2010 JAGUAR XFR head light
[x] Cancel search: head lightPage 799 of 3039
8 Steering column LH (left-hand) multifunction switch 9 Steering column RH (right-hand) multifunction switch 10 Instrument cluster 11 Speed control switches 12 Audio/telephone switches 13 Clockspring 14 Information and entertainment module 15 Media Oriented System Transport (MOST) ring connection to other vehicle systems 16 Medium speed CAN (controller area network) bus to other vehicle systems
LEFT HAND MULTIFUNCTION SWITCH
Turn Signal Indicators System Operation
The instrument cluster outputs a reference voltage to the turn signal indicator switch. When the switch is in the central off
position, the voltage flows through 3 resistors which are connected in series and back to the instrument cluster which monitors
the signal and determines the turn signal indicators are off. This information is broadcast on the medium speed CAN bus to the CJB.
When the switch is operated in the LH turn signal indicator position, the reference voltage from the instrument cluster is routed via 1 of the resistors. The returned signal voltage is detected by the instrument cluster which outputs a message on
the medium speed CAN bus to the CJB. The CJB activates the applicable turn signal indicators until it receives an off message from the instrument cluster.
When the switch is operated in the RH turn signal indicator position, the reference voltage from the instrument cluster is routed via 2 of the resistors. The returned signal voltage is detected by the instrument cluster which outputs a message on
the medium speed CAN bus to the CJB. The CJB activates the applicable turn signal indicators until it receives an off message from the instrument cluster.
Lighting Control Switch
The instrument cluster outputs 2 reference voltages to the rotary lighting control switch; one feed being supplied to the light
selection function of the switch and the second feed being supplied to the autolamp exit delay function. The switch position is
determined by instrument cluster by the change in returned signal voltage which is routed through up to 4 resistors in series
depending on the selection made.
When the lighting control switch is in the off position, the reference voltage flows through 1 of the resistors. The returned
signal voltage is detected by the instrument cluster which outputs a message on the medium speed CAN bus to the CJB that no lighting selection is made. The reference voltage to the autolamp exit delay switch is routed through 4 resistors which is
detected by the instrument cluster which outputs a message on the medium speed CAN bus to the CJB that autolamp or exit delay has not been selected.
When the lighting control switch is in the sidelamp position, the reference voltage flows through 2 of the resistors. The
returned signal voltage is detected by the instrument cluster which outputs a message on the medium speed CAN bus to the CJB to activate the sidelamps. The reference voltage to the autolamp exit delay switch is routed through 4 resistors which is detected by the instrument cluster which outputs a message on the medium speed CAN bus to the CJB that autolamp or exit delay has not been selected.
When the lighting control switch is in the headlamp position, the reference voltage flows through 3 of the resistors. The
returned signal voltage is detected by the instrument cluster which outputs a message on the medium speed CAN bus to the CJB to activate the headlamps. The reference voltage to the autolamp exit delay switch is routed through 4 resistors which is detected by the instrument cluster which outputs a message on the medium speed CAN bus to the CJB that autolamp or exit delay has not been selected.
When the lighting control switch is in the autolamp position, the reference voltage flows through 4 of the resistors. The
returned signal voltage is detected by the instrument cluster which outputs a message on the medium speed CAN bus to the CJB to activate the autolamp function. The reference voltage to the autolamp exit delay switch is routed through 4 resistors which is detected by the instrument cluster which outputs a message on the medium speed CAN bus to the CJB that autolamp has been selected.
Autolamp Exit Delay
When the lighting control switch is in any of the autolamp exit delay position, the lighting control switch reference voltage
flows through 4 of the resistors. The returned signal voltage is detected by the instrument cluster which outputs a message on
the medium speed CAN bus to the CJB that autolamps has been selected.
Depending on the selected position, the reference voltage to the autolamp exit delay switch is routed through 3, 2 or 1
resistors which is detected by the instrument cluster. The cluster outputs a message on the medium speed CAN bus to the CJB that autolamp exit delay period has been selected at 30, 60 or 120 seconds respectively.
