Page 224 of 1575
during testing. An example would be if a problem appears only when the vehicle is cold but has not appeared when
warm. In this case, the technician should thoroughly make out a "CUSTOMER PROBLEM ANALYSIS SHEET" and
recreate (simulate) the environment and condition which occurred when the vehicle was having the issue.1. Clear Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC).
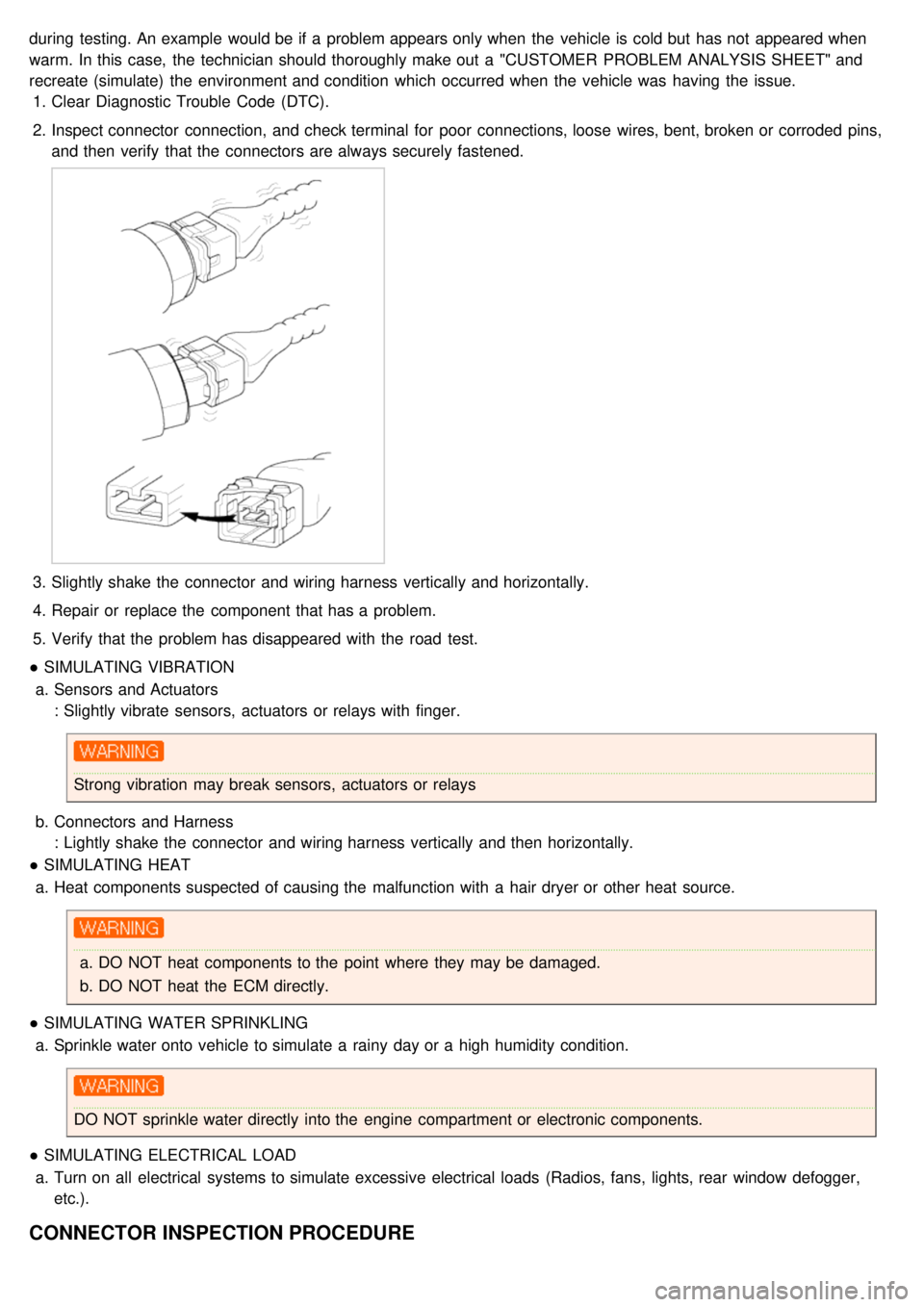
2. Inspect connector connection, and check terminal for poor connections, loose wires, bent, broken or corroded pins,
and then verify that the connectors are always securely fastened.
3.Slightly shake the connector and wiring harness vertically and horizontally.
