2010 JAGUAR XFR abs module
[x] Cancel search: abs modulePage 1355 of 3039
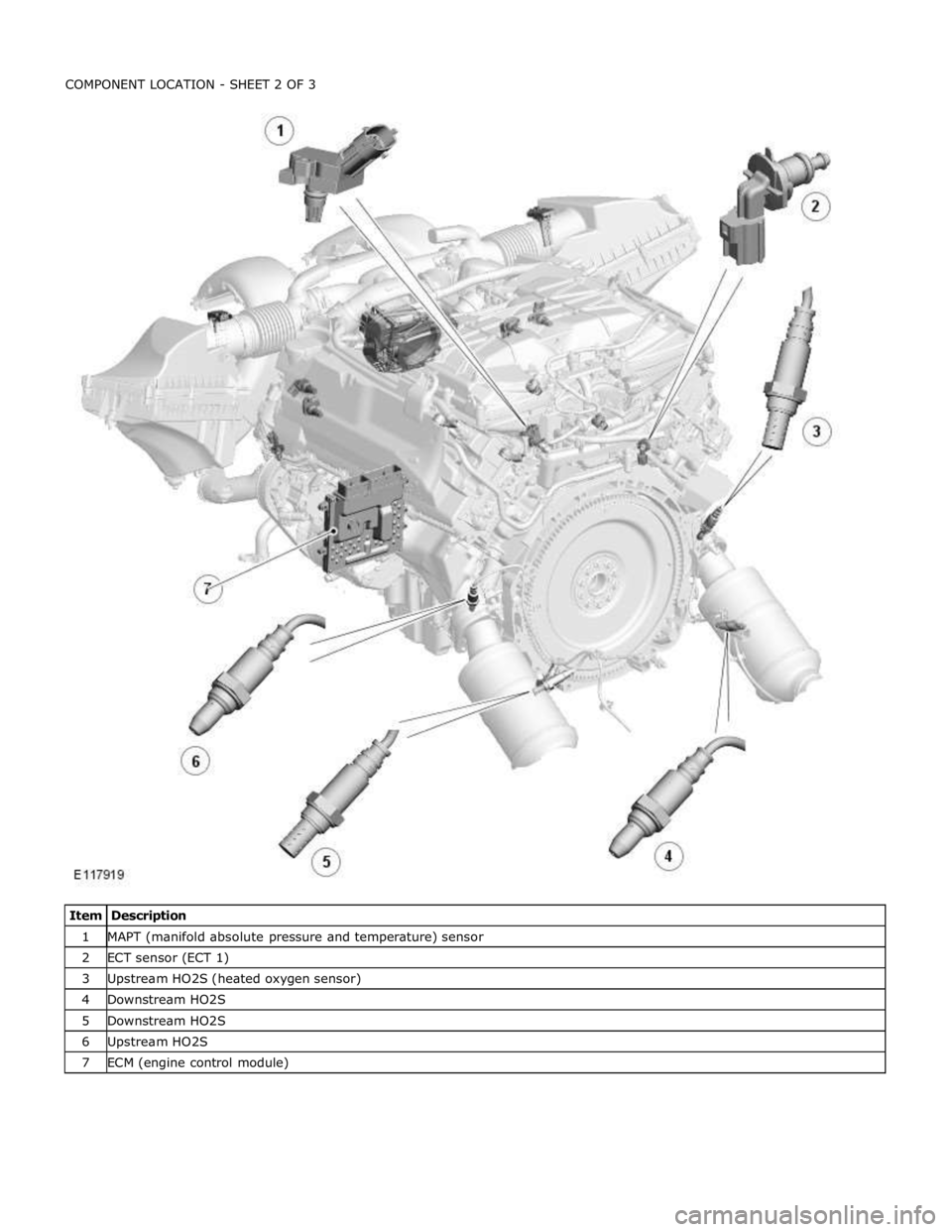
1 MAPT (manifold absolute pressure and temperature) sensor 2 ECT sensor (ECT 1) 3 Upstream HO2S (heated oxygen sensor) 4 Downstream HO2S 5 Downstream HO2S 6 Upstream HO2S 7 ECM (engine control module)
Page 1360 of 3039

4 Diagnostic socket 5 To other system control modules 6 ECM 7 Electronic throttle 8 APP sensor 9 AAT sensor 10 ECT sensor (ECT 1) 11 LH upstream HO2S 12 LH downstream HO2S 13 MAPT (manifold absolute pressure and temperature) sensor 14 RH downstream HO2S 15 RH upstream HO2S
ECM ADAPTIONS System Operation
The ECM (engine control module) has the ability to adapt the input values it uses to control certain outputs. This capability
maintains engine refinement and ensures the engine emissions remain within the legislated limits. The components which
have adaptions associated with them are:
The APP (accelerator pedal position) sensor
The heated oxygen sensors
The MAFT (mass air flow and temperature) sensors
The CKP (crankshaft position) sensor
Electronic throttle.
