2010 JAGUAR XFR Electrical
[x] Cancel search: ElectricalPage 1534 of 3039

Published: 19-Jun-2013
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle External Controls - TDV6 3.0L Diesel /V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - External Controls
Diagnosis and Testing
Principles of Operation
For a detailed description of the transmission external controls, refer to the relevant Description and Operation sections in the
workshop manual. REFER to: (307-05)
External Controls (Description and Operation),
External Controls (Description and Operation),
External Controls (Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle.
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of damage and system integrity.
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Check for stuck/jammed switches and buttons
Visibly damaged or worn components
Loose or missing fasteners
Fuse(s)
Loose or corroded electrical connector(s)
Transmission control module
Transmission control switch
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step.
4. If the cause is not visually evident, check for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and refer to the DTC Index.
DTC Index
For a list of DTCs that could be logged on this vehicle, please refer to Section 100-00.
REFER to: Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Index - DTC: Transmission Control Module (TCM) (100-00, Description and Operation)
/
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Index - DTC: Transmission Control Switch (TCS) (100-00, Description and Operation).
Page 1586 of 3039
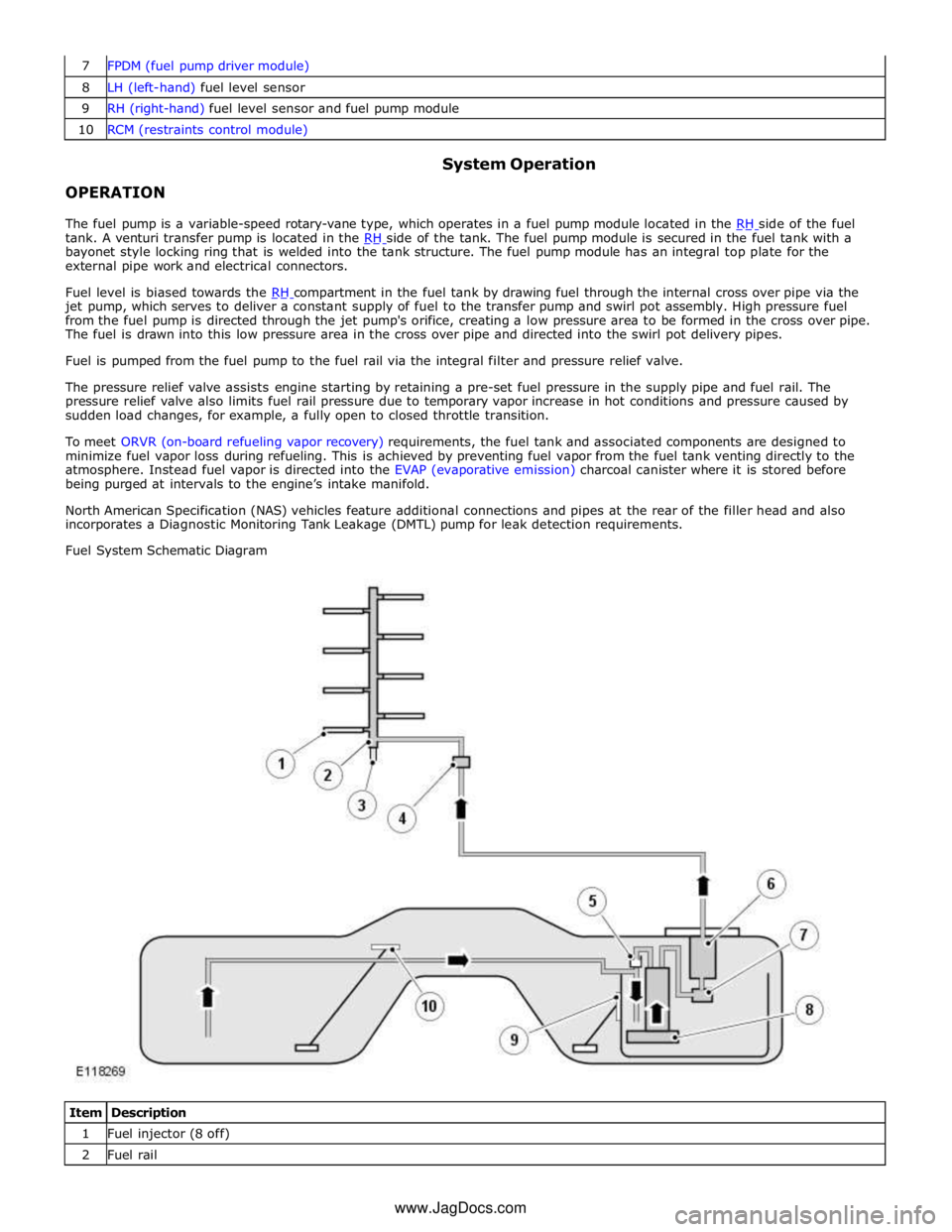
8 LH (left-hand) fuel level sensor 9 RH (right-hand) fuel level sensor and fuel pump module 10 RCM (restraints control module)
OPERATION System Operation
The fuel pump is a variable-speed rotary-vane type, which operates in a fuel pump module located in the RH side of the fuel tank. A venturi transfer pump is located in the RH side of the tank. The fuel pump module is secured in the fuel tank with a bayonet style locking ring that is welded into the tank structure. The fuel pump module has an integral top plate for the
external pipe work and electrical connectors.
