2010 JAGUAR XFR Shock
[x] Cancel search: ShockPage 436 of 3039

3. Vehicles without adaptive damping.
Install a new retaining nut.
Tighten to 50 Nm.
4. Vehicles with adaptive damping.
Install a new retaining nut.
Tighten to 27 Nm.
5. Release the road spring.
6. Remove the shock absorber and spring assembly from the
special tool.
Page 488 of 3039

Vehicle Dynamic Suspension - Vehicle Dynamic Suspension
Diagnosis and Testing
Principle of Operation Published: 09-Jul-2014
For a detailed description of the adaptive damping system operation, refer to the relevant Description and Operation section of
the workshop manual. REFER to: (204-05 Vehicle Dynamic Suspension)
Vehicle Dynamic Suspension - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol (Description and Operation),
Inspection and Verification
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of damage and system integrity.
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Coil spring(s)
Shock absorber(s)
Accelerometer(s) installation
Height sensor(s) installation
Fuse(s)
Wiring harness/electrical connectors
Accelerometer(s)
Adaptive Damping Control Module
Height sensor(s)
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step.
4. If the cause is not visually evident, check the system for any logged Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and refer to the
DTC index.
DTC Index
For a list of Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) that could be logged on this vehicle, please refer to Section 100-00.
REFER to: Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Index - DTC: Adaptive Damping Module (SUMB) (100-00 General Information, Description and Operation).
Page 851 of 3039
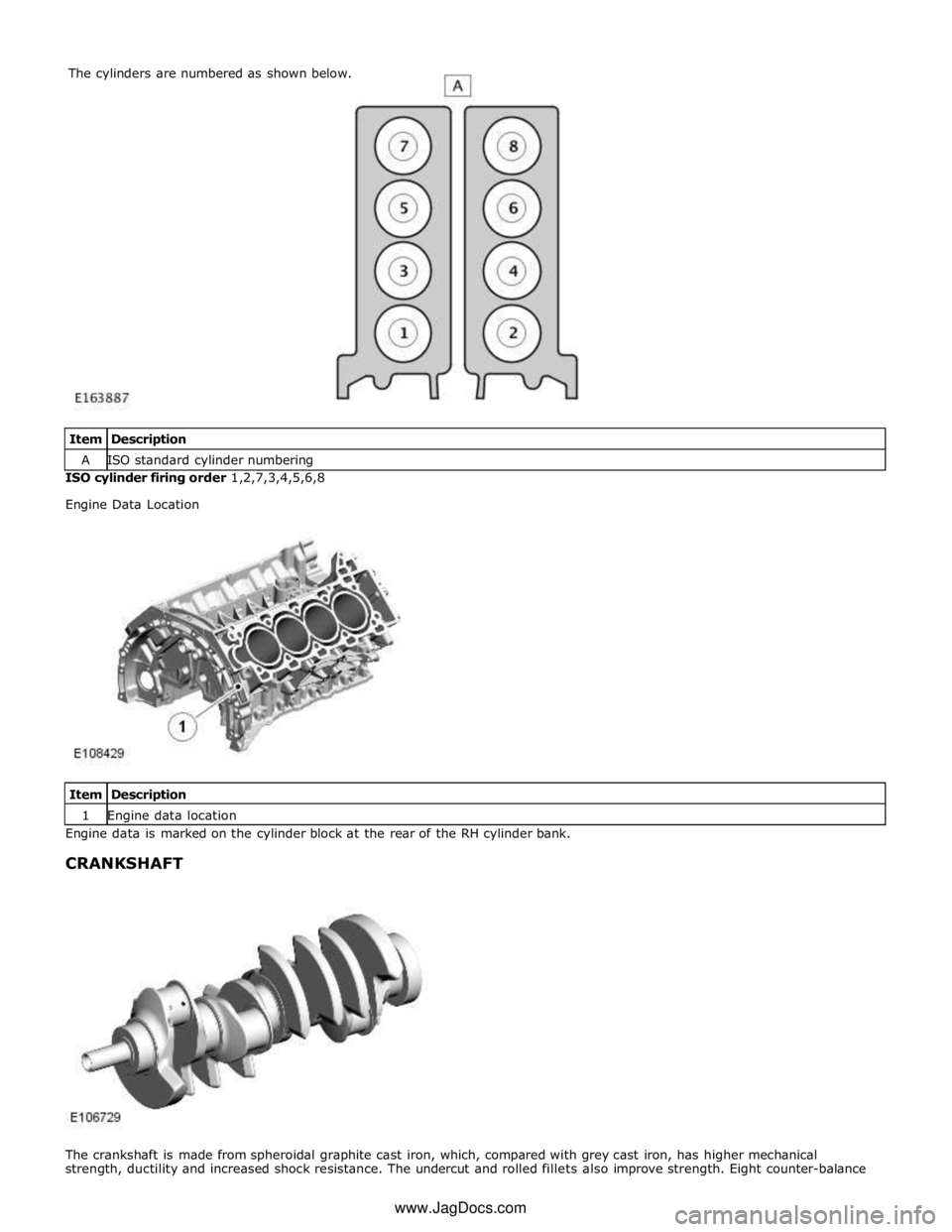
A ISO standard cylinder numbering ISO cylinder firing order 1,2,7,3,4,5,6,8
Engine Data Location
Item Description 1 Engine data location Engine data is marked on the cylinder block at the rear of the RH cylinder bank.