OXYGEN AND MAFT SENSORS
There are several adaptive maps associated with the fueling strategy. Within the fueling strategy the ECM calculates short-term adaptions and long term adaptions. The ECM will monitor the deterioration of the heated oxygen sensors over a period of time. It will also monitor the current correction associated with the sensors.
The ECM will store a fault code in circumstances where an adaption is forced to exceed its operating parameters. At the same time, the ECM will record the engine speed, engine load and intake air temperature.
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
The characteristics of the signal supplied by the CKP sensor are learned by the ECM. This enables the ECM to set an adaption and support the engine misfire detection function. Due to the small variation between different drive plates and different CKP sensors, the adaption must be reset if either component is renewed, or removed and refitted. It is also necessary to reset the
drive plate adaption if the ECM is renewed or replaced. The ECM supports four drive plate adaptions for the CKP sensor. Each adaption relates to a specific engine speed range. The engine speed ranges are detailed in the table below:
Adaption Engine Speed, rev/min 1 1800 - 3000 2 3001 - 3800 3 3801 - 4600 4 4601 - 5400 MISFIRE DETECTION
Legislation requires that the ECM must be able to detect the presence of an engine misfire. It must be able to detect misfires at two separate levels. The first level is a misfire that could lead to the legislated emissions limit being exceeded by a given
amount. The second level is a misfire that may cause catalytic converter damage.
The ECM monitors the number of misfire occurrences within two engine speed ranges. If the ECM detects more than a predetermined number of misfire occurrences within either of these two ranges, over two consecutive journeys, it will record a
fault code and details of the engine speed, engine load and engine coolant temperature. In addition, the ECM monitors the number of misfire occurrences that happen in a 'window' of 200 engine revolutions. The misfire occurrences are assigned a
weighting according to their likely impact on the catalytic converters. If the number of misfires exceeds a given value, the ECM stores catalytic converter damage fault codes, along with the engine speed, engine load and engine coolant temperature.
The signal from the CKP sensor indicates how fast the poles on the drive plate are passing the sensor tip. A sine wave is generated each time a pole passes the sensor tip. The ECM can detect variations in drive plate speed by monitoring the sine wave signal supplied by the crankshaft position sensor. By assessing this signal, the ECM can detect the presence of an engine misfire. At this time, the ECM will assess the amount of variation in the signal received from the CKP sensor and assign a roughness value to it. This roughness value can be viewed within the real time monitoring feature using Jaguar approved
diagnostic equipment. TheECM will evaluate the signal against a number of factors and will decide whether to record the occurrence or ignore it. The ECM can assign a roughness and misfire signal for each cylinder.
Page 1361 of 3039

DIAGNOSTICS
The ECM stores each fault as a DTC (diagnostic trouble code). The DTC and associated environmental and freeze frame data can be read using Jaguar approved diagnostic equipment, which can also read real time data from each sensor, the adaption
values currently being employed and the current fueling, ignition and idle speed settings.
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE Component Description
The ECM is installed in the front passenger side of the engine compartment, on a bracket attached to the engine bulkhead. The ECM has the capability of adapting its fuel and ignition control outputs in response to several sensor inputs. The ECM receives inputs from the following:
CKP sensor. CMP (camshaft position) sensors (4 off).
