw
1
Toothed segment
2
Throttle flap spindle
3
Throttle flap return spring
4
Joint shaft
5
Electric motor with pinion
6
CAUTION: The throttle control unit must
not be repaired or adjusted. The stop of
the throttle valve must on no account be
adjusted.
If there is a fault, the throttle is returned to its
original position by means of the throttle valve
return spring. In this position, the throttle valve is
still slightly open. As a result, a higher idle speed
is set, enabling the vehicle to be driven, though
within narrow limits.
ECT sensor
E94804
The ECT sensor is designed as an NTC resistor.
A voltage of 5V is applied to the ECT sensor by
the PCM. The PCM is able to determine the coolant
temperature from the temperature-dependent
voltage drop at the sensor.
Cooling fan module
E94806
The cooling fan module is directly supplied with
battery power via a 60A fuse in the BJB. The
radiator fan speed is controlled by the PWM via a
PCM signal.
G1021908en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14- 31
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
31
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1807 of 2057
Description
Item
Coil-on-plug ignition coil
1
Spark plug connector
2
Low-voltage connection
3
Laminated soft-iron core
4Description
Item
Primary winding
5
Secondary winding
6
Spark plug
7
High-voltage connection via spring contact
8
In an ignition system with coil-on-plug ignition coils,
each cylinder is actuated individually and only once
per cycle (working stroke). The coil-on-plug ignition
coils are mounted directly on the spark plugs,
therefore no ignition cables are required between
the ignition coils and the spark plugs.
Each individual ignition coil is actuated on the
low-voltage side by the PCM. The power
end-stages are incorporated into the coil-on-plug
ignition coils. Only the actuating current for these
power end-stages is controlled by the PCM.
Fuel pressure/fuel temperature sensor
E73531
The fuel pressure/fuel temperature sensor is a
combination of two sensors, one for the fuel
absolute pressure and one for the fuel temperature.
The sensors register the fuel values in the fuel
injection supply manifold. The sensor is supplied
with a 5V voltage by the PCM.
The fuel pressure sensor is a piezoresistor and
works using an analog signal. The change in output
voltage mirrors the change in pressure in the fuel
rail. If the pressure is low, the output voltage is also
low.
The fuel temperature sensor is an NTC resistor.
When the fuel pressure/fuel temperature sensor is
disconnected, the resistance of the fuel
temperature sensor between connections 1 and 2
of the sensor can be measured.
Resistor
Temperature
5896 Ohm
0° C
3792 Ohm
10° C
2500 Ohm
20° C
1707 Ohm
30° C
1175 Ohm
40° C
The values of the fuel pressure/fuel temperature
sensor can be read out with IDS. The displayed
values are absolute values (fuel pressure +
atmospheric pressure).
Wastegate control valve
E73539
The boost control solenoid valve is a 2/3-way valve
that is actuated with a PWM signal. This allows the
valve opening to be steplessly adjusted.
Power (battery voltage) is supplied via the
Powertrain Control Module relay in the BJB. The
solenoid coil resistance is around 23 ohms at 20°
C.