4. Repair or replace the component that has a problem.
5. Verify that the problem has disappeared with the road test.
● SIMULATING VIBRATION
a. Sensors and Actuators
: Slightly vibrate sensors, actuators or relays with finger.
Strong vibration may break sensors, actuators or relays
b. Connectors and Harness
: Lightly shake the connector and wiring harness vertically and then horizontally.
● SIMULATING HEAT
a. Heat components suspected of causing the malfunction with a hair dryer or other heat source.
a.DO NOT heat components to the point where they may be damaged.
b. DO NOT heat the ECM directly.
● SIMULATING WATER SPRINKLING
a. Sprinkle water onto vehicle to simulate a rainy day or a high humidity condition.
DO NOT sprinkle water directly into the engine compartment or electronic components.
● SIMULATING ELECTRICAL LOAD
a. Turn on all electrical systems to simulate excessive electrical loads (Radios, fans, lights, rear window defogger,
etc.).
CONNECTOR INSPECTION PROCEDURE
Page 230 of 1575
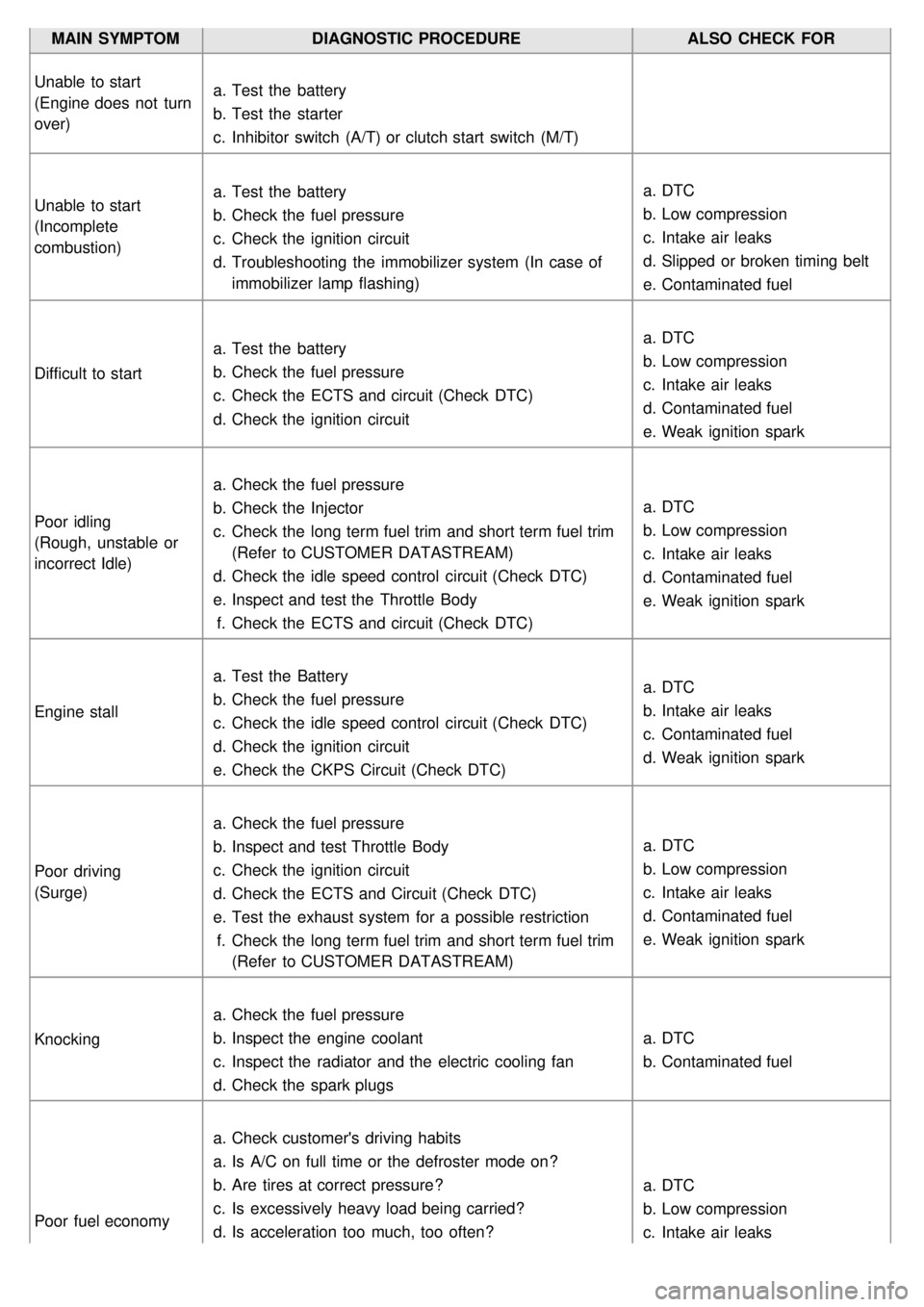
MAIN SYMPTOMDIAGNOSTIC PROCEDURE ALSO CHECK FOR
Unable to start
(Engine does not turn
over) a.
