2010 JAGUAR XFR fuel pressure
[x] Cancel search: fuel pressurePage 174 of 3039

DTC Description Possible Causes Action P007D-00
Charge Air Cooler
Temperature Sensor Circuit
High (Bank 1) - No sub type
information
NOTE: - Circuit TMAP_TEMP_SENSOR
-
Charge air cooler temperature
sensor (Bank 1) circuit short circuit
to power, open circuit, high
resistance
Charge air cooler temperature
sensor (Bank 1) failure
Refer to the electrical circuit
diagrams and check charge air cooler
temperature sensor (Bank 1) circuit
for short circuit to power, open
circuit, high resistance
Check and install a new charge air
cooler temperature sensor (Bank 1)
as required. Refer to the warranty
policy and procedures manual, or
determine if any prior approval
programme is in operation, prior to
the installation of a new
module/component P0087-00
Fuel Rail/System Pressure -
Too Low - No sub type
information
NOTE: - Circuit
FUEL_HIGH_PRESS_SENSOR -
Fuel rail pressure sensor circuit
short circuit to ground, open
circuit, high resistance
Fuel rail pressure sensor failure
Fuel lines leaking or restricted
Fuel pump failure
Using the manufacturer approved
diagnostic system check datalogger
signal, Fuel Rail Pressure Sensor -
High Range Sensor Voltage (0x0377)
Refer to the electrical circuit
diagrams and check fuel rail pressure
sensor circuit for short circuit to
ground, open circuit, high resistance
Check for fuel pump related DTCs.
Check fuel lines for leakage or
restriction
Check and install new fuel rail
pressure sensor as required. Check
and install a new fuel pump as
required. Refer to the warranty policy
and procedures manual, or determine
if any prior approval programme is in
operation, prior to the installation of
a new module/component P0088-00
Fuel Rail/System Pressure -
Too High - No sub type
information
NOTE: - Circuit
FUEL_HIGH_PRESS_SENSOR -
Fuel rail pressure sensor circuit
short to each other, high
resistance, short circuit to power
Fuel rail pressure sensor failure
Using the manufacturer approved
diagnostic system check datalogger
signal, Fuel Rail Pressure Sensor -
High Range Sensor Voltage (0x0377)
Refer to the electrical circuit
diagrams and check fuel rail pressure
sensor circuit for short to each other,
high resistance, short circuit to
power
Check and install new fuel rail
pressure sensor as required. Refer to
the warranty policy and procedures
manual, or determine if any prior
approval programme is in operation,
prior to the installation of a new
module/component P008A-00
Low Pressure Fuel System
Pressure - Too Low - No sub
type information
NOTE: - Circuit
LOW_PRESS_FUEL_PRESS_SENSOR -
Low pressure fuel sensor circuit
failure, short circuit to ground,
short circuit to power, open circuit
Fuel pump driver module circuit
short circuit to ground, short circuit
to power, open circuit
Low pressure fuel
Fuel pump driver module failure
Using the manufacturer approved
diagnostic system check datalogger
signal, Fuel Rail Pressure - Low
Range Sensor Voltage (0x0376)
Check fuel system for leakage
Refer to the electrical circuit
diagrams and check low pressure
fuel sensor circuit for short circuit to
ground, short circuit to power, open
circuit
Refer to the electrical circuit
diagrams and check fuel pump driver
module circuit short circuit to
ground, short circuit to power, open
circuit
Check and install a new low pressure
fuel sensor as required. Check and
install a new fuel pump driver
module as required. Refer to the
warranty policy and procedures
manual, or determine if any prior
approval programme is in operation,
prior to the installation of a new
module/component
Page 306 of 3039

Suspension System - General Information -
Vehicle Ride Height Published: 27-Aug-2013
NOTE: All figures are at "Kerb" height - For additional information, refer to Vehicle Ride Height below.
