2007 ISUZU KB P190 lock
[x] Cancel search: lockPage 4390 of 6020
7A2-106 TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E)
B5: Engine Stalls When Selector Lever is Changed from N to R, D, 3, 2 or L Range
B6: Engine Does Not Crank in P or N Range
B7: Engine Cranks in other than P or N Range
B8: Extended Time Lag When Selector Lever is Changed from N to D
Checks Action
Definition:
The engine stalls when selector lever is changed from N or P position to a run position during engine idling.
Diagnosis Hints • As the correct cause is attributable to the engine, faulty idle up, insufficient
engine output, etc. are suspected.
• As this is a cause of the transmission, faulty torque converter clutch (TCC) piston is suspected.
• If the transmission fluid through resistance increases due to clogged oil cooler or some other reason, or if the transmission fluid level decreases, the TCC piston
works causing the engine stall.
Transmission Fluid Checks Inspect the transmission fluid for the following conditions. If the transmission fluid is
extremely blacked, contaminated or smells burnt, slipping of clutch is suspected.
• Low quantity
• Contamination
• Smell
Line Pressure Checks Inspect the line pressure in forward ranges for a possible dropped pressure. Refer to
Line Pressure Test in Test Instruction section.
Stall Speed Checks Inspect the stall speed in forward ranges. Refer to Stall Test in Test Instruction
section.
Control Valve Body Checks Inspect the valve body for the following conditions.
• Faulty operation
• Sticking lock up spool valve
• Sticking TCC solenoid valve. Perform function check. Refer to On-Vehicle Service section.
• Clogged hydraulic circuit
Additional Checks • Inspect the engine for proper outputs. Refer to appropriate inspection chart in
engine section.
• Inspect the engine for proper idle speed.
Checks Action
Definition: • The engine starter does not run even though the P or N range.
• The engine starter runs even though the R, D, 3, 2 or L range.
Transmission Range Switch & Selector
Lever Cable Checks Inspect the transmission range switch and selector lever cable for misadjusting or
disordering. Refer to On-Vehicle Service section.
Checks Action
Definition:
The shift time lag is longer than the standard value when the selector lever is changed from N to D.
Transmission Fluid Checks Inspect the transmission fluid for low quantity.
Line Pressure Checks Inspect the line pressure in D range for a possible dropped pressure. Refer to Line
Pressure Test in Test Instruction section.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4394 of 6020

7A2-110 TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E)
C12: Large Shock When Gearshift from 1st to 2nd or 2nd to 1st
C13: Large Shock When Gearshift from 2nd to 3rd or 3rd to 2nd
C14: Large Shock When Gearshift from 3rd to 4th or 4th to 3rd
C15: Large Shock When Kick-down
C16: Large Shock When Accelerator Pedal is Stepped ON or OFF without Gearshift
C17: Large Shock When Gearshift from 2nd to 1st in L Range
C18: Large Shock Others
C19: Large Shock When Vehicle Speed is Reduced by No Accelerator Pedal or Vehicle is Stopped
C20: Large Shock at Lock Up
C21: Shift Down or Engine Overrun When Accelerator Pedal is Stepped ON in 4th Gear
D1: Faulty Gearshift Schedule (Different from Shift Speed Chart)
Checks Action
Definition: • A large shock is felt when the accelerator pedal is stepped on for acceleration and the gear is shifted up or down.
• A large shock is felt when the accelerator pedal is stepped on for kick-down.
• A large shock is felt when the accelerator pedal is not stepped on.
• A large shock is felt when the selector lever is selected in L range.
Diagnosis Hints The same causes as in category No. “C1 - C8: Engine Race Up (Slipping)” are
suspected.
Checks Action
Definition:
A large shock is felt at lock up.
Diagnosis Hints Incorrect input signals or faulty operation of torque converter clutch is suspected.
Refer to category No. “I1: No Lock Up.”
Checks Action
Definition:
Shift down or engine overrun occurs above than kick-down area.
Diagnosis Hints The same causes as in category No. “C1 - C8: Engine Race Up (Slipping)” are
suspected.
Checks Action
Definition:
Faulty gearshift schedule, it is differ from the shift speed chart.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4401 of 6020
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E) 7A2-117
H1: Judder Occurs at Lock Up
H2: Large Shock at Lock Up
H3: Lock Up Point is High or Low
I1: No Lock Up
Diagnosis Hints • Causes such as the solenoid operating sound or a faulty oil pump are
suspected.