Test the battery
b. Test the starter
c. Inhibitor switch (A/T) or clutch start switch (M/T)
Unable to start
(Incomplete
combustion) a.
Test the battery
b. Check the fuel pressure
c. Check the ignition circuit
d. Troubleshooting the immobilizer system (In case of
immobilizer lamp flashing) a.
DTC
b. Low compression
c. Intake air leaks
d. Slipped or broken timing belt
e. Contaminated fuel
Difficult to start a.
Test the battery
b. Check the fuel pressure
c. Check the ECTS and circuit (Check DTC)
d. Check the ignition circuit a.
DTC
b. Low compression
c. Intake air leaks
d. Contaminated fuel
e. Weak ignition spark
Poor idling
(Rough, unstable or
incorrect Idle) a.
Check the fuel pressure
b. Check the Injector
c. Check the long term fuel trim and short term fuel trim
(Refer to CUSTOMER DATASTREAM)
d. Check the idle speed control circuit (Check DTC)
e. Inspect and test the Throttle Body
f. Check the ECTS and circuit (Check DTC) a.
DTC
b. Low compression
c. Intake air leaks
d. Contaminated fuel
e. Weak ignition spark
Engine stall a.
Test the Battery
b. Check the fuel pressure
c. Check the idle speed control circuit (Check DTC)
d. Check the ignition circuit
e. Check the CKPS Circuit (Check DTC) a.
DTC
b. Intake air leaks
c. Contaminated fuel
d. Weak ignition spark
Poor driving
(Surge) a.
Check the fuel pressure
b. Inspect and test Throttle Body
c. Check the ignition circuit
d. Check the ECTS and Circuit (Check DTC)
e. Test the exhaust system for a possible restriction
f. Check the long term fuel trim and short term fuel trim
(Refer to CUSTOMER DATASTREAM) a.
DTC
b. Low compression
c. Intake air leaks
d. Contaminated fuel
e. Weak ignition spark
Knocking a.
Check the fuel pressure
b. Inspect the engine coolant
c. Inspect the radiator and the electric cooling fan
d. Check the spark plugs a.
DTC
b. Contaminated fuel
Poor fuel economy a.
Check customer's driving habits
a. Is A/C on full time or the defroster mode on?
b. Are tires at correct pressure?
c. Is excessively heavy load being carried?
d. Is acceleration too much, too often? a.
DTC
b. Low compression
c. Intake air leaks
Page 239 of 1575

2007 > 2.7L V6 GASOLINE >
DESCRIPTION
1.Engine is hard to start or does not start at all.
2. Unstable idle.
3. Poor driveability
If any of the above conditions are noted, first perform a routine diagnosis that includes basic engine checks (ignition
system malfunction, incorrect engine adjustment, etc.). Then, inspect the Gasoline Engine Control system components
with the HI- SCAN (Pro).
a. Before removing or installing any part, read the diagnostic trouble codes and then disconnect the battery
negative ( - ) terminal.
b. Before disconnecting the cable from battery terminal, turn the ignition switch to OFF. Removal or connection
of the battery cable during engine operation or while the ignition switch is ON could cause damage to the
ECM.
c. The control harnesses between the ECM and heated oxygen sensor are shielded with the shielded ground
wires to the body in order to prevent the influence of ignition noises and radio interference. When the shielded
wire is faulty, the control harness must be replaced.
d. When checking the generator for the charging state, do not disconnect the battery '+' terminal to prevent the
ECM from damage due to the voltage.
e. When charging the battery with the external charger, disconnect the vehicle side battery terminals to prevent
damage to the ECM.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
Faults with the following items will illuminate the MIL.
a. Catalyst
b. Fuel system
c. Mass Air Flow Sensor (MAFS)
d. Intake Air Temperature Sensor (IATS)
e. Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (ECTS)
f. Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
g. Upstream Oxygen Sensor
h. Upstream Oxygen Sensor Heater
i. Downstream Oxygen Sensor
j. Downstream Oxygen Sensor Heater
k. Injector
l. Misfire
m. Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKPS)
n. Camshaft Position Sensor (CMPS)
o. Evaporative Emission Control System
p. Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS)
q. Idle Speed Control Actuator (ISCA)
r. Power Supply
s. ECM/ PCM
t. MT/AT Encoding
u. Acceleration Sensor
v. MIL- on Request Signal
w. Power Stage
Refer to "INSPECTION CHART FOR DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTC)" for more information.