Description Measurement Description Front/Rear Kerb mm (inch) Tolerance mm (inch) Vehicles without supercharger Front 388 (15.28) ±12 (0.5) Rear 391 (15.39) ±12 (0.5) Vehicles with supercharger Front 385 (15.16) ±12 (0.5) Rear 384 (15.12) ±12 (0.5) Vehicles with All wheel drive Front 404 (15.90) ±12 (0.5) Rear 391 (15.39) ±12 (0.5)
Ride height is measured from the centre of the wheel to the apex of the wheel arch, through the wheel centre line.
Kerb - with all fluids at full and a full tank of fuel, no occupants/luggage.
Tires must be inflated to normal pressure -
For additional information, refer to: Specifications (204-04 Wheels and Tires, Specifications). Wheel Alignment - Front Camber
NOTE: *1 Camber Balance = left-hand camber - right-hand camber.
Description Left-hand Right-hand Balance*1 Markets Degrees/Minutes Nominal Tolerance Nominal Tolerance Nominal Tolerance All right-hand drive and Japan Degrees/Minutes -0° 36' ±45' -0° 12' ±45' -0° 24' ±45' Decimal Degrees -0.6° ±0.75° -0.2° ±0.75° -0.4° ±0.75° USA, Canada, Mexico and Dominican Republic
(Federal) Degrees/Minutes -0° 12' ±45' -0° 33' ±45' 0° 21' ±45' Decimal Degrees -0.2° ±0.75° -0.55° ±0.75° 0.35° ±0.75° Rest of world Degrees/Minutes -0° 12' ±45' -0° 24' ±45' 0° 12' ±45' Decimal Degrees -0.2° ±0.75° -0.4° ±0.75° 0.2° ±0.75° Vehicles with All wheel drive Degrees/Minutes -0° 11' ±45' -0º 32' ±0.45' 21' ±45' Decimal Degrees -0.19° ±0.75º -0.54º ±0.75º 0.35º ±0.75° Wheel Alignment - Front Caster
NOTE: *2 Caster Balance = left-hand caster - right-hand caster.
Description Left-hand Right-hand Balance*2 Markets Degrees/Minutes Nominal Tolerance Nominal Tolerance Nominal Tolerance All right-hand drive and Japan Degrees/Minutes 6° 53' ±45' 6° 20' ±45' 0° 33' ±45' Decimal Degrees 6.88° ±0.75° 6.33° ±0.75° 0.55° ±0.75° USA, Canada, Mexico and Dominican Republic
(Federal) Degrees/Minutes 6° 36' ±45' 6° 45' ±45' -0° 8' ±45' Decimal Degrees 6.61° ±0.75° 6.74° ±0.75° -0.14° ±0.75° Rest of world Degrees/Minutes 6° 36' ±45' 6° 36' ±45' 0° 0' ±45' Decimal Degrees 6.61° ±0.75° 6.61° ±0.75° 0° ±0.75° Vehicles with All wheel drive Degrees/Minutes 6° 2' ± 45' 6° 11' ± 45' - 9' ± 45' Decimal Degrees 6.04º ±0.75° 6.19° ± 0.75° -0.15° ± 0.75° Wheel Alignment - Front Toe
Description Total Toe Markets Degrees/Minutes Nominal Tolerance All right-hand drive and Japan Degrees/Minutes 0° 13' ±12' Decimal Degrees 0.22° ±0.20° USA, Canada, Mexico and Dominican Republic (Federal) Degrees/Minutes 0° 13' ±12' Decimal Degrees 0.22° ±0.20° Rest of world Degrees/Minutes 0° 13' ±12' Decimal Degrees 0.22° ±0.20° Vehicles with All wheel drive Degrees/Minutes 16' ± 12' Decimal Degrees 0.27° ± 0.20° Wheel Alignment - Rear Camber (Vehicles without supercharger)
Description Left-hand Right-hand Markets Degrees/Minutes Nominal Tolerance Nominal Tolerance All Markets Degrees/Minutes -0° 47' ±45' -0° 47' ±45' Decimal Degrees -0.78° ±0.75° -0.78° ±0.75° Wheel Alignment - Rear Camber (Vehicles with supercharger)
Description Left-hand Right-hand Markets Degrees/Minutes Nominal Tolerance Nominal Tolerance All Markets Degrees/Minutes -0° 59' ±45' -0° 59' ±45'
Page 441 of 3039

provides the following benefits:
Maintain optimal fuel consumption.
