2010 JAGUAR XFR brakes
[x] Cancel search: brakesPage 695 of 3039

Press and hold the DSC switch for less than 10 seconds.
The message center will temporarily display either Trac DSC or DSC ON.
The warning indicator in the instrument panel will illuminate while Trac DSC is selected.
The warning indicator will flash when DSC or Trac DSC is active.
NOTE: If cruise control is engaged, it will automatically disengage if DSC activates.
Refer to: Speed Control (310-03 Speed Control - 2.7L V6 - TdV6, Description and Operation).
Corner Brake Control
CBC (corner brake control) influences the brake pressures, below and within DSC and ABS thresholds, to counteract the yawing moment produced when braking in a corner. CBC produces a correction torque by limiting the brake pressure on one side of the
vehicle.
Electronic Brake Force Distribution
EBD (electronic brake force distribution) limits the brake pressure applied to the rear wheels. When the brakes are applied, the
weight of the vehicle transfers forwards, reducing the ability of the rear wheels to transfer braking effort to the road surface.
This may cause the rear wheels to slip and make the vehicle unstable.
EBD uses the ABS braking hardware to automatically optimize the pressure to the rear brakes, below the point where ABS is normally invoked.
NOTE: Only the rear brakes are controlled by the EBD function.
Electronic Traction Control
ETC (electronic traction control) attempts to optimize forward traction by reducing engine torque, or by applying the brake of a
spinning wheel until traction is regained.
ETC is activated if an individual wheel speed is above that of the vehicle reference speed (positive slip) and the brake pedal is
not pressed. The brake is applied to the spinning wheel, allowing the excess torque to be transmitted to the non-spinning
wheel through the drive line. If necessary, the ABS module also sends a high speed CAN bus message to the ECM to request a reduction in engine torque.
When the DSC function is selected off using the DSC switch, the braking and engine torque reduction features are both
disabled, except when the JaguarDrive control is in winter mode. When the JaguarDrive control is in winter mode, selecting the
DSC function off retains the braking and engine torque reduction features, but reduces intervention levels compared to DSC
and Trac DSC modes.
Emergency Brake Assist
EBA (emergency brake assist) assists the driver in emergency braking situations by automatically increasing the applied
braking effort. The ABS module invokes EBA when: The brake pedal is rapidly pressed.
The brake pedal is pressed hard enough to bring the front brakes into ABS operation.
When the brake pedal is rapidly pressed, the ABS module increases the hydraulic pressure to all of the brakes until the threshold for ABS operation is reached. This action applies the maximum braking effort for the available traction. The ABS module monitors for the sudden application of the brakes, using inputs from the brake pedal switch and from the pressure
sensor within the HCU (hydraulic control unit). With the brake pedal pressed, if the rate of increase of hydraulic pressure
exceeds the predetermined limit, the ABS module invokes emergency braking.
When the brake pedal is pressed hard enough to bring the front brakes into ABS operation, the ABS module increases the hydraulic pressure to the rear brakes up to the ABS threshold.
EBA operation continues until the driver releases the brake pedal, sufficiently for the hydraulic pressure in the HCU to drop below a threshold value stored in the ABS module.
Engine Drag-Torque Control
EDC (engine drag-torque control) prevents wheel slip caused by any of the following: A
sudden decrease in engine torque when the accelerator is suddenly released.
A downshift using the Jaguar sequential shift function on automatic transmission vehicles.
When the ABS module detects the onset of wheel slip without the brakes being applied, the ABS module signals the ECM via the high speed CAN bus to request a momentary increase in engine torque.
Understeer Control
Understeer Logic Control is a proactive system which monitors the vehicle for understeer by comparing signals from the yaw
rate and lateral acceleration sensor with signals from the steering angle sensor and wheel speed sensors. www.JagDocs.com
Page 696 of 3039

a decrease in engine torque. At the same time the ABS module will control the HCU to apply brake pressure to the relevant wheels to correct the understeer.
Electronic Brake Prefill (Vehicles With ACC Only)
Electronic brake prefill (Bosch ESP®plus8.1), senses any rapid throttle lift off, activating a small brake hydraulic pressure
build-up of approximately 3 to 5 bar (43.5 to 72.5 lbf/in²) in anticipation of the brakes being applied.