Fuel level is biased towards the RH compartment in the fuel tank by drawing fuel through the internal cross over pipe via the jet pump, which serves to deliver a constant supply of fuel to the transfer pump and swirl pot assembly. High pressure fuel
from the fuel pump is directed through the jet pump's orifice, creating a low pressure area to be formed in the cross over pipe.
The fuel is drawn into this low pressure area in the cross over pipe and directed into the swirl pot delivery pipes.
Fuel is pumped from the fuel pump to the fuel rail via the integral filter and pressure relief valve.
The pressure relief valve assists engine starting by retaining a pre-set fuel pressure in the supply pipe and fuel rail. The
pressure relief valve also limits fuel rail pressure due to temporary vapor increase in hot conditions and pressure caused by
sudden load changes, for example, a fully open to closed throttle transition.
To meet ORVR (on-board refueling vapor recovery) requirements, the fuel tank and associated components are designed to
minimize fuel vapor loss during refueling. This is achieved by preventing fuel vapor from the fuel tank venting directly to the
atmosphere. Instead fuel vapor is directed into the EVAP (evaporative emission) charcoal canister where it is stored before
being purged at intervals to the engine’s intake manifold.
North American Specification (NAS) vehicles feature additional connections and pipes at the rear of the filler head and also
incorporates a Diagnostic Monitoring Tank Leakage (DMTL) pump for leak detection requirements.
Fuel System Schematic Diagram
Item Description 1 Fuel injector (8 off) 2 Fuel rail www.JagDocs.com
Page 1588 of 3039
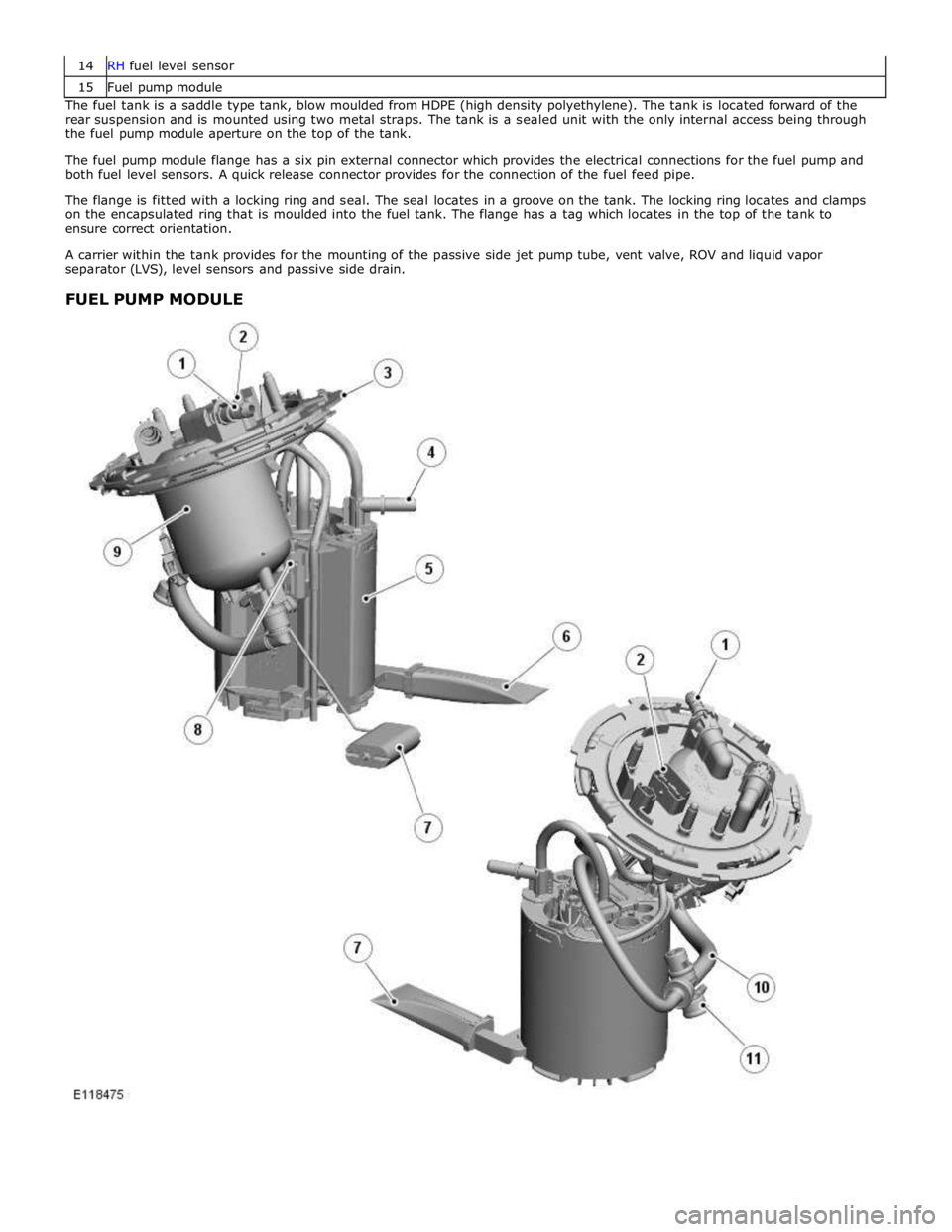
15 Fuel pump module The fuel tank is a saddle type tank, blow moulded from HDPE (high density polyethylene). The tank is located forward of the
rear suspension and is mounted using two metal straps. The tank is a sealed unit with the only internal access being through
