Page 13 of 419

Brief introduction on Geely model “FC” Basic parametersTable 2 Types and parameters of main assemblyModel
TypeElectric injection system modelBore
StrokeDelivery capacityCompression ratioMax. power
Max. torque
Idling speedIgnition sequenceMin. fuel consumptionTypeMain gear box ratioTypes and parameters
JL4G184-cylinderin-line, four-stroke, water-cooling, double over-head
camshaft, 16-valve, CVVT multipoint injection gasoline engineUnited Automotive Electronic Systems Co., Ltd. M7.9.7 electric injection system5 gears synchronizer of constant mesh gearDry single, diaphragm spring, constant pressure
Rack-and-pinion steering gear with hydraulic powerDouble pipeline, vacuum boosterwith ABS +EBD anti-lock systemDisc brake
Disc brake
Strut-type front independent suspensionLongitudinal swinging arm and anti-twist beam compound rear suspensionBreakawayBalI cage and tripot type constant velocity universal jointLoaded all-metal body
Honeycomb cordierite carrier, noble metal catalyst
Swirl or swash plate compressorItem nameNumber
Engine1st gear
2nd gear
3rd gear
4th gear
5th gearReverse gearClutch type
Steering gear
Tire
Body structureSpecification
Air pressureRadial
tireTail gasAir
condi-
tioning
systemUnit
��
��
�
��/�/���
�.
�/�/���
�/���
�/��.
�
���
�
2
Transmission
Each gear ratio
Braking
system
Sus-
pension
Drive
axleType
Front brake
Rear brakeFront suspension type
Rear suspension typeRim
Type
Drive shaftCatalytic converterCompressor typeNominal refrigerating capacityRefrigerant
Page 16 of 419
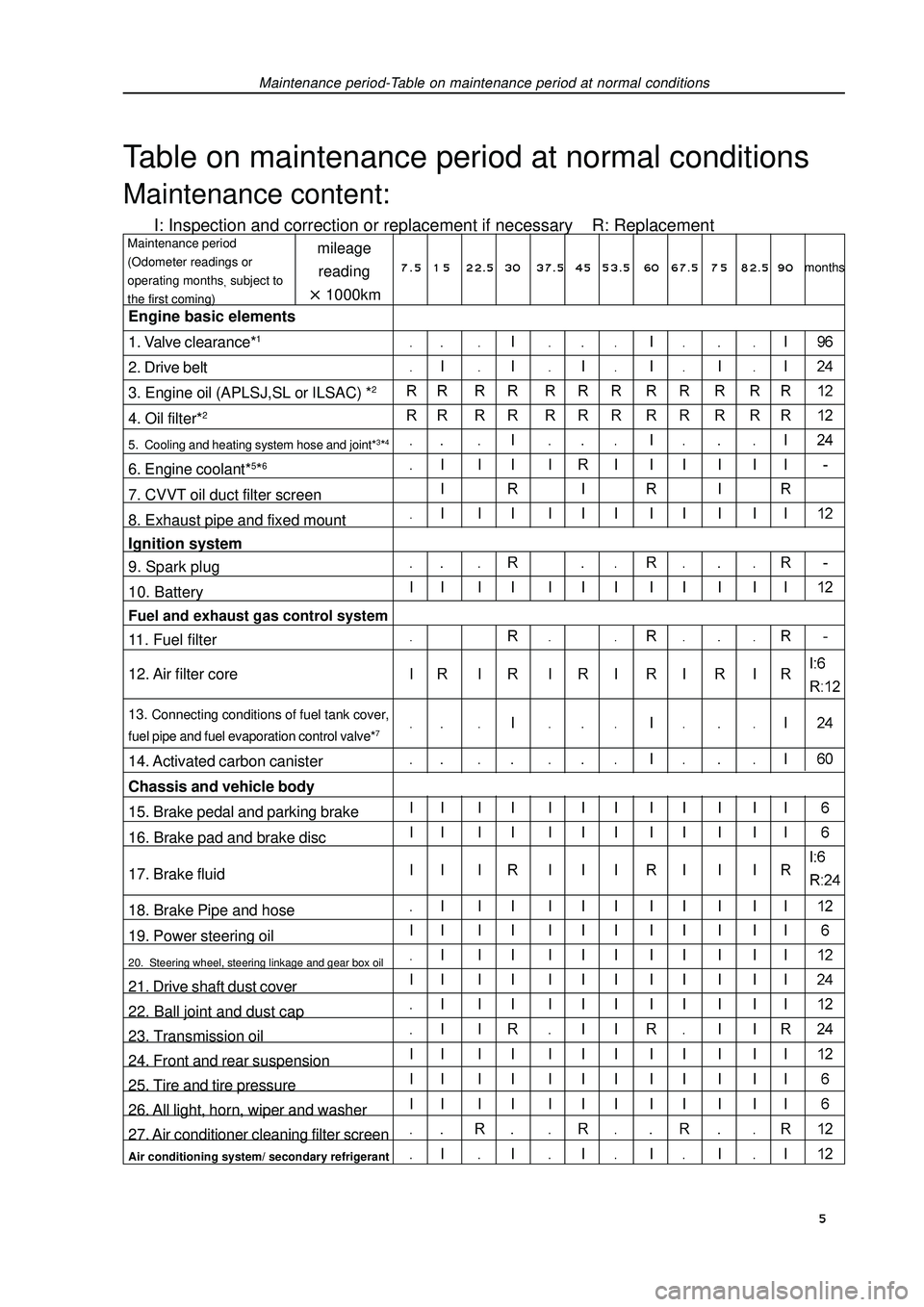
Maintenance period-Table on maintenance period at normal conditionsTable on maintenance period at normal conditionsMaintenance content:I: Inspection and correction or replacement if necessary R: Replacementmileage
reading1000kmMaintenance period
(Odometer readings or
operating monthssubject to
the first coming)Engine basic elements
1. Valve clearance*12. Drive belt
3. Engine oil (APLSJ,SL or ILSAC) *24. Oil filter*25. Cooling and heating system hose and joint*3*46. Engine coolant*5*67. CVVT oil duct filter screen
8. Exhaust pipe and fixed mount
Ignition system
9. Spark plug
10. BatteryFuel and exhaust gas control system11. Fuel filter
12. Air filter core13. Connecting conditions of fuel tank cover,
fuel pipe and fuel evaporation control valve*714. Activated carbon canister
Chassis and vehicle body
15. Brake pedal and parking brake
16. Brake pad and brake disc
17. Brake fluid
18. Brake Pipe and hose
19. Power steering oil20. Steering wheel, steering linkage and gear box oil21. Drive shaft dust cover
22. Ball joint and dust cap
23. Transmission oil
24. Front and rear suspension
25. Tire and tire pressure
26. All light, horn, wiper and washer
27. Air conditioner cleaning filter screenAir conditioning system/ secondary refrigerant7 . 5 1 5 22.5 3037.5 4553.5 60 67.5 7 582.5 90months 5
Page 97 of 419