Trip Function Button
The instrument cluster outputs a reference voltage to the trip function button. When the function button is pressed a ground
Page 801 of 3039

battery power supply to be passed via the slip ring assembly in the steering wheel to the heated steering wheel control
module. The steering wheel module supplies power to the steering wheel heater element and also monitors the temperature
via a NTC (negative temperature coefficient) temperature sensor incorporated into the heater element. The control module
varies the power supply to the element to maintain the steering wheel rim at the optimum temperature.
Component Description STEERING COLUMN MULTIFUNCTION SWITCHES
The steering column multifunction switches are situated on the steering column and consists of the wiper switch, the turn
signal indicator/lighting switch and the trip computer switch.
The steering column adjustment switch is located in the steering column lower shroud on the LH side. The switch is a 4 position 'joystick' which controls reach and rake adjustment.
Steering wheel mounted switches on the LH side of the driver's airbag, control the audio and telephone functions. Switches on the RH side of the driver's airbag, control the speed control functions. For additional information, refer to:
Audio System (415-01A Information and Entertainment System, Description and Operation), Speed Control (310-03A, Description and Operation),
Speed Control (310-03B, Description and Operation),
Speed Control (310-03C, Description and Operation).
Two transmission paddle switches are located at the rear of the steering wheel.
Refer to: External Controls (307-05, Description and Operation).
LH Multifunction Switch
Item Description 1 High beam 2 Lighting control rotary switch 3 RH turn signal indicator 4 Headlamp flash 5 LH turn signal indicator 6 Trip computer function button The LH multifunction switch controls the following windshield wiper functions:
Page 858 of 3039
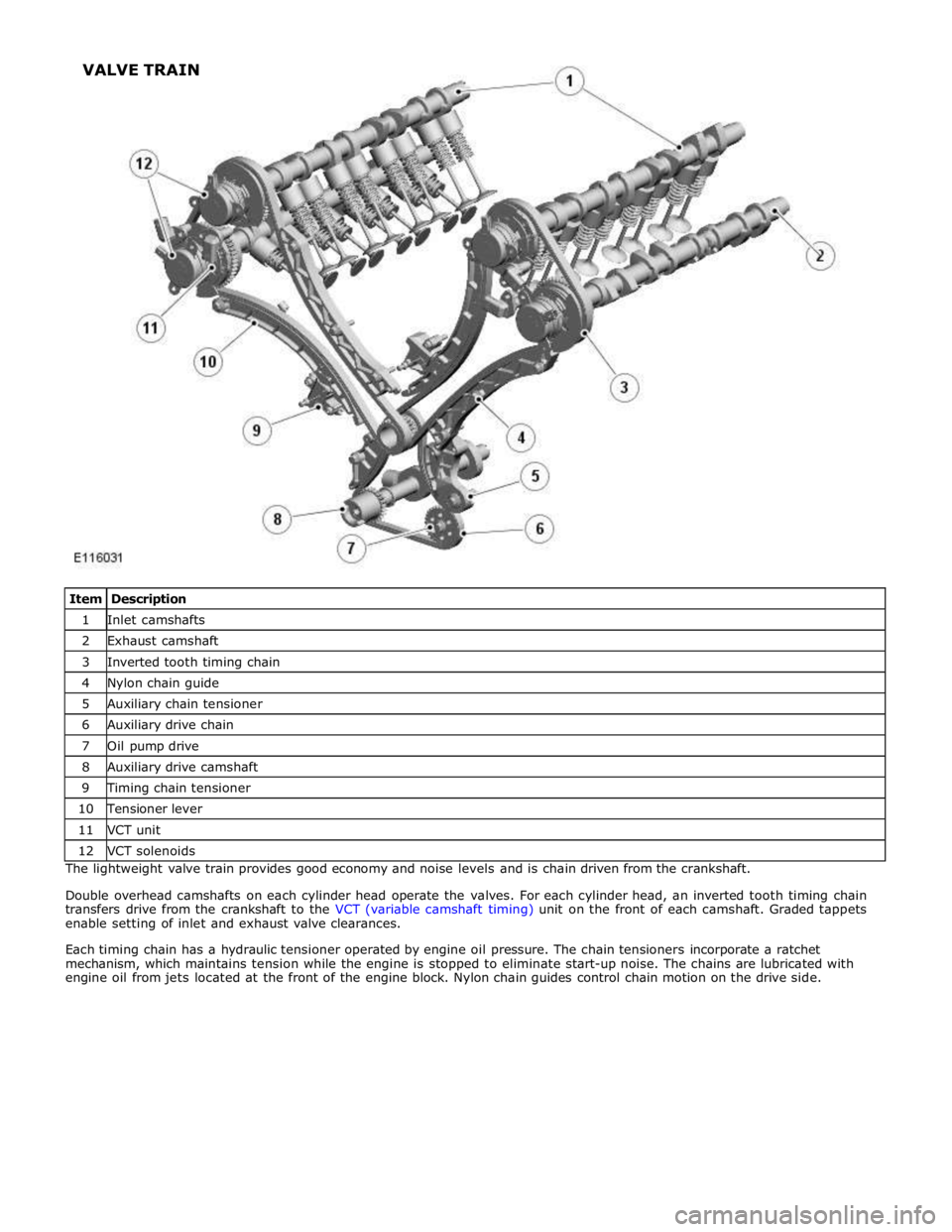
