2009 CHERY TIGGO engine oil
[x] Cancel search: engine oilPage 42 of 1903

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine DIAGNOSIS & TESTING
Engine Performance Diagnostics
CONDITIONPOSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
Engine Does Not Start 1. Weak battery.
2. Corroded or loose battery
connections.
3. Faulty starter.
4. Faulty coil(s) or control unit.
5. Incorrect spark plug gap.
6. Contamination in fuel system.
7. Faulty fuel pump.
8. Incorrect timing.1. Test battery. Charge or replace if
necessary.
2. Clean and tighten battery
connections. Apply a coat of light
mineral grease to terminals.
3. Test starting system. Check for
codes. (Refer to Appropriate
Diagnostic Information)
4. Test and replace if needed. (Refer
to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
5. Set gap.
6. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
7. Test fuel pump and replace as
needed. (Refer to Appropriate
Diagnostic Information)
8. Check for a skipped timing belt.
Engine Stalls Or Idles Rough 1. Idle speed too low.
2. Incorrect fuel mixture.
3. Intake manifold leakage.
4. Faulty ignition coil(s).1. Test minimum air flow. (Refer to
Appropriate Diagnostic Information)
2. (Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
3. Inspect intake manifold, manifold
gasket, and vacuum hoses.
4. Test and replace if necessary.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
Engine Loss Of Power 1. Dirty or incorrectly gapped spark
plugs.
2. Contamination in fuel system.
3. Faulty fuel pump.
4. Incorrect valve timing.
5. Leaking cylinder head gasket.
6. Low compression.
7. Burned, warped, excessive
clearance, or pitted valves.
8. Plugged or restricted exhaust
system.
9. Faulty ignition coil(s).
10. Burned spark plugs.1. Clean spark plugs and set gap.
2. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
3. Test and replace if necessary.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
4. Correct valve timing.
5. Replace cylinder head gasket.
6. Test compression of each
cylinder.
7. Replace valves.
8. Perform exhaust restriction test.
Install new parts.
9. Test and replace if necessary.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
10. Replace spark plugs.
DIAGNOSIS & TESTING
02
02–13Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
Page 43 of 1903
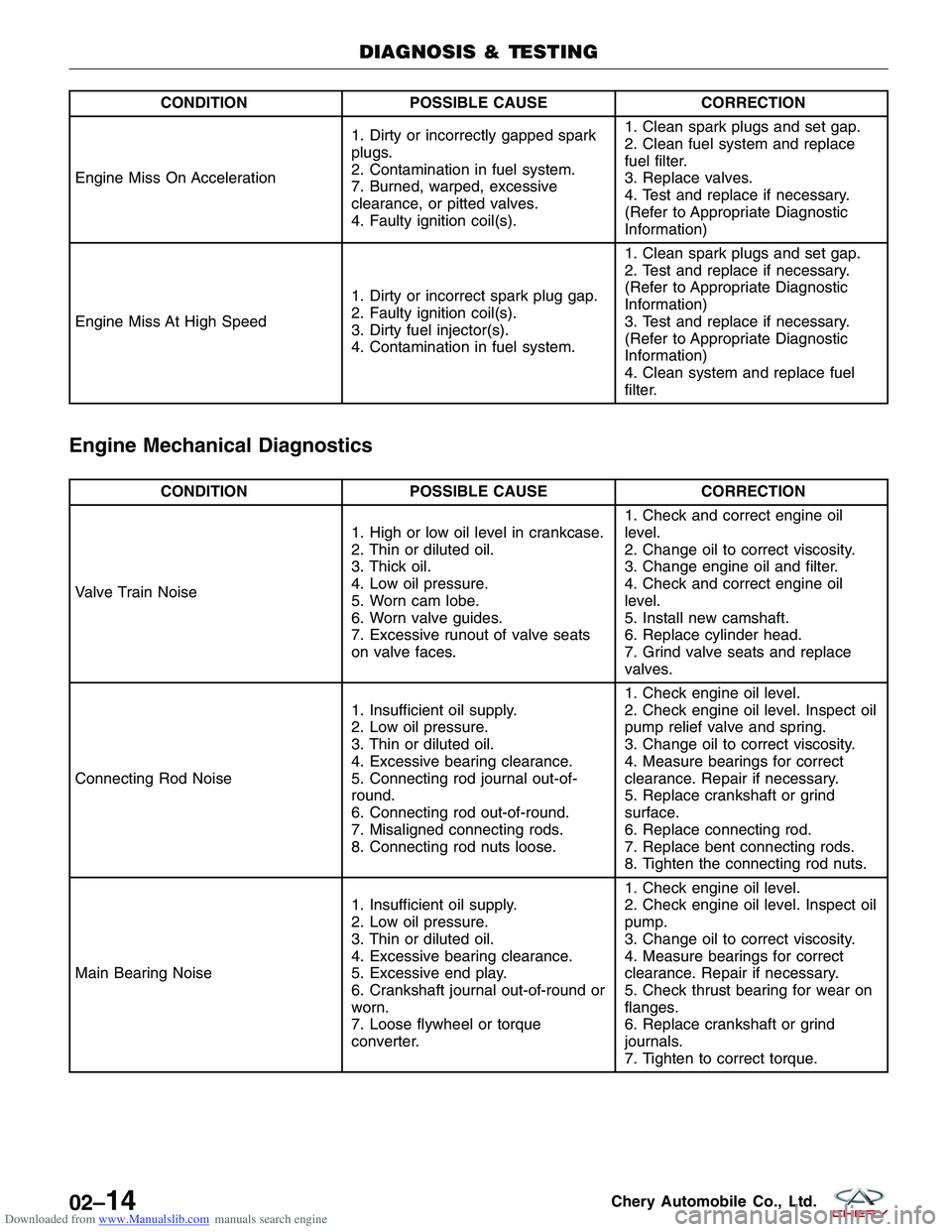
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine CONDITIONPOSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
Engine Miss On Acceleration 1. Dirty or incorrectly gapped spark
plugs.
