2010 HUMMER H3 warning
[x] Cancel search: warningPage 149 of 410
Lighting 6-5
During that delay, the instrument
panel cluster may not be as bright
as usual. Make sure the instrument
panel brightness control is in the
full bright position. SeeInstrument
Panel Illumination Control
on
page 6‑7.
Hazard Warning Flashers
|
(Hazard Warning Flasher):
Press this button located on the
instrument panel, to make the front
and rear turn signal lamps flash on
and off. This warns others that you
are having trouble.
Press
|again to turn the
flashers off.
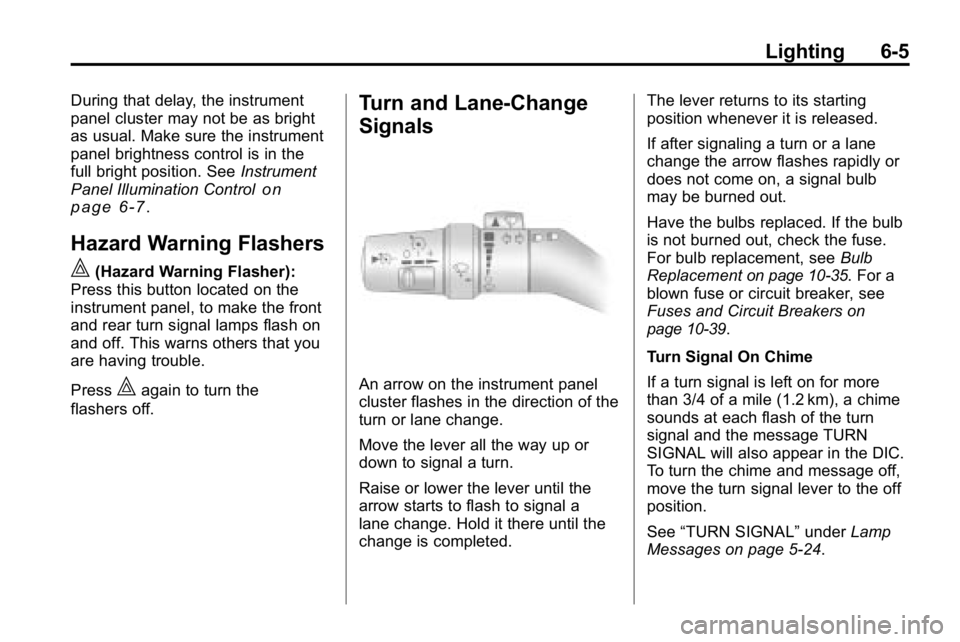
Turn and Lane-Change
Signals
An arrow on the instrument panel
cluster flashes in the direction of the
turn or lane change.
Move the lever all the way up or
down to signal a turn.
Raise or lower the lever until the
arrow starts to flash to signal a
lane change. Hold it there until the
change is completed. The lever returns to its starting
position whenever it is released.
If after signaling a turn or a lane
change the arrow flashes rapidly or
does not come on, a signal bulb
may be burned out.
Have the bulbs replaced. If the bulb
is not burned out, check the fuse.
For bulb replacement, see
Bulb
Replacement
on page 10‑35. For a
blown fuse or circuit breaker, see
Fuses and Circuit Breakers
on
page 10‑39.
Turn Signal On Chime
If a turn signal is left on for more
than 3/4 of a mile (1.2 km), a chime
sounds at each flash of the turn
signal and the message TURN
SIGNAL will also appear in the DIC.
To turn the chime and message off,
move the turn signal lever to the off
position.
See “TURN SIGNAL” underLamp
Messages on page 5‑24.
Page 155 of 410

