Page 1377 of 3039
Published: 11-May-2011
Electronic Engine Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Camshaft Position (CMP)
Sensor RH
Removal and Installation
Removal
NOTE: Removal steps in this procedure may contain installation details.
1. Disconnect the battery ground cable.
Refer to: Specifications (414-00 Charging System - General Information,
Specifications).
2. WARNING: Make sure to support the vehicle with axle stands.
Raise and support the vehicle.
3. Refer to: Thermostat Housing - 5.0L SC V8 - AJ133 (303-03 Engine
Cooling - 5.0L NA V8 - AJ133/5.0L SC V8 - AJ133, Removal and
Installation).
Installation
4. NOTE: Some variation in the illustrations may occur,
but the essential information is always correct.
Torque: 10 Nm
1. CAUTIONS:
Make sure that the mating faces are clean and free of foreign
material.
Make sure that the sensor tip is clean and free of foreign material.
NOTE: Lubricate the O-ring seal with clean engine oil.
To install, reverse the removal procedure.
Page 1389 of 3039
Published: 11-May-2011
Electronic Engine Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Engine Oil Level Sensor
Removal and Installation
Removal
NOTE: Removal steps in this procedure may contain installation details.
1. WARNING: Do not work on or under a vehicle supported only by a jack.
Always support the vehicle on safety stands.
Raise and support the vehicle.
2. Refer to: Air Deflector (501-02 Front End Body Panels, Removal and Installation).
3. Refer to: Engine Oil Draining and Filling (303-01D Engine - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, General Procedures).
Installation
4. CAUTION: Be prepared to collect escaping fluids.
Torque: 11 Nm
1. CAUTION: A new O-ring seal is to be installed.
To install, reverse the removal procedure.
Page 1404 of 3039
Published: 11-May-2011
Electronic Engine Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Variable Valve Timing (VVT)
Oil Control Solenoid LH
Removal and Installation
Removal
NOTE: Removal steps in this procedure may contain installation details.
1. Disconnect the battery ground cable.
Refer to: Specifications (414-00, Specifications).
2. WARNING: Make sure to support the vehicle with axle stands.
Raise and support the vehicle.
3. Refer to: Thermostat Housing - Vehicles With: Supercharger (303-03,
Removal and Installation).
4. NOTE: Some variation in the illustrations may occur, but
the essential information is always correct.
Torque: 10 Nm
5. CAUTION: Evenly and progressively, remove the VVT
units from each side.
NOTE: Some variation in the illustrations may occur,
but the essential information is always correct.
Page 1405 of 3039
Installation
1. CAUTION: Make sure that the mating faces are clean and free of
foreign material.
NOTE: Lubricate the O-ring seal with clean engine oil.
To install, reverse the removal procedure.
2. NOTE: For NAS vehicles only.
If required, carry out a short drive cycle.
Refer to: Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Short Drive Cycle Self-Test (303-14D Electronic Engine Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, General
Procedures).
Page 1406 of 3039
Published: 11-May-2011
Electronic Engine Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Variable Valve Timing (VVT)
Oil Control Solenoid RH
Removal and Installation
Removal
NOTE: Removal steps in this procedure may contain installation details.
1. Disconnect the battery ground cable.
Refer to: Specifications (414-00, Specifications).
2. WARNING: Make sure to support the vehicle with axle stands.
Raise and support the vehicle.
3. Refer to: Thermostat Housing - Vehicles With: Supercharger (303-03,
Removal and Installation).
4. NOTE: Some variation in the illustrations may occur, but
the essential information is always correct.
5. NOTE: Some variation in the illustrations may occur,
but the essential information is always correct.
Torque: 10 Nm www.JagDocs.com
Page 1407 of 3039
Installation 6. CAUTION: Evenly and progressively, remove the VVT
units from each side.
NOTE: Some variation in the illustrations may occur,
but the essential information is always correct.
1. CAUTION: Make sure that the mating faces are clean and free of
foreign material.
NOTE: Lubricate the O-ring seal with clean engine oil.
To install, reverse the removal procedure.
2. NOTE: For NAS vehicles only.
If required, carry out a short drive cycle.
Refer to: Powertrain Control Module (PCM) Short Drive Cycle Self-Test (303-14D Electronic Engine Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, General
Procedures).