2. Contamination in fuel system.
7. Burned, warped, excessive
clearance, or pitted valves.
4. Faulty ignition coil(s).1. Clean spark plugs and set gap.
2. Clean fuel system and replace
fuel filter.
3. Replace valves.
4. Test and replace if necessary.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
Engine Miss At High Speed 1. Dirty or incorrect spark plug gap.
2. Faulty ignition coil(s).
3. Dirty fuel injector(s).
4. Contamination in fuel system.1. Clean spark plugs and set gap.
2. Test and replace if necessary.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
3. Test and replace if necessary.
(Refer to Appropriate Diagnostic
Information)
4. Clean system and replace fuel
filter.
Engine Mechanical Diagnostics
CONDITION
POSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
Valve Train Noise 1. High or low oil level in crankcase.
2. Thin or diluted oil.
3. Thick oil.
4. Low oil pressure.
5. Worn cam lobe.
6. Worn valve guides.
7. Excessive runout of valve seats
on valve faces.1. Check and correct engine oil
level.
2. Change oil to correct viscosity.
3. Change engine oil and filter.
4. Check and correct engine oil
level.
5. Install new camshaft.
6. Replace cylinder head.
7. Grind valve seats and replace
valves.
Connecting Rod Noise 1. Insufficient oil supply.
2. Low oil pressure.
3. Thin or diluted oil.
4. Excessive bearing clearance.
5. Connecting rod journal out-of-
round.
6. Connecting rod out-of-round.
7. Misaligned connecting rods.
8. Connecting rod nuts loose.1. Check engine oil level.
2. Check engine oil level. Inspect oil
pump relief valve and spring.
3. Change oil to correct viscosity.
4. Measure bearings for correct
clearance. Repair if necessary.
5. Replace crankshaft or grind
surface.
6. Replace connecting rod.
7. Replace bent connecting rods.
8. Tighten the connecting rod nuts.
Main Bearing Noise 1. Insufficient oil supply.
2. Low oil pressure.
3. Thin or diluted oil.
4. Excessive bearing clearance.
5. Excessive end play.
6. Crankshaft journal out-of-round or
worn.
7. Loose flywheel or torque
converter.1. Check engine oil level.
2. Check engine oil level. Inspect oil
pump.
3. Change oil to correct viscosity.
4. Measure bearings for correct
clearance. Repair if necessary.
5. Check thrust bearing for wear on
flanges.
6. Replace crankshaft or grind
journals.