Infotainment System 7-1
Infotainment
System
Introduction
Introduction . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-1
Theft-Deterrent Feature . . . . . . . 7-2
Operation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-2
Radio
AM-FM Radio . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-5
Satellite Radio . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-6
Radio Reception . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-9
Fixed Mast Antenna . . . . . . . . . 7-10
Satellite Radio Antenna . . . . . . 7-10
Audio Players
CD Player . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-10
Phone
Bluetooth . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 7-15
Introduction
Determine which radio the vehicle
has and read the following pages to
become familiar with its features.
{WARNING
Taking your eyes off the road
for extended periods could
cause a crash resulting in injury
or death to you or others. Do not
give extended attention to
entertainment tasks while driving.
This system provides access to
many audio and non‐audio listings.
To minimize taking your eyes off the
road while driving, do the following
while the vehicle is parked:
.Become familiar with the
operation and controls of the
audio system.
.Set up the tone, speaker
adjustments, and preset radio
stations. For more information, see
Defensive
Driving on page 9‑2.
Notice: Contact your dealer
before adding any equipment.
Adding audio or communication
equipment could interfere with
the operation of the vehicle's
engine, radio, or other systems,
and could damage them. Follow
federal rules covering mobile
radio and telephone equipment.
The vehicle has Retained
Accessory Power (RAP). With RAP,
the audio system can be played
even after the ignition is turned off.
See Retained Accessory Power
(RAP)
on page 9‑35for more
information.
For vehicles with a navigation radio
system, see the separate Navigation
System manual.
Page 186 of 410

9-2 Driving and Operating
Fuels in Foreign Countries . . . 9-65
Fuel Additives . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-65
Fuel E85 (85% Ethanol) . . . . . 9-66
Filling the Tank . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-68
Filling a Portable FuelContainer . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-69
Towing
General TowingInformation . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-70
Driving Characteristics and Towing Tips . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-70
Trailer Towing . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-74
Towing Equipment . . . . . . . . . . . 9-78
Trailer Recommendations . . . . 9-81
Conversions and Add-Ons
Add-On Electrical Equipment . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 9-81
Driving Information
Defensive Driving
Defensive driving means “always
expect the unexpected.” The
first step in driving defensively is
to wear your safety belt, see Safety
Belts on page 3‑10.
{WARNING
Assume that other road users
(pedestrians, bicyclists, and other
drivers) are going to be careless
and make mistakes. Anticipate
what they might do and be ready.
In addition:
.Allow enough following
distance between you and
the driver in front of you.
.Focus on the task of driving.
(Continued)
WARNING (Continued)
Driver distraction can cause
collisions resulting in injury or
possible death. These simple
defensive driving techniques
could save your life.
Drunk Driving
{WARNING
Drinking and then driving is
very dangerous. Your reflexes,
perceptions, attentiveness, and
judgment can be affected by even
a small amount of alcohol. You
can have a serious —or even
fatal —collision if you drive after
drinking. Do not drink and drive or
ride with a driver who has been
drinking. Ride home in a cab; or if
you are with a group, designate a
driver who will not drink.
Page 187 of 410

Driving and Operating 9-3
Death and injury associated with
drinking and driving is a global
tragedy.
Alcohol affects four things that
anyone needs to drive a vehicle:
judgment, muscular coordination,
vision, and attentiveness.
Police records show that
almost 40 percent of all motor
vehicle-related deaths involve
alcohol. In most cases, these
deaths are the result of someone
who was drinking and driving.
In recent years, more than
17,000 annual motor vehicle-related
deaths have been associated with
the use of alcohol, with about
250,000 people injured.
For persons under 21, it is against
the law in every U.S. state to drink
alcohol. There are good medical,
psychological, and developmental
reasons for these laws.
The obvious way to eliminate the
leading highway safety problem is
for people never to drink alcohol
and then drive.Medical research shows that
alcohol in a person's system
can make crash injuries worse,
especially injuries to the brain,
spinal cord, or heart. This means
that when anyone who has been
drinking
—driver or passenger —is
in a crash, that person's chance of
being killed or permanently disabled
is higher than if the person had not
been drinking.
Control of a Vehicle
The following three systems
help to control the vehicle while
driving —brakes, steering, and
accelerator. At times, as when
driving on snow or ice, it is easy to
ask more of those control systems
than the tires and road can provide.
Meaning, you can lose control of
the vehicle. See Traction Control
System (TCS)
on page 9‑52and
StabiliTrak System on page 9‑53. Adding non‐dealer/non‐retailer
accessories can affect vehicle
performance. See
Accessories and
Modifications on page 10‑3.
Braking
See Brake System Warning Lighton page 5‑14.
Braking action involves perception
time and reaction time. Deciding to
push the brake pedal is perception
time. Actually doing it is
reaction time.
Average reaction time is about
three‐fourths of a second. But that is
only an average. It might be less
with one driver and as long as
two or three seconds or more with
another. Age, physical condition,
alertness, coordination, and
eyesight all play a part. So do
alcohol, drugs, and frustration. But
even in three‐fourths of a second,
a vehicle moving at 100 km/h
(60 mph) travels 20 m (66 ft).
Page 190 of 410

