2010 JAGUAR XFR suspension
[x] Cancel search: suspensionPage 723 of 3039

Symptom Possible Causes Action
Knock
Loose fixings (universal joint
pinch bolt and steering column
fixings)
Tighten fixings to correct specification.
REFER to: Specifications (211-00 Steering System - General Information, Specifications).
Rattle
Foreign objects
Remove foreign objects from between steering
column shroud and steering wheel/steering
column rotating components
Loose fixings
Tighten steering column fixings to correct
specification.
REFER to: Specifications (211-00 Steering System - General Information, Specifications).
Noise while adjusting
column
Electric motor/solenoid
NOTE: Before carrying out repairs/replacement,
assess column adjustment noise levels against other
vehicles of the same model
Install new components as required
Motor spindle/lead screw
Lubricate lead screw Vibration
Symptom Possible Causes Action
Wheel Fight (Kick Back) - condition
where roughness is felt in the
steering wheel by the driver when
the vehicle is driven over rough
surfaces
Loose or worn steering
components/bushings
CAUTION: DO NOT attempt to adjust the
steering gear yoke. Failure to follow this
instruction will invalidate the steering gear
warranty.
Tighten and install new steering
components/bushings as required
Loose or worn suspension
components/bushings
Tighten and install new suspension
components/bushings as required
Nibble (Shimmy) - condition where
oscillation of the steering wheel
occurs (not vertical which is Shake).
This is driven by road wheel
imbalance
Road wheel and tire
condition
Check for wheel and tire damage. Install
new components as required
Check for tire uniformity. Install new
tire(s) as required
Road wheel imbalance
Check and adjust road wheel balance as
required
Shake - condition where vertical
vibration of the steering
wheel/column occurs (not
oscillation which is Nibble)
NOTE: Vibration smooths out
after several miles of driving
Road wheel imbalance due
to tire flat-spotting
Ensure tires installed are to Jaguar
specification. Install new tires as
required
Check and adjust tire pressures to
correct specification Component Tests
Steering Linkage Inspection and Backlash (Free play) Check
CAUTION: Steering gear boots must be handled carefully to avoid damage. Use new clamps when installing steering gear
boots.
Inspect the boots for cuts, deterioration, twisting or distortion. Check the steering gear boots to make sure they are tight.
Install new boots or clamps as required.
NOTE: The following steps must be carried out with assistance.
1. With the wheels in the straight ahead position, gently turn the steering wheel to the left and the right to check for free
play.
Page 727 of 3039

between moving components such as the steering wheel to steering column shroud.
Grunt (Squawk/Whoop)
Grunt is a 'honking' sound elicited when coming off one of the steering stops. Grunt is generally excited during parking
manoeuvres with a low to medium speed steering input.
Hiss (Swish)
Hiss or Valve Hiss is a high-frequency sound coming from the steering gear when the system is loaded. It is a rushing or
'swish' noise that doesn't change frequency with RPM. Hiss is the general noise generated by the flow of hydraulic fluid through
restrictions in the steering system. Restrictions include the rotary steering valve, power steering tubes, connectors, tuning
orifices, etc. Hiss can be air-borne and structure-borne, but the structure-borne path through the steering intermediate shaft is
usually dominant.
Moan (Groan)
Moan is the general structure-borne noise of the steering system. Moan is primarily transmitted to the driver via the body
structure through the pump mount, engine mounts, power steering lines and power steering brackets. On some vehicles, moan
is a loud humming noise, often present when the wheel is turned and the system is loaded. It may change frequency with
engine RPM and if the system is loaded or unloaded.
Steering Gear Knock (Steering Gear Slap)
CAUTION: DO NOT attempt to adjust the steering gear yoke. Failure to follow this instruction will invalidate the steering
gear warranty.
Steering gear knock is a rattle sound and steering wheel vibration caused by separation of the steering gear and pinion while
driving over bumps. It is a structure-borne noise transmitted through the intermediate shaft and column. Steering gear knock
can also be heard as a 'thump' or impact noise that occurs with the vehicle stationary when the steering wheel is released
from a loaded position and allowed to return to rest. Noise occurs with the engine on or off.
Rattles
Rattles are noises caused by knocking or hitting of components in the steering system. Steering rattles can occur in the engine
compartment, the suspension, or the passenger compartment. Rattles can be caused by loose components, movable and
flexible components, and improper clearances.
Squeaks/Scrapes
Squeaks/Scrapes are noises due to friction or component rubbing anywhere in the steering system. Squeaks/Scrapes have
appeared in steering linkages and joints, in column components and in column and steering wheel trim.
Weep
Weep is an air-borne noise, occasionally generated when turning the steering across lock at a constant rate. When present on
a vehicle the noise, once initiated can often be maintained across a large proportion of the available steering movement.
Whistle
Whistle is similar to hiss but is louder and of a higher frequency. It is also more of a pure tone noise than hiss. Whistle is
air-borne and is generated by a high flow rate of hydraulic fluid through a small restriction.
Zip
Zip noise is the air-borne noise generated by power steering pump cavitation when power steering fluid does not flow freely
through the suction hose from the reservoir to the pump. Zip primarily occurs during cold weather at start-up.
Steering System Vibrations and Harshness
Buzz
Buzz is a tactile rotary vibration felt in the steering wheel when steering inputs are slow. Buzz can also be called a grinding
feel and it is closely related to grunt and is caused by high system gain with low damping. Buzz is generally excited during
parking manoeuvres with low to medium speed steering input.
Buzz (Electrical)
A different steering buzz can be caused by pulse width modulated (PWM) electric actuators used in variable assist steering
systems. This buzz is felt by turning the ignition key to run without starting the engine and holding onto the steering wheel.
In extreme cases, the buzz can be felt with the engine running also.
Column/Steering Wheel Shake
Column shake is a low frequency vertical vibration excited by primary engine vibrations.
Nibble (Shimmy)
Page 728 of 3039

