2010 JAGUAR XFR brake
[x] Cancel search: brakePage 720 of 3039

Symptom Possible Causes Action
Wear in steering gear tie-rod end ball joints
Check and install new tie-rod
ends as required, refer to the
new module/component
installation note at the top of
the Symptom Charts
NOTE: Inner ball joint wear is rare. The steering
gear installed to all Jaguar vehicles has a spring
loaded pinion to ensure the correct level of
engagement between the rack and pinion. This play
is optimized with the steering gear in the central
position and should not be confused with inner ball
joint wear. Check for vertical motion in the inner ball
joint with the steering gear in the central position.
Wear in steering gear inner ball joints
Check and install new steering
gear as required, refer to the
new module/component
installation note at the top of
the Symptom Charts
Wear in suspension ball joints/bushings
Check and install new
components as required
Veer under braking
Steering gear not correctly adjusted
CAUTION: DO NOT attempt to
adjust the steering gear yoke. Failure to
follow this instruction will invalidate the
steering gear warranty
Check and install a new steering
gear as required, refer to the
new module/component
installation note at the top of
the Symptom Charts
Contamination of brake pads and discs
Check and rectify the source of
the contamination and install
new brake pads and discs as
required, refer to the new
module/component installation
note at the top of the Symptom
Charts
Seized front brake caliper slide pins or piston
Damaged brake discs
Check and rectify sticking slide
pins and install new calipers as
required, refer to the new
module/component installation
note at the top of the Symptom
Charts
Check and install new brake discs
as required, refer to the new
module/component installation
note at the top of the Symptom
Charts
Vehicle pulls to one side
when driving on a level
surface
Uneven tire wear
Incorrect tire pressure
For information on diagnosis of
uneven tire wear.
REFER to: Suspension System (204-00 Suspension System -
General Information, Diagnosis
and Testing).
Check and adjust tire pressures
as required.
REFER to: Specifications (204-04 Wheels and Tires,
Specifications).
Incorrect geometry settings
NOTE: Dealerships must keep a
copy of the BEFORE and AFTER
geometry figures with job card for future
reference
Check and adjust geometry as
required. REFER to: (204-00
Page 721 of 3039

Symptom Possible Causes Action Suspension System - General
Information)
Camber and Caster Adjustment (General Procedures),
Front Toe Adjustment (General Procedures),
Rear Toe Adjustment (General Procedures).
Vehicle is unevenly loaded or overloaded
Notify the customer of incorrect
vehicle loading
Steering gear is not correctly adjusted
CAUTION: DO NOT attempt to
adjust the steering gear yoke. Failure to
follow this instruction will invalidate the
steering gear warranty
Check and install a new steering
gear as required, refer to the
new module/component
installation note at the top of
the Symptom Charts
Loose, damaged or worn front suspension
components
Check/tighten and install new
front suspension components as
required.
REFER to: Specifications (204-00 Suspension System - General
Information, Specifications).
Loose, damaged or worn rear suspension
components
Check/tighten and install new
rear suspension components as
required.
REFER to: Specifications (204-00 Suspension System - General
Information, Specifications).
Incorrect brake operation
For information on diagnosis of
the brake system.
REFER to: Brake System (206-00 Brake System - General
Information, Diagnosis and
Testing).
Incorrect underbody alignment
Set underbody alignment
referring to the Removal and
Installation procedures in section
502-00 of the workshop manual
for instruction
Vehicle wanders from
side to side when driven
straight ahead and the
steering wheel is held in
a firm position
Incorrect tire pressure or tire size
Check and adjust the tire
pressures as required.
REFER to: Specifications (204-04 Wheels and Tires,
Specifications).
Check and install a new tire as
required
Vehicle is unevenly or excessively loaded
Notify the customer of incorrect
vehicle loading
Incorrect toe adjustment
Check and adjust as required.
REFER to: (204-00 Suspension
System - General Information)
Camber and Caster Adjustment (General Procedures),
Front Toe Adjustment (General Procedures),
Rear Toe Adjustment (General Procedures).
