Page 563 of 3039
Published: 11-May-2011
Rear Drive Halfshafts - Rear Drive Halfshafts - System Operation and
Component Description
Description and Operation
System Operation
Rear Drive Halfshafts Component Description
The solid-steel halfshafts are of unequal length, with each halfshaft comprising inner and outer CV (constant velocity) joints.
The CV joints are the 'ball and socket' type packed with grease and protected by gaiters.
The outer CV joint is an interference fit into the wheel hub and secured by a locking nut. The inner CV joint is a slide fit and is
retained in the differential with a spring clip.
www.JagDocs.com
Page 568 of 3039
8.
9.
10.
11. Release the lower arm.
CAUTION: Do not use a hammer to detach the
halfshaft from the hub assembly, failure to follow this
instruction may result in damage to the halfshaft.
Using the special tools, release the halfshaft from the drive
flange.
Special Tool(s): 204-269, 205-491-1, 205-491
NOTE: Use an additional wrench to prevent the
component from rotating.
Remove the wheel knuckle.
Release the halfshaft from the differential.
Page 574 of 3039
15.
16. CAUTION: Do not use air tools to install the nut.
Failure to follow this instruction may result in damage to
the component.
Torque: 300 Nm
Check and top-up the differential case.
17.
Install the LH rear wheel and tire.
Refer to: Wheel and Tire (204-04 Wheels and Tires, Removal and Installation).
Page 664 of 3039
Parking Brake and Actuation - Parking Brake Release Actuator
Removal and Installation
Removal Published: 06-May-2014
WARNING: Failure to release the tension and calibrate the electric parking brake during rear parking brake related service
procedures, could cause the parking brake to function incorrectly or become inoperative.
1. Refer to: Parking Brake Cable Tension Release (206-05 Parking Brake and Actuation, General Procedures).
2. WARNING: Make sure to support the vehicle with axle stands.
Raise and support the vehicle.
3. Remove the differential case.
Refer to: Differential Case - TDV6 3.0L Diesel /V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol (205-02 Rear Drive Axle/Differential, Removal and Installation).
Refer to: Differential Case - TD4 2.2L Diesel/TDV6 3.0L Diesel (205-02,
Removal and Installation).
4. Torque: 7 Nm
Page 1348 of 3039
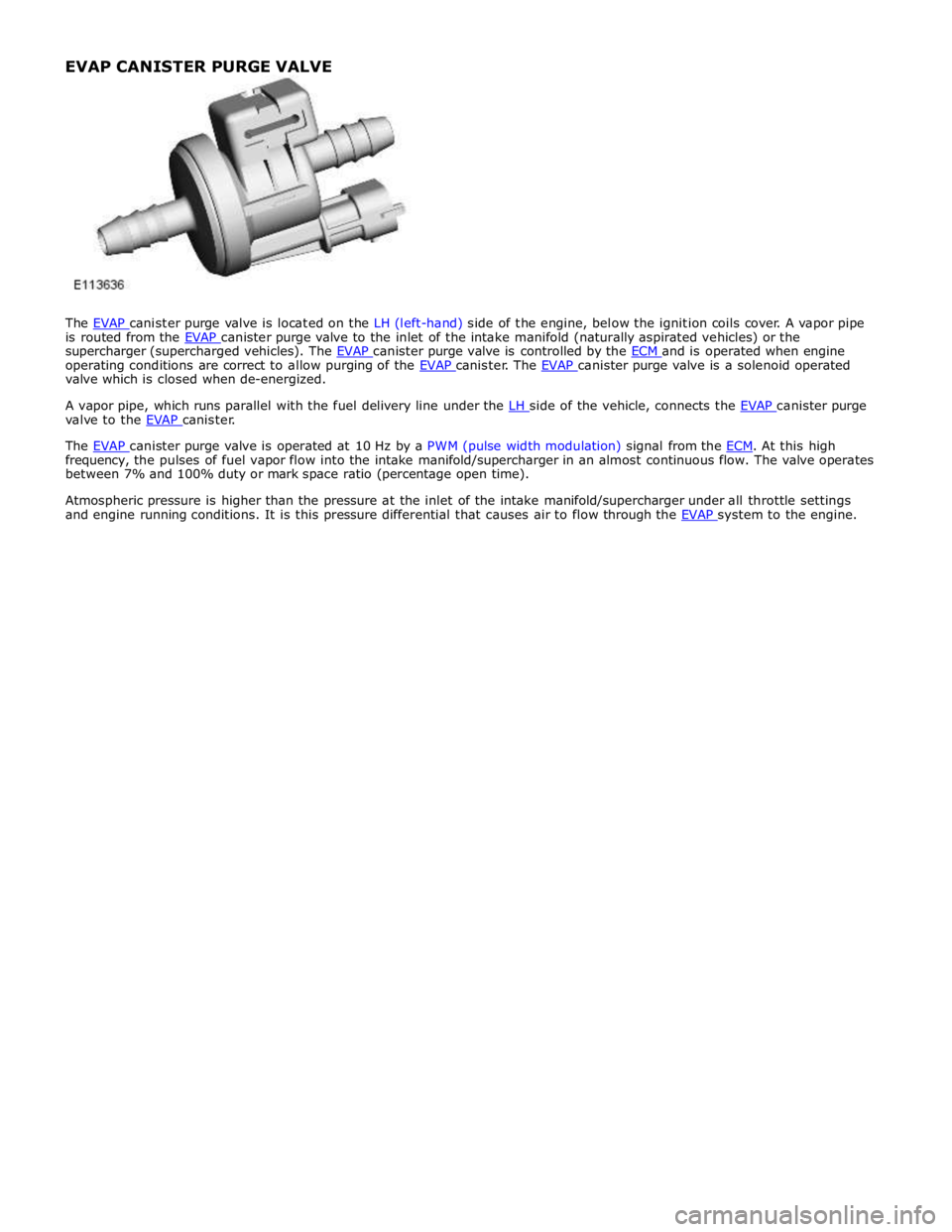
is routed from the EVAP canister purge valve to the inlet of the intake manifold (naturally aspirated vehicles) or the supercharger (supercharged vehicles). The EVAP canister purge valve is controlled by the ECM and is operated when engine operating conditions are correct to allow purging of the EVAP canister. The EVAP canister purge valve is a solenoid operated valve which is closed when de-energized.