Maintain ride and handling characteristics.
Reduce the risk of rapid tire deflation - which may be caused by under inflated tires.
Comply with legislation requirements in relevant markets.
CAUTION: TPMS is not intended as a replacement for regular tire pressure and tire condition checks and should be
considered as additional to good tire maintenance practices.
The TPMS measures the pressure in each of the vehicle's tires and issues warnings to the driver if any of the pressures deviate
from defined tolerances. The space saver spare wheel is not monitored.
NOTE: TPMS is not designed to warn the driver of a tire 'blow-out', as due to the short duration of a 'blow-out', it is not
possible to give the driver sufficient warning that such an event is occurring. The design of the TPMS is to assist the driver in
keeping the tires at the correct pressure, which will assist to reduce the likelihood of a tire 'blow-out' occurring.
Page 811 of 3039
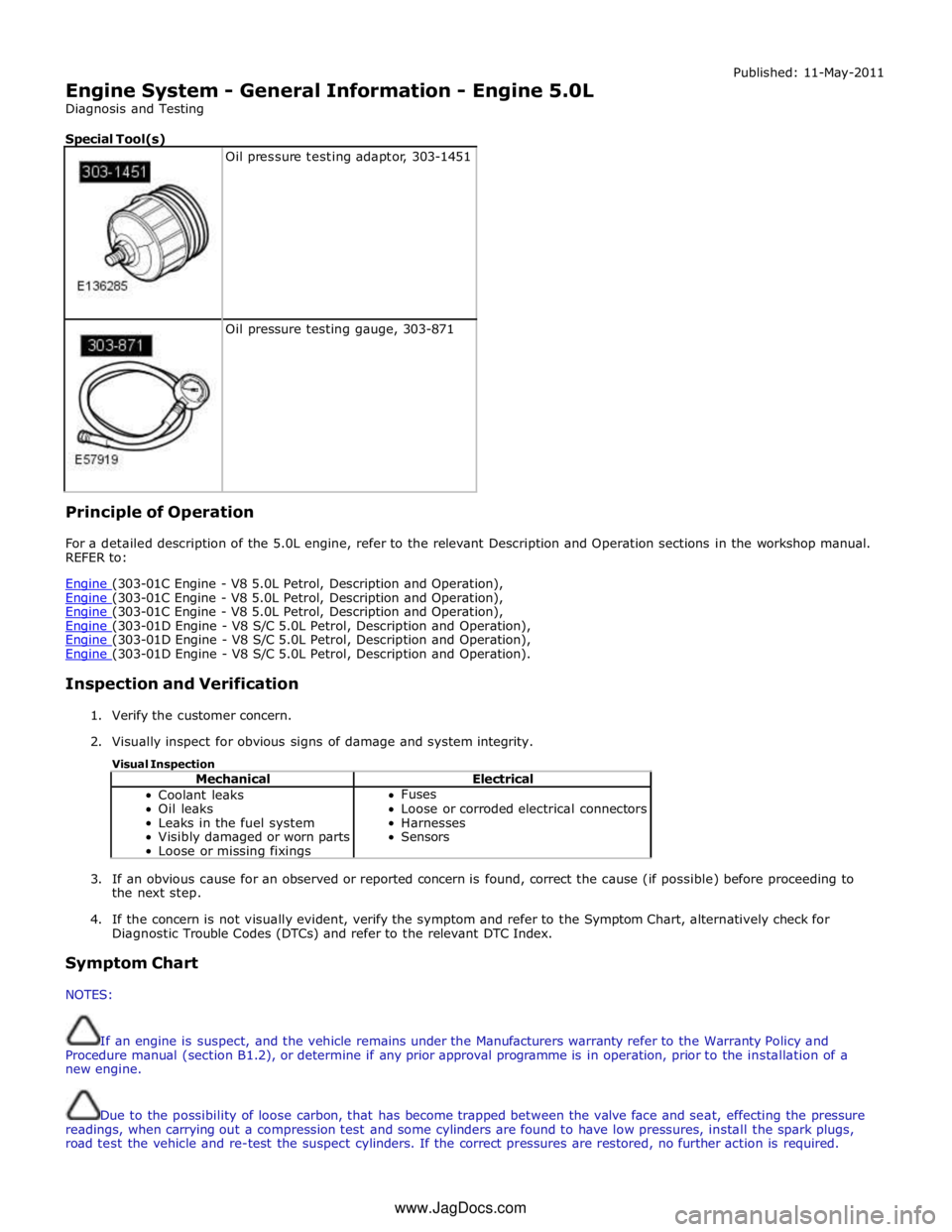
Engine System - General Information - Engine 5.0L
Diagnosis and Testing
Special Tool(s)
Oil pressure testing adaptor, 303-1451
Oil pressure testing gauge, 303-871 Principle of Operation Published: 11-May-2011
For a detailed description of the 5.0L engine, refer to the relevant Description and Operation sections in the workshop manual.
REFER to:
Engine (303-01C Engine - V8 5.0L Petrol, Description and Operation), Engine (303-01C Engine - V8 5.0L Petrol, Description and Operation), Engine (303-01C Engine - V8 5.0L Petrol, Description and Operation), Engine (303-01D Engine - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, Description and Operation), Engine (303-01D Engine - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, Description and Operation), Engine (303-01D Engine - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of damage and system integrity.
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical Coolant leaks
Oil leaks
Leaks in the fuel system
Visibly damaged or worn parts
Loose or missing fixings Fuses
Loose or corroded electrical connectors
Harnesses
Sensors
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step.
4. If the concern is not visually evident, verify the symptom and refer to the Symptom Chart, alternatively check for
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and refer to the relevant DTC Index.
Symptom Chart
NOTES:
If an engine is suspect, and the vehicle remains under the Manufacturers warranty refer to the Warranty Policy and
Procedure manual (section B1.2), or determine if any prior approval programme is in operation, prior to the installation of a
new engine.
Due to the possibility of loose carbon, that has become trapped between the valve face and seat, effecting the pressure
readings, when carrying out a compression test and some cylinders are found to have low pressures, install the spark plugs,
road test the vehicle and re-test the suspect cylinders. If the correct pressures are restored, no further action is required. www.JagDocs.com
Page 812 of 3039