Page 782 of 3039
16 Ball (12 off) 17 Distance keeper 18 Crash tube The column comprises a cast magnesium mounting bracket which provides the attachment to the cross-beam. Attached to the
mounting bracket is a rake lever which is attached to the mounting bracket at the lower end with two pivot bearings. The
bearings allow the rake lever to rotate upwards or downward to adjust the column rake.
The rake lever also provides for the attachment of the rake housing which can slide within the lever to provide the reach
adjustment. Within the rake housing is the axial housing which is supported on each side with 6 ball bearings which allow the
rake housing to move forward or backwards. The bearings on each side are arranged in groups of 3 bearings and are separated
by a distance keeper which allows the housing to supported on bearings along its length. Within the axial housing is a tube
which is supported at the upper end of the column on the upper bearing. The tube has a central splined hole which provides for
the fitment of the splined shaft. The splined shaft can slide within the tube on the splines when the column reach is adjusted
or the column collapses in a crash condition. The splined shaft also passes rotary motion from the steering wheel through the
length of the column to the outer clamping yoke which is supported on the lower bearing.
The electric steering column lock is attached to the top of the rake lever. A lock bolt within the steering column lock engages in
one of 8 slots in the locking sleeve located at the lower end of the column preventing rotation of the steering wheel. The
locking sleeve is retained by a tolerance ring which in turn is located on the outer diameter of the tube yoke. The tolerance
ring allows a specified amount of torque to be applied to the splined shaft before it slips, preventing damage to the column
lock due to excessive force being applied to the steering wheel when the lock is engaged. The tolerance ring is designed to
slip on the splined shaft when the applied torque exceeds the fitted slip load of 200 Nm minimum. Repeated rotation of the
lock collar will reduce its slipping torque to 100 Nm minimum. The lock is controlled by the CJB.
A steering angle sensor is located at the upper end of the steering column and is attached to the crash adaptor. The sensor
measures steering rotation via a toothed wheel located on the splined tube at the upper end of the column. The sensor
receives a power supply from the CJB and supplies 2 signals (A and B) relating to the steering rotation to the ABS (anti-lock brake system) module. The module transmits this data on the high speed CAN bus for use by other vehicle systems. Refer to: Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist (206-09 Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist, Description and Operation).
The steering column is adjustable electrically, for reach and rake. The adjustment mechanism comprises an electric adjustment
motor, a lead screw, a rake solenoid, a reach solenoid, a reach clutch and a rake clutch. The column adjustment is controlled
manually using a joystick switch located on the LH (left-hand) side of the column lower cowl. The joystick can be moved
forward and backward to adjust the column reach in and out and moved up and down to adjust the rake. The switch selection
energizes the adjustment motor in the applicable direction and also engages the applicable solenoid and clutch.
When the joystick switch is rotated to the 'auto' position, the steering column will adjust to the uppermost rake position when
the ignition is switched off. It will re-adjust to the position corresponding to the memory position for the remote handset when
the ignition is switched on.
The memory function of the electric column is linked to and controlled by the driver's seat module. The module provides for the
storage of three separate memory positions which are stored against 3 individual remote handsets.
Refer to: Seats (501-10 Seating, Description and Operation).
The steering wheel locates on a splined shaft in the upper column assembly and is secured with a bolt. The steering wheel
houses the driver's airbag and switches for the audio system, gear change and speed control. A clockspring is used to connect
the steering wheel electrical components to the vehicle harness.
Two plastic shrouds are fitted to the upper column assembly. The lower shroud is fitted with an energy absorbing foam pad to
minimize leg injury in the event of an accident.
www.JagDocs.com
Page 813 of 3039

Component Tests
Engine Oil Leaks
NOTE: Before installing new gaskets or oil seals, make sure that the fault is clearly established.