Front suspension - front suspension systemFront suspensionFront suspension systemTable on trouble occurrenceThis table could help you find out failure causes, and each figure in the table indicates the possible
sequence of failure causes, please check every part as the sequence, and replace if necessary.Trouble occurrence Possible trouble part Pages to refer to
1. Tire (abrasion or improper tire pressure) 109
2. Wheel alignment (incorrect) 87
Deflection/single side 3. Steering linkage (looseness or abrasion) -
4. Shaft hub bearing (abrasion) 123
5. Suspension parts (abrasion) -
6. Steering gear (poor adjustment or breakage) -
1. Vehicle (overload) -
Bottoming 2. Spring (elastic fatigue) 90
3. Absorber (abrasion) 90
1. Tire (abrasion or improper tire pressure) 109
Swaying left and right/ 2. Stabilizer bar (bending or breakage) 96shaking forward and backward3. Absorber (abrasion) 90
1. Tire (abrasion or improper tire pressure) 109
2. Wheel (poor balance) 109
3. Absorber (abrasion) 90
Front wheel shimmy 4. Wheel alignment (incorrect) 87
5. Ball joint (abrasion) 99
6. Shaft hub bearing (looseness or abrasion) 123
7. Steering linkage (looseness or abrasion) -
8. Steering gear (poor adjustment or breakage) -
1. Tire (abrasion or improper tire pressure) 109
Abnormal tire abrasion 2. Wheel alignment (incorrect) 87
3. Absorber(abrasion) 90
4. Suspension parts (abrasion) -86
Page 98 of 419