ECT (engine coolant temperature) sensor.
Knock sensors (4 off).
MAP (manifold absolute pressure) sensor.
MAFT sensors (2 off). MAPT (manifold absolute pressure and temperature) sensor.
Throttle position sensor.
Heated oxygen sensors (4 off).
APP sensor. Ambient air temperature sensor.
FRP (fuel rail pressure) sensor. For additional information, refer to 303-04G Fuel Charging and Controls.
Engine cooling fan. For additional information, refer to 303-03D Engine Cooling.
Stoplamp switch. For additional information, refer to 206-09 Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist.
Speed control cancel/suspend switch. For additional information, refer to 310-03D Speed Control.
Oil level and temperature sensor. For additional information, refer to 303-01F Engine.
Fuel LP (low pressure) sensor. For additional information, refer to 310-01D Fuel Tank and Lines.
Fuel pump driver module. For additional information, refer to 310-01D Fuel Tank and Lines.
The ECM provides outputs to the following: Electronic throttle.
Main relay.
Heater elements of the heated oxygen sensors (4 off).
Fuel injectors (8 off). For additional information, refer to 303-04G Fuel Charging and Controls. www.JagDocs.com
Page 1373 of 3039
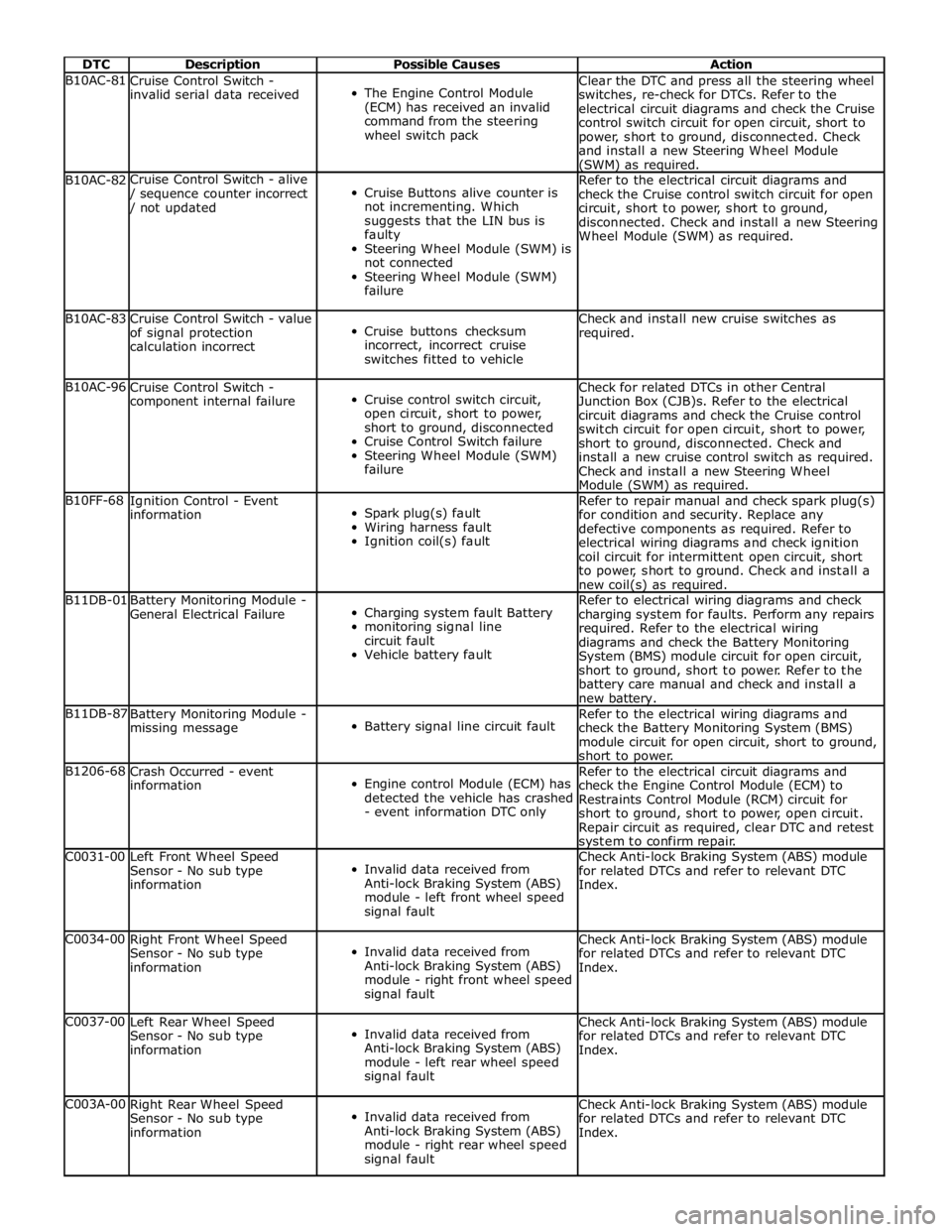
DTC Description Possible Causes Action B10AC-81
Cruise Control Switch -
invalid serial data received
The Engine Control Module
(ECM) has received an invalid
command from the steering
wheel switch pack Clear the DTC and press all the steering wheel
switches, re-check for DTCs. Refer to the
electrical circuit diagrams and check the Cruise
control switch circuit for open circuit, short to
power, short to ground, disconnected. Check
and install a new Steering Wheel Module (SWM) as required. B10AC-82 Cruise Control Switch - alive / sequence counter incorrect / not updated
Cruise Buttons alive counter is
not incrementing. Which
suggests that the LIN bus is
faulty
Steering Wheel Module (SWM) is
not connected
Steering Wheel Module (SWM)
failure Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the Cruise control switch circuit for open
circuit, short to power, short to ground,
disconnected. Check and install a new Steering
Wheel Module (SWM) as required. B10AC-83