This application produces a quicker brake pedal response and consequently slightly shorter stopping distances. The system
supports vehicles with ACC (adaptive cruise control).
When the ABS module detects rapid throttle lift off (from the signals received from the ECM over the high speed CAN bus), it controls the HCU to apply a low brake pressure to assist in a quicker brake application.
Brake Vacuum Assist (3.0L Vehicles Only)
Operation of Brake Vacuum Assist generally occurs at the beginning of an ignition cycle when brake booster vacuum levels are
low; refer to Brake Booster Vacuum sensor, below.
Brake vacuum assist operation will be recognized by the driver experiencing a vibrating brake pedal and slight modulator noise.
This will be similar to that experienced when ABS system is operating.
As the engine warms up, Brake Vacuum Assist operation will become less frequent. However, it can be become more active
when vacuum levels are low due to driving at high-altitudes, or during frequent heavy-braking.
Noise levels during Brake Vacuum Assist may vary with initial system activity being the loudest observed. In some
circumstances initial activity may be interpreted as a 'thump' noise, particularly if there is no immediate and significant Brake
Vacuum Assist functionality.
In this circumstance system behavior is normal and should not be a cause for fault investigation.
Dynamic Stability Control Switch Component Description
Item Description 1 DSC switch The DSC switch is mounted in the floor console adjacent to the JaguarDrive selector.
Page 702 of 3039

ABS Module
Item Description 1 LH front brake 2 RH rear brake 3 LH rear brake 4 RH front brake 5 Primary inlet 6 Secondary inlet The ABS module is located in the passenger side, rear engine bay and incorporates the HCU. The module is mounted on the rear face of the HCU, which it uses to control all braking and stability functions by modulating hydraulic pressure to the individual wheel brakes.
Two types of ABS modules are available; one for vehicles with standard Speed Control, one for vehicles fitted with Adaptive Speed Control.
If an ABS modulator fault is detected, 'ABS FAULT' will be displayed in the instrument cluster message center and the amber warning indicator will illuminate.
Refer to: Information and Message Center (413-08 Information and Message Center, Description and Operation).
CAUTION: The ABS module and the HCU comprise a single unit and must not be separated.
Hydraulic Control Unit
The HCU is a four channel unit, secured to a mounting bracket located in the passenger side, rear engine bay. The HCU modulates the supply of hydraulic pressure to the brakes under the control of the ABS module. Refer to: Hydraulic Brake Actuation (206-06 Hydraulic Brake Actuation, Description and Operation).
Page 1189 of 3039

Published: 11-May-2011
Fuel Charging and Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Fuel Injection Component Cleaning
General Procedures
General Equipment
WARNINGS: Cleaning
Do not carry out any repairs to the fuel system with the engine running. Failure to follow this instruction may result in
personal injury.
Do not smoke or carry lighted tobacco or open flame of any type when working on or near any fuel related components.
Highly flammable vapors are always present and may ignite. Failure to follow these instructions may result in personal injury.
If fuel contacts the eyes, flush the eyes with cold water or eyewash solution and seek immediate medical attention.
Place the vehicle in a well ventilated, quarantined area and arrange ' No Smoking/Petrol Fumes' signs about the vehicle.
Wash hands thoroughly after fuel handling, as prolonged contact may cause irritation. Should irritation develop, seek
medical attention.
Do not carry or operate cellular phones when working on or near any fuel related components. Highly flammable vapors
are always present and may ignite. Failure to follow these instructions may result in personal injury.
CAUTIONS:
Before using the cleaning fluid, protect all electrical components and connectors with lint-free non-flocking material.
Make sure that all parts removed from the vehicle are placed on the lint-free non-flocking material.
Make sure that any protective clothing worn is clean and made from lint-free non-flocking material.
Make sure that clean non-plated tools are used. Clean tools using a new brush that will not lose its bristles, prior to
starting work on the vehicle.
Use a steel topped workbench and cover it with clean, lint-free non-flocking material.
