2009 NISSAN LATIO engine oil
[x] Cancel search: engine oilPage 14 of 4331

AT
N
O P
• The valve body contains precision parts and requires extreme care when parts are removed and serviced.
Place disassembled valve body parts in order for easier and proper assembly. Care will also prevent springs
and small parts from becoming scattered or lost.
• Properly installed valves, sleeves, plugs, etc. will slide along bores in valve body under their own weight.
• Before assembly, apply a coat of recommended ATF to all parts. Apply petroleum jelly to protect O-rings and
seals, or hold bearings and washers in pl ace during assembly. Do not use grease.
• Extreme care should be taken to avoid damage to O-rings, seals and gaskets when assembling.
• Clean or replace ATF cooler if excessive foreign material is found in oil pan or clogging strainer. Refer to AT-18, " A/T Fluid Cooler Cleaning " .
• After overhaul, refill the A/T with new ATF.
• When the A/T drain plug is removed, only some of the fluid is drained. Old A/T fluid will remain in torque con- verter and ATF cooling system.
Always follow the procedures under “Changing A/T Fluid” in the AT section when changing A/T fluid. Refer to
AT-17, " Changing A/T Fluid " ,
AT-17, " Checking A/T Fluid " .
Service Notice or Precaution INFOID:0000000004305292
ATF COOLER SERVICE If A/T fluid contains frictional material (clutches, bands, etc.), or if an A/T is repaired, overhauled, or replaced,
inspect and clean the A/T oil cooler mounted in the radiator or replace the radiator. Flush cooler lines using
cleaning solvent and compressed air after repair. Check Serv ice Bulletins for latest A/T oil cooler cleaning pro-
cedure. For radiator replacement, refer to CO-16, " Removal and Installation " (HR16DE engine models),
CO-38, " Removal and Installation " (MR18DE engine models).
TORQUE CONVERTER SERVICE The torque converter should be replaced under any of the following conditions:
• External leaks in the hub weld area.
• Converter hub is scored or damaged.
• Converter pilot is broken, damaged or fits poorly into crankshaft.
• Steel particles are found after flushing the cooler and cooler lines.
• Pump is damaged or steel particles are found in the converter.
• Vehicle has TCC shudder and/or no TCC apply. Replace only after all hydraulic and electrical diagnoses
have been made. (Converter clutch material may be glazed.)
• Converter is contaminated with engi ne coolant containing antifreeze.
• Internal malfunction of stator roller clutch.
• Heavy clutch debris due to overheating (blue converter).
• Steel particles or clutch lining material found in flui d filter or on magnet when no internal parts in unit are
worn or damaged — indicates that lining material came from converter.
The torque converter should not be replaced if:
• The fluid has an odor, is discolored, and there is no evidence of metal or clutch facing particles.
• The threads in one or more of the converter bolt holes are damaged.
• A/T malfunction did not display evidence of damaged or worn internal parts, steel particles or clutch plate lin-
ing material in unit and inside the fluid filter.
• Vehicle has been exposed to high mileage (only). The e xception may be where the torque converter clutch
dampener plate lining has seen excess wear by vehicles operated in heavy and/or constant traffic, such as
taxi, delivery or police use.
OBD-II SELF-DIAGNOSIS • A/T self-diagnosis is performed by the TCM in combination with the ECM. The results can be read through the blinking pattern of the OD OFF indicator lamp or the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL). Refer to the table
on AT-83, " Diagnosis Procedure without CONSULT-III " for the indicator used to display each self-diagnostic
result.
• The self-diagnostic results indicated by the MIL ar e automatically stored in both the ECM and TCM memo-
ries.
Always perform the procedure “HOW TO ERASE DTC” on AT-39, " OBD-II Diagnostic Trouble Code
(DTC) " to complete the repair and avo
id unnecessary blinking of the MIL.
• The following self-diagnostic items can be detected us ing ECM self-diagnostic results mode* only when the
OD OFF indicator lamp does not indicate any malfunctions.
- PNP switch
- A/T 1st, 2nd, 3rd, or 4th gear function
*: For details of OBD-II, refer to AT-39 .