the fuel pump module aperture on the top of the tank.
The fuel pump module flange has a six pin external connector which provides the electrical connections for the fuel pump and
both fuel level sensors. A quick release connector provides for the connection of the fuel feed pipe.
The flange is fitted with a locking ring and seal. The seal locates in a groove on the tank. The locking ring locates and clamps
on the encapsulated ring that is moulded into the fuel tank. The flange has a tag which locates in the top of the tank to
ensure correct orientation.
A carrier within the tank provides for the mounting of the passive side jet pump tube, vent valve, ROV and liquid vapor
separator (LVS), level sensors and passive side drain.
FUEL PUMP MODULE
Page 1589 of 3039
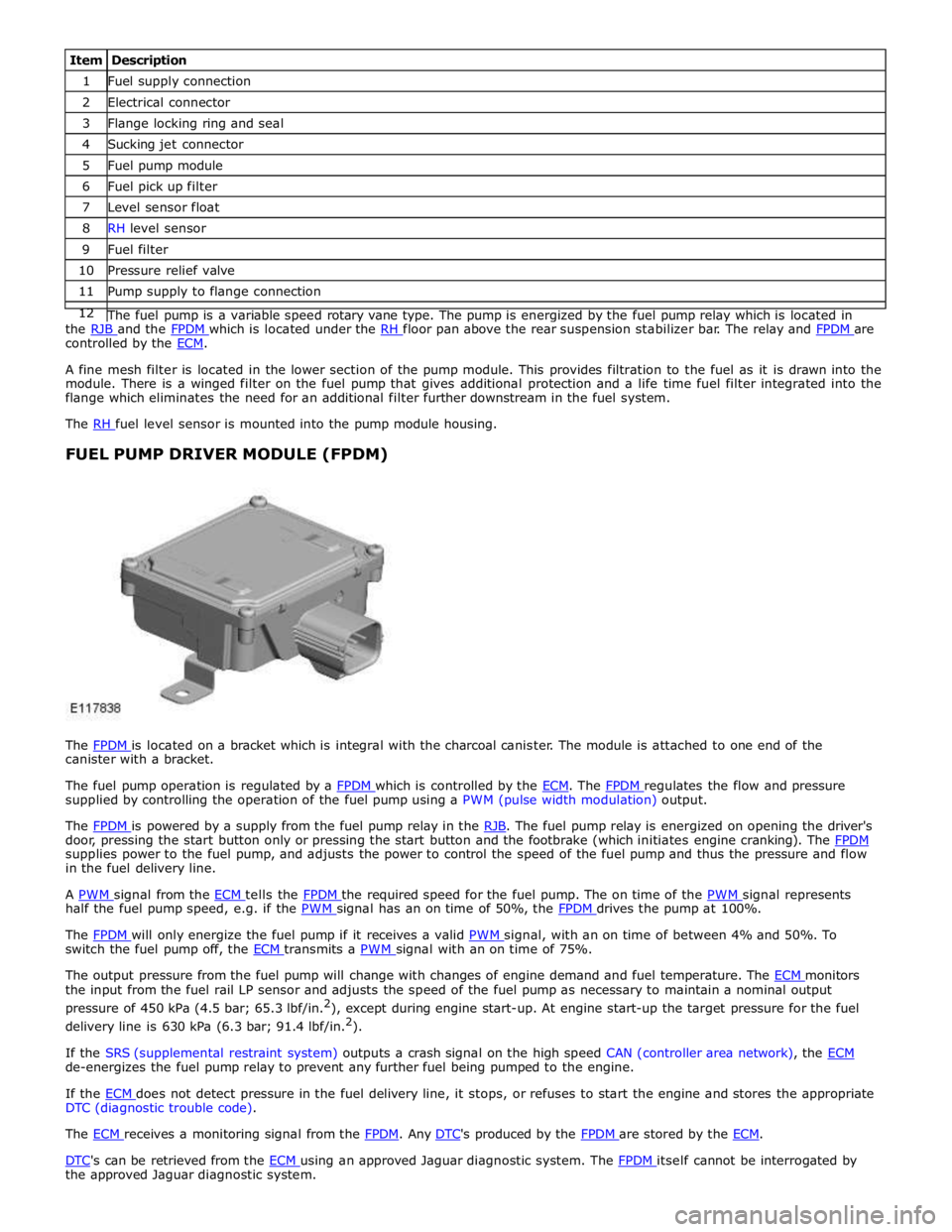
1 Fuel supply connection 2 Electrical connector 3 Flange locking ring and seal 4 Sucking jet connector 5 Fuel pump module 6 Fuel pick up filter 7 Level sensor float 8 RH level sensor 9 Fuel filter 10 Pressure relief valve 11 Pump supply to flange connection 12 The fuel pump is a variable speed rotary vane type. The pump is energized by the fuel pump relay which is located in the RJB and the FPDM which is located under the RH floor pan above the rear suspension stabilizer bar. The relay and FPDM are controlled by the ECM.
A fine mesh filter is located in the lower section of the pump module. This provides filtration to the fuel as it is drawn into the
module. There is a winged filter on the fuel pump that gives additional protection and a life time fuel filter integrated into the
flange which eliminates the need for an additional filter further downstream in the fuel system.
The RH fuel level sensor is mounted into the pump module housing.
FUEL PUMP DRIVER MODULE (FPDM)
The FPDM is located on a bracket which is integral with the charcoal canister. The module is attached to one end of the canister with a bracket.