• Distinguishing is possible by stopping the solenoid operation temporarily, checking the correlation for the former case and, changing
the line pressure and confirming the correlation with noise.
• As a matter of course, noise other than the transmission may be generated around the engine, and should be checked carefully.
Notice: When the noise is generated only at the time of a gear shift, it may
be the sound of transmission fluid flowing or gear noise. If the sound varies
depending on the gear speed to be shifted, it may be the gear noise
generated from the planetary gear and its components. If the sound varies
depending on the vehicle speed, it may be the gear noise of the output
system, or the gear noise of the input system or a faulty torque converter.
Checks
Action
Checks Action
Definition:
Judder occurs when lock up area.
Diagnosis Hints Slip due to burning of the torque converter clutch (TCC) facing or insufficient
engagement due to dropped working pressure are suspected. Refer to
category No. “l1: No Lock Up “.
Notice: When the TCC facing has burnt, foreign material mixed in the oil
cooler is suspected. In such a case, inspect the oil cooler circuit for clogging
of the oil cooler.
Checks Action
Definition: • A large shock is felt at lock up.
• Lock up point is excessively high or low.
Diagnosis Hints Incorrect input signals or faulty operation of torque converter clutch (TCC) is
suspected. Refer to category No. “I1: No Lock Up”.
Checks Action
Definition:
Lock up is not performed even though lock up control conditions being satisfied.
Diagnosis Hints • Monitor the signal to the torque converter clutch (TCC) solenoid valve
while carrying out a running test.
• When the transmission fluid temperature is lower than 20 °C (68 °F),
lock up control is inhibited.
• When the output signal to the TCC solenoid valve is sent correctly, causing no lock up, clogged hydraulic circuits or malfunction of the TCC
piston may be suspected.
• Even with the lock up area, the output signal to the TCC solenoid valve is not sent, a fault of the transmission fluid temperature (TFT) sensor
controlling the lock up may be suspected.
Notice: When the TCC facing has burnt, foreign material mixed in the oil
cooler is suspected. In such a case, inspect the oil cooler circuit for clogging
of the oil cooler.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4409 of 6020
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E) 7A2-125
Road Test
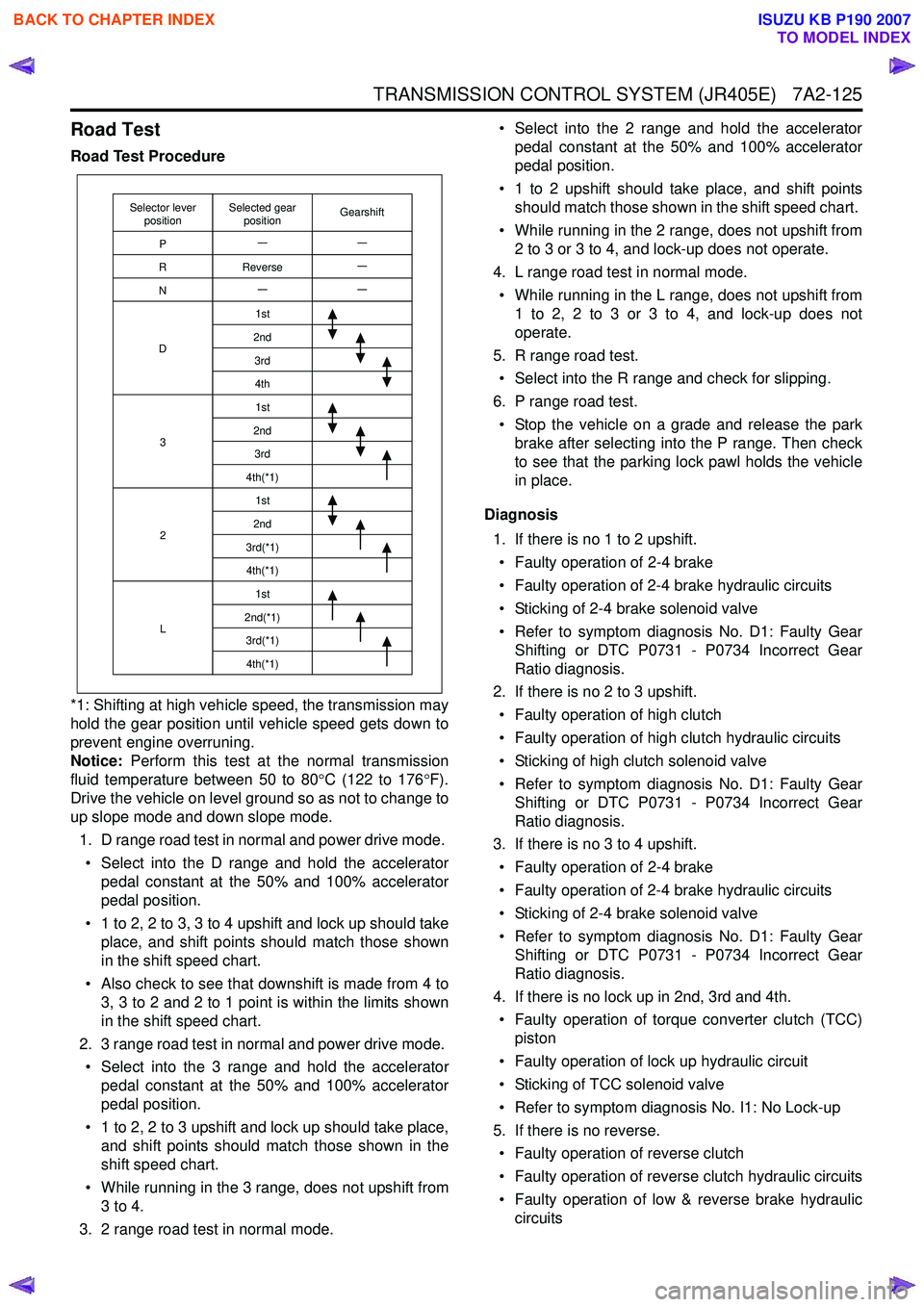
Road Test Procedure
*1: Shifting at high vehicle speed, the transmission may
hold the gear position until vehicle speed gets down to