CRANKSHAFT
The crankshaft is made from spheroidal graphite cast iron, which, compared with grey cast iron, has higher mechanical
strength, ductility and increased shock resistance. The undercut and rolled fillets also improve strength. Eight counter-balance The cylinders are numbered as shown below.
www.JagDocs.com
Page 1365 of 3039
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE AND TEMPERATURE SENSOR
The MAPT sensor allows the ECM to calculate the air charge density immediately before it enters the cylinders. This is used to adjust the ignition timing relative to the boost pressure, and to monitor the performance of the charge air coolers.
The MAPT sensor is installed in the rear of the LH intake manifold. The sensor is secured with a single screw and sealed with an O-ring. A four pin electrical connector provides the interface with the engine harness.
THROTTLE POSITION SENSORS
The TP (throttle position) sensors allow the ECM to determine the position and angular rate of change of the throttle blade. There are two TP sensors located in the electronic throttle. See below for details of the electronic throttle. If aTP sensor fails, the ECM:
Adopts a limp home mode where engine speed is limited to a maximum of approximately 2000 rev/min
Discontinues evaporative emissions control
Discontinues closed loop control of engine idle speed.
With a failed TP sensor, the engine will suffer from poor running and throttle response.
HEATED OXYGEN SENSORS
Item Description A Upstream heated oxygen sensor B Downstream heated oxygen sensor The heated oxygen sensors allow the ECM to measure the oxygen content of the exhaust gases, for closed loop control of the fuel:air mixture and for catalytic converter monitoring.
An upstream heated oxygen sensor is installed in the outlet of each exhaust manifold, which enables independent control of
the fuel:air mixture for each cylinder bank. A downstream heated oxygen sensor is installed in each catalytic converter, which
enables the performance of the catalytic converters to be monitored.
Oxygen sensors need to operate at high temperatures in order to function correctly. To achieve the high temperatures required,
the sensors are fitted with heater elements that are controlled by a PWM (pulse width modulation) signal from the ECM. The heater elements are operated immediately after each engine start and during low load conditions when the temperature of the
exhaust gases is insufficient to maintain the required sensor temperature. The PWM duty cycle is carefully controlled to prevent thermal shock to cold sensors. A non-functioning heater delays the sensor’s readiness for closed loop control and
increases emissions.
The upstream heated oxygen sensors produce a constant voltage, with a variable current that is proportional to the lambda
ratio. The downstream heated oxygen sensors produce an output voltage dependant on the ratio of the exhaust gas oxygen to
Page 1431 of 3039

transmission functions. The Mechatronic valve block comprises the following components:
TCM
Pressure regulator solenoids
Shift control solenoid
Damper
Hydraulic spool valves
Selector valve
Temperature sensor
Turbine speed sensor
Output shaft speed sensor.
Sensors
Speed Sensors
The turbine speed sensor and the output shaft speed sensor are Hall effect type sensors located in the Mechatronic valve block
and are not serviceable items. The TCM monitors the signals from each sensor to determine the input (turbine) speed and the output shaft speed.