The fuel pump operation is regulated by a FPDM which is controlled by the ECM. The FPDM regulates the flow and pressure supplied by controlling the operation of the fuel pump using a PWM (pulse width modulation) output.
The FPDM is powered by a supply from the fuel pump relay in the RJB. The fuel pump relay is energized on opening the driver's door, pressing the start button only or pressing the start button and the footbrake (which initiates engine cranking). The FPDM supplies power to the fuel pump, and adjusts the power to control the speed of the fuel pump and thus the pressure and flow
in the fuel delivery line.
A PWM signal from the ECM tells the FPDM the required speed for the fuel pump. The on time of the PWM signal represents half the fuel pump speed, e.g. if the PWM signal has an on time of 50%, the FPDM drives the pump at 100%.
The FPDM will only energize the fuel pump if it receives a valid PWM signal, with an on time of between 4% and 50%. To switch the fuel pump off, the ECM transmits a PWM signal with an on time of 75%.
The output pressure from the fuel pump will change with changes of engine demand and fuel temperature. The ECM monitors the input from the fuel rail LP sensor and adjusts the speed of the fuel pump as necessary to maintain a nominal output
pressure of 450 kPa (4.5 bar; 65.3 lbf/in.2
), except during engine start-up. At engine start-up the target pressure for the fuel
delivery line is 630 kPa (6.3 bar; 91.4 lbf/in.2
).
If the SRS (supplemental restraint system) outputs a crash signal on the high speed CAN (controller area network), the ECM de-energizes the fuel pump relay to prevent any further fuel being pumped to the engine.
If the ECM does not detect pressure in the fuel delivery line, it stops, or refuses to start the engine and stores the appropriate DTC (diagnostic trouble code).
The ECM receives a monitoring signal from the FPDM. Any DTC's produced by the FPDM are stored by the ECM.