1 Inlet camshafts 2 Exhaust camshaft 3 Inverted tooth timing chain 4 Nylon chain guide 5 Auxiliary chain tensioner 6 Auxiliary drive chain 7 Oil pump drive 8 Auxiliary drive camshaft 9 Timing chain tensioner 10 Tensioner lever 11 VCT unit 12 VCT solenoids The lightweight valve train provides good economy and noise levels and is chain driven from the crankshaft.
Double overhead camshafts on each cylinder head operate the valves. For each cylinder head, an inverted tooth timing chain
transfers drive from the crankshaft to the VCT (variable camshaft timing) unit on the front of each camshaft. Graded tappets
enable setting of inlet and exhaust valve clearances.
Each timing chain has a hydraulic tensioner operated by engine oil pressure. The chain tensioners incorporate a ratchet
mechanism, which maintains tension while the engine is stopped to eliminate start-up noise. The chains are lubricated with
engine oil from jets located at the front of the engine block. Nylon chain guides control chain motion on the drive side. VALVE TRAIN
Page 1086 of 3039
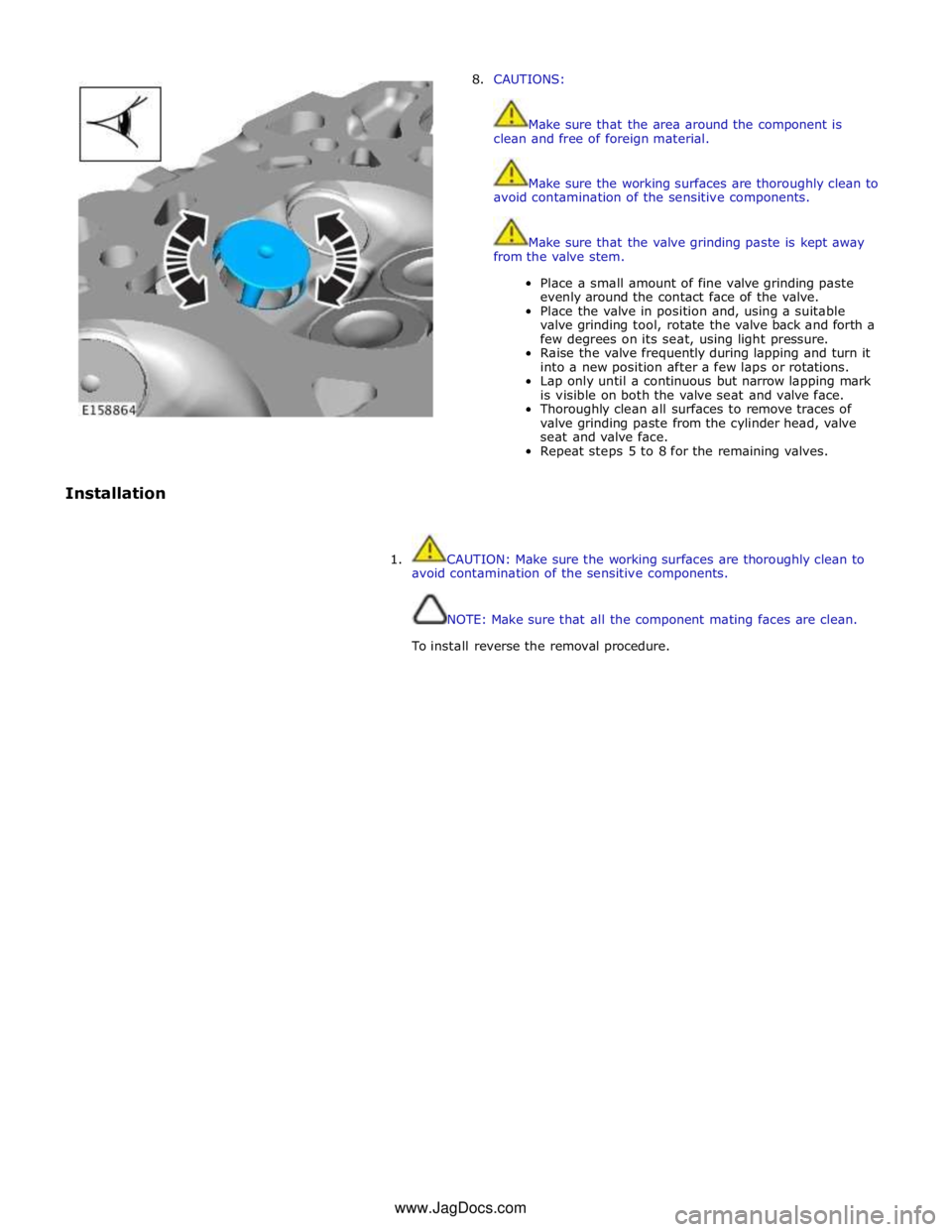
8. CAUTIONS:
Make sure that the area around the component is
clean and free of foreign material.
Make sure the working surfaces are thoroughly clean to
avoid contamination of the sensitive components.
Make sure that the valve grinding paste is kept away
from the valve stem.
Place a small amount of fine valve grinding paste
evenly around the contact face of the valve.
Place the valve in position and, using a suitable
valve grinding tool, rotate the valve back and forth a
few degrees on its seat, using light pressure.
Raise the valve frequently during lapping and turn it
into a new position after a few laps or rotations.
Lap only until a continuous but narrow lapping mark
is visible on both the valve seat and valve face.
Thoroughly clean all surfaces to remove traces of
valve grinding paste from the cylinder head, valve
seat and valve face.
Repeat steps 5 to 8 for the remaining valves.
Installation