The turbine speed is monitored by the TCM to calculate the slip of the torque converter clutch and internal clutch slip. This signal allows the TCM to accurately control the slip timing during shifts and adjust clutch application or release pressure for overlap shift control.
The output shaft speed is monitored by the TCM and compared to engine speed signals received on the CAN bus from the ECM. Using a comparison of the two signals the TCM calculates the transmission slip ratio for plausibility and maintains adaptive pressure control.
Temperature Sensor
The temperature sensor is also located in the Mechatronic valve block. The TCM uses the temperature sensor signals to determine the temperature of the transmission fluid. These signals are used by the TCM to control the transmission operation to promote faster warm-up in cold conditions or to assist with fluid cooling by controlling the transmission operation when high
fluid temperatures are experienced. If the sensor fails, the TCM will use a default value and a fault code will be stored in the TCM.
Damper
There is one damper located in the valve housing. The damper is used to regulate and dampen the regulated pressure supplied
via EPRS. The damper is load dependent through modulation of the damper against return spring pressure.
The damper comprises a piston, a housing bore and a spring. The piston is subject to the pressure applied by the spring. The
bore has a connecting port to the function to which it applies. Fluid pressure applied to the applicable component (i.e. a
clutch) is also subjected to the full area of the piston, which moves against the opposing force applied by the spring. The
movement of the piston creates an action similar to a shock absorber, momentarily delaying the build up of pressure in the
circuit. This results in a more gradual application of clutches improving shift quality.
Spool Valves
The valve block spool valves control various functions of the transmission. The spool valves are of conventional design and are
operated by fluid pressure.
Each spool valve is located in its spool bore and held in a default (unpressurized) position by a spring. The spool bore has a
number of ports which allow fluid to flow to other valves and clutches to enable transmission operation. Each spool has a
piston which is waisted to allow fluid to be diverted into the applicable ports when the valve is operated.
When fluid pressure moves a spool, one or more ports in the spool bore are covered or uncovered. Fluid is prevented from
flowing or is allowed to flow around the applicable waisted area of the spool and into another uncovered port. The fluid is
either passed through galleries to actuate another spool, operate a clutch or is returned to the fluid pan.
Page 2354 of 3039

Seating - Seat Smoothing
General Procedures Published: 01-May-2014
WARNINGS: Check
Make sure that the steamer is in the OFF position before connecting or disconnecting from the electrical outlet.
Do not use another high wattage device on the same electrical circuit.
If the use of an extension cord is absolutely necessary, the cord must be rated at a minimum of 10 amps.
To avoid the risk of electrical shock, check the condition of the power cord and the steamer before use.
Make sure that the steamer is disconnected from the electrical outlet before filling or emptying the water reservoir.
The steamer must only be used and placed on its stand on a stable surface.
To prevent injury such as burns, take care whilst using the steamer. Avoid coming into contact with the hot surface of the
steamer and do not direct steam toward any persons.
The steamer must ALWAYS be switched off when not in use or left unattended.
Do not allow the power cord to come into contact with the hot surface of the steamer.
CAUTIONS:
Protect the surrounding paintwork to avoid damage.
Protect the paintwork during this operation.
Do not use any additives in the steamer. Damage to the steamer or the seat cover can result if used.
NOTE: Some variation in the illustrations may occur, but the essential information is always correct.
1. CAUTIONS:
Steam the leather cushions evenly and progressively. Do not use
excessive force.
Take care not to damage the leather whilst steaming into the
corners.
Do not hold the steamer in one place for longer than 10 seconds,
as this will burn the leather and damage the covers. www.JagDocs.com
Page 2785 of 3039
Transmission (307-01A Automatic Transmission/Transaxle - V6 3.0L Petrol, Removal) /
Transmission - 4.2L (307-01, Removal) /
Transmission - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol (307-01B Automatic Transmission/Transaxle - TDV6 3.0L Diesel /V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L
Petrol, Removal) /
Front Shock Absorber (204-01 Front Suspension, Removal and Installation) /
Front Subframe - 2.7L Diesel (502-00, Removal and Installation) /
Front Subframe - V6 3.0L Petrol (502-00 Uni-Body, Subframe and Mounting System, Removal and Installation) /
Front Subframe - 4.2L, Vehicles Without: Supercharger (502-00, Removal
and Installation) /
Front Subframe - 4.2L, Vehicles With: Supercharger (502-00, Removal
and Installation).