DTC's can be retrieved from the ECM using an approved Jaguar diagnostic system. The FPDM itself cannot be interrogated by the approved Jaguar diagnostic system.
Page 1590 of 3039
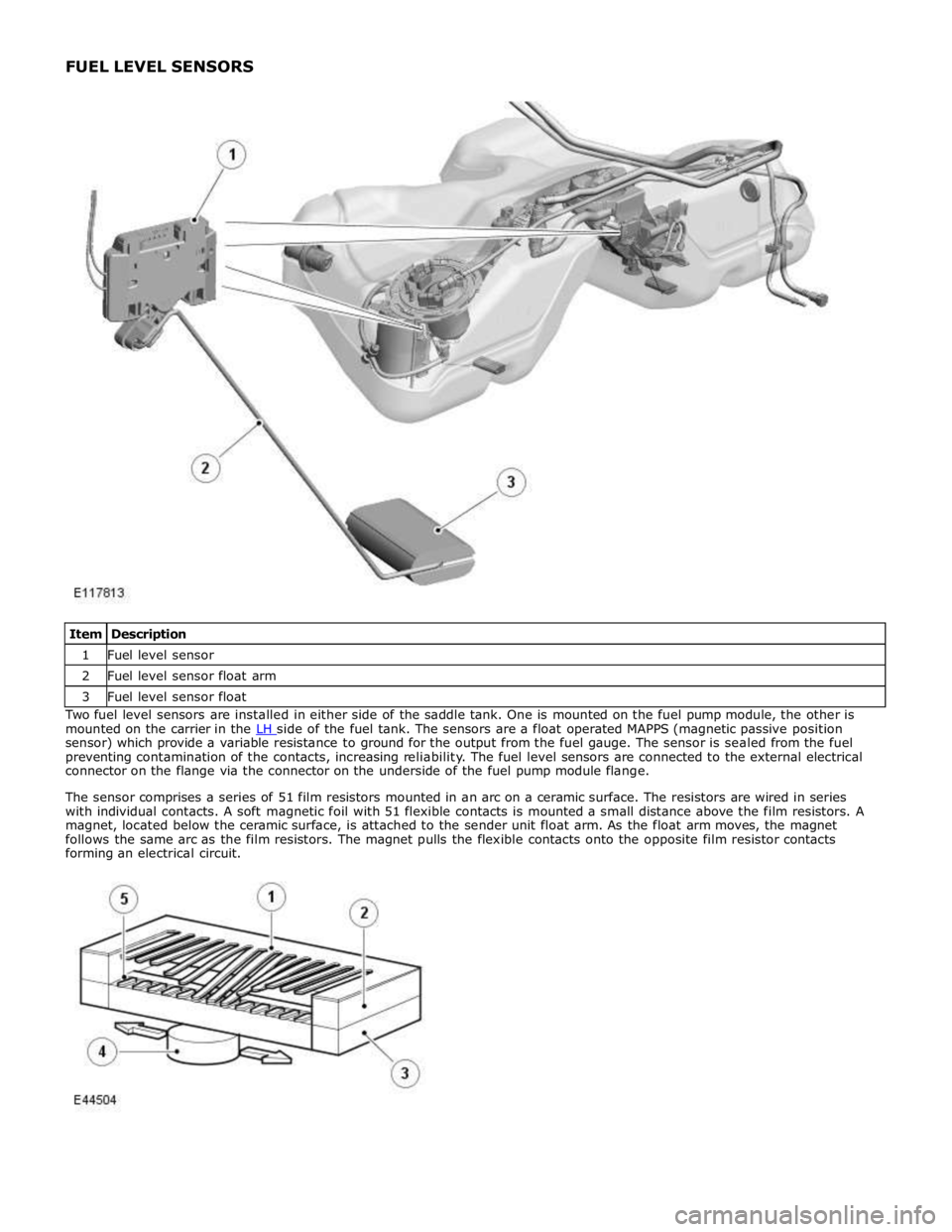
1 Fuel level sensor 2 Fuel level sensor float arm 3 Fuel level sensor float Two fuel level sensors are installed in either side of the saddle tank. One is mounted on the fuel pump module, the other is
mounted on the carrier in the LH side of the fuel tank. The sensors are a float operated MAPPS (magnetic passive position sensor) which provide a variable resistance to ground for the output from the fuel gauge. The sensor is sealed from the fuel
preventing contamination of the contacts, increasing reliability. The fuel level sensors are connected to the external electrical
connector on the flange via the connector on the underside of the fuel pump module flange.