1. CAUTION: Make sure the working surfaces are thoroughly clean to
avoid contamination of the sensitive components.
NOTE: Make sure that all the component mating faces are clean.
To install reverse the removal procedure. www.JagDocs.com
Page 1643 of 3039

Automatic braking is limited to approximately 30% of full pressure (0.3G deceleration) and is intended to provide a
smooth, gradual deceleration in follow mode conditions. Harsh braking by the target vehicle or following the target
vehicle down to very low speeds or to a halt will require driver override of the brakes.
While the radar sensor detects moving and stationary targets for assessment of the environment ahead, the system
does not react to or provide any control in situations other than follow mode conditions. Stationary or slow moving
vehicles (below 10 km/h), pedestrians, objects on the road and oncoming vehicles in the same lane are not recognized.
WARNING: The adaptive speed control system is not a collision warning or avoidance system and that, other than the
limited conditions of follow mode, driver intervention will be necessary to control the vehicle speed.
In follow mode, some situations may cause target ambiguities for the detection system. These situations include:
The nearby presence of a third vehicle when driving on a line slightly offset to the target vehicle.
Vehicles edging into the lane ahead which are not detected by the system until they have moved into the radar beam.
On the approach to, or exit from a bend, a target vehicle may be lost or a new target acquired as vehicles ahead change their
angular position with respect to the radar sensor. On a straight road, if the sensing vehicle is in follow mode below its selected
set speed, losing the target vehicle will cause the sensing vehicle to accelerate to this set speed. This acceleration is
undesirable either on, or entering a bend when the target is suddenly lost, and in this situation the system inhibits the
resumption of the set speed.