7. Tighten to correct torque.
DIAGNOSIS & TESTING
02–14Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
Page 44 of 1903
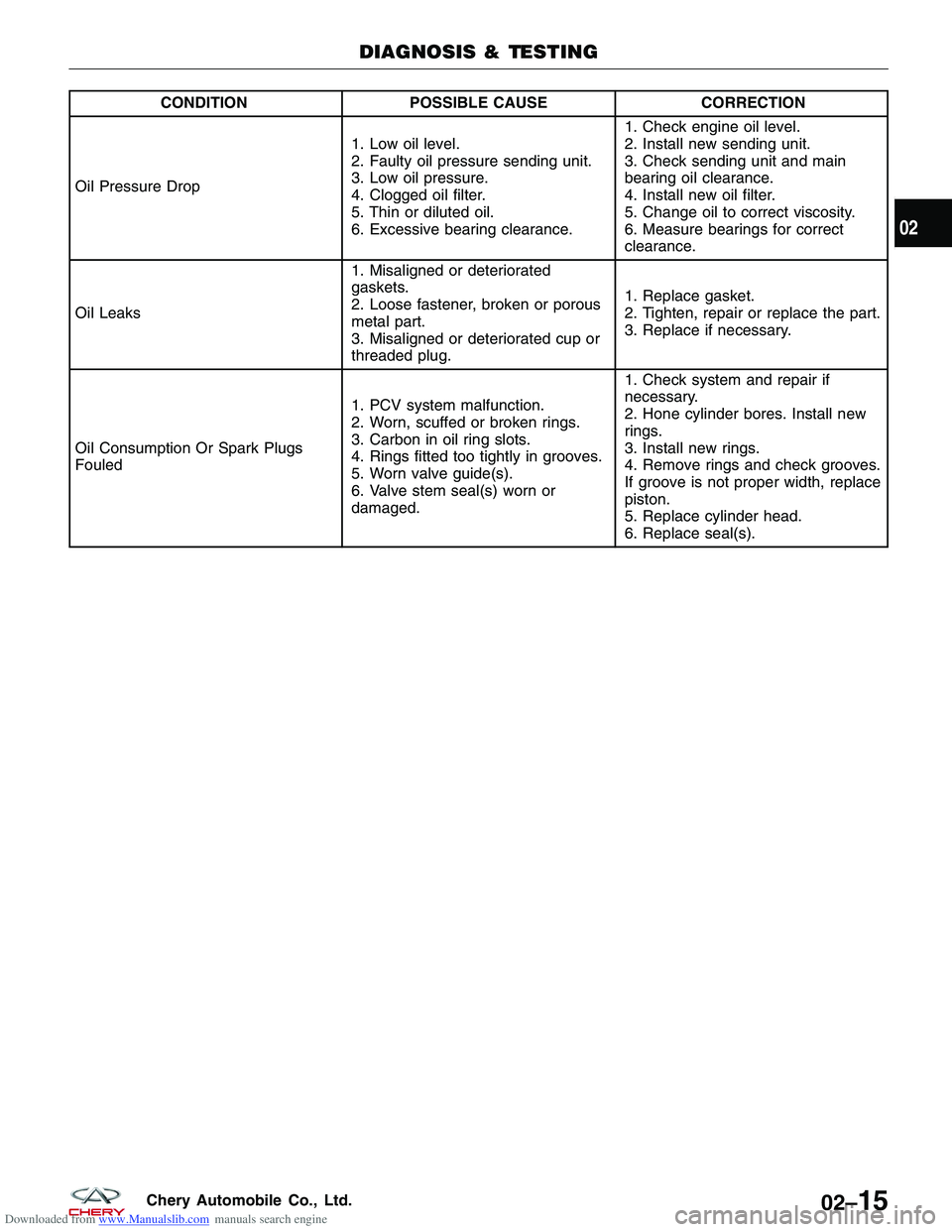
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine CONDITIONPOSSIBLE CAUSE CORRECTION
Oil Pressure Drop 1. Low oil level.
2. Faulty oil pressure sending unit.
3. Low oil pressure.
4. Clogged oil filter.
5. Thin or diluted oil.
6. Excessive bearing clearance.1. Check engine oil level.
2. Install new sending unit.
3. Check sending unit and main
bearing oil clearance.
4. Install new oil filter.
5. Change oil to correct viscosity.
6. Measure bearings for correct
clearance.
Oil Leaks 1. Misaligned or deteriorated
gaskets.
2. Loose fastener, broken or porous
metal part.
3. Misaligned or deteriorated cup or
threaded plug.1. Replace gasket.
2. Tighten, repair or replace the part.
3. Replace if necessary.
Oil Consumption Or Spark Plugs
Fouled 1. PCV system malfunction.
2. Worn, scuffed or broken rings.
3. Carbon in oil ring slots.
4. Rings fitted too tightly in grooves.
5. Worn valve guide(s).
6. Valve stem seal(s) worn or
damaged.1. Check system and repair if
necessary.
2. Hone cylinder bores. Install new
rings.
3. Install new rings.
4. Remove rings and check grooves.
If groove is not proper width, replace
piston.
5. Replace cylinder head.
6. Replace seal(s).
DIAGNOSIS & TESTING
02
02–15Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
Page 45 of 1903

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Cylinder Compression Pressure Test
•The result of a cylinder compression pressure test can be utilized to diagnose several engine malfunctions.
• Ensure the battery is completely charged and the engine starter motor is in good operating condition. Otherwise
the indicated compression pressures may not be valid for diagnostic purposes.
� Check engine oil level and add oil if necessary.
� Disconnect the spark plug wires.
� Remove all spark plugs from engine (as spark plugs are being removed, check electrodes for abnormal
firing indicators fouled, hot, oily, etc.).