The sensor comprises a series of 51 film resistors mounted in an arc on a ceramic surface. The resistors are wired in series
with individual contacts. A soft magnetic foil with 51 flexible contacts is mounted a small distance above the film resistors. A
magnet, located below the ceramic surface, is attached to the sender unit float arm. As the float arm moves, the magnet
follows the same arc as the film resistors. The magnet pulls the flexible contacts onto the opposite film resistor contacts
forming an electrical circuit.
Page 1591 of 3039
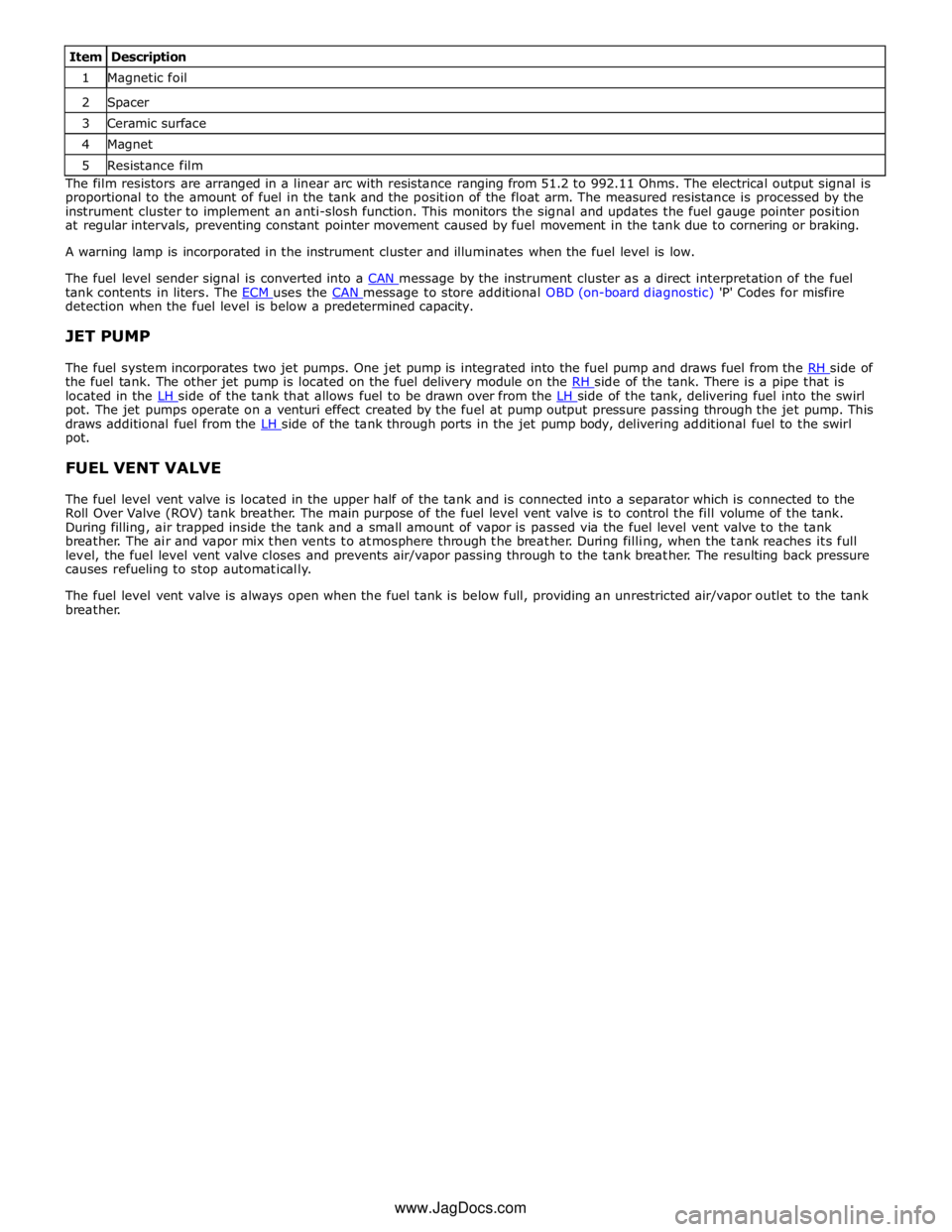
1 Magnetic foil 2 Spacer 3 Ceramic surface 4 Magnet 5 Resistance film The film resistors are arranged in a linear arc with resistance ranging from 51.2 to 992.11 Ohms. The electrical output signal is
proportional to the amount of fuel in the tank and the position of the float arm. The measured resistance is processed by the
instrument cluster to implement an anti-slosh function. This monitors the signal and updates the fuel gauge pointer position
at regular intervals, preventing constant pointer movement caused by fuel movement in the tank due to cornering or braking.