G1021908en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14- 33
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
33
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1810 of 2057
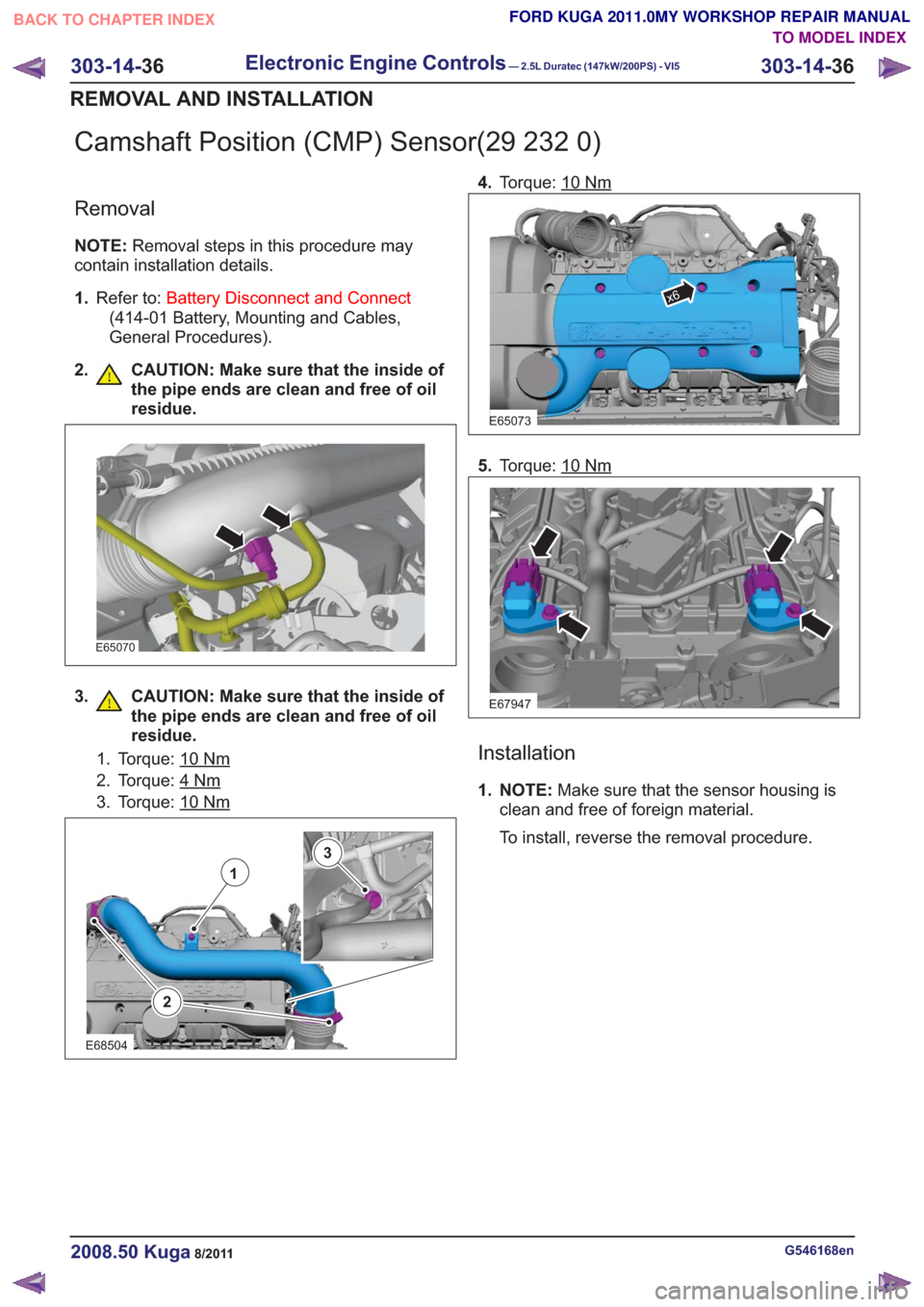
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor(29 232 0)
Removal
NOTE:Removal steps in this procedure may
contain installation details.
1. Refer to: Battery Disconnect and Connect
(414-01 Battery, Mounting and Cables,
General Procedures).
2. CAUTION: Make sure that the inside of the pipe ends are clean and free of oil
residue.
E65070
3. CAUTION: Make sure that the inside ofthe pipe ends are clean and free of oil
residue.
1. Torque: 10Nm
2. Torque: 4Nm
3. Torque: 10Nm
2
1
3
E68504
4.Torque: 10Nm
E65073
x6
5.Torque: 10Nm
E67947
Installation
1. NOTE: Make sure that the sensor housing is
clean and free of foreign material.
To install, reverse the removal procedure.