Page 16 of 4331
AT
N
O P
PREPARATION
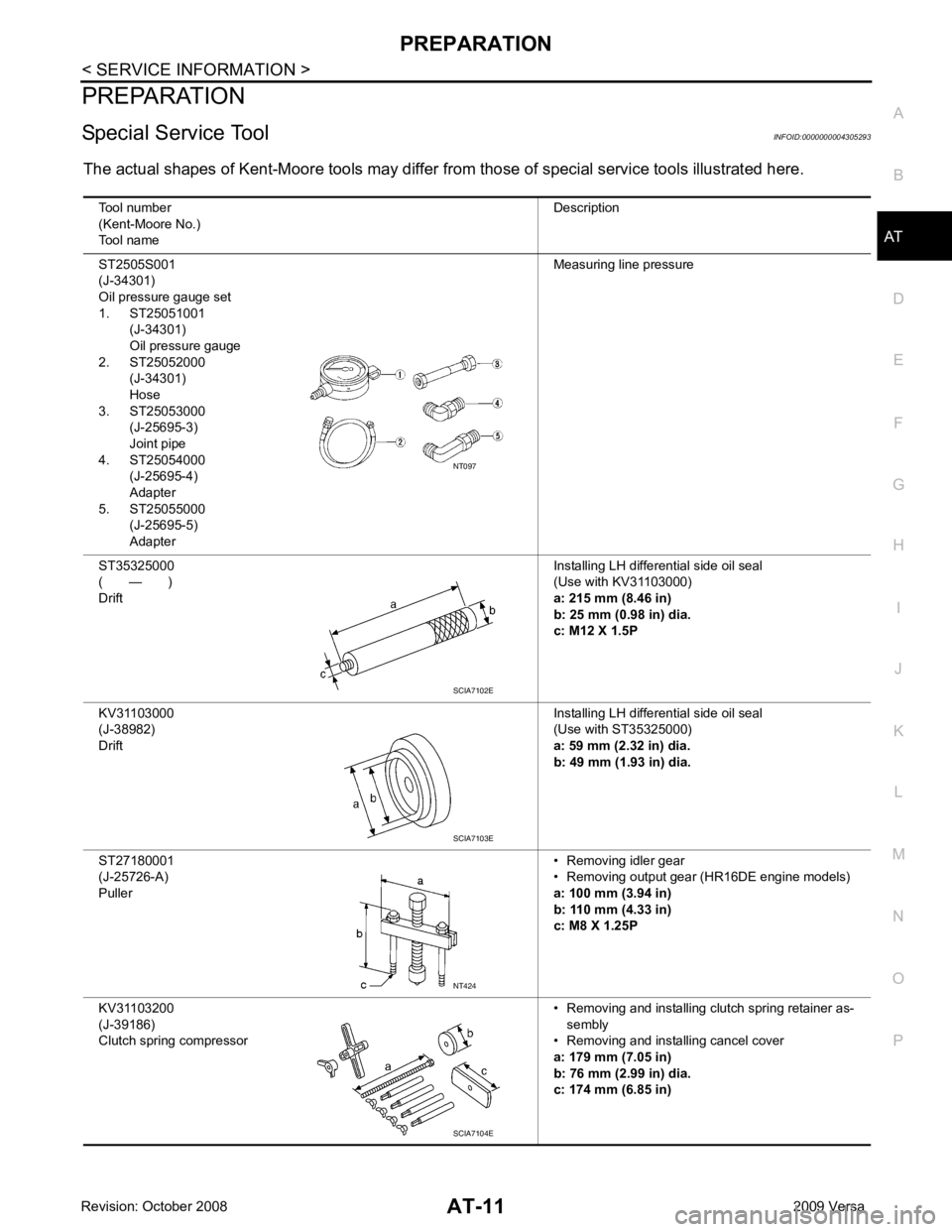
Special Service Tool INFOID:0000000004305293
The actual shapes of Kent-Moore tools may differ fr om those of special service tools illustrated here.
Tool number
(Kent-Moore No.)
Tool name Description
ST2505S001
(J-34301)
Oil pressure gauge set
1. ST25051001 (J-34301)
Oil pressure gauge
2. ST25052000 (J-34301)
Hose
3. ST25053000
(J-25695-3)
Joint pipe
4. ST25054000
(J-25695-4)
Adapter
5. ST25055000
(J-25695-5)
Adapter Measuring line pressure
ST35325000
( — )
Drift Installing LH differential side oil seal
(Use with KV31103000)
a: 215 mm (8.46 in)
b: 25 mm (0.98 in) dia.
c: M12 X 1.5P
KV31103000
(J-38982)
Drift Installing LH differential side oil seal
(Use with ST35325000)
a: 59 mm (2.32 in) dia.
b: 49 mm (1.93 in) dia.