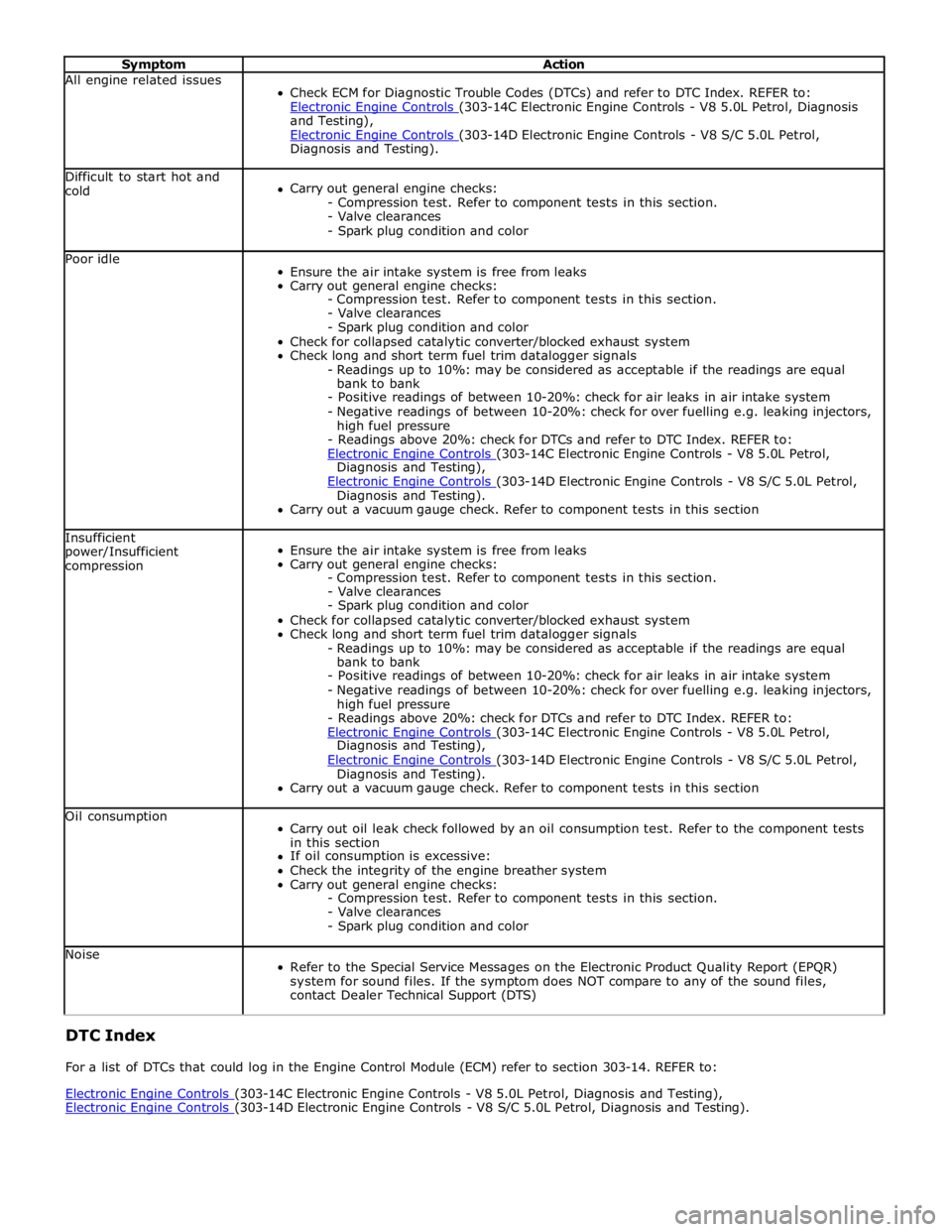
Symptom Action All engine related issues
Check ECM for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and refer to DTC Index. REFER to:
Electronic Engine Controls (303-14C Electronic Engine Controls - V8 5.0L Petrol, Diagnosis and Testing),
Electronic Engine Controls (303-14D Electronic Engine Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, Diagnosis and Testing). Difficult to start hot and
cold
Carry out general engine checks:
- Compression test. Refer to component tests in this section.
- Valve clearances
- Spark plug condition and color Poor idle
Ensure the air intake system is free from leaks
Carry out general engine checks:
- Compression test. Refer to component tests in this section.
- Valve clearances
- Spark plug condition and color
Check for collapsed catalytic converter/blocked exhaust system
Check long and short term fuel trim datalogger signals
- Readings up to 10%: may be considered as acceptable if the readings are equal
bank to bank
- Positive readings of between 10-20%: check for air leaks in air intake system
- Negative readings of between 10-20%: check for over fuelling e.g. leaking injectors,
high fuel pressure
- Readings above 20%: check for DTCs and refer to DTC Index. REFER to:
Electronic Engine Controls (303-14C Electronic Engine Controls - V8 5.0L Petrol, Diagnosis and Testing),
Electronic Engine Controls (303-14D Electronic Engine Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, Diagnosis and Testing).