G546168en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14- 36
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
36
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1817 of 2057
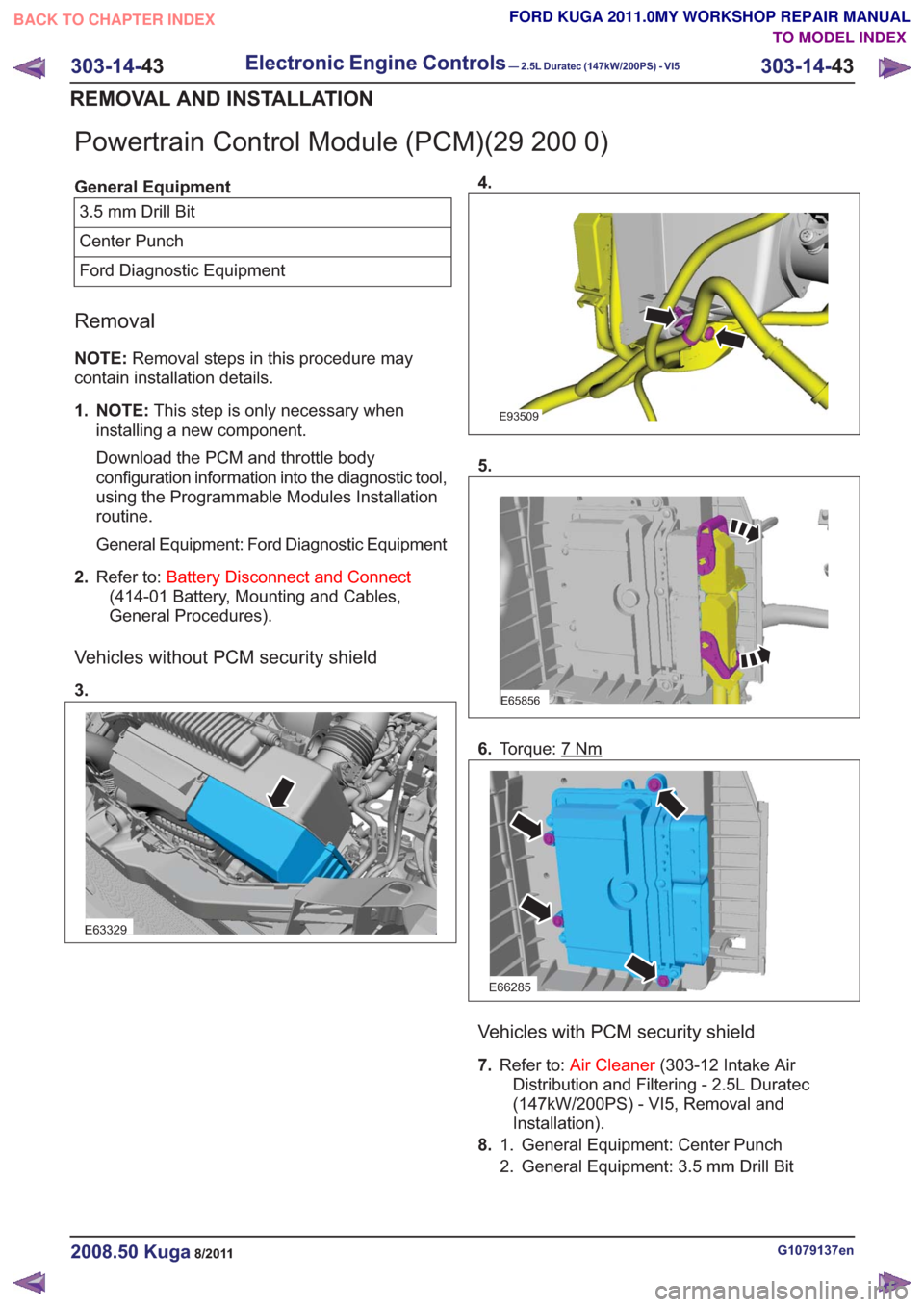
Powertrain Control Module (PCM)(29 200 0)
General Equipment3.5 mm Drill Bit
Center Punch
Ford Diagnostic Equipment
Removal
NOTE: Removal steps in this procedure may
contain installation details.
1. NOTE: This step is only necessary when
installing a new component.
Download the PCM and throttle body
configuration information into the diagnostic tool,
using the Programmable Modules Installation
routine.
General Equipment: Ford Diagnostic Equipment
2. Refer to: Battery Disconnect and Connect
(414-01 Battery, Mounting and Cables,
General Procedures).
Vehicles without PCM security shield
3.
E63329
4.
E93509
5.
E65856
6. Torque: 7Nm
E66285
Vehicles with PCM security shield
7.Refer to: Air Cleaner (303-12 Intake Air
Distribution and Filtering - 2.5L Duratec
(147kW/200PS) - VI5, Removal and
Installation).
8. General Equipment: Center Punch
1.