If the oil leak cannot be identified clearly by a visual inspection, carry out an Ultraviolet test:
Fluorescent Oil Additive Method
1. Clean the engine with a suitable cleaning fluid (brake cleaner).
2. Drain the engine oil and refill with recommended oil, premixed with Diesel Engine Oil Dye or equivalent. Use a minimum
14.8 ml (0.5 ounce) to a maximum 29.6 ml (1 ounce) of fluorescent additive to all engines. If oil is not premixed,
fluorescent additive must first be added to the crankcase.
3. Run engine for 15 minutes. Stop the engine and inspect all seal and gasket areas for leaks using a 12 Volt Master UV
Diagnostic Inspection Kit or equivalent. A clear bright yellow or orange area will identify leak. For extremely small
leaks, several hours may be required for the leak to appear.
4. As necessary, pressurize the main oil gallery system to locate leaks due to incorrectly sealed, loose or cocked plugs. If
the flywheel bolts leak oil, look for sealer on the threads.
5. Repair all leaks as necessary.
Compression Test General Remarks
NOTES:
Removing fuses and disconnecting electrical components may cause the Engine Control Module (ECM) to log Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTCs). After the measurements have been carried out, DTCs should be cleared from memory by connecting to
the Manufacturer Approved Diagnostic System.
Only check the compression pressure with the valves set to the prescribed clearance (if this can be adjusted).
The compression pressure should be checked with the engine at normal operating temperature.
Check the Compression Pressure
WARNING: Move gear selector lever to 'P' position. Failure to follow this instruction may result in personal injury.
1. Remove the fuel pump relay.
2. Start the engine - the engine will start, run for a few seconds then stall.
3. Remove the spark plugs.
4. Install the compression tester.
5. Install an auxiliary starter switch in the starting circuit. With the ignition switch OFF, using the auxiliary starter switch,
crank the engine a minimum of five compression strokes and record the highest reading. Note the approximate number
of compression strokes required to obtain the highest reading.
6. Repeat the test on each cylinder, cranking the engine approximately the same number of compression strokes.
7. Install the removed components in reverse order, observing the specified tightening torques.
8. Clear all DTCs from the ECM.
Interpretation of the Results
NOTE: Due to the possibility of loose carbon that has become trapped between the valve face and seat effecting the
pressure readings, when carrying out a compression test and cylinders are found to have low pressures, install the spark plugs,
road test the vehicle and re-test the suspect cylinders. If the correct pressures are restored, no further action is required.
The indicated compression pressures are considered within specification if the lowest reading cylinder is within 75% of the
highest reading.
If the cylinder pressures are found to be low, carry out a leakdown test to determine the location of the fault (if any leakback
can be heard through the engine breather system suspect the piston rings, if any leakback can be heard through the inlet
system suspect the inlet valve or seat, if any leakback can be heard through the exhaust manifold suspect the exhaust valve
or seat. If the measurements for two cylinders next to each other are both too low then it is very likely that the cylinder head
gasket between them is burnt through. This can also be recognized by traces of engine oil in the coolant and/or coolant in the
Page 816 of 3039

9. WEAK VALVE SPRINGS: When the needle oscillation becomes more violent as engine RPM is increased, weak valve
springs are indicated. The reading at idle could be relatively steady.
10. LATE VALVE TIMING: A steady but low reading could be caused by late valve timing.
11.
IGNITION TIMING RETARDED: Retarded ignition timing will produce a steady but somewhat low reading.
12.
INSUFFICIENT SPARK PLUG GAP: When spark plugs are gapped too close, a regular, small pulsation of the needle can
occur.
13. INTAKE LEAK: A low, steady reading can be caused by an intake manifold or throttle body gasket leak.
14.
BLOWN HEAD GASKET: A regular drop of fair magnitude can be caused by a blown head gasket or warped cylinder head
to cylinder block surface.
15.
RESTRICTED EXHAUST SYSTEM: When the engine is first started and is idled, the reading may be normal, but as the
engine RPM is increased, the back pressure caused by a clogged muffler, kinked tail pipe or other concerns will cause
the needle to slowly drop to 0 kPa (0 in-Hg). The needle then may slowly rise. Excessive exhaust clogging will cause
the needle to drop to a low point even if the engine is only idling.