Steering nibble is a rotary oscillation or vibration of the steering wheel, which can be excited at a specific vehicle speed.
Nibble is driven by wheel and tire imbalance exciting a suspension recession mode, which then translates into steering gear
travel and finally steering wheel nibble.
Shudder (Judder)
Shudder is a low frequency oscillation of the entire steering system (tire, wheels, steering gear and linkage, etc.) when the
vehicle is steered during static-park or at low speeds. Shudder is very dependent on road surface.
Torque/Velocity Variation (Phasing/Effort Cycling)
Steering wheel torque variation occurring twice in one revolution is normally as a result of problems with the lower steering
column (intermediate shaft), but foul conditions generally result in either constant stiffness or single point stiffness.
Depending upon the orientation of the joints, the steering can feel asymmetric (torque falling off in one direction and rising in
the other) or else it can simply have pronounced peaks and troughs as the steering moves from lock to lock.
Wheel Fight (Kick Back)
Wheel fight is excess feedback of sudden road forces through the steering system and back to the driver. It is evaluated at all
vehicle speeds over cobblestones, rough roads, and potholes. The tires, wheels, and suspension generate forces into the
steering systems. Steering friction, hydraulic damping, hydraulic compliance, mechanical compliance, steering ratio, and assist
gain all affect how much is transmitted to the driver.
Page 741 of 3039