Make sure the workshop area in which the vehicle is being worked on is as clean and as dust free as possible. Foreign
matter from work on clutches, brakes or from machining or welding operations can contaminate the fuel system and may result
in later malfunction.
1. Using a new brush that will not lose its bristles, brush the components
being removed and the surrounding area.
2. Using a pneumatic vacuum gun, remove all traces of foreign material.
General Equipment: Pneumatic vacuum gun Pneumatic vacuum gun
Page 1413 of 3039
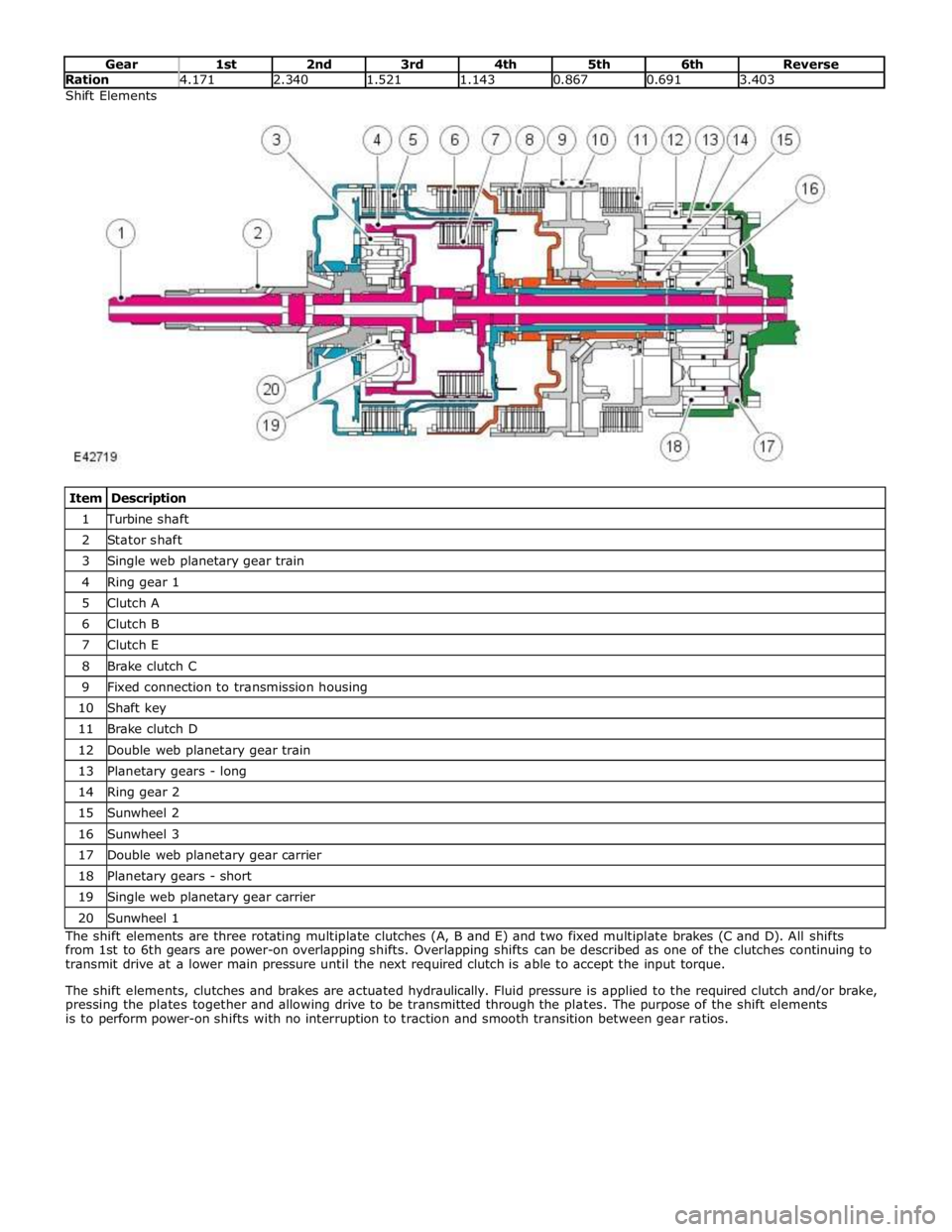
Ration 4.171 2.340 1.521 1.143 0.867 0.691 3.403 Shift Elements
Item Description 1 Turbine shaft 2 Stator shaft 3 Single web planetary gear train 4 Ring gear 1 5 Clutch A 6 Clutch B 7 Clutch E 8 Brake clutch C 9 Fixed connection to transmission housing 10 Shaft key 11 Brake clutch D 12 Double web planetary gear train 13 Planetary gears - long 14 Ring gear 2 15 Sunwheel 2 16 Sunwheel 3 17 Double web planetary gear carrier 18 Planetary gears - short 19 Single web planetary gear carrier 20 Sunwheel 1 The shift elements are three rotating multiplate clutches (A, B and E) and two fixed multiplate brakes (C and D). All shifts
from 1st to 6th gears are power-on overlapping shifts. Overlapping shifts can be described as one of the clutches continuing to
transmit drive at a lower main pressure until the next required clutch is able to accept the input torque.