� Record cylinder number of each spark plug for future reference.
� Disconnect fuel injector electrical connectors.
� Be sure throttle blade is fully open during the compression check.
� Insert compression pressure adaptor or the equivalent into each spark plug hole in cylinder head.
� Crank engine until maximum pressure is reached on gauge. Record each cylinder pressure.
� Compression should not be less than 1000 kPa and not vary more than 25 percent from cylinder to cylinder.
� If one or more cylinders have abnormally low compression pressures, repeat the compression test.
� If the same cylinder or cylinders repeat an abnormally low reading on the second compression test, it could indicate the existence of a problem with the cylinder in question.
NOTE :
The recommended compression pressures are to be used only as a guide to diagnosing engine problems. An engine
should not be disassembled to determine the cause of low compression unless some malfunction is present.
Cylinder Head Gasket Test
• A cylinder head gasket leak can be located between adjacent cylinders, between a cylinder and the adjacent
water jacket or from an oil passage to the exterior of the engine.
• Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket leaking between adjacent cylinders are:
� Loss of engine power
� Engine misfiring
� Poor fuel economy
• Possible indications of the cylinder head gasket leaking between a cylinder and an adjacent water jacket are:
� Engine overheating
� Loss of coolant
� Excessive steam (white smoke) emitting from exhaust
� Coolant foaming
DIAGNOSIS & TESTING
02–16Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
Page 52 of 1903

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Cylinder Head
Removal & Installation
NOTE :
Replacement cylinder head comes complete with valves, seals, springs, retainers, keepers, and camshafts.1. Remove engine timing belt (See Engine Timing Belt Removal & Installation in Section 02 Engine).
2. Remove the cylinder head cover (See Cylinder Head Cover Removal & Installation in Section 02 Engine).
3. Remove the camshafts (See Camshaft Removal & Installation in Section 02 Engine).
4. Remove intake manifold (See Intake Manifold Removal & Installation in Section 02 Engine).
5. Remove exhaust manifold (See Exhaust Manifold Removal & Installation in Section 02 Engine).
6. Remove water pipe and thermostat assembly.
1 - Rocker Arms
2 - Hydraulic Tappets
3 - Valve Keepers
4 - Valve Spring Upper Retainers5 - Valve Springs
6 - Valve Oil Seals
7 - Valve Spring Lower Retainers
8 - Valves
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
LTSM020167
02–23Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
Page 53 of 1903

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 7. Remove the cylinder head bolts in the ordershown.
8. Remove cylinder head gasket.
9. Installation is in the reverse order of removal.
Installation Notes:
• Ensure cylinder head bolt holes in the block are clean, dry (free of residual oil or coolant), and threads are not
damaged.
• The cylinder head bolts should not be reused. The new bolts should be examined before use. If the bolts are
stretched, the bolts should be replaced.
• Position the new cylinder head gasket on the engine block with the part number facing up. Ensure gasket is
seated over the locating dowels in the block.
• Before installing the bolts, the threads should be lightly coated with engine oil.
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
BESM020065
02
02–24Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
Page 54 of 1903

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine •Install the cylinder head bolts in the order shown.
• Torque the cylinder head bolts in the following three
step sequence:
� 1st Step: Tighten the bolt to 40±5N·m
� 2nd Step: Tighten the bolt an additional 90 ±
5°
� 3rd Step: Tighten the bolt an additional 90 ± 5°
Front Crankshaft Oil Seal
Removal & Installation
NOTE :
The following special tools are required to perform the repair procedure:
• CH-20007 - Front Crankshaft Seal Installer
• CH-20008 - Front Crankshaft Seal Guide
• CH-20019 - Crankshaft Belt Pulley Fixture
1. Remove the accessory drive belt (See Accessory Drive Belt Removal & Installation in Section 02 Engine).
2. Remove the crankshaft vibration damper bolts (1). (Tighten: Crankshaft vibration damper bolts to
25 N·m)
3. Remove the engine timing belt (See Engine Timing Belt Removal & Installation in Section 02 Engine).
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
LTSM020236
BESM020055
02
02–25Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.
Page 55 of 1903

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4. Remove the crankshaft timing belt pulley bolt (2)from the crankshaft.
(Tighten: Crankshaft timing belt pulley bolt to
130 N·m and an additional 65°)
5. Remove the key-way from the crankshaft.
6. Use an appropriate tool and remove the front crankshaft oil seal (1).
CAUTION:
Be careful not to damage the front cover seal
surface while removing the seal.
7. Installation is in the reverse order of removal.
Installation Notes:
• Lubricate the new front seal with engine oil prior to assembly.
• Use the front crankshaft seal installer CH-20008 (1), to install the new seal.
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
LTSM020199
LTSM020216
02–26Chery Automobile Co., Ltd.