The speed control system compares vehicle speed data from the ABS system with the relative speed of an external object as
detected by the radar sensor to ascertain whether the object is stationary or not.
NOTE: If tires are fitted which are different in diameter from those specified for the vehicle, the vehicle speed calculated
by the ABS will not be the true road speed. This situation may cause stationary objects to be falsely identified as moving
vehicles and result in automatic deceleration on a clear road.
SPEED CONTROL SWITCHES Component Description
www.JagDocs.com
Page 1651 of 3039

DTC Description Possible Causes Action for further assistance P0501-62
Vehicle Speed Sensor A
Range/Performance - Signal
compare failure
Vehicle speed - range
performance
Check ABS/TCM for related DTCs and refer
to relevant DTC Index P0504-00 Brake Switch A / B Correlation
- No sub type information
The brake pressure reading
does not agree with the
brake light switch value
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with
this DTC using the manufacturer approved
diagnostic system. Refer to the electrical
circuit diagrams and check brake switch
circuits for short, open circuit, high
resistance P0504-01 Brake Switch A / B Correlation
- General electrical failure
Brake switch high fault:
- Brake lights stuck
on
- Gearshift interlock
inoperative
- Speed control
inoperative
Brake switch low fault:
- Brake lights
inoperative
- Gearshift stuck in
Park
- Reduced engine
braking
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with
this DTC using the manufacturer approved
diagnostic system. Refer to the electrical
circuit diagrams and check brake switch
circuits for short, open circuit, high
resistance P0566-00
Cruise Control OFF Signal - No
sub type information
Speed control Cancel
switch 2 stuck closed
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check speed control switch circuits for short,
open circuit. Check for stuck switch. Check
and install a new speed control switch as
required P0567-00
Cruise Control DECREASE
DISTANCE Signal - No sub
type information
Speed control Resume
switch 7 stuck closed
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check speed control switch circuits for short,
open circuit. Check for stuck switch. Check
and install a new speed control switch as
required P0568-00
Cruise Control INCREASE
DISTANCE Signal - No sub
type information
Speed control Accel Set
Plus Switch 6 stuck closed
Check and install a new speed control
switch as required P0569-00
Cruise Control COAST Signal -
No sub type information
Speed control Coast Set
Minus switch 3 stuck
closed
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check speed control switch circuits for short,
open circuit. Check for stuck switch. Check
and install a new speed control switch as
required P056A-00
Cruise Control INCREASE
DISTANCE Signal - No sub
type information
Speed control Headway
Plus switch 4 stuck closed
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check speed control switch circuits for short,
open circuit. Check for stuck switch. Check
and install a new speed control switch as
required P056B-00
Cruise Control DECREASE
DISTANCE Signal - No sub
type information
Speed control Headway
Minus switch 5 stuck
closed
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check speed control switch circuits for short,
open circuit. Check for stuck switch. Check
and install a new speed control switch as
required P0571-62
Brake Switch A Circuit - Signal
compare failure
Plausibility error
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check brake light switch signal circuits for
short, open circuit. Check and install a new
brake light switch as required P0575-01
Cruise Control Input Circuit -
General electrical failure
General electrical failure
Check speed control system for related
DTCs and refer to relevant DTC Index. Carry
out CAN network integrity tests using the
Page 1785 of 3039

The functionality for each of the above warning indicators is described in the following sections:
1 and 2. Turn Signal Indicators
The turn signal indicators are controlled by the CJB on receipt of medium speed CAN bus signals from the instrument cluster.
The instrument cluster outputs a voltage to the turn signal indicator switch. The switch contains resistors of different values.
When the switch is operated in either the LH or RH direction, the voltage is passed to a ground connection in the instrument cluster which detects the reduced voltage supplied via the resistors. When the turn signal indicator switch is operated in the
LH or RH direction, the instrument cluster detects the ground voltage and determines whether a LH or RH selection is made.
The instrument cluster transmits a medium speed CAN message to the CJB for operation of the applicable turn signal indicators. The message can contain a number of states for each possible switch position and also an out of range low and
high state for circuit faults and an initial value for the switch neutral position. The turn signal indicators are not subject to the
3 second indicator check when the ignition is switched on.