The shift elements, clutches and brakes are actuated hydraulically. Fluid pressure is applied to the required clutch and/or brake,
pressing the plates together and allowing drive to be transmitted through the plates. The purpose of the shift elements
is to perform power-on shifts with no interruption to traction and smooth transition between gear ratios.
Page 1639 of 3039

Published: 11-May-2011
Speed Control - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Speed Control - Overview
Description and Operation
OVERVIEW
Speed Control
The speed control system is integrated with the engine management system and uses fueling intervention to automatically
maintain a set vehicle speed. Once engaged, the system can also be used to accelerate the vehicle without using the
accelerator pedal.
The speed control system comprises the following components:
On/Off/Suspend switch
'+' and '-' (set/accelerate and decelerate) steering wheel switches
Resume switch
Clock spring
Speed control warning indicator.
Adaptive Speed Control
The adaptive speed control system uses a forward looking radar sensor to scan the road ahead, looking for objects that are
moving at a different rate to itself. When a target is identified the adaptive speed control system will monitor the time gap
between it and the target vehicle. When that gap falls below a set driver selected level the adaptive speed control system will
intervene slowing the vehicle by backing off the throttle and/ or applying the brakes, until the correct gap is attained.
The adaptive speed control system comprises the following components:
Adaptive speed control sensor
Adaptive speed control module
Steering wheel control switches
ECM (engine control module)
Electric throttle actuator
ABS (anti-lock brake system) module and pump
Adaptive speed control warning indicator (in the instrument cluster).
Page 1641 of 3039

6 Clockspring 7 APP (accelerator pedal position) sensor 8 Electric throttle actuator 9 Brake lamp/brake test switch 10 Adaptive speed control radar sensor 11 Diagnostic socket 12 Instrument cluster 13 TCM (transmission control module) 14 Adaptive speed control module
SPEED CONTROL System Operation
The speed control system uses inputs from the brake lamp/brake test switch, the APP sensor, the ECM and the ABS module.
Speed control is operated by the driver using only the steering wheel switches. When speed control is active, the ECM regulates the PWM (pulse width modulation) signals to the fuel injectors to adjust the fuel supply as required to maintain the
set speed.
During speed control operation, the ECM controls vehicle speed by adjusting fuel injection duration and timing. When the accelerator pedal is pressed with speed control active, the ECM outputs a calculated throttle angle signal in place of the actual throttle angle signals produced by the APP sensor. The calculated throttle angle is derived from fuel demand.
The minimum set speed for speed control is 18 mph (30 (km/h). Speed control is automatically suspended if the following
conditions apply:
Vehicle speed falls below 18 mph (30 km/h)
The brake pedal is pressed
The cancel button is pressed
Neutral, park or reverse gear is selected
The difference between actual speed and the set speed is too great
If the engine speed becomes near to the red line (maximum engine speed)
If the accelerator pedal is used to accelerate beyond the set speed for too long.