Page 240 of 1575
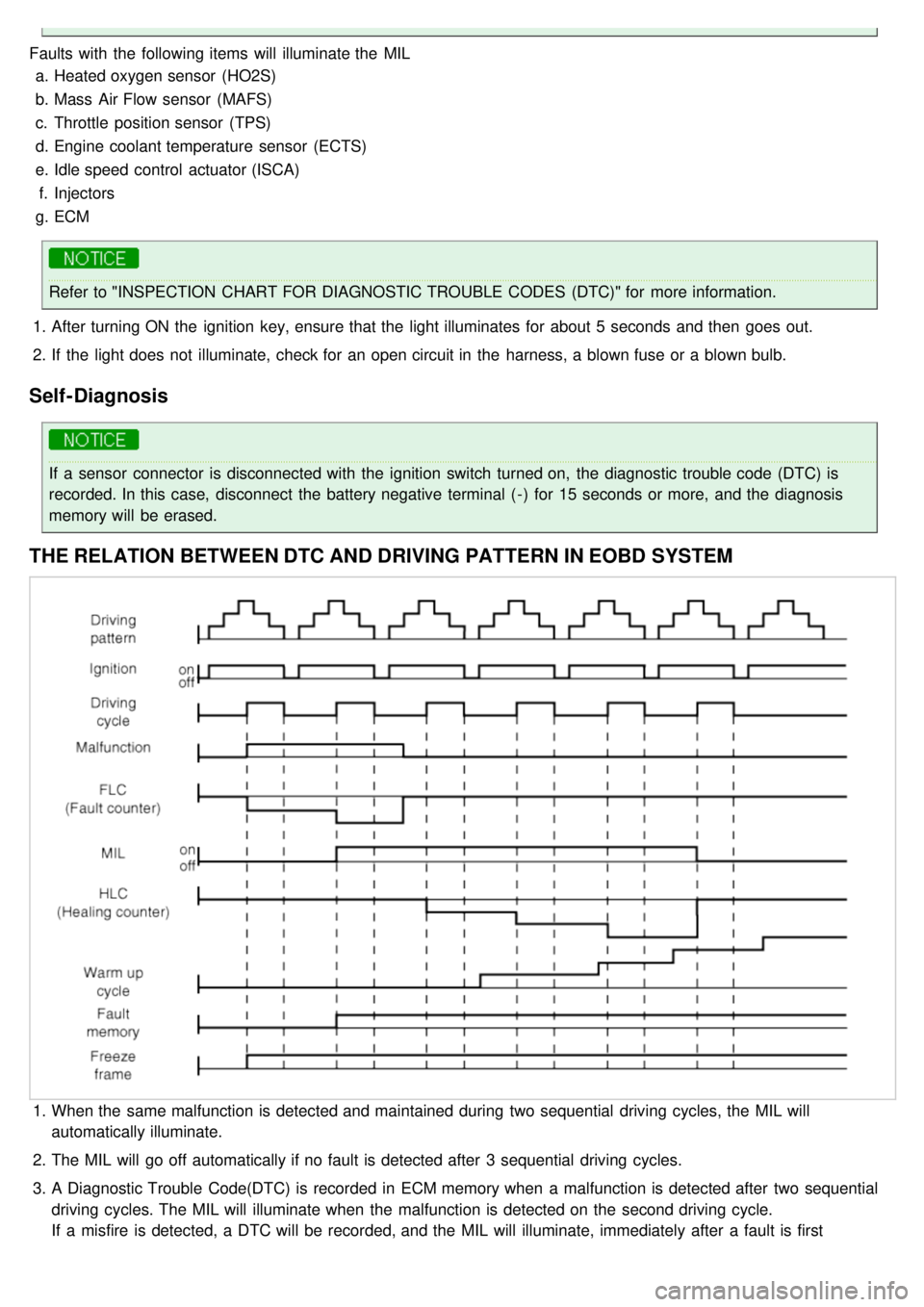
Faults with the following items will illuminate the MILa. Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S)
b. Mass Air Flow sensor (MAFS)
c. Throttle position sensor (TPS)
d. Engine coolant temperature sensor (ECTS)
e. Idle speed control actuator (ISCA)
f. Injectors
g. ECM
Refer to "INSPECTION CHART FOR DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTC)" for more information.