Cruise Control Switch - value
of signal protection
calculation incorrect
Cruise buttons checksum
incorrect, incorrect cruise
switches fitted to vehicle Check and install new cruise switches as
required. B10AC-96
Cruise Control Switch -
component internal failure
Cruise control switch circuit,
open circuit, short to power,
short to ground, disconnected
Cruise Control Switch failure
Steering Wheel Module (SWM)
failure Check for related DTCs in other Central
Junction Box (CJB)s. Refer to the electrical
circuit diagrams and check the Cruise control
switch circuit for open circuit, short to power,
short to ground, disconnected. Check and
install a new cruise control switch as required.
Check and install a new Steering Wheel
Module (SWM) as required. B10FF-68
Ignition Control - Event
information
Spark plug(s) fault
Wiring harness fault
Ignition coil(s) fault Refer to repair manual and check spark plug(s)
for condition and security. Replace any
defective components as required. Refer to
electrical wiring diagrams and check ignition
coil circuit for intermittent open circuit, short
to power, short to ground. Check and install a
new coil(s) as required. B11DB-01
Battery Monitoring Module -
General Electrical Failure
Charging system fault Battery
monitoring signal line
circuit fault
Vehicle battery fault Refer to electrical wiring diagrams and check
charging system for faults. Perform any repairs
required. Refer to the electrical wiring
diagrams and check the Battery Monitoring
System (BMS) module circuit for open circuit,
short to ground, short to power. Refer to the
battery care manual and check and install a
new battery. B11DB-87
Battery Monitoring Module -
missing message
Battery signal line circuit fault Refer to the electrical wiring diagrams and
check the Battery Monitoring System (BMS)
module circuit for open circuit, short to ground,
short to power. B1206-68
Crash Occurred - event
information
Engine control Module (ECM) has
detected the vehicle has crashed
- event information DTC only Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check the Engine Control Module (ECM) to
Restraints Control Module (RCM) circuit for
short to ground, short to power, open circuit.