A vapor pipe, which runs parallel with the fuel delivery line under the LH side of the vehicle, connects the EVAP canister purge valve to the EVAP canister.
The EVAP canister purge valve is operated at 10 Hz by a PWM (pulse width modulation) signal from the ECM. At this high frequency, the pulses of fuel vapor flow into the intake manifold/supercharger in an almost continuous flow. The valve operates
between 7% and 100% duty or mark space ratio (percentage open time).
Atmospheric pressure is higher than the pressure at the inlet of the intake manifold/supercharger under all throttle settings
and engine running conditions. It is this pressure differential that causes air to flow through the EVAP system to the engine. EVAP CANISTER PURGE VALVE
Page 1350 of 3039
Published: 11-May-2011
Evaporative Emissions - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Evaporative
Emission Canister
Removal and Installation
Removal
NOTE: Removal steps in this procedure may contain installation details.
1. Refer to: Petrol and Petrol-Ethanol Fuel Systems Health and Safety Precautions (100-00 General Information, Description and Operation).
2. WARNING: Do not work on or under a vehicle supported only by a jack.
Always support the vehicle on safety stands.
Raise and support the vehicle.
3. Refer to: Differential Case - TDV6 3.0L Diesel /V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol (205-02 Rear Drive Axle/Differential, Removal and Installation).
Installation
4.
5. Torque: 9 Nm
1. To install, reverse the removal procedure. www.JagDocs.com
Page 1436 of 3039

Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical Hydraulic
Damaged/stuck shift mechanism
Damaged automatic transmission casing
Blown fuse(s)
Damaged, loose or corroded connectors
Wiring harness
Fluid level too high/low
Poor condition of fluid
Fluid leak
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step.
4. If the cause is not visually evident check for diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) and refer to the DTC Index.
DTC Index
CAUTION: When probing connectors to take measurements in the course of the pinpoint tests, use the adaptor kit, part
number 3548-1358-00.
NOTES:
If the control module/transmission is suspect and the vehicle remains under manufacturer warranty, refer to the Warranty
Policy and Procedures manual (section B1.2), or determine if any prior approval programme is in operation, prior to the
installation of a new module/transmission.
Generic scan tools may not read the codes listed, or may read only five digit codes. Match the five digits from the scan
tool to the first five digits of the seven digit code listed to identify the fault (the last two digits give additional information
read by the manufacturer approved diagnostic system).
When performing electrical voltage or resistance tests, always use a digital multimeter (DMM) accurate to three decimal
places, and with an up-to-date calibration certificate. When testing resistance, always take the resistance of the DMM leads
into account.
Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
Inspect connectors for signs of water ingress, and pins for damage and/or corrosion.
If DTCs are recorded and, after performing the pinpoint tests, a fault is not present, an intermittent concern may be the
cause. Always check for loose connections and corroded terminals.
DTC Description Possible Cause Action P0121-86 Throttle/Pedal Position
Sensor A Circuit
Range/Performance - signal
invalid
Throttle/Pedal Position
Sensor Fault (Data
received over CAN Bus) Check Engine Control Module for stored DTCs P0219-86 Engine Overspeed Condition
- signal invalid
Engine speed too low or
too high (Data received
over CAN Bus) Check Engine Control Module for stored DTCs P0500-81
Vehicle Speed Sensor A -
invalid serial data received
Vehicle Speed Sensor
fault (Data received over
CAN Bus) Check DSC module for stored DTCs P0501-81 Vehicle Speed Sensor A
Vehicle Speed receive Check Anti-lock braking system module for stored Range/Performance invalid DTCs. Check correct Differential is installed to the serial data received over CAN Bus does not
vehicle match Transmission Output-Shaft speed P0561-1C
System Voltage Unstable -
Circuit voltage out of range
Power supply voltage out
of range when engine
running Check Engine control module for stored DTCs. Check
Charging System and Battery condition P0562-21
System Voltage Low - signal
amplitude < minimum
Circuit low voltage.
Battery supply voltage to
Transmission Control
Module (Transmission Refer to Circuit diagrams and check Power and Ground
Circuit for fault. Check Engine control module for
stored DTCs. Check Charging System and Battery
condition
Page 1694 of 3039
inlet duct downstream of the blower, where any heat generated during operation is dissipated by the air flow.
Auxiliary Coolant Pump
On all vehicles except 3.0L, an auxiliary coolant pump is installed on the rear right side of the radiator housing, in the return
line from the heater core. The auxiliary coolant pump is an electric pump that boosts the flow of coolant through the heater
core.
Ventilation Outlets
The ventilation outlets allow the free flow of air through the passenger compartment. The outlets are installed in the LH and
RH rear quarter panels, below the rear lamps. Each ventilation outlet consists of a grille covered by a soft rubber flap, and is
effectively a non-return valve. The flaps open and close automatically depending on the pressure differential between the air
inside and outside the vehicle.