When vacuum leaks are indicated, search out and correct the cause. Excess air leaking into the system will upset the fuel
mixture and cause concerns such as rough idle, missing on acceleration or burned valves. If the leak exists in an accessory
such as the power brake booster, the unit will not function correctly. Always repair vacuum leaks.
Engine Oil Pressure Check
NOTE: Prior to checking the engine oil pressure, a road test of 6 miles (10 kilometres), must be carried out. Do not
attempt to attain engine normal operating temperature by allowing the engine to idle.
1. Disconnect the battery ground cable. Refer to section 414-00 - Charging System - General Information of the workshop
manual
2. WARNINGS:
The spilling of hot engine oil is unavoidable during this procedure, care must be taken to prevent scalding.
Wear protective gloves.
Remove the engine oil filter element
REFER to: Oil Filter Element (303-01C Engine - V8 5.0L Petrol, Removal and Installation).
NOTE: Ensure the oil filter element is not contaminated during this procedure
3. Install the oil filter element into special tool (Oil filter adapter number 303-1451)
4. Install the special tool (Oil filter adapter number 303-1451) to the engine. Torque: 25 Nm
5. Install the special tool (Oil pressure testing gauge, 303-871) and tighten the union
6. Connect the battery ground cable
7. Refer to owner hand book, check and top-up the engine oil if required
8. Start and run the engine
9. Note the oil pressure readings with the engine running at idle and 3500 RPM
10.
Turn off the engine