Carry out a vacuum gauge check. Refer to component tests in this section Insufficient
power/Insufficient
compression
Ensure the air intake system is free from leaks
Carry out general engine checks:
- Compression test. Refer to component tests in this section.
- Valve clearances
- Spark plug condition and color
Check for collapsed catalytic converter/blocked exhaust system
Check long and short term fuel trim datalogger signals
- Readings up to 10%: may be considered as acceptable if the readings are equal
bank to bank
- Positive readings of between 10-20%: check for air leaks in air intake system
- Negative readings of between 10-20%: check for over fuelling e.g. leaking injectors,
high fuel pressure
- Readings above 20%: check for DTCs and refer to DTC Index. REFER to:
Electronic Engine Controls (303-14C Electronic Engine Controls - V8 5.0L Petrol, Diagnosis and Testing),
Electronic Engine Controls (303-14D Electronic Engine Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, Diagnosis and Testing).
Carry out a vacuum gauge check. Refer to component tests in this section Oil consumption
Carry out oil leak check followed by an oil consumption test. Refer to the component tests
in this section
If oil consumption is excessive:
Check the integrity of the engine breather system
Carry out general engine checks:
- Compression test. Refer to component tests in this section.
- Valve clearances
- Spark plug condition and color Noise
Refer to the Special Service Messages on the Electronic Product Quality Report (EPQR)
system for sound files. If the symptom does NOT compare to any of the sound files,
contact Dealer Technical Support (DTS) DTC Index
For a list of DTCs that could log in the Engine Control Module (ECM) refer to section 303-14. REFER to:
Electronic Engine Controls (303-14C Electronic Engine Controls - V8 5.0L Petrol, Diagnosis and Testing), Electronic Engine Controls (303-14D Electronic Engine Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, Diagnosis and Testing).
Page 813 of 3039

Component Tests
Engine Oil Leaks
NOTE: Before installing new gaskets or oil seals, make sure that the fault is clearly established.
If the oil leak cannot be identified clearly by a visual inspection, carry out an Ultraviolet test:
Fluorescent Oil Additive Method
1. Clean the engine with a suitable cleaning fluid (brake cleaner).
2. Drain the engine oil and refill with recommended oil, premixed with Diesel Engine Oil Dye or equivalent. Use a minimum
14.8 ml (0.5 ounce) to a maximum 29.6 ml (1 ounce) of fluorescent additive to all engines. If oil is not premixed,
fluorescent additive must first be added to the crankcase.
3. Run engine for 15 minutes. Stop the engine and inspect all seal and gasket areas for leaks using a 12 Volt Master UV
Diagnostic Inspection Kit or equivalent. A clear bright yellow or orange area will identify leak. For extremely small
leaks, several hours may be required for the leak to appear.
4. As necessary, pressurize the main oil gallery system to locate leaks due to incorrectly sealed, loose or cocked plugs. If
the flywheel bolts leak oil, look for sealer on the threads.
5. Repair all leaks as necessary.
Compression Test General Remarks
NOTES:
Removing fuses and disconnecting electrical components may cause the Engine Control Module (ECM) to log Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTCs). After the measurements have been carried out, DTCs should be cleared from memory by connecting to
the Manufacturer Approved Diagnostic System.
Only check the compression pressure with the valves set to the prescribed clearance (if this can be adjusted).
The compression pressure should be checked with the engine at normal operating temperature.
Check the Compression Pressure
WARNING: Move gear selector lever to 'P' position. Failure to follow this instruction may result in personal injury.
1. Remove the fuel pump relay.
2. Start the engine - the engine will start, run for a few seconds then stall.
3. Remove the spark plugs.
4. Install the compression tester.
5. Install an auxiliary starter switch in the starting circuit. With the ignition switch OFF, using the auxiliary starter switch,
crank the engine a minimum of five compression strokes and record the highest reading. Note the approximate number
of compression strokes required to obtain the highest reading.