2. General Equipment: 3.5 mm Drill Bit
G1079137en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
303-14- 43
Electronic Engine Controls— 2.5L Duratec (147kW/200PS) - VI5303-14-
43
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1835 of 2057

Description
Item
ABS (anti-lock brake system)
5
Speed control
6
Select-shift switch module
7
PCM
8
Selector lever lock
9
PWM solenoid valve – shift pressure (SLS)
10
PWM solenoid valve for main line pressure
(SLT)
11
PWM- solenoid valve – TCC (SLU)
12Description
Item
Shift solenoid S1 (open when dormant)
13
Shift solenoid S2 (closed when dormant)
14
Shift solenoid S3 (closed when dormant)
15
Shift solenoid S4 (open when dormant)
16
Shift solenoid S5 (closed when dormant)
17
The TSS sensor
18
The OSS sensor
19
The TFT sensor
20
TR sensor in TCM
21
Knowing and Understanding Customer
Concerns
Knowing and understanding customer concerns is
necessary in order to perform diagnosis.
First of all, ask the customer under which operating
conditions the problem occurs. If possible, try to
reproduce the concern by road testing the vehicle
with the customer.
You should be familiar with the following operating
conditions:
• Engine operating state
– Cold, warm-up phase, or at operatingtemperature
• Ambient temperature – Below 0 °C (32 °F), 0 to 20 °C (32 to 68 °F),or above 20 °C (68 °F)
• Road conditions – Good, poor, or off-road
• Vehicle load status – Unloaded, loaded, or fully loaded
• Transaxle status in manual mode – Upshift, downshift, overrun or acceleration
Testing Possible Causes of Transmission
Control Faults
Before performing a symptom-based diagnosis,
first carry out checks to eliminate various other
potential causes of the fault.
These situations include:
• Battery state of charge
• Defective fuses • Loose or corroded cables or electrical
connectors
• Ground connections to the transmission
• Retrofitted add-on units which are not approved by Ford, such as air conditioning, car telephone,
cruise control
• Unapproved tire sizes
• Incorrect tire size programmed with IDS (Integrated Diagnostic System)
• Engine tuning
IDS Diagnosis
NOTE: Customer concerns relating to the transaxle
can also be caused by engine-related faults.
The transmission control system of the AW55 is
closely linked to the engine management system.
Faults in the engine management system may
affect the transmission control system.
Before repairing the transaxle, it should be ensured
that the fault is not caused by the engine
management system or other non-transaxle
components.
The diagnosis can be performed on the AW55 with
the aid of von IDS.
visual inspection
A thorough visual inspection of the transaxle is
necessary for successful diagnosis.
A visual inspection is made of the following
components:
• Connectors and plug connections
• Ease of operation of the selector lever
G1163604en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01- 14
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 14
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL
Page 1836 of 2057
• Selector lever position and selector leverposition display
• Fluid leakage
• Transmission fluid level check
• Transmission fluid quality check
• Modification/retrofitting
• Mechanical damage to the transmission
When inspecting connectors, remember that the
plugs may only be disconnected when they are not
energized.
The transaxle electronics may be destroyed by
static charge. To prevent damage, it must be
ensured that the technician complies with the
corresponding safeguards.
NOTE: Refer to the service literature for an exact
description of these safeguards.
Towing the vehicle
E66463
In general, vehicles with the AW55 transaxle can
be towed. Vehicles must never be towed
backwards.
As a result of the reduced lubrication of the
transaxle during towing, the following must be
remembered:
• The selector lever must be in the 'N' position.
• The maximum towing speed must not exceed 50 km/h.
• The maximum towing distance must not exceed 50 kilometers.
Push-starting the Vehicle
No torque is transmitted when towing or pushing
the vehicle. For this reason, vehicles with an
automatic transaxle cannot and must not be
tow-started or push-started.
Jump-starting the Vehicle
CAUTION: When jump-starting the vehicle
using a jumper lead there may be voltage
peaks. These may destroy the transaxle
electronics.
NOTE: When jump-starting the vehicle, the external
battery must remain connected for several minutes.
The voltage peaks dissipate after a few minutes.
Only then may the external battery be disconnected
without the risk of damage.