ST27180001
(J-25726-A)
Puller • Removing idler gear
• Removing output gear (HR16DE engine models)
a: 100 mm (3.94 in)
b: 110 mm (4.33 in)
c: M8 X 1.25P
KV31103200
(J-39186)
Clutch spring compressor • Removing and installing clutch spring retainer as-
sembly
• Removing and installing cancel cover
a: 179 mm (7.05 in)
b: 76 mm (2.99 in) dia.
c: 174 mm (6.85 in) SCIA7102E
NT424
SCIA7104E
Page 19 of 4331
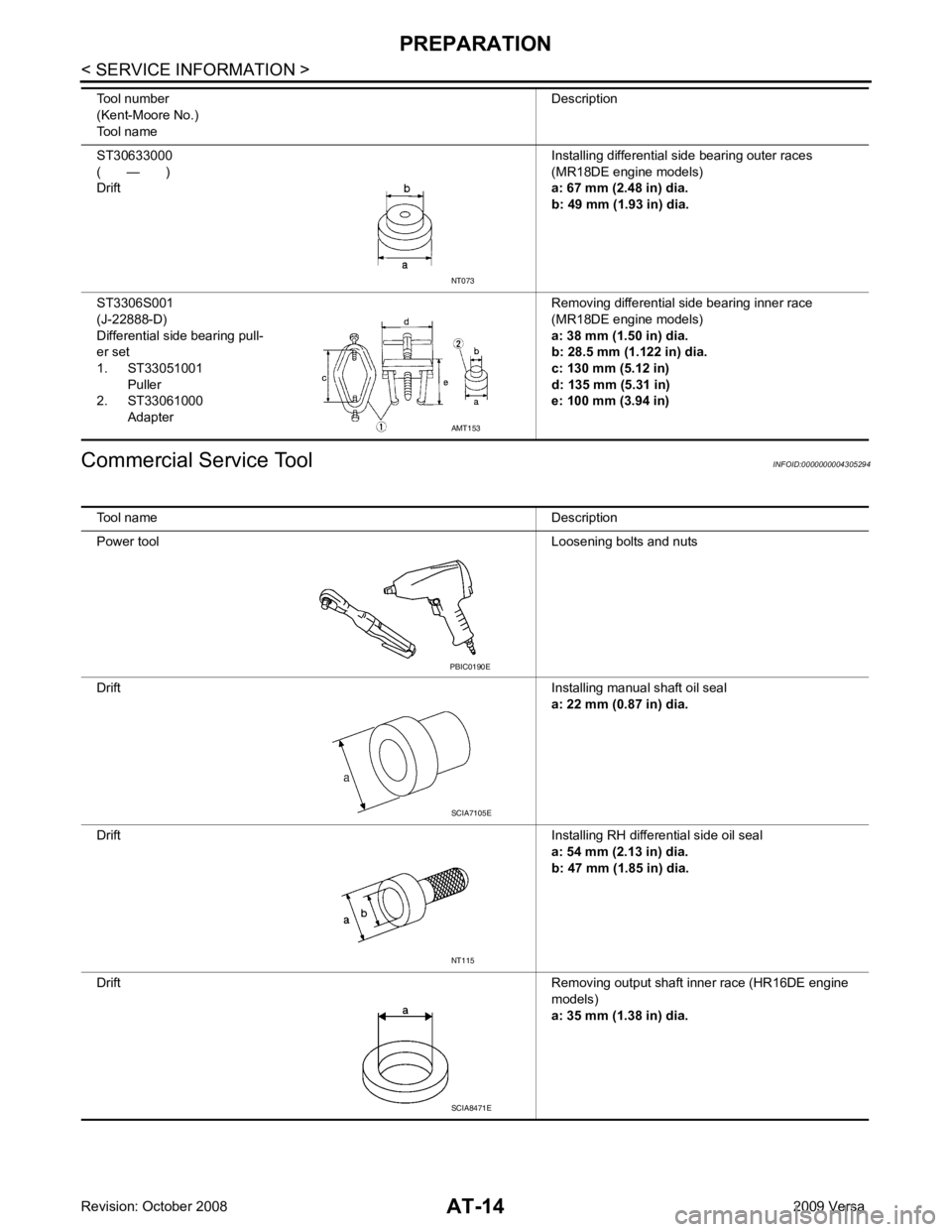
AMT153
Tool name Description
Power tool Loosening bolts and nuts
Drift Installing manual shaft oil seal
a: 22 mm (0.87 in) dia.
Drift Installing RH differential side oil seal
a: 54 mm (2.13 in) dia.
b: 47 mm (1.85 in) dia.