prevent engine overruning.
Notice: Perform this test at the normal transmission
fluid temperature between 50 to 80 °C (122 to 176 °F).
Drive the vehicle on level ground so as not to change to
up slope mode and down slope mode.
1. D range road test in normal and power drive mode. • Select into the D range and hold the accelerator pedal constant at the 50% and 100% accelerator
pedal position.
• 1 to 2, 2 to 3, 3 to 4 upshift and lock up should take place, and shift points should match those shown
in the shift speed chart.
• Also check to see that downshift is made from 4 to 3, 3 to 2 and 2 to 1 point is within the limits shown
in the shift speed chart.
2. 3 range road test in normal and power drive mode. • Select into the 3 range and hold the accelerator pedal constant at the 50% and 100% accelerator
pedal position.
• 1 to 2, 2 to 3 upshift and lock up should take place, and shift points should match those shown in the
shift speed chart.
• While running in the 3 range, does not upshift from 3 to 4.
3. 2 range road test in normal mode. • Select into the 2 range and hold the accelerator
pedal constant at the 50% and 100% accelerator
pedal position.
• 1 to 2 upshift should take place, and shift points should match those shown in the shift speed chart.
• While running in the 2 range, does not upshift from 2 to 3 or 3 to 4, and lock-up does not operate.
4. L range road test in normal mode.
• While running in the L range, does not upshift from 1 to 2, 2 to 3 or 3 to 4, and lock-up does not
operate.
5. R range road test. • Select into the R range and check for slipping.
6. P range road test. • Stop the vehicle on a grade and release the park brake after selecting into the P range. Then check
to see that the parking lock pawl holds the vehicle
in place.
Diagnosis 1. If there is no 1 to 2 upshift.• Faulty operation of 2-4 brake
• Faulty operation of 2-4 brake hydraulic circuits
• Sticking of 2-4 brake solenoid valve
• Refer to symptom diagnosis No. D1: Faulty Gear Shifting or DTC P0731 - P0734 Incorrect Gear
Ratio diagnosis.
2. If there is no 2 to 3 upshift.
• Faulty operation of high clutch
• Faulty operation of high clutch hydraulic circuits
• Sticking of high clutch solenoid valve
• Refer to symptom diagnosis No. D1: Faulty Gear Shifting or DTC P0731 - P0734 Incorrect Gear
Ratio diagnosis.
3. If there is no 3 to 4 upshift.
• Faulty operation of 2-4 brake
• Faulty operation of 2-4 brake hydraulic circuits
• Sticking of 2-4 brake solenoid valve
• Refer to symptom diagnosis No. D1: Faulty Gear Shifting or DTC P0731 - P0734 Incorrect Gear
Ratio diagnosis.