Front suspension - Front wheel alignmentFrontRearIf toe-in is not within specification, please adjust left and
right levers of steering gear.4. Adjustment of toe-in(a) Remove dust cover fixing clip.FrontRearToe-in(Total)Front wheel alignmentAdjustment1. Inspection(a) Check tire is worn and inflation pressure is proper.
Tire inflation pressure under normal temperature:Tire size Front and rear kPa*1 It is used under the condition of speed below 160 km/h.
*2 It is used under the condition of speed above 160 km/h.
(b) Check tire run-out with dial indicator.
Tire run-out: 3.0mm.2. Measurement of vehicle heightVehicle height:
(General road)
(Coarse road)
Measuring point:
A. Height for ground and front wheel center
B. Height for ground and bolt center in front of lower
control arm
C. Height for ground and fixed bolt center of rear axle beam
D. Height for ground and rear wheel center
Note: adjust vehicle height to standard value before checking front wheel alignment.
If vehicle height does not conform to regulations, please shake upward and downward or lift vehicle
body to adjust vehicle height.3. Inspection of toe-inToe-in:Front87
Page 111 of 419

Rear suspension - rear suspension systemRear suspensionRear suspension systemTable on trouble occurrenceThis table could help you find out failure causes, and each figure in the table indicates the possible
sequence of failure causes, please check every part as the sequence, and replace if necessary. Trouble occurrence Possible trouble part Pages to refer to
1. Tire (abrasion or improper tire pressure) 109
Wandering 2. Wheel alignment (incorrect) 101
3. Shaft hub bearing (abrasion) 129
4. Suspension parts (abrasion) -
1. Vehicle (overload) -
Bottoming 2. Spring (elastic fatigue) 102
3. Absorber (abrasion) 102
Swaying left and right/ 1. Tire (abrasion or improper tire pressure) 109
shaking forward and 2. Rear stabilizer bar (bending or breakage) 105
backward 3. Absorber (abrasion) 102
1. Tire (abrasion or improper tire pressure) 109
Rear wheel shimmy 2. Wheel (poor balance) 109
3. Absorber (abrasion) 102
4. Wheel alignment (incorrect) 101
1. Tire (abrasion or improper tire pressure) 109
Abnormal tire abrasion 2. Wheel alignment (incorrect) 101
3. Absorber (abrasion) 102
4. Suspension parts (abrasion) -100
Page 120 of 419

Tire and wheel- wheel and tire systemTire and wheelWheel and tire systemInspection1. Check tire.(a) Check tire is worn and inflation pressure is proper.
Cold tire inflation pressure:
*1 It is used under the condition of speed below 160 km/h.
(b) Check tire run-out with dial indicator.
Tire run-out: 2. Adjust tire position.
Hint:see adjusting position of tire shown in the dia-
gram whether there is spare tire or not.3. Check wheel balance.(a) Check and adjust with off-the-car balancing machine.
(b) Check and adjust with in-the-car balancing machine if
necessary.
Unbalanced mass after adjusting: 4. Check axial clearance of front wheel bearing
(see Page 123).
5. Check end surface run-out of front wheel shaft hub
(see Page 123).
6. Check axial clearance of rear wheel bearing
(see Page 129).
7. Check end surface run-out of rear wheel shaft hub
(see Page 129).
8. Check front suspension is loose.
9. Check steering linkage is loose.
10. Check ball joint is loose.Tire size Front and rear kPaFront109