A warning lamp is incorporated in the instrument cluster and illuminates when the fuel level is low.
The fuel level sender signal is converted into a CAN message by the instrument cluster as a direct interpretation of the fuel tank contents in liters. The ECM uses the CAN message to store additional OBD (on-board diagnostic) 'P' Codes for misfire detection when the fuel level is below a predetermined capacity.
JET PUMP
The fuel system incorporates two jet pumps. One jet pump is integrated into the fuel pump and draws fuel from the RH side of the fuel tank. The other jet pump is located on the fuel delivery module on the RH side of the tank. There is a pipe that is located in the LH side of the tank that allows fuel to be drawn over from the LH side of the tank, delivering fuel into the swirl pot. The jet pumps operate on a venturi effect created by the fuel at pump output pressure passing through the jet pump. This
draws additional fuel from the LH side of the tank through ports in the jet pump body, delivering additional fuel to the swirl pot.
FUEL VENT VALVE
The fuel level vent valve is located in the upper half of the tank and is connected into a separator which is connected to the
Roll Over Valve (ROV) tank breather. The main purpose of the fuel level vent valve is to control the fill volume of the tank.
During filling, air trapped inside the tank and a small amount of vapor is passed via the fuel level vent valve to the tank
breather. The air and vapor mix then vents to atmosphere through the breather. During filling, when the tank reaches its full
level, the fuel level vent valve closes and prevents air/vapor passing through to the tank breather. The resulting back pressure
causes refueling to stop automatically.
The fuel level vent valve is always open when the fuel tank is below full, providing an unrestricted air/vapor outlet to the tank
breather.
www.JagDocs.com
Page 1593 of 3039
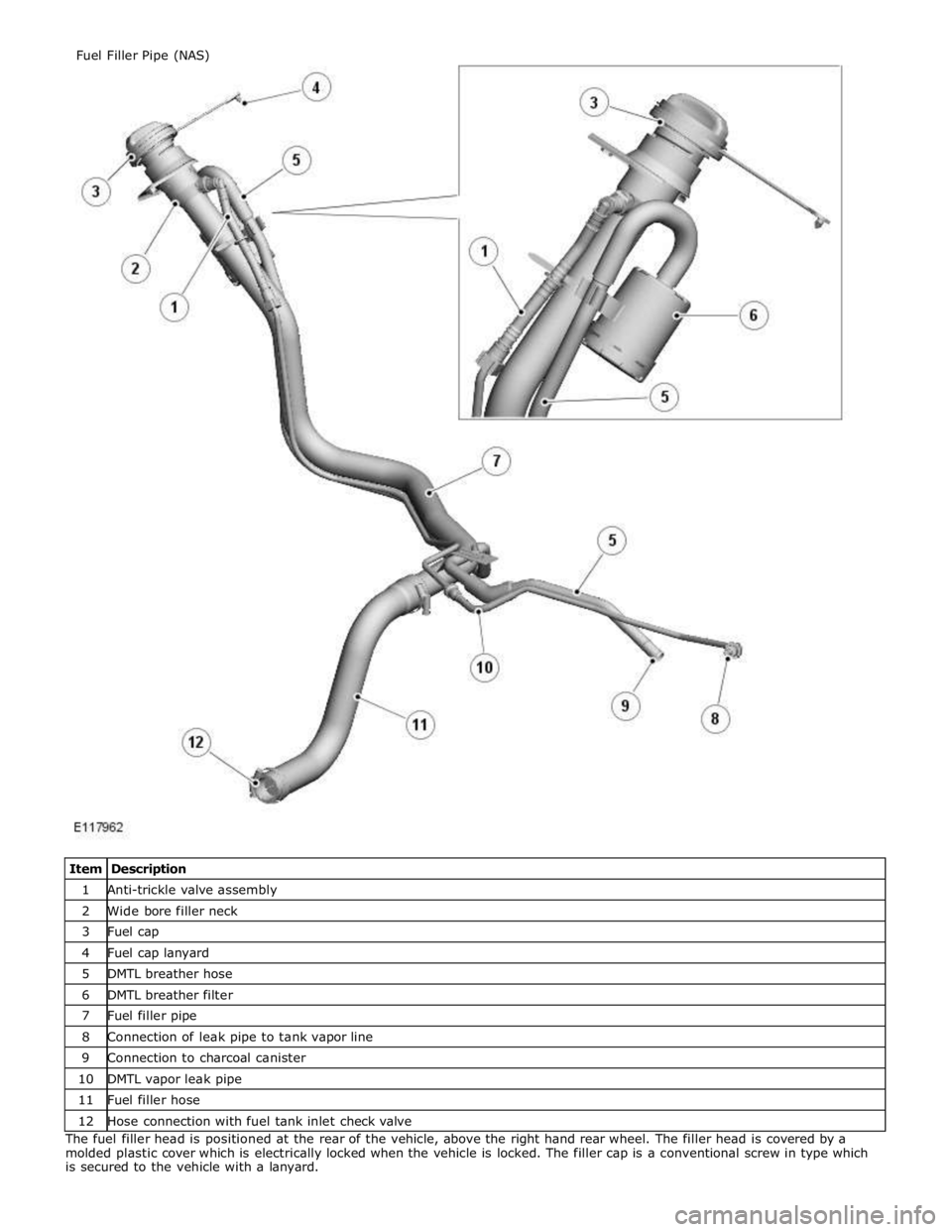
1 Anti-trickle valve assembly 2 Wide bore filler neck 3 Fuel cap 4 Fuel cap lanyard 5 DMTL breather hose 6 DMTL breather filter 7 Fuel filler pipe 8 Connection of leak pipe to tank vapor line 9 Connection to charcoal canister 10 DMTL vapor leak pipe 11 Fuel filler hose 12 Hose connection with fuel tank inlet check valve The fuel filler head is positioned at the rear of the vehicle, above the right hand rear wheel. The filler head is covered by a
molded plastic cover which is electrically locked when the vehicle is locked. The filler cap is a conventional screw in type which
is secured to the vehicle with a lanyard. Fuel Filler Pipe (NAS)
Page 1596 of 3039
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Low/contaminated fuel
Fuel supply/return line(s)
Fuel tank and filler pipe
Fuel leak(s)
Fuel filler cap
Fuel filter
Push connect fittings
Fuel pump
Fuses
Links
Relays
Fuel Pump Driver Module (FPDM)