1. After turning ON the ignition key, ensure that the light illuminates for about 5 seconds and then goes out.
2. If the light does not illuminate, check for an open circuit in the harness, a blown fuse or a blown bulb.
Self-Diagnosis
If a sensor connector is disconnected with the ignition switch turned on, the diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is
recorded. In this case, disconnect the battery negative terminal ( - ) for 15 seconds or more, and the diagnosis
memory will be erased.
THE RELATION BETWEEN DTC AND DRIVING PATTERN IN EOBD SYSTEM
1.When the same malfunction is detected and maintained during two sequential driving cycles, the MIL will
automatically illuminate.
2. The MIL will go off automatically if no fault is detected after 3 sequential driving cycles.
3. A Diagnostic Trouble Code(DTC) is recorded in ECM memory when a malfunction is detected after two sequential
driving cycles. The MIL will illuminate when the malfunction is detected on the second driving cycle.
If a misfire is detected, a DTC will be recorded, and the MIL will illuminate, immediately after a fault is first
detected.
Page 275 of 1575
COMPONENT INSPECTION
1.Turn ignition switch OFF.
2. Disconnect ECTS connector.
3. Remove the ECTS.
4. After immersing the thermistor of the sensor into engine coolant, measure resistance between ECTS terminals 1
and 3.
5.Check that the resistance is within the specification.
Specification: Refer to SPECIFICATION.
Page 278 of 1575
COMPONENT INSPECTION
1.Connect a scantool on Diagnoisis Link Connector (DLC).
2. Start engine and check output voltages of APS 1 and 2 at C.T and W.O.T.
Specification
Condition Output Voltage (V)
APS1 APS2
C.T 0.70 ~ 0.80 0.29 ~ 0.46
W.O.T 3.85 ~ 4.35 1.93 ~ 2.18
3. Turn ignition switch OFF and disconnect the scantool from the DLC.
4. Disconnect APS connector and measure resistance between APS terminals 5(6) and 4(5) (APS 1).
Specification: Refer to SPECIFICATION.
5. Disconnect APS connector and measure resistance between APS terminals 6(3) and 2(4) (APS 2).
Page 287 of 1575
COMPONENT INSPECTION