ADAPTIVE SPEED CONTROL
The adaptive speed control system comprises the following components:
Adaptive speed control sensor
Adaptive speed control module
Steering wheel control switches
ECM
Electric throttle actuator
ABS module and pump Adaptive speed control warning indicator.
The adaptive speed control system uses a forward looking radar sensor to scan the road ahead, looking for objects that are
moving at a different rate to itself. When a target is identified the adaptive speed control system will monitor the time gap
between it and the target vehicle. When that gap falls below a set driver selected level the adaptive speed control system will
intervene slowing the vehicle by backing off the throttle and/ or applying the brakes, until the correct gap is attained. The
driver can chose between four gap settings, 1, 1.4, 1.8 and 2.2 seconds.
The system will detect but not react to the following:
Vehicles in the oncoming lane
Stationary vehicles
Pedestrians
Vehicles not in the same lane.
Adaptive speed control is active when the vehicle is moving. Adaptive Speed Control only functions when a set speed is
entered in normal speed control mode. The adaptive speed control system only intervenes with the set speed when it detects
a target vehicle, and then only if the minimum time gap is breached.
It is important to note that the system is intended for use in limited driving situations, does not remove control and
responsibility from the driver, and at all times can be quickly overridden. The adaptive speed control system is not a collision
warning system and will not react to stationary objects. The system does not operate below a minimum speed of
approximately 30 km/h (20 mph) since it is unsuitable for use in cities or congested traffic. The system is best suited to main
roads/ highways with gradual bends.
The ECM, throttle body and throttle control are unchanged from those used for non adaptive speed control variants.
The adaptive speed control system is based on the use of a front mounted radar sensor. The sensor transmits a 1.5° wide
beam forward of the vehicle and detects the returning signals reflected off other vehicles and objects ahead.
The 1.5° wide radar beam is mechanically scanned at a rate of 10 sweeps/second across a total arc of 15° centered on the
Page 1642 of 3039
longitudinal axis of the vehicle. The radar operates at millimetric wavelengths (76 - 77 GHz) and transmits a frequency
modulated continuous wave signal at a relatively low power level (no high power pulses).
With the ignition ON, the adaptive speed control module is powered up but no radar transmissions are emitted until the
vehicle is in motion.
In follow mode a set speed is selected in the normal speed control manner and this speed is maintained until a slower vehicle
is encountered in the lane ahead. When the vehicle ahead comes within the effective range of the radar sensor, the system
identifies it as a target vehicle and an icon is illuminated on the instrument cluster to indicate that the system is in "follow
mode". When the distance between the two vehicles closes to a set time gap, the adaptive speed control system closes the
throttle and if necessary applies the brakes to maintain the set time gap. Follow mode is effectively a closed loop system. If
several vehicles are ahead, the closest vehicle is chosen as the target to follow. If the target vehicle moves out of radar range,
or if either vehicle changes lane or drops below the minimum operating speed, the system exits follow mode and the follow
mode icon is extinguished. The adaptive speed control system will only raise its speed to the originally set speed, it will not
accelerate past this speed to maintain a time gap.