The RJB (rear junction box) software controls the flash rate of the warning indicator which sends 'ON' and 'OFF' signals to the
instrument cluster which flashes the indicators in a green color. During normal operation, the warning indicator flashes slowly,
accompanied simultaneously by a sound from the instrument cluster sounder. If a fault exists, the RJB transmits a message to the instrument cluster which responds by displaying an appropriate message in the message center.
The hazard warning indicators are controlled by the CJB on receipt of a completed ground path from the hazard warning indicator switch. The CJB outputs a medium speed CAN message to the instrument cluster which operates both the LH and RH turn signal indicators simultaneously. The hazard warning indicators can operate with the ignition switched off, therefore the
CAN message from the CJB will also carry a 'wake-up' message for the instrument cluster. 3. Brake Warning Indicator
This warning indicator is displayed in a red or amber color (dependant on market) as a brake symbol in all markets except
United States of America (USA) which have the word 'BRAKE' in place of the symbol. The indicator is controlled by high speed
CAN messages from the ABS module and the parking brake control module. The indicator is illuminated in a red color for a 3 second indicator check when the ignition is switched on.
The instrument cluster monitors the fluid level in the brake fluid reservoir using a hardwired level switch. If the fluid level falls
to below a determined level, the switch contact is broken and the ABS module detects the low fluid level condition. The instrument cluster illuminates the warning indicator and simultaneously displays a 'BRAKE FLUID LOW' message in the
message center.
NOTE: If both the brake warning indicator and the ABS warning indicator illuminate simultaneously, a major fault in the brake system will have occurred.
The warning indicator also displays parking brake status. When the parking brake is applied, the warning indicator will be
illuminated by the instrument cluster and, if the vehicle is moving, the message 'PARK BRAKE APPLIED' will be also displayed
in the message center in response to a CAN message from the parking brake control module.
If a condition exists where the parking brake cannot be applied, the parking brake control module issues a CAN message to the instrument cluster which flashes the warning lamp on and off and is accompanied with a message 'CANNOT APPLY PARK BRAKE'.
If a fault occurs in the parking brake system, the parking brake control module issues a CAN message to the instrument cluster which illuminates the warning indicator and displays the message 'PARK BRAKE FAULT' in the message
center.
4. Forward Alert Indicator
The forward alert system uses the components of the adaptive speed control system to alert the driver of the presence of a
vehicle ahead. The system can be turned on and off using a switch located in the auxiliary lighting switch when the adaptive
speed control system is off. The indicator is illuminated in an amber color for a 3 second indicator check when the ignition is
switched on.
The forward alert system is controlled by the adaptive speed control module. When the switch is pressed, the forward alert
system is activated and the adaptive speed control module issues a forward alert active message on the high speed CAN bus to the instrument cluster. The forward alert icon in the instrument cluster will illuminate in an amber color and a 'FORWARD
ALERT' message will be displayed in the message center. When the button is pressed a second time, the module issues a
forward alert off CAN message. The forward alert system will be deactivated, the forward alert icon will go off and a message 'FORWARD ALERT OFF' will be displayed in the message center.
5. Automatic Speed Limiter (ASL) Indicator
The ASL is controlled by the ECM (engine control module). An ASL switch is located in the floor console, adjacent to the gear
selector lever. When the ASL switch is pressed, this is sensed by the ECM which issues a high speed CAN message to the instrument cluster. The instrument cluster illuminates the ASL warning indicator in an amber color to show the driver that ASL
is active. The driver sets the required speed using the speed control SET +/- switches on the steering wheel. The selected
speed is shown by the message ' LIMITER SET XXX MPH / K/MH' in the message center. The indicator is illuminated in an
amber color for a 3 second indicator check when the ignition is switched on. ASL can be deselected by pressing the ASL switch,
by depressing the throttle pedal initiating kick-down or by pressing the 'cancel' switch on the steering wheel. The ASL indicator
will go off and the message center will display the message 'limiter cancelled' for 4 seconds. If a fault occurs in the ASL
system, the ECM will send a message to the instrument cluster to illuminate the ASL indicator and display the message 'LIMITER NOT AVAILABLE'.