Fuel pump module
Sensor(s)
Engine control module (ECM)
Rear Junction Box (RJB)
Restraints Control Module (RCM)
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step
4. If the cause is not visually evident, verify the symptom and refer to the Symptom Chart, alternatively check for
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and proceed to the DTC Index
Symptom Chart
Symptom Possible Causes Action Engine cranks, but does not
fire
Engine breather system
disconnected/restricted
Ignition system
Fuel system
Electronic engine control
Ensure the engine breather system is free from
restriction and is correctly installed
Check for ignition system, fuel system and electronic
engine control DTCs and refer to the relevant DTC
Index Engine cranks and fires, but
will not start
Evaporative emissions purge
valve
Fuel pump
Spark plugs
HT short to ground (tracking)
check rubber boots for
cracks/damage
Ignition system
Check for evaporative emissions, fuel system and
ignition system related DTCs and refer to the
relevant DTC Index Difficult cold start
Engine coolant level/anti-
freeze content
Battery
Electronic engine controls
Fuel pump
Purge valve
Check the engine coolant level and condition
Ensure the battery is in a fully charged and
serviceable condition
Check for electronic engine controls, engine
emissions, fuel system and evaporative emissions
system related DTCs and refer to the relevant DTC
Index Difficult hot start
Injector leak
Electronic engine control
Purge valve
Fuel pump
Ignition system
Check for injector leak, install new injector as
required
Check for electronic engine controls, evaporative
emissions, fuel system, ignition system and engine
emission system related DTCs and refer to the
relevant DTC Index Difficult to start after hot
soak (vehicle standing,
engine off, after engine has
reached operating
temperature)
Injector leak
Electronic engine control
Purge valve
Fuel pump
Ignition system
Check for injector leak, install new injector as
required
Check for electronic engine controls, evaporative
emissions, fuel system, ignition system and engine
emission system related DTCs and refer to the
relevant DTC Index Engine stalls soon after start
Breather system
disconnected/restricted
ECM relay
Electronic engine control
Ignition system
Air intake system restricted
Air leakage
Fuel lines
Ensure the engine breather system is free from
restriction and is correctly installed
Check for electronic engine control, ignition system
and fuel system related DTCs and refer to the
relevant DTC Index
Check for blockage in air filter element and air
intake system
Check for air leakage in air intake system Engine hesitates/poor
acceleration
Fuel pressure, fuel pump,
fuel lines
Injector leak
Air leakage
Check for fuel system related DTCs and refer to the
relevant DTC Index
Check for injector leak, install new injector as
required www.JagDocs.com