9-6 Driving and Operating
Turn the steering wheel 8 to 13 cm
(3 to 5 inches), about one-eighth
turn, until the right front tire contacts
the pavement edge. Then turn the
steering wheel to go straight down
the roadway.
Loss of Control
Let us review what driving experts
say about what happens when the
three control systems—brakes,
steering, and acceleration —do not
have enough friction where the tires
meet the road to do what the driver
has asked.
In any emergency, do not give up.
Keep trying to steer and constantly
seek an escape route or area of
less danger.
Skidding
In a skid, a driver can lose control of
the vehicle. Defensive drivers avoid
most skids by taking reasonable
care suited to existing conditions,
and by not overdriving those
conditions. But skids are always
possible.
The three types of skids correspond
to the vehicle's three control
systems. In the braking skid, the
wheels are not rolling. In the
steering or cornering skid, too much
speed or steering in a curve causes
tires to slip and lose cornering force.
And in the acceleration skid, too
much throttle causes the driving
wheels to spin.
If the vehicle starts to slide, ease
your foot off the accelerator pedal
and quickly steer the way you
want the vehicle to go. If you start
steering quickly enough, the vehicle
may straighten out. Always be ready
for a second skid if it occurs. Of course, traction is reduced when
water, snow, ice, gravel, or other
material is on the road. For safety,
slow down and adjust your driving to
these conditions. It is important to
slow down on slippery surfaces
because stopping distance is longer
and vehicle control more limited.
While driving on a surface with
reduced traction, try your best to
avoid sudden steering, acceleration,
or braking, including reducing
vehicle speed by shifting to a lower
gear. Any sudden changes could
cause the tires to slide. You might
not realize the surface is slippery
until the vehicle is skidding. Learn to
recognize warning clues
—such as
enough water, ice, or packed snow
on the road to make a mirrored
surface —and slow down when you
have any doubt.
Remember: Antilock brakes help
avoid only the braking skid.
Page 192 of 410

9-8 Driving and Operating
Loading Your Vehicle for
Off-Road Driving
{WARNING
.Cargo on the load floor piled
higher than the seatbacks
can be thrown forward during
a sudden stop. You or your
passengers could be injured.
Keep cargo below the top of
the seatbacks.
.Unsecured cargo on the load
floor can be tossed about
when driving over rough
terrain. You or your
passengers can be struck
by flying objects. Secure
the cargo properly.(Continued)
WARNING (Continued)
.Heavy loads on the roof raise
the vehicle's center of gravity,
making it more likely to roll
over. You can be seriously or
fatally injured if the vehicle
rolls over. Put heavy loads
inside the cargo area, not on
the roof. Keep cargo in the
cargo area as far forward and
low as possible.
There are some important things to
remember about how to load your
vehicle.
.The heaviest things should be
on the floor, forward of the rear
axle. Put heavier items as far
forward as you can.
.Be sure the load is properly
secured, so things are not
tossed around. You will find other important
information under
Vehicle Load
Limits
on page 9‑27and Tireson
page 10‑44.
Environmental Concerns
Off-road driving can provide
wholesome and satisfying
recreation. However, it also
raises environmental concerns.
We recognize these concerns
and urge every off-roader to follow
these basic rules for protecting the
environment:
.Always use established trails,
roads, and areas that have been
specially set aside for public
off-road recreational driving and
obey all posted regulations.
.Avoid any driving practice
that could damage shrubs,
flowers, trees, or grasses or
disturb wildlife. This includes
wheel-spinning, breaking down
trees, or unnecessary driving
through streams or over soft
ground.
Page 196 of 410