8. Remove the pedestrian protection hood actuator.
For additional information, refer to: Pedestrian Protection Hood Actuator LH (501-20C Pedestrian Protection System, Removal and Installation) / Pedestrian Protection Hood Actuator RH (501-20C Pedestrian Protection System, Removal and Installation).
9. If the drivers side front side member and suspension top mount is to be
repaired, remove the brake master cylinder and reservoir.
For additional information, refer to: Brake Master Cylinder (206-06 Hydraulic Brake Actuation, Removal and Installation) /
Brake Fluid Reservoir (206-06 Hydraulic Brake Actuation, Removal and Installation).
10. If the left-hand front side member and suspension top mount assembly
is to be repaired, remove the fuel supply and return lines.
11. Release and position the front side member wiring harness to one side.
12. Remove any remaining miscellaneous components from the repair area.
13. NOTE: Retain the front fender support bracket
mounting if it is to be reused. If the front fender support
bracket mounting is to be renewed, it is not necessary to
remove or retain it.
Drill out the spot welds to remove the front fender support
bracket mounting.
Page 2797 of 3039

(100-00 General Information, Description and Operation) /
Body Repairs (501-25A Body Repairs - General Information, Description and Operation) /
Corrosion Protection (501-25B Body Repairs - Corrosion Protection, Description and Operation) /
Body and Frame (501-26 Body Repairs - Vehicle Specific Information and Tolerance Checks, Description and Operation).
5. Remove the fender apron panel front extension.
For additional information, refer to: Fender Apron Panel Front Extension (501-27 Front End Sheet Metal Repairs, Removal and Installation).
6. Remove the front fender support bracket.
For additional information, refer to: Front Fender Support Bracket (501-27 Front End Sheet Metal Repairs, Removal and Installation).
7. Remove the fender apron panel.
For additional information, refer to: Fender Apron Panel (501-27 Front End Sheet Metal Repairs, Removal and Installation).
8. Remove the engine, transmission / transaxle, front subframe and front
suspension, as an assembly.
For additional information, refer to: Engine (303-01A, Removal) /
Engine (303-01B Engine - V6 3.0L Petrol, Removal) / Engine (303-01D, Removal) /
Engine (303-01E, Removal) /
Transmission - 2.7L Diesel (307-01, Removal) /
Transmission - TDV6 3.0L Diesel (307-01B Automatic Transmission/Transaxle - TDV6 3.0L Diesel /V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L
Petrol, Removal) /
Transmission (307-01A Automatic Transmission/Transaxle - V6 3.0L Petrol, Removal) /
Transmission - 4.2L (307-01, Removal) /
Transmission - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol (307-01B Automatic Transmission/Transaxle - TDV6 3.0L Diesel /V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L
Petrol, Removal) /
Front Shock Absorber (204-01 Front Suspension, Removal and Installation) /
Front Subframe - 2.7L Diesel (502-00, Removal and Installation) /
Front Subframe - V6 3.0L Petrol (502-00 Uni-Body, Subframe and Mounting System, Removal and Installation) /
Front Subframe - 4.2L, Vehicles Without: Supercharger (502-00, Removal
and Installation) /
Front Subframe - 4.2L, Vehicles With: Supercharger (502-00, Removal
and Installation).
9. Remove the pedestrian protection hood actuator.
For additional information, refer to: Pedestrian Protection Hood Actuator LH (501-20C Pedestrian Protection System, Removal and Installation) / Pedestrian Protection Hood Actuator RH (501-20C Pedestrian Protection System, Removal and Installation).
10. If the drivers side front side member and suspension top mount is to be
repaired, remove the brake master cylinder and reservoir.
For additional information, refer to: Brake Master Cylinder (206-06 Hydraulic Brake Actuation, Removal and Installation) /
Brake Fluid Reservoir (206-06 Hydraulic Brake Actuation, Removal and Installation).
11. If the drivers side front side member and suspension top mount is to be
repaired, remove the brake booster.