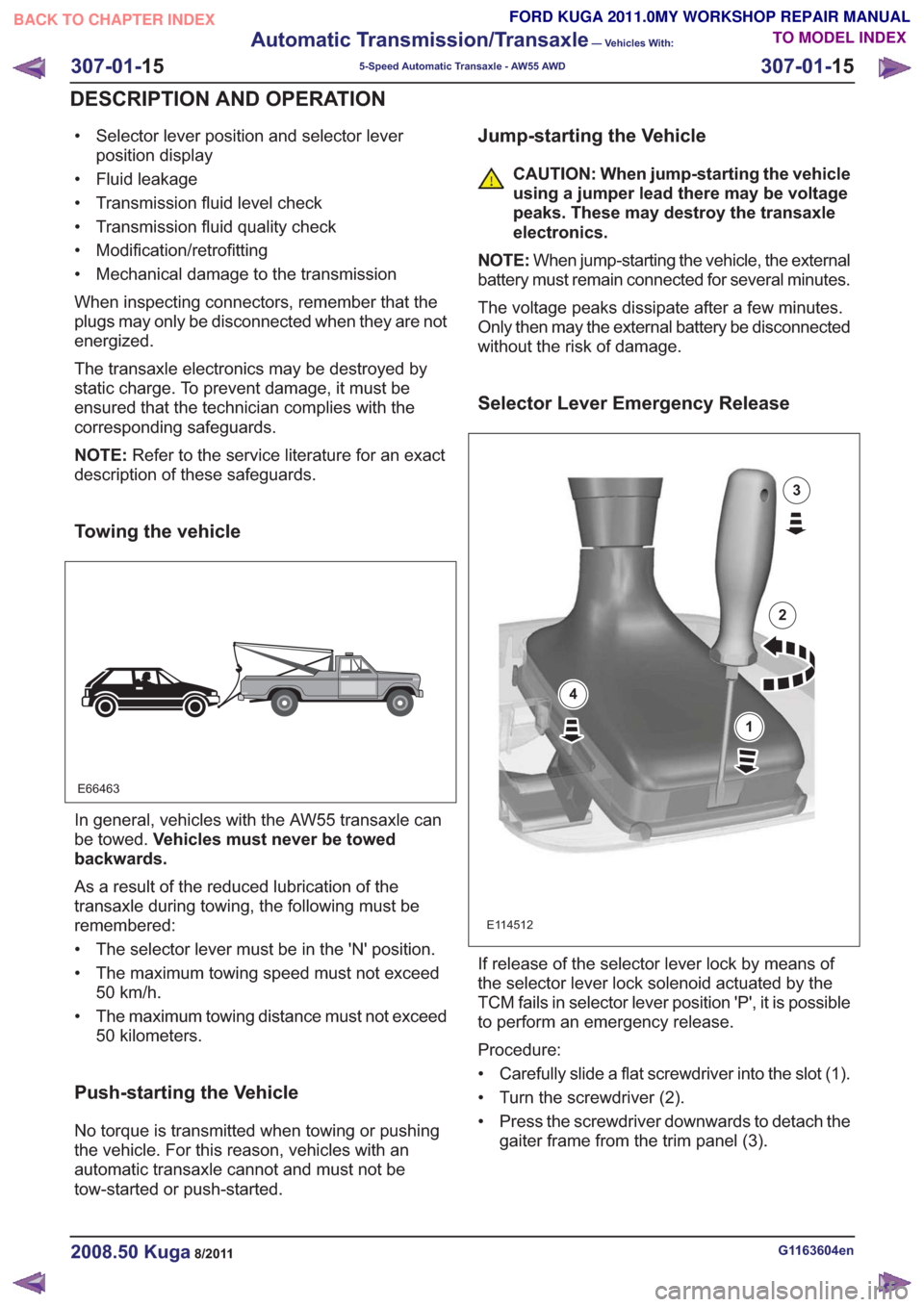
Selector Lever Emergency Release
E114512
1
2
3
4
If release of the selector lever lock by means of
the selector lever lock solenoid actuated by the
TCM fails in selector lever position 'P', it is possible
to perform an emergency release.
Procedure:
• Carefully slide a flat screwdriver into the slot (1).
• Turn the screwdriver (2).
• Press the screwdriver downwards to detach the gaiter frame from the trim panel (3).
G1163604en2008.50 Kuga8/2011
307-01- 15
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle
— Vehicles With:
5-Speed Automatic Transaxle - AW55 AWD
307-01- 15
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
TO MODEL INDEX
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
FORD KUGA 2011.0MY WORKSHOP REPAIR MANUAL