9-12 Driving and Operating
For mounds, washouts, loose
up-hill slopes, ditches, etc.
When wheel spin occurs as the
vehicle is moving, the driver
may notice a slight shaking or
shuddering of the vehicle. This
should be stopped as soon as
possible to prevent damage to
vehicle components. This is the
indication that a loss of traction is
occurring on this terrain. The
operator should:
1. Reduce speed and apply thebrakes.
2. Assess the terrain properly and adjust vehicle speed and gear
ranges accordingly: Four‐Wheel
High position for higher speeds
and Four‐Wheel‐Low Lock for
more torque and lower speeds.
Transmission 1 (First) gear is
generally recommended. 3. Apply slight pressure to the
brake when the shaking or
shuddering sensation is felt,
keeping the vehicle moving in
a controlled manner.
4. Be prepared to alternate between braking and
accelerating through the
adverse terrain.
Getting Familiar with Off-Road
Driving
It is a good idea to practice in an
area that is safe and close to home
before you go into the wilderness.
Off-roading requires some new and
different skills.
Tune your senses to different kinds
of signals. Your eyes need to
constantly sweep the terrain for
unexpected obstacles. Your ears
need to listen for unusual tire or
engine sounds. Use your arms,
hands, feet, and body to respond to
vibrations and vehicle bounce. Controlling the vehicle is the key to
successful off-road driving. One of
the best ways to control the vehicle
is to control the speed. At higher
speeds:
.You approach things faster and
have less time to react.
.There is less time to scan the
terrain for obstacles.
.The vehicle has more bounce
when driving over obstacles.
.More braking distance is
needed, especially on an
unpaved surface.
{WARNING
When you are driving off-road,
bouncing and quick changes in
direction can easily throw you
out of position. This could cause
you to lose control and crash.
So, whether you are driving on
or off the road, you and your
passengers should wear safety
belts.
Page 199 of 410

Driving and Operating 9-15
{WARNING
Many hills are simply too steep
for any vehicle. If you drive up
them, you will stall. If you drive
down them, you cannot control
your speed. If you drive across
them, you will roll over. You could
be seriously injured or killed.
If you have any doubt about the
steepness, do not drive the hill.
Approaching a Hill
When you approach a hill, decide if
it is too steep to climb, descend,
or cross. Steepness can be hard to
judge. On a very small hill, for
example, there may be a smooth,
constant incline with only a small
change in elevation where you can
easily see all the way to the top.
On a large hill, the incline may get
steeper as you near the top, but you
might not see this because the crest
of the hill is hidden by bushes,
grass, or shrubs.Consider this as you approach a hill:
.Is there a constant incline,
or does the hill get sharply
steeper in places?
.Is there good traction on the
hillside, or will the surface cause
tire slipping?
.Is there a straight path up or
down the hill so you will not
have to make turning
maneuvers?
.Are there obstructions on the hill
that can block your path, such
as boulders, trees, logs, or ruts?
.What is beyond the hill? Is there
a cliff, an embankment, a
drop-off, a fence? Get out and
walk the hill if you do not know.
It is the smart way to find out.
.Is the hill simply too rough?
Steep hills often have ruts,
gullies, troughs, and exposed
rocks because they are more
susceptible to the effects of
erosion.See
Hill Start Assist (HSA)
on
page 9‑52for information on
vehicles stopped on a grade.
Driving Uphill
Once you decide it is safe to drive
up the hill:
.Use transmission and transfer
case low gear and get a firm grip
on the steering wheel.
.Get a smooth start up the hill
and try to maintain speed. Not
using more power than needed
can avoid spinning the wheels or
sliding.
.Let the traction system work to
control any wheel slippage. The
traction control system allows for
moderate wheel spin with some
capability to dig in and power up
the hill.