Page 1429 of 3039
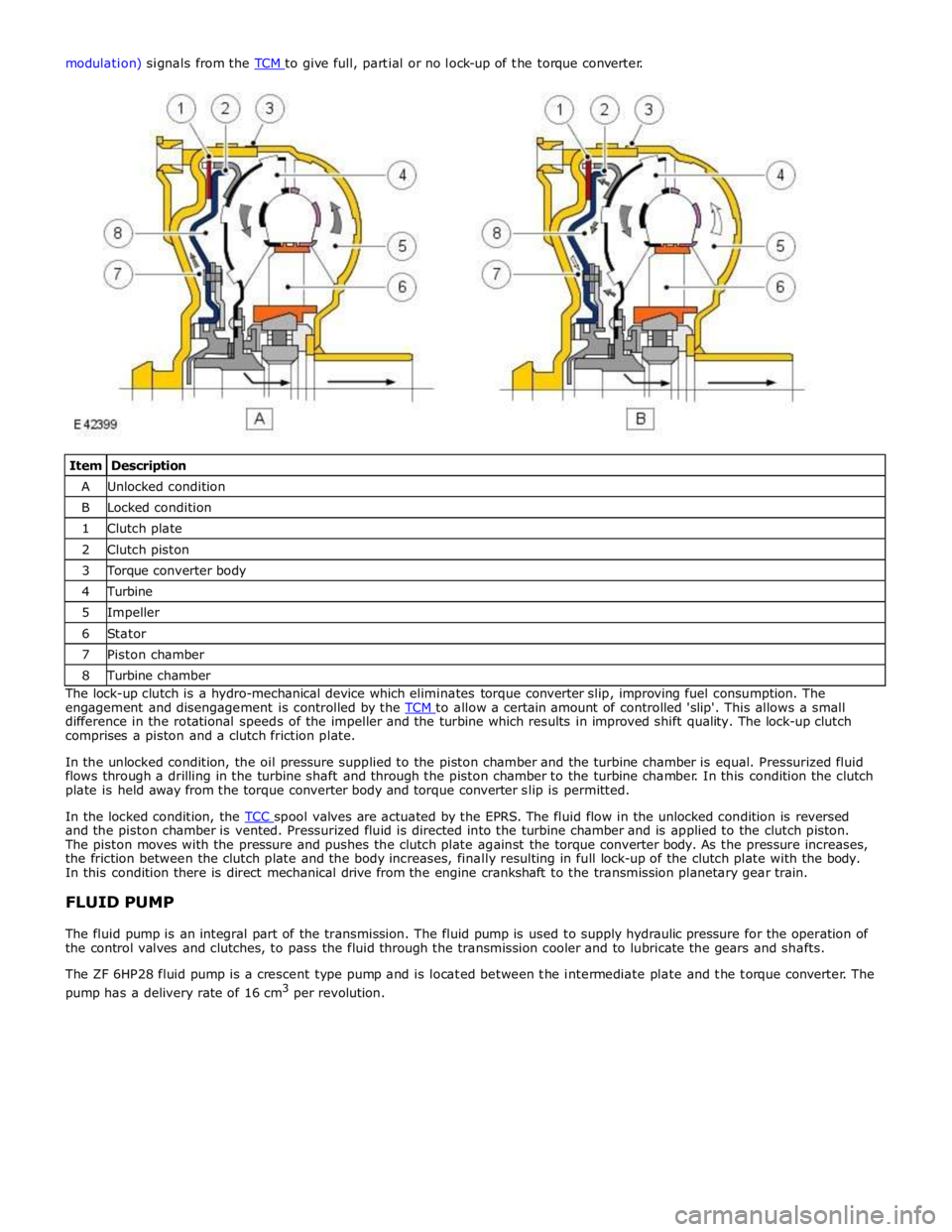
Item Description A Unlocked condition B Locked condition 1 Clutch plate 2 Clutch piston 3 Torque converter body 4 Turbine 5 Impeller 6 Stator 7 Piston chamber 8 Turbine chamber The lock-up clutch is a hydro-mechanical device which eliminates torque converter slip, improving fuel consumption. The
engagement and disengagement is controlled by the TCM to allow a certain amount of controlled 'slip'. This allows a small difference in the rotational speeds of the impeller and the turbine which results in improved shift quality. The lock-up clutch
comprises a piston and a clutch friction plate.
In the unlocked condition, the oil pressure supplied to the piston chamber and the turbine chamber is equal. Pressurized fluid
flows through a drilling in the turbine shaft and through the piston chamber to the turbine chamber. In this condition the clutch
plate is held away from the torque converter body and torque converter slip is permitted.
In the locked condition, the TCC spool valves are actuated by the EPRS. The fluid flow in the unlocked condition is reversed and the piston chamber is vented. Pressurized fluid is directed into the turbine chamber and is applied to the clutch piston.
The piston moves with the pressure and pushes the clutch plate against the torque converter body. As the pressure increases,
the friction between the clutch plate and the body increases, finally resulting in full lock-up of the clutch plate with the body.
In this condition there is direct mechanical drive from the engine crankshaft to the transmission planetary gear train.
FLUID PUMP
The fluid pump is an integral part of the transmission. The fluid pump is used to supply hydraulic pressure for the operation of
the control valves and clutches, to pass the fluid through the transmission cooler and to lubricate the gears and shafts.
The ZF 6HP28 fluid pump is a crescent type pump and is located between the intermediate plate and the torque converter. The
pump has a delivery rate of 16 cm3
per revolution.