Repair circuit as required, clear DTC and retest
system to confirm repair. C0031-00
Left Front Wheel Speed
Sensor - No sub type
information
Invalid data received from
Anti-lock Braking System (ABS)
module - left front wheel speed
signal fault Check Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) module
for related DTCs and refer to relevant DTC
Index. C0034-00
Right Front Wheel Speed
Sensor - No sub type
information
Invalid data received from
Anti-lock Braking System (ABS)
module - right front wheel speed
signal fault Check Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) module
for related DTCs and refer to relevant DTC
Index. C0037-00
Left Rear Wheel Speed
Sensor - No sub type
information
Invalid data received from
Anti-lock Braking System (ABS)
module - left rear wheel speed
signal fault Check Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) module
for related DTCs and refer to relevant DTC
Index. C003A-00
Right Rear Wheel Speed
Sensor - No sub type
information
Invalid data received from
Anti-lock Braking System (ABS)
module - right rear wheel speed
signal fault Check Anti-lock Braking System (ABS) module
for related DTCs and refer to relevant DTC
Index.
Page 1422 of 3039
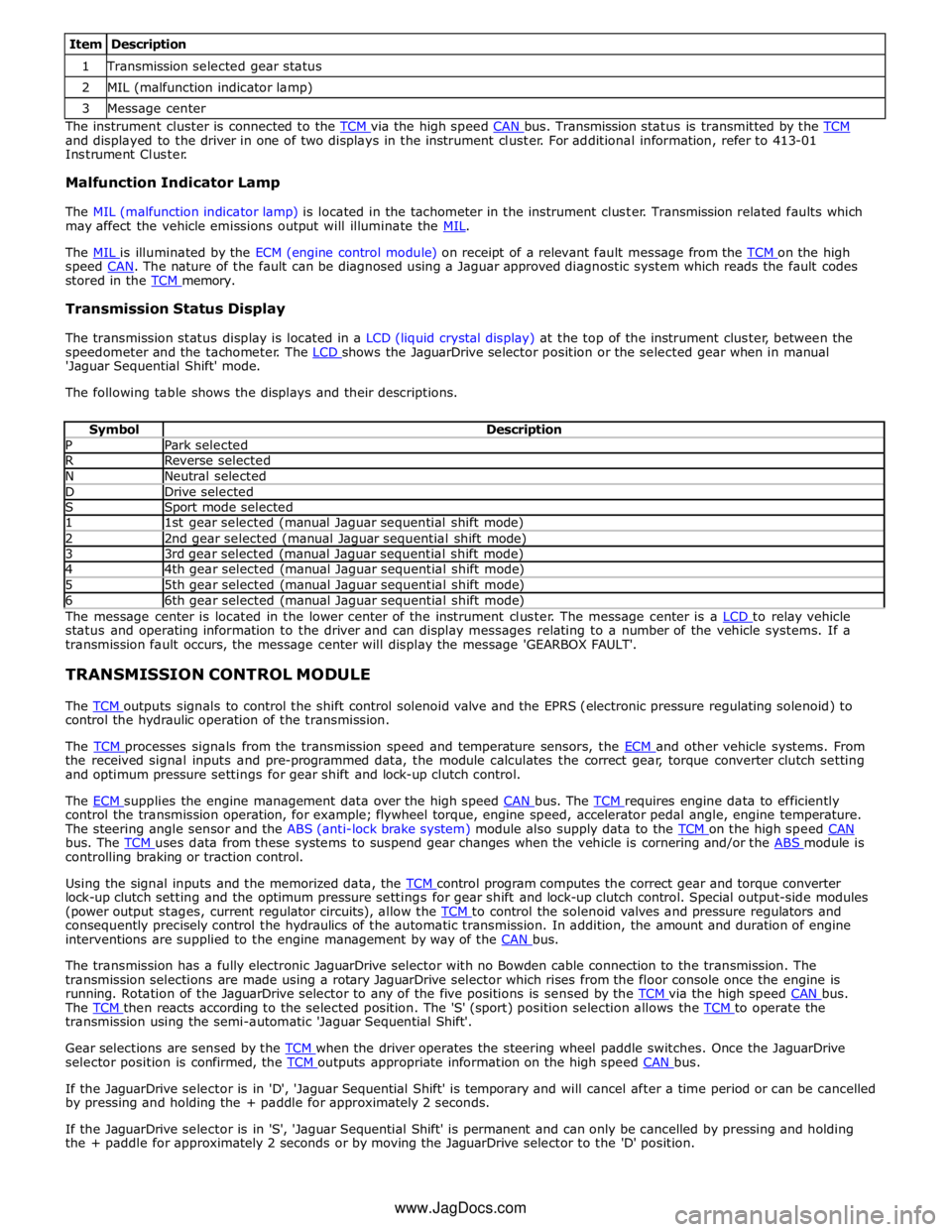
1 Transmission selected gear status 2 MIL (malfunction indicator lamp) 3 Message center The instrument cluster is connected to the TCM via the high speed CAN bus. Transmission status is transmitted by the TCM and displayed to the driver in one of two displays in the instrument cluster. For additional information, refer to 413-01
Instrument Cluster.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp
The MIL (malfunction indicator lamp) is located in the tachometer in the instrument cluster. Transmission related faults which
may affect the vehicle emissions output will illuminate the MIL.