6. Repeat the test on each cylinder, cranking the engine approximately the same number of compression strokes.
7. Install the removed components in reverse order, observing the specified tightening torques.
8. Clear all DTCs from the ECM.
Interpretation of the Results
NOTE: Due to the possibility of loose carbon that has become trapped between the valve face and seat effecting the
pressure readings, when carrying out a compression test and cylinders are found to have low pressures, install the spark plugs,
road test the vehicle and re-test the suspect cylinders. If the correct pressures are restored, no further action is required.
The indicated compression pressures are considered within specification if the lowest reading cylinder is within 75% of the
highest reading.
If the cylinder pressures are found to be low, carry out a leakdown test to determine the location of the fault (if any leakback
can be heard through the engine breather system suspect the piston rings, if any leakback can be heard through the inlet
system suspect the inlet valve or seat, if any leakback can be heard through the exhaust manifold suspect the exhaust valve
or seat. If the measurements for two cylinders next to each other are both too low then it is very likely that the cylinder head
gasket between them is burnt through. This can also be recognized by traces of engine oil in the coolant and/or coolant in the
Page 816 of 3039

9. WEAK VALVE SPRINGS: When the needle oscillation becomes more violent as engine RPM is increased, weak valve
springs are indicated. The reading at idle could be relatively steady.
10. LATE VALVE TIMING: A steady but low reading could be caused by late valve timing.
11.
IGNITION TIMING RETARDED: Retarded ignition timing will produce a steady but somewhat low reading.
12.
INSUFFICIENT SPARK PLUG GAP: When spark plugs are gapped too close, a regular, small pulsation of the needle can
occur.
13. INTAKE LEAK: A low, steady reading can be caused by an intake manifold or throttle body gasket leak.
14.
BLOWN HEAD GASKET: A regular drop of fair magnitude can be caused by a blown head gasket or warped cylinder head
to cylinder block surface.
15.
RESTRICTED EXHAUST SYSTEM: When the engine is first started and is idled, the reading may be normal, but as the
engine RPM is increased, the back pressure caused by a clogged muffler, kinked tail pipe or other concerns will cause
the needle to slowly drop to 0 kPa (0 in-Hg). The needle then may slowly rise. Excessive exhaust clogging will cause
the needle to drop to a low point even if the engine is only idling.
When vacuum leaks are indicated, search out and correct the cause. Excess air leaking into the system will upset the fuel
mixture and cause concerns such as rough idle, missing on acceleration or burned valves. If the leak exists in an accessory
such as the power brake booster, the unit will not function correctly. Always repair vacuum leaks.
Engine Oil Pressure Check
NOTE: Prior to checking the engine oil pressure, a road test of 6 miles (10 kilometres), must be carried out. Do not
attempt to attain engine normal operating temperature by allowing the engine to idle.
1. Disconnect the battery ground cable. Refer to section 414-00 - Charging System - General Information of the workshop
manual
2. WARNINGS:
The spilling of hot engine oil is unavoidable during this procedure, care must be taken to prevent scalding.
Wear protective gloves.
Remove the engine oil filter element
REFER to: Oil Filter Element (303-01C Engine - V8 5.0L Petrol, Removal and Installation).
NOTE: Ensure the oil filter element is not contaminated during this procedure
3. Install the oil filter element into special tool (Oil filter adapter number 303-1451)
4. Install the special tool (Oil filter adapter number 303-1451) to the engine. Torque: 25 Nm
5. Install the special tool (Oil pressure testing gauge, 303-871) and tighten the union
6. Connect the battery ground cable
7. Refer to owner hand book, check and top-up the engine oil if required
8. Start and run the engine
9. Note the oil pressure readings with the engine running at idle and 3500 RPM
10.
Turn off the engine
11.
Disconnect the battery ground cable
12. Remove the special tools
1. Clean the components
13.