11.
Disconnect the battery ground cable
12. Remove the special tools
1. Clean the components
13.
Install the engine oil filter element
REFER to: Oil Filter Element (303-01C Engine - V8 5.0L Petrol, Removal and Installation).
NOTE: Ensure the oil filter element is not contaminated during this procedure
14.
Connect the battery ground cable
15. Refer to owner hand book, check and top-up the engine oil if required
www.JagDocs.com
Page 1077 of 3039
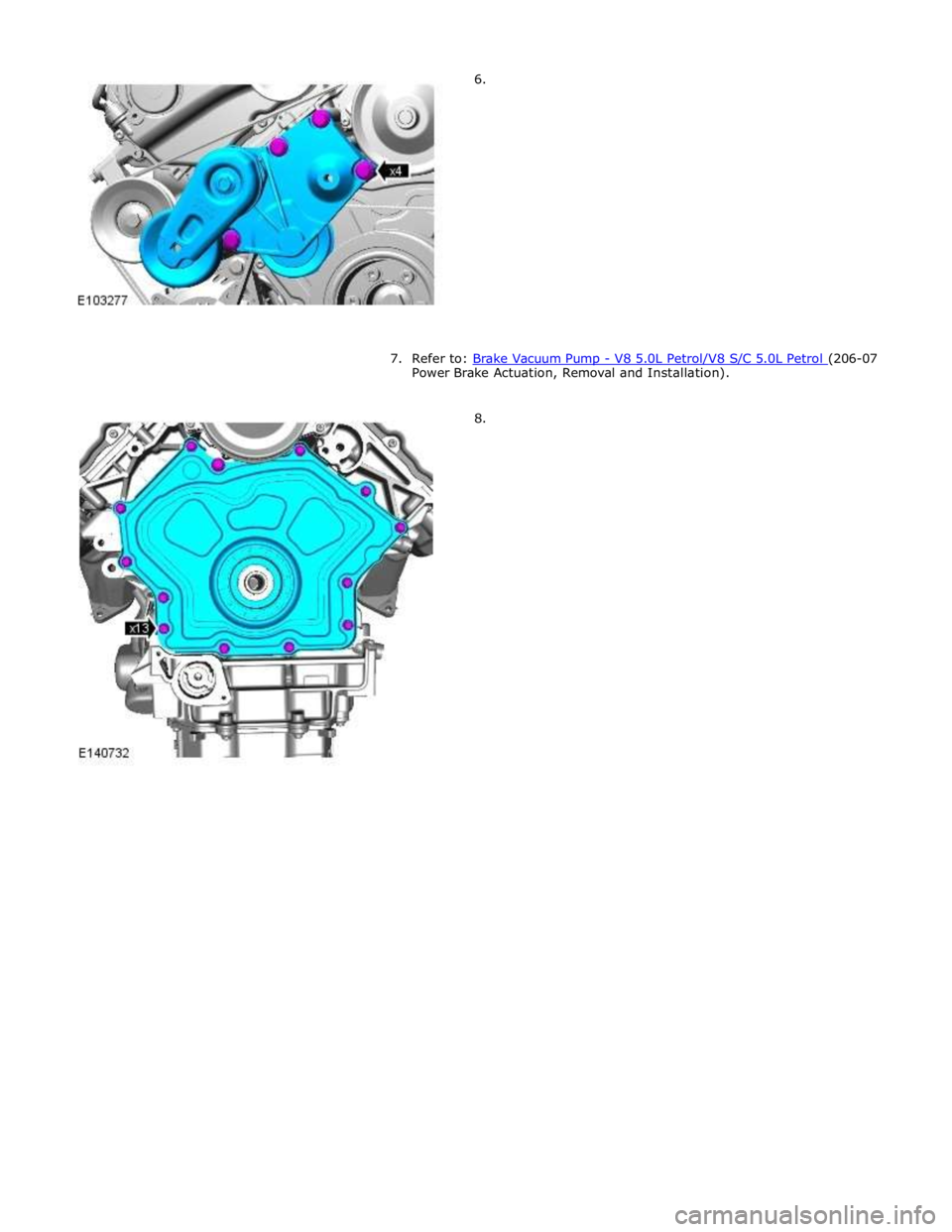
Power Brake Actuation, Removal and Installation).
8.
Page 1079 of 3039
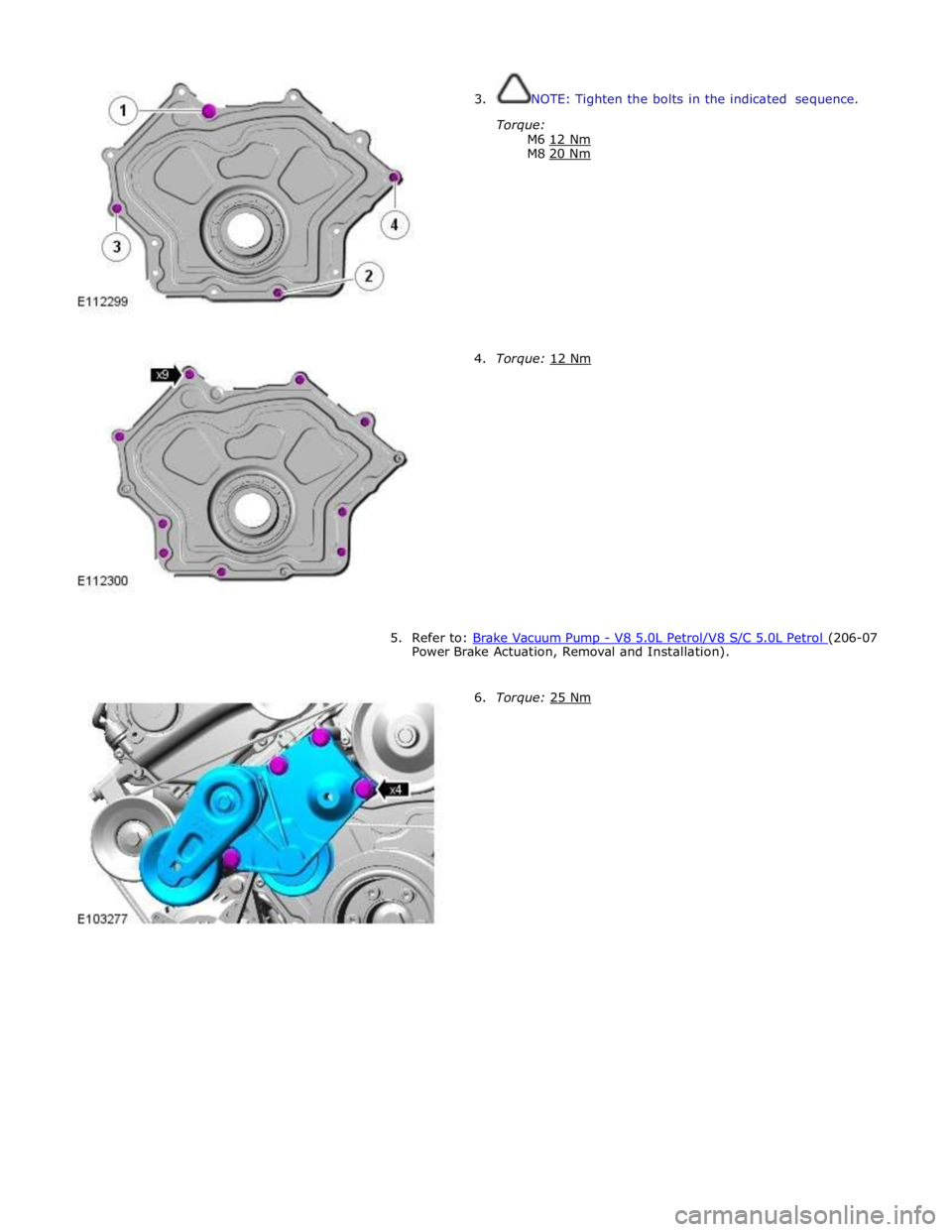
3. NOTE: Tighten the bolts in the indicated sequence.
Torque:
M6 12 Nm M8 20 Nm
4. Torque: 12 Nm
5. Refer to: Brake Vacuum Pump - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol (206-07 Power Brake Actuation, Removal and Installation).
6. Torque: 25 Nm
Page 1189 of 3039

Published: 11-May-2011
Fuel Charging and Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Fuel Injection Component Cleaning
General Procedures
General Equipment
WARNINGS: Cleaning
Do not carry out any repairs to the fuel system with the engine running. Failure to follow this instruction may result in
personal injury.
Do not smoke or carry lighted tobacco or open flame of any type when working on or near any fuel related components.
Highly flammable vapors are always present and may ignite. Failure to follow these instructions may result in personal injury.
If fuel contacts the eyes, flush the eyes with cold water or eyewash solution and seek immediate medical attention.