Drift Removing output shaft inner race (HR16DE engine
models)
a: 35 mm (1.38 in) dia. NT115
SCIA8471E
Page 42 of 4331

AT
N
O P
Control Valve
INFOID:0000000004305307
FUNCTION OF CONTROL VALVES
Centrifugal Cancel Mechanism INFOID:0000000004305308
FUNCTION The centrifugal cancel mechanism is a mechanism to c ancel the centrifugal hydraulic pressure instead of the
conventional check balls. It cancels the centrifugal hy draulic pressure which is generated as high clutch drum
rotates, and it allows for preventing high clutch from dragging and for providing stable high clutch piston press-
ing force in all revolution speeds.
STRUCTURE/OPERATION Valve name Function
Pressure regulator valve, plug and sleeve
plug Regulates oil discharged from the oil pump to provide optimum line pressure for all driving
conditions.
Pressure modifier valve and sleeve Used as a signal supplementary valve to the pressure regulator valve. Regulates pres- sure-modifier pressure (signal pressure) which controls optimum line pressure for all driv-
ing conditions.
Pilot valve Regulates line pressure to maintain a constant pilot pressure level which controls lock-up mechanism, overrun clutch, shift timing.
Accumulator control valve Regulates accumulator back-pressure to pressure suited to driving conditions.
Manual valve Directs line pressure to oil circuits corresponding to select positions. Hydraulic pressure drains when the shift lever is in Neutral.
Shift valve A Simultaneously switches three oil circuits using output pressure of shift solenoid valve A to meet driving conditions (vehicle speed, throttle opening, etc.).
Provides automatic downshifting and upshifting (1st → 2nd → 3rd → 4th gears/4th → 3rd
→ 2nd → 1st gears) in combination with shift valve B.
Shift valve B Simultaneously switches two oil circuits using output pressure of shift solenoid valve B in relation to driving conditions (vehicle speed, throttle opening, etc.).
Provides automatic downshifting and upshifting (1st → 2nd → 3rd → 4th gears/4th → 3rd
→ 2nd → 1st gears) in combination with shift valve A.
Overrun clutch control valve Switches hydraulic circuits to prevent engagement of the overrun clutch simultaneously with application of the brake band in D4. (Interlocking occurs if the overrun clutch engages
during D 4.)
1st reducing valve Reduces low & reverse brake pressure to dampen engine-brake shock when downshift- ing from the 1st position 12 to 1 1.
Overrun clutch reducing valve Reduces oil pressure directed to the overrun clutch and prevents engine-brake shock. In the 1st and 2nd positions, line pressure acts on the overrun clutch reducing valve to
increase the pressure-regulating point, with resultant engine brake capability.
Torque converter relief valve Prevents an excessive rise in torque converter pressure.
Torque converter clutch control valve, plug
and sleeve Activates or inactivates the lock-up function.
Also provides smooth lock-up through transient application and release of the lock-up
system.
1-2 accumulator valve and piston Lessens the shock find when the 2nd gear band servo contracts, and provides smooth shifting.
3-2 timing valve Switches the pace that oil pressure is released depending on vehicle speed; maximizes the high clutch release timing, and allows for soft downshifting.
Shuttle valve Determines if the overrun clutch solenoid valve should control the 3-2 timing valve or the overrun clutch control valve and switches between the two.
Cooler check valve At low speeds and with a small load when a little heat is generated, saves the volume of cooler flow, and stores the oil pressure for lock-up.
Page 48 of 4331

AT
N
O P
�z
: Solenoid ON
× : Solenoid OFF
–: Non-standard condition
Line Pressure Solenoid Valve If non-standard solenoid signal is sent to TCM, line pre ssure solenoid valve is turned OFF to achieve maxi-
mum oil pressure.
Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid Valve If non-standard solenoid signal is sent to TCM, torque conv erter clutch solenoid valve is turned OFF to release
lock-up.
Overrun Clutch Solenoid Valve If non-standard solenoid signal is sent to TCM, overr un clutch solenoid valve is turned OFF to engage overrun
clutch. This will result in more effective engine brake during deceleration.
How to Perform Trouble Diagnosis for Quick and Accurate Repair INFOID:0000000004305316
INTRODUCTION The TCM receives a signal from the vehicle speed sensor, accelera-
tor pedal position sensor or PNP switch and provides shift control or
lock-up control via A/T solenoid valves.
The TCM also communicates with the ECM by means of a signal
sent from sensing elements used wit h the OBD-related parts of the
A/T system for malfunction-diagnostic purposes. The TCM is capa-
ble of diagnosing malfunctioning parts while the ECM can store mal-
functions in its memory.