The MIL is illuminated by the ECM (engine control module) on receipt of a relevant fault message from the TCM on the high speed CAN. The nature of the fault can be diagnosed using a Jaguar approved diagnostic system which reads the fault codes stored in the TCM memory.
Transmission Status Display
The transmission status display is located in a LCD (liquid crystal display) at the top of the instrument cluster, between the
speedometer and the tachometer. The LCD shows the JaguarDrive selector position or the selected gear when in manual 'Jaguar Sequential Shift' mode.
The following table shows the displays and their descriptions.
Symbol Description P Park selected R Reverse selected N Neutral selected D Drive selected S Sport mode selected 1 1st gear selected (manual Jaguar sequential shift mode) 2 2nd gear selected (manual Jaguar sequential shift mode) 3 3rd gear selected (manual Jaguar sequential shift mode) 4 4th gear selected (manual Jaguar sequential shift mode) 5 5th gear selected (manual Jaguar sequential shift mode) 6 6th gear selected (manual Jaguar sequential shift mode) The message center is located in the lower center of the instrument cluster. The message center is a LCD to relay vehicle status and operating information to the driver and can display messages relating to a number of the vehicle systems. If a
transmission fault occurs, the message center will display the message 'GEARBOX FAULT'.
TRANSMISSION CONTROL MODULE
The TCM outputs signals to control the shift control solenoid valve and the EPRS (electronic pressure regulating solenoid) to control the hydraulic operation of the transmission.
The TCM processes signals from the transmission speed and temperature sensors, the ECM and other vehicle systems. From the received signal inputs and pre-programmed data, the module calculates the correct gear, torque converter clutch setting
and optimum pressure settings for gear shift and lock-up clutch control.
The ECM supplies the engine management data over the high speed CAN bus. The TCM requires engine data to efficiently control the transmission operation, for example; flywheel torque, engine speed, accelerator pedal angle, engine temperature.
The steering angle sensor and the ABS (anti-lock brake system) module also supply data to the TCM on the high speed CAN bus. The TCM uses data from these systems to suspend gear changes when the vehicle is cornering and/or the ABS module is controlling braking or traction control.
Using the signal inputs and the memorized data, the TCM control program computes the correct gear and torque converter lock-up clutch setting and the optimum pressure settings for gear shift and lock-up clutch control. Special output-side modules
(power output stages, current regulator circuits), allow the TCM to control the solenoid valves and pressure regulators and consequently precisely control the hydraulics of the automatic transmission. In addition, the amount and duration of engine
interventions are supplied to the engine management by way of the CAN bus.
The transmission has a fully electronic JaguarDrive selector with no Bowden cable connection to the transmission. The
transmission selections are made using a rotary JaguarDrive selector which rises from the floor console once the engine is
running. Rotation of the JaguarDrive selector to any of the five positions is sensed by the TCM via the high speed CAN bus. The TCM then reacts according to the selected position. The 'S' (sport) position selection allows the TCM to operate the transmission using the semi-automatic 'Jaguar Sequential Shift'.
Gear selections are sensed by the TCM when the driver operates the steering wheel paddle switches. Once the JaguarDrive selector position is confirmed, the TCM outputs appropriate information on the high speed CAN bus.