Page 1430 of 3039
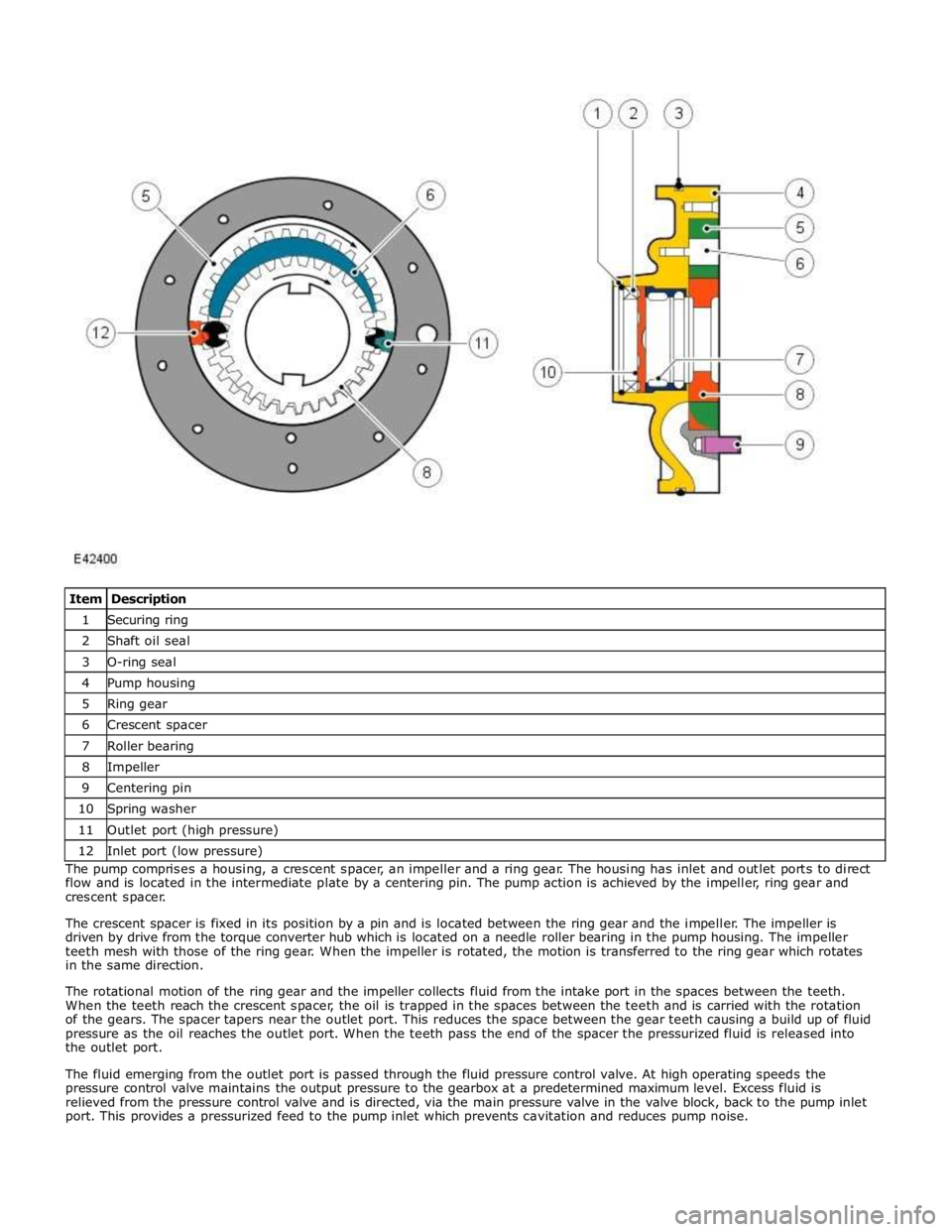
1 Securing ring 2 Shaft oil seal 3 O-ring seal 4 Pump housing 5 Ring gear 6 Crescent spacer 7 Roller bearing 8 Impeller 9 Centering pin 10 Spring washer 11 Outlet port (high pressure) 12 Inlet port (low pressure) The pump comprises a housing, a crescent spacer, an impeller and a ring gear. The housing has inlet and outlet ports to direct
flow and is located in the intermediate plate by a centering pin. The pump action is achieved by the impeller, ring gear and
crescent spacer.
The crescent spacer is fixed in its position by a pin and is located between the ring gear and the impeller. The impeller is
driven by drive from the torque converter hub which is located on a needle roller bearing in the pump housing. The impeller
teeth mesh with those of the ring gear. When the impeller is rotated, the motion is transferred to the ring gear which rotates
in the same direction.
The rotational motion of the ring gear and the impeller collects fluid from the intake port in the spaces between the teeth.
When the teeth reach the crescent spacer, the oil is trapped in the spaces between the teeth and is carried with the rotation
of the gears. The spacer tapers near the outlet port. This reduces the space between the gear teeth causing a build up of fluid
pressure as the oil reaches the outlet port. When the teeth pass the end of the spacer the pressurized fluid is released into
the outlet port.
The fluid emerging from the outlet port is passed through the fluid pressure control valve. At high operating speeds the
pressure control valve maintains the output pressure to the gearbox at a predetermined maximum level. Excess fluid is
relieved from the pressure control valve and is directed, via the main pressure valve in the valve block, back to the pump inlet
port. This provides a pressurized feed to the pump inlet which prevents cavitation and reduces pump noise.