Install the engine oil filter element
REFER to: Oil Filter Element (303-01C Engine - V8 5.0L Petrol, Removal and Installation).
NOTE: Ensure the oil filter element is not contaminated during this procedure
14.
Connect the battery ground cable
15. Refer to owner hand book, check and top-up the engine oil if required
www.JagDocs.com
Page 845 of 3039

Item Specification Camshaft journal maximum run out limit (mm) Camshaft journals to end journals 0.03 Camshaft journals to adjacent journals 0.015 Camshaft journal maximum out of round (mm) - all journals 0.005 Torque Specification
NOTE: A = Refer to procedure for correct torque sequence.
Description Nm lb-ft lb-in Engine cover mounting bolts 10 7 - Accessory drive belt tensioner retaining bolt 40 30 - Supercharger belt idler/tensioner bracket retaining bolts 25 18 - Secondary drive belt idler retaining bolts 40 30 - Power steering pump pulley retaining bolts 25 18 - Power steering pump retaining bolts 25 18 - Power steering pump bracket to engine retaining bolts 25 18 - Generator retaining bolts 48 35 - Starter motor retaining bolts 48 35 - Air conditioning compressor retaining bolts 25 18 - Engine mounting to engine mounting bracket retaining nuts 48 35 - Engine mounting to subframe retaining nuts 63 46 - Engine mounting bracket to engine retaining bolts 48 35 - Crankshaft damper pulley retaining LH threaded bolt 200 + 270° 148 + 180° - Flexplate retaining bolts 45 + 90° 33 + 90° - Exhaust manifold heat shield retaining bolts A - - Exhaust manifold retaining bolts A - - Engine wiring harness bracket retaining bolts 10 7 - Coolant outlet pipe 10 7 - Intercooler retaining bolts 25 18 - Intake manifold retaining bolts 25 18 - Oil Cooler retaining bolts 13 10 - Knock sensor (KS) retaining bolt 20 14 - Ignition coil retaining bolts 8 - 71 Spark plugs 20 15 - Fuel rail retaining bolts A - - High pressure fuel pipe retaining bolts A - - High pressure fuel pump retaining bolts 12 9 - Oil filter housing assembly retaining bolts 12 9 - Oil filter cap 28 21 - Lifting eye bolts 25 + 90° 18 + 90° - Manifold absolute pressure and temperature (MAPT) sensor sensor retaining bolts 5 - 44 Coolant pump retaining bolts 12 9 - Variable valve timing (VVT) oil control solenoid retaining bolts 10 7 - Camshaft position (CMP) sensor retaining bolts 10 7 - Camshaft cover retaining bolts 13 10 - Front upper timing cover retaining bolts 12 9 - Front lower timing cover retaining bolts A - - Engine rear cover retaining bolts A - - VVT to camshaft retaining bolts 32 24 - Camshaft bearing caps retaining bolts 11 8 - Primary timing chain fixed guide retaining bolts 12 9 - Primary timing chain tensioner retaining bolts 12 9 - Primary timing chain tensioner guide blade retaining bolts 25 18 - Auxiliary chain tensioner guide retaining bolts 21 15 - Auxiliary chain fixed guide retaining bolt 12 9 - Oil pump sprocket retaining bolt 21 15 - Cylinder head retaining bolts A - - Engine oil level (EOL) sensor retaining bolt 12 9 - Oil pan to oil sump body retaining bolts 12 9 - Oil sump body to engine retaining bolts 25 18 - Oil pan drain plug 23 17 - Oil transfer tube to Oil pan body retaining bolts 11 8 - Oil pump to engine block retaining bolts 25 18 - Pick-up pipe to oil pump retaining bolts 12 9 - Windage tray retaining bolts 25 18 - Piston cooling jet retaining bolts 12 9 - Engine block coolant draining plug 50 37 - Connecting Rod bolts Stage 1 10 7 - Stage 2 50 37 -