1.Turn ignition switch OFF.
2. Disconnect OTS connector.
3. Remove the OTS.
4. After immersing the thermistor of the sensor into water (or engine coolant), measure resistance between OTS
terminals 1 and 2.
5.Check that the resistance is within the specification.
Specification: Refer to SPECIFICATION.
Page 312 of 1575
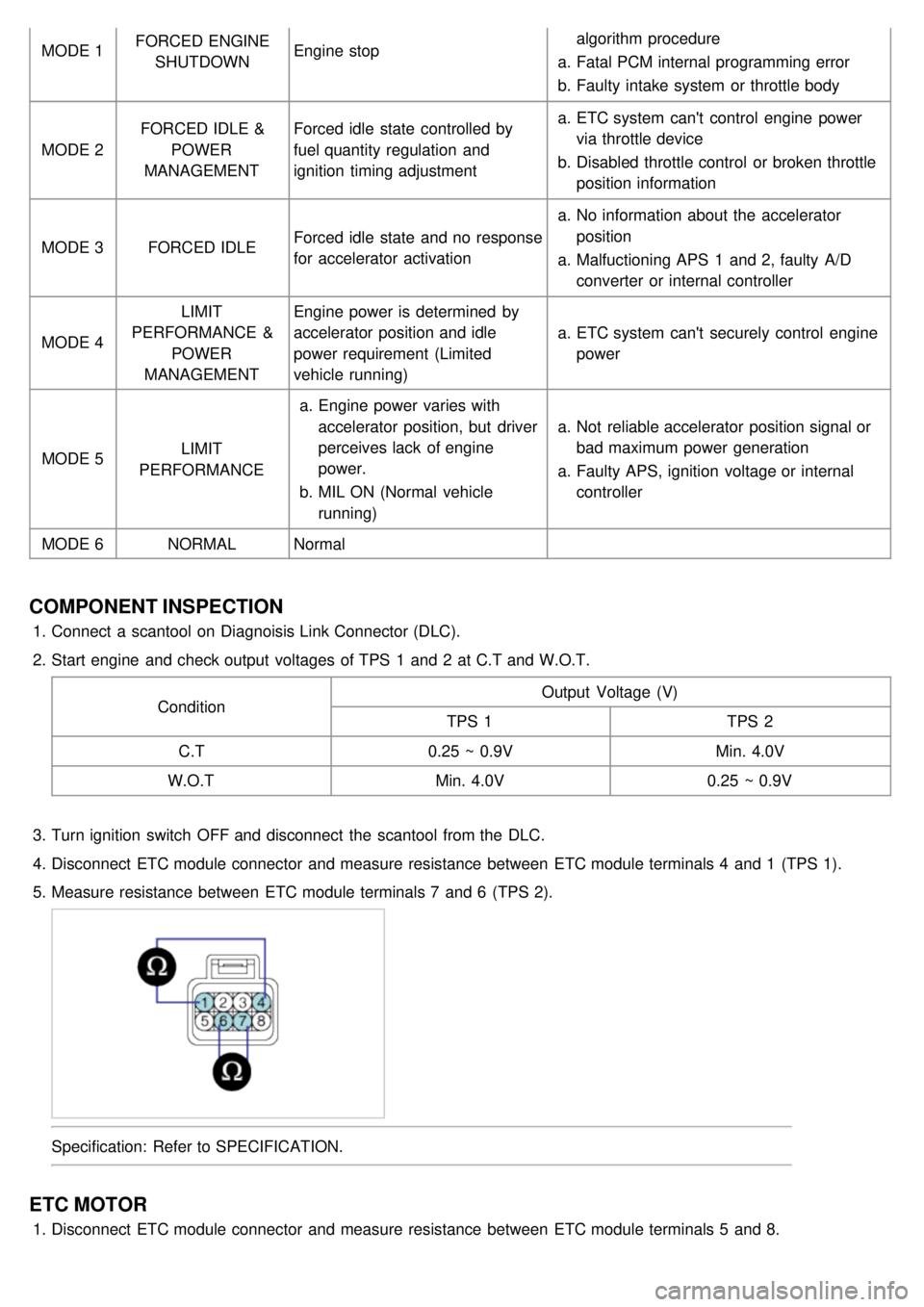
MODE 1FORCED ENGINE
SHUTDOWN Engine stop algorithm procedure
a. Fatal PCM internal programming error
b. Faulty intake system or throttle body
MODE 2 FORCED IDLE &
POWER
MANAGEMENT Forced idle state controlled by
fuel quantity regulation and
ignition timing adjustment a.
ETC system can't control engine power
via throttle device
b. Disabled throttle control or broken throttle
position information
MODE 3 FORCED IDLE Forced idle state and no response
for accelerator activation a.
No information about the accelerator
position
a. Malfuctioning APS 1 and 2, faulty A/D
converter or internal controller
MODE 4 LIMIT
PERFORMANCE & POWER
MANAGEMENT Engine power is determined by
accelerator position and idle
power requirement (Limited
vehicle running)
a.
ETC system can't securely control engine
power
MODE 5 LIMIT
PERFORMANCE a.
Engine power varies with
accelerator position, but driver
perceives lack of engine
power.
b. MIL ON (Normal vehicle
running) a.
Not reliable accelerator position signal or
bad maximum power generation
a. Faulty APS, ignition voltage or internal
controller
MODE 6 NORMALNormal
COMPONENT INSPECTION
1.Connect a scantool on Diagnoisis Link Connector (DLC).
2. Start engine and check output voltages of TPS 1 and 2 at C.T and W.O.T.
Condition Output Voltage (V)
TPS 1 TPS 2
C.T 0.25 ~ 0.9V Min. 4.0V
W.O.T Min. 4.0V 0.25 ~ 0.9V
3. Turn ignition switch OFF and disconnect the scantool from the DLC.
4. Disconnect ETC module connector and measure resistance between ETC module terminals 4 and 1 (TPS 1).
5. Measure resistance between ETC module terminals 7 and 6 (TPS 2).
Specification: Refer to SPECIFICATION.
ETC MOTOR
1.Disconnect ETC module connector and measure resistance between ETC module terminals 5 and 8.