Input and output signals must always be correct and stable in the
operation of the A/T system. T he A/T system must be in good oper-
ating condition and be free of valve seizure, solenoid valve malfunc-
tion, etc.
It is much more difficult to diagnose a malfunction t hat occurs intermittently rather than continuously. Most
intermittent malfunctions are caused by poor electric c onnections or improper wiring. In this case, careful
checking of suspected circuits may hel p prevent the replacement of good parts.
Shift position
Normal
Malfunction in solenoid
valve A Malfunction in solenoid
valve B Malfunction in solenoid
valves A and B
A B Gear A B Gear A B Gear A B Gear
“D” position �z �z
1st –�z→×
3rd �z
→× –
3rd – –
3rd
×
�z2nd – �z→× × – – –
× × 3rd – x ×– – –
�z ×4th – x �z→× – – –
“2” position �z �z
1st –�z→× �z→× – – –
× �z2nd – �z→× × – – –
× × 3rd – x ×– – –
“1” position �z �z
1st –�z→× �z→× – – –
× �z2nd – �z→× × – – –
× × 3rd – x ×– – –
Page 56 of 4331
AT
N
O P
Inspections Before Trouble Diagnosis
INFOID:0000000004305319
A/T FLUID CHECK
Fluid Leakage and Fluid Level Check Check fluid leakage and check the fluid level. Refer to AT-17, " Checking A/T Fluid " .
Fluid Condition Check Check the A/T fluid condition.
STALL TEST
Stall Test Procedure 1. Check ATF and engine oil levels. If necessary, add ATF and engine oil.
2. Drive vehicle for approximately 10 minutes or until ATF and engine oil reach operating temperature.
3. Set parking brake and block wheels.
4. Install a tachometer where it can be seen by driver during test. •It is good practice to mark the point of specified engine
rpm on indicator.
5. Start engine, apply foot brake, and place selector lever in “D” position.Fluid status Conceivable Cause Required Operation
Varnished (viscous
varnish state) Clutch, brake
scorched Replace the ATF and check the A/T
main unit and the vehicle for mal-
functions (wire harnesses, cooler
pipes, etc.)
Milky white or
cloudy Water in the ATFReplace the ATF and check for plac-
es where water is getting in.
Large amount of
metal powder mixed
in Unusual wear of
sliding parts within
A/T Replace the ATF and check for im-
proper operation of the A/T. SAT775B
Page 59 of 4331
AT-54< SERVICE INFORMATION >
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
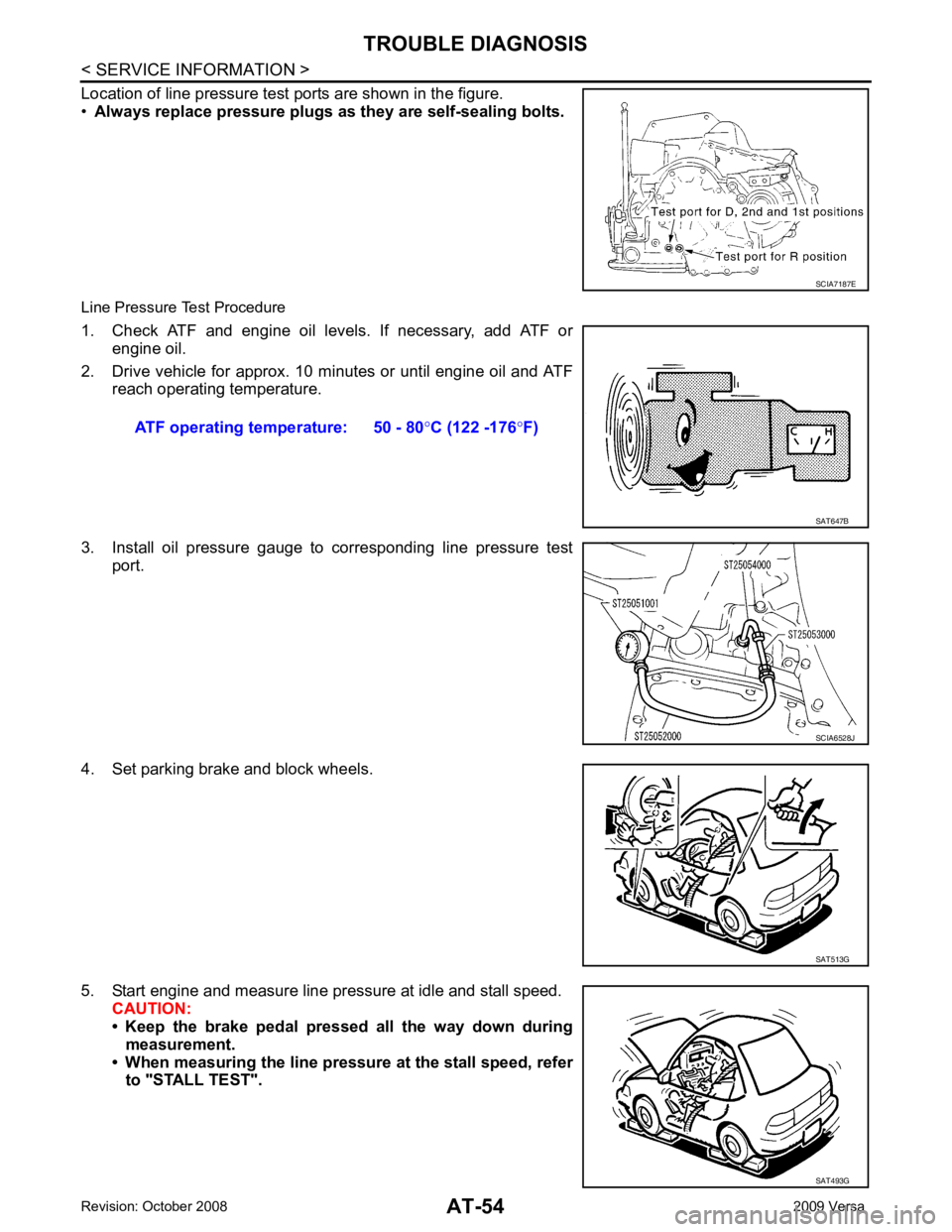
Location of line pressure test ports are shown in the figure.
• Always replace pressure plugs as they are self-sealing bolts.