Place the vehicle in a well ventilated, quarantined area and arrange ' No Smoking/Petrol Fumes' signs about the vehicle.
Wash hands thoroughly after fuel handling, as prolonged contact may cause irritation. Should irritation develop, seek
medical attention.
Do not carry or operate cellular phones when working on or near any fuel related components. Highly flammable vapors
are always present and may ignite. Failure to follow these instructions may result in personal injury.
CAUTIONS:
Before using the cleaning fluid, protect all electrical components and connectors with lint-free non-flocking material.
Make sure that all parts removed from the vehicle are placed on the lint-free non-flocking material.
Make sure that any protective clothing worn is clean and made from lint-free non-flocking material.
Make sure that clean non-plated tools are used. Clean tools using a new brush that will not lose its bristles, prior to
starting work on the vehicle.
Use a steel topped workbench and cover it with clean, lint-free non-flocking material.
Make sure the workshop area in which the vehicle is being worked on is as clean and as dust free as possible. Foreign
matter from work on clutches, brakes or from machining or welding operations can contaminate the fuel system and may result
in later malfunction.
1. Using a new brush that will not lose its bristles, brush the components
being removed and the surrounding area.
2. Using a pneumatic vacuum gun, remove all traces of foreign material.
General Equipment: Pneumatic vacuum gun Pneumatic vacuum gun