compartment, forward of the front suspension housing.
On petrol engine vehicles, a fluid cooler is located in front of the engine cooling radiator. Diesel models do not have a fluid
cooler.
Servotronic 2 adds electronic control and speed sensitive steering to the steering gear. The Servotronic 2 feature provides easy
and comfortable steering operation when parking, improved 'road feel' at increased road speeds and adds an integrated,
positive center feel feature which optimises steering wheel torque during high speed driving. The Servotronic 2 system is
controlled by software which is incorporated into the instrument cluster. The software responds to road speed signals and
controls the power assistance via a transducer valve located on the steering gear valve housing.
Page 750 of 3039
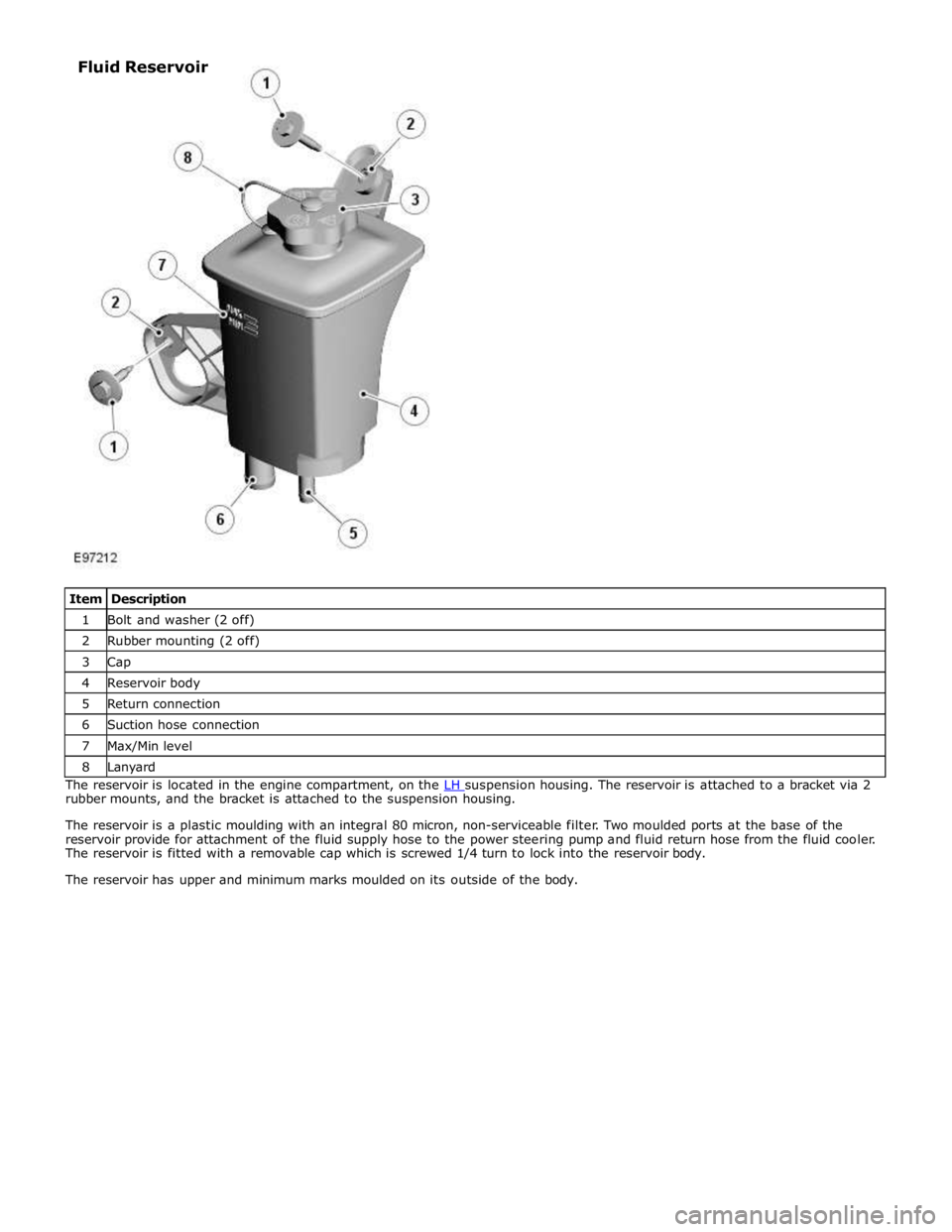
1 Bolt and washer (2 off) 2 Rubber mounting (2 off) 3 Cap 4 Reservoir body 5 Return connection 6 Suction hose connection 7 Max/Min level 8 Lanyard The reservoir is located in the engine compartment, on the LH suspension housing. The reservoir is attached to a bracket via 2 rubber mounts, and the bracket is attached to the suspension housing.
The reservoir is a plastic moulding with an integral 80 micron, non-serviceable filter. Two moulded ports at the base of the
reservoir provide for attachment of the fluid supply hose to the power steering pump and fluid return hose from the fluid cooler.
The reservoir is fitted with a removable cap which is screwed 1/4 turn to lock into the reservoir body.
The reservoir has upper and minimum marks moulded on its outside of the body. Fluid Reservoir
Page 757 of 3039

Suspension System - General Information, General Procedures).
www.JagDocs.com
Page 774 of 3039

Installation
1. Install the tie rod end, note the number of turns until adjacent to the
locknut.
2. CAUTION: Make sure that the ball joint ball does not rotate.
Connect the tie-rod end ball joint.
Clean the component mating faces.
Install a new nut and tighten to 133 Nm.
3. Tighten the tie-rod locking nut.
Clean the component mating faces.
Tighten the nut to 55 Nm.
4. Install the front wheel.
For additional information, refer to: Wheel and Tire (204-04 Wheels and Tires, Removal and Installation).
5. Using only four-wheel alignment equipment approved by Jaguar, check
and adjust the wheel alignment.
For additional information, refer to: Four-Wheel Alignment (204-00 Suspension System - General Information, General Procedures).
Page 1119 of 3039

Item Description 1 Filler cap 2 Vent hose connection 3 Expansion hose connection 4 Level sensor The expansion tank is installed in the engine compartment, on the LH upper suspension housing.
A filler cap and level sensor are incorporated into the expansion tank. A MAX level marking is molded into the interior of the
tank below the filler cap. Cold fill levels are molded onto the exterior of the tank.
The expansion tank provides the following functions:
Service fill.
Coolant expansion during warm-up.
Air separation during operation.
System pressurization by the filler cap.
The expansion tank has an air space of approximately 0.5 liter (1.06 US pints), above the MAX level, to allow for coolant
expansion. EXPANSION TANK