Line Pressure Test Procedure
1. Check ATF and engine oil levels. If necessary, add ATF or engine oil.
2. Drive vehicle for approx. 10 minutes or until engine oil and ATF reach operating temperature.
3. Install oil pressure gauge to corresponding line pressure test port.
4. Set parking brake and block wheels.
5. Start engine and measure line pressure at idle and stall speed. CAUTION:
• Keep the brake pedal pressed all the way down during
measurement.
• When measuring the line pressure at the stall speed, refer to "STALL TEST". SCIA7187E
ATF operating temperature: 50 - 80
°C (122 -176 °F) SAT647B
SCIA6528J
SAT513G
SAT493G
Page 60 of 4331
AT
N
O P
Line Pressure
Judgement of Line Pressure Test
Road Test INFOID:0000000004305320
DESCRIPTION • The purpose of the test is to det ermine overall performance of A/T
and analyze causes of malfunctions.
• The road test consists of the following three parts:
1. Check before engine is started. Refer to AT-56 .
2. Check at idle. Refer to AT-56 .
3. Cruise test • Inspection all the item from Part 1 to Part 3. Refer to AT-58 ,
AT-61 and
AT-62 .
Engine speed
Line pressure [kPa (kg/cm
2
, psi)]
D, 2nd and 1st positions R position
Idle speed AT-373, " Line Pressure "
Stall speed
Judgement Suspected parts
At idle Line pressure is low in all positions. • Oil pump wear
• Control piston damage
• Pressure regulator valve or plug sticking
• Spring for pressure regulator valve damaged
• Fluid pressure leakage between oil strainer and pressure regulator valve
• Clogged strainer
Line pressure is low in particular posi-
tion. • Fluid pressure leakage between manual valve and particular clutch
• For example, line pressure is: − Low in “R” and “1 ” positions, but
− Normal in “D”, and “2” positions.
Therefore, fluid leakage exists at or around low and reverse brake circuit.
Refer to AT-22, " Shift Mechanism " .
Line pressure is high. • Accelerator pedal position signal malfunction • A/T fluid temperature sensor damaged
• Line pressure solenoid valve sticking
• Short circuit of line pressure solenoid valve circuit
• Pressure modifier valve sticking
• Pressure regulator valve or plug sticking
• Open in dropping resistor circuit
At stall
speed Line pressure is low. • Accelerator pedal position signal malfunction
• Line pressure solenoid valve sticking
• Short circuit of line pressure solenoid valve circuit
• Pressure regulator valve or plug sticking
• Pressure modifier valve sticking
• Pilot valve sticking