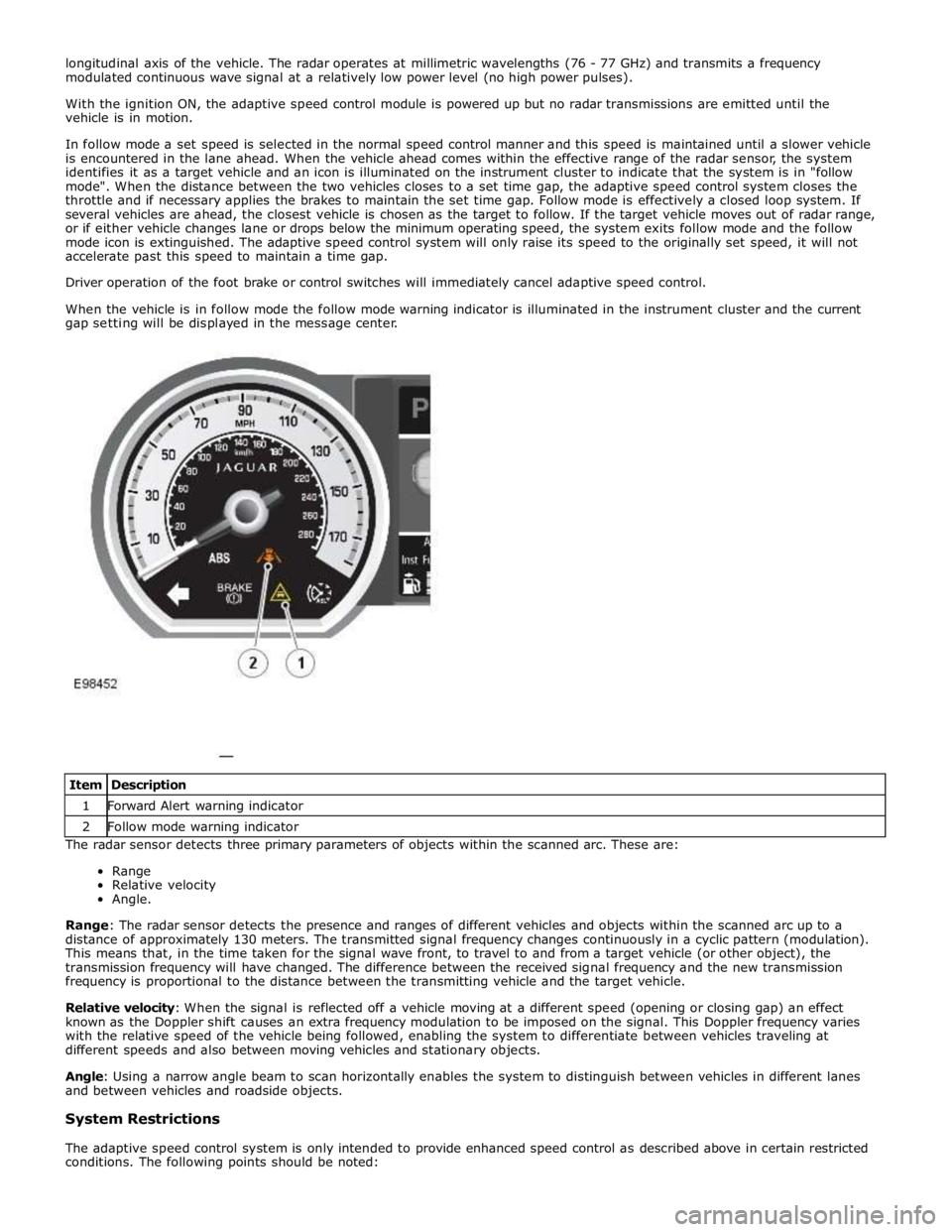
Driver operation of the foot brake or control switches will immediately cancel adaptive speed control.
When the vehicle is in follow mode the follow mode warning indicator is illuminated in the instrument cluster and the current
gap setting will be displayed in the message center.
The radar sensor detects three primary parameters of objects within the scanned arc. These are:
Range
Relative velocity
Angle.
Range: The radar sensor detects the presence and ranges of different vehicles and objects within the scanned arc up to a
distance of approximately 130 meters. The transmitted signal frequency changes continuously in a cyclic pattern (modulation).
This means that, in the time taken for the signal wave front, to travel to and from a target vehicle (or other object), the
transmission frequency will have changed. The difference between the received signal frequency and the new transmission
frequency is proportional to the distance between the transmitting vehicle and the target vehicle.
Relative velocity: When the signal is reflected off a vehicle moving at a different speed (opening or closing gap) an effect
known as the Doppler shift causes an extra frequency modulation to be imposed on the signal. This Doppler frequency varies
with the relative speed of the vehicle being followed, enabling the system to differentiate between vehicles traveling at
different speeds and also between moving vehicles and stationary objects.
Angle: Using a narrow angle beam to scan horizontally enables the system to distinguish between vehicles in different lanes
and between vehicles and roadside objects.
System Restrictions
The adaptive speed control system is only intended to provide enhanced speed control as described above in certain restricted
conditions. The following points should be noted: Item Description 1 Forward Alert warning indicator 2 Follow mode warning indicator