If the JaguarDrive selector is in 'D', 'Jaguar Sequential Shift' is temporary and will cancel after a time period or can be cancelled
by pressing and holding the + paddle for approximately 2 seconds.
If the JaguarDrive selector is in 'S', 'Jaguar Sequential Shift' is permanent and can only be cancelled by pressing and holding
the + paddle for approximately 2 seconds or by moving the JaguarDrive selector to the 'D' position.
www.JagDocs.com
Page 1595 of 3039

Published: 28-Jul-2014
Fuel Tank and Lines - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Fuel Tank and
Lines
Diagnosis and Testing
Principle of Operation
For a detailed description of the fuel tank and lines system and operation, refer to the relevant Description and Operation
section of the workshop manual. REFER to: (310-01C Fuel Tank and Lines - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol)
Fuel Tank and Lines (Description and Operation), Fuel Tank and Lines (Description and Operation), Fuel Tank and Lines (Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
WARNINGS:
Eye protection must be worn at all times when working on or near any fuel related components. Failure to follow this
instruction may result in personal injury.
This procedure involves fuel handling. Be prepared for fuel spillage at all times and always observe fuel handling
precautions. Failure to follow this instruction may result in personal injury.
After carrying out repairs, the fuel system must be checked visually for leaks. This should be done after the engine has
been run, but with the engine switched OFF. Failure to follow this instruction may result in personal injury.
If taken internally, DO NOT induce vomiting. Seek immediate medical attention. Failure to follow this instruction may
result in personal injury.
If fuel contacts the eyes, flush the eyes with cold water or eyewash solution and seek medical attention. Failure to follow
this instruction may result in personal injury.
Wash hands thoroughly after handling, as prolonged contact may cause irritation. Should irritation develop, seek medical
attention. Failure to follow this instruction may result in personal injury.
CAUTIONS:
Before disconnecting any part of the system, it is imperative that all dust, dirt and debris is removed from around
components to prevent ingress of foreign matter into the fuel system. Failure to follow this instruction may result in damage to
the vehicle.
It is essential that absolute cleanliness is observed when working with these components. Always install blanking plugs
to any open orifices or lines. Failure to follow this instruction may result in damage to the vehicle.
Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not guarantee
confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle.
NOTES:
Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
When measuring fuel sender resistance values with a multimeter, it is critical to use the correct multimeter setting. The
multimeter should not be on the 'Auto' setting and must be set to 'Manual'. This will help prevent incorrect diagnosis and
unnecessary replacement of fuel senders. If the multimeter range is set at 'Auto' then, during a sweep of the sender from 50
Ohms to 998 Ohms, the multimeter has to change its measurement range. For approximately 1 second, during the range switch
over point, the multimeter display indicates an open circuit. This can lead to a mis-diagnosis of a fuel sender fault.
1. Verify the customer concern
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of damage and system integrity
Page 1638 of 3039

10 Electric throttle actuator 11 ABS (anti-lock brake system) module www.JagDocs.com
Page 1639 of 3039

Published: 11-May-2011
Speed Control - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Speed Control - Overview
Description and Operation
OVERVIEW
Speed Control
The speed control system is integrated with the engine management system and uses fueling intervention to automatically
maintain a set vehicle speed. Once engaged, the system can also be used to accelerate the vehicle without using the
accelerator pedal.
The speed control system comprises the following components:
On/Off/Suspend switch
'+' and '-' (set/accelerate and decelerate) steering wheel switches
Resume switch
Clock spring
Speed control warning indicator.
Adaptive Speed Control
The adaptive speed control system uses a forward looking radar sensor to scan the road ahead, looking for objects that are
moving at a different rate to itself. When a target is identified the adaptive speed control system will monitor the time gap
between it and the target vehicle. When that gap falls below a set driver selected level the adaptive speed control system will
intervene slowing the vehicle by backing off the throttle and/ or applying the brakes, until the correct gap is attained.
The adaptive speed control system comprises the following components:
Adaptive speed control sensor
Adaptive speed control module
Steering wheel control switches
ECM (engine control module)
Electric throttle actuator
ABS (anti-lock brake system) module and pump
Adaptive speed control warning indicator (in the instrument cluster).