Page 1787 of 3039

the RCM and illuminated by the instrument cluster on receipt of high speed CAN bus messages. The safety belt warning indicator is not subject to the 3 second indicator check when the ignition is switched on.
The operation of the passenger seat buckle switch is as described below with the exception that the instrument cluster must
receive a hardwired signal from the belt minder control module to indicate that a passenger is occupying the seat.
The safety belt warning indicator is subject to a timer. The warning indicator is activated when the following conditions exist:
Ignition is switched on
One of the front seat belts is unbuckled
USA market only - 75 seconds has elapsed after ignition on mode is selected
Vehicle is not in reverse gear
Vehicle speed is more than 8 km/h (5 mph).
Once the above parameters are met, the instrument cluster flashes the warning indicator at 2 Hz for 10 seconds accompanied
by a simultaneous chime. After 10 seconds the chime ceases and the warning indicator is permanently illuminated for 20
seconds. This sequence is repeated every 30 seconds until one of the following events occurs:
300 seconds has elapsed
The safety belt of the occupied front seats is fastened
The ignition is switched to off mode
The vehicle speed decreases to below 5 km/h (3 mph).
NOTE: On USA market vehicles, the warning indicator in not permanently illuminated.
The safety belt minder function cannot be disabled. The seat belt minder function can be disabled.
Refer to: Safety Belt System (501-20A Safety Belt System, Description and Operation). 14. Side Lamp Indicator
The instrument cluster controls the green colored side lamp indicator on receipt of a side lamp status message on the medium
speed CAN bus from the CJB and the auxiliary junction box. The lighting switch on the LH steering column multifunction switch is connected to the instrument cluster. Selections using this switch are detected by the cluster which requests the side or
headlamp operation via a message to the CJB and the RJB. The CJB and the RJB responds with a side lamp active message and the cluster illuminates the side lamp indicator. The side lamp indicator is not subject to the 3 second indicator check when
the ignition is switched on.
15. High Beam Indicator
The instrument cluster controls the blue colored high beam indicator on receipt of a high beam status message on the medium
speed CAN bus from the CJB. The lighting switch on the LH steering column multifunction switch is connected to the instrument cluster. High beam or flash selections using this switch are detected by the cluster which requests the light
operation via a CAN message to the CJB. The CJB responds with a high beam active message and the cluster illuminates the high beam indicator. The high beam indicator is not subject to the 3 second indicator check when the ignition is switched on.
16. Rear Fog Lamp Indicator
The amber colored rear fog lamp indicator is controlled by the auxiliary junction box and illuminated by the instrument cluster
on receipt of a rear fog lamp on message on the medium speed CAN bus from the RJB. The indicator is illuminated for as long as the rear fog lamps are active. The rear fog lamp indicator is not subject to the 3 second indicator check when the ignition is
switched on.
SPEEDOMETER
The speedometer is driven by high speed CAN signals transmitted by the ABS module. The wheel speeds are measured by sensors reading the rotational speed of the rear wheels from toothed targets on the hubs. An average of the two wheel speeds
are passed from the sensors to the ABS module in the form of pulsed signals. The ABS module converts these signals into a speed output on the high speed CAN to the instrument cluster. The same speed outputs from the wheel speed sensors are also used to calculate the distance the vehicle has travelled.
TACHOMETER
The tachometer is driven by an engine speed signal transmitted on the high speed CAN from the ECM. The signal is derived from the CKP (crankshaft position) sensor. The signal is received by the instrument cluster microprocessor and the output from
the microprocessor drives the tachometer.
FUEL GAGE
The fuel gage is controlled by CAN messages from the RJB. The RJB reads the values output by the fuel level sensors every 131 ms and transmits a fuel tank contents value, corrected for battery voltage, in a CAN message to the instrument cluster. A fuel pump symbol is displayed to the left of the linear gage. An arrow above the symbol shows the driver on which side of the
vehicle the fuel filler cap is located. Above the linear fuel gage, is a LCD (liquid crystal display) area which displays odometer
and trip readouts. When a trip computer function is selected, these are replaced by a trip computer display for the trip function
selected.
LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY
In the area above and below the message center is a LCD display. The area below the message center displays a linear fuel www.JagDocs.com