4. If there is no lock up in 2nd, 3rd and 4th. • Faulty operation of torque converter clutch (TCC) piston
• Faulty operation of lock up hydraulic circuit
• Sticking of TCC solenoid valve
• Refer to symptom diagnosis No. I1: No Lock-up
5. If there is no reverse. • Faulty operation of reverse clutch
• Faulty operation of reverse clutch hydraulic circuits
• Faulty operation of low & reverse brake hydraulic circuits
Selector lever
position GearshiftSelected gear
position
P
R
N
D
3
2
L 1st
2nd 3rd4th1st
2nd 3rd
4th(*1) 1st
2nd
3rd(*1) 4th(*1) 1st
2nd(*1) 3rd(*1)4th(*1)
Reverse
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4423 of 6020

TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E) 7A2-139
Repair Instructions
Transmission Controls Module (TCM) Replacement
Description
The following A - C steps provide an overview
procedure to replace and reprogram a TCM. Each A -C
steps is explained further in this section.
A. Replace the old TCM with the new TCM.
B. Program the latest software and calibrations into the
new TCM using the Service Programming System
(SPS) if released. If not released, do not perform this
and skip to Step C.
C. Program the vehicle identification number (VIN) into
the TCM.
A. Removal and Installation
Removal Procedure 1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect the TCM harness connectors (1).
3. Loosen nuts (2) and remove the TCM (3) from the bracket (4).
Installation Procedure
Follow the removal steps in the reverse order. Be sure
that the connectors are securely fastened.
B. Programming Software and Calibrations
Program the latest software/ calibrations if released.
Refer to Service Programming System (SPS)
Description and SPS (Remote Procedure) or SPS
(Pass-Thru Procedure) in this section. If not released,
do not perform this and skip to Step C.
C. Programming Vehicle Identification Number
(VIN) Notice:
If you have performed SPS in the previous
step, VIN has prgrommaned already. Programming VIN
is not necessary in this step.
1. Install a scan tool.
2. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
3. Select Diagnostics > appropriate vehicle identification > AT JR405E > Programming >
Program VIN.
4. If you installed a new, skip to step 8. If you installed a reused TCM from another vehicle or incorrect
VIN is programmed before, the TCM might be
locked already. In order to get programming
approval, the on-screen displays a message to
user. Get programming approval from the TIS
2000 using the following procedure:
a. Connect a scan tool to the terminal that installed TIS 2000 with the latest software and
the hardware key is plugged into port.
b. Turn ON the scan tool and keep at title screen.
c. Launch the TIS application.
d. Select the Security Access at the main screen.
e. Highlight the “Tech 2" on the Diagnostic Tool Selection screen and click “Next”.
f. Click “Close” on the Security Access Enabled screen.
g. Turn OFF the scan tool.
h. Disconnect the scan tool from the terminal.
5. Install a scan tool to the vehicle.
6. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
7. Select Diagnostics > appropriate vehicle identification > AT JR405E > Programming >
Program VIN.
8. Input 17 digits of correct VIN.
9. After complete the programming, turn OFF/ ON the ignition.
10. Select Diagnostics > Lock ECU.
11. Follow the on-screen instructions and turn OFF/ ON the ignition.
Service Programming System (SPS)
Description
The service programming system (SPS) allows a
technician to program a control module through the
data link connector (DLC). The information transfer
circuit that is used at the DLC is the same serial data
circuit used by the scan tool for retrieving DTCs,
displaying data, clearing DTCs etc. This procedure
offers the ability to install software/ calibrations
matched to a particular vehicle.
Most control modules have two types of memory. The
software/ calibrations reside in the flash memory. The
two types of memory are listed below:
1
3 42
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4428 of 6020
7A2-144 TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E)
The JR405E automatic transmission is electrically
controlled by a transmission control module (TCM).
There are four forward speeds and one reverse speed.
This JR405E automatic transmission employs a clutch
pressure direct control system (Direct Electronic Shift
Control: DESC) using duty cycle type solenoid valves,
which ensure high shift quality. This transmission also
has a learning function and constantly checks the time
of each clutch and brake required for the shift in order
to match this time with the target value for the optimum
shift. The TCM will automatically select the most
appropriate shift points and lock-up points depending
on the accelerator pedal opening, the vehicle speed
and the vehicle load. If any trouble arises in the speed
sensor, solenoid valve, etc., the fail-safe control
function is activated to keep the running performance.
The JR405E automatic transmission consists of the
torque converter, oil pump, input shaft, out put shaft,
planetary gears and valve body. The gear train consists
of two planetary gear sets and three multiple plate
clutches in combination with two multiple plate brakes
and a one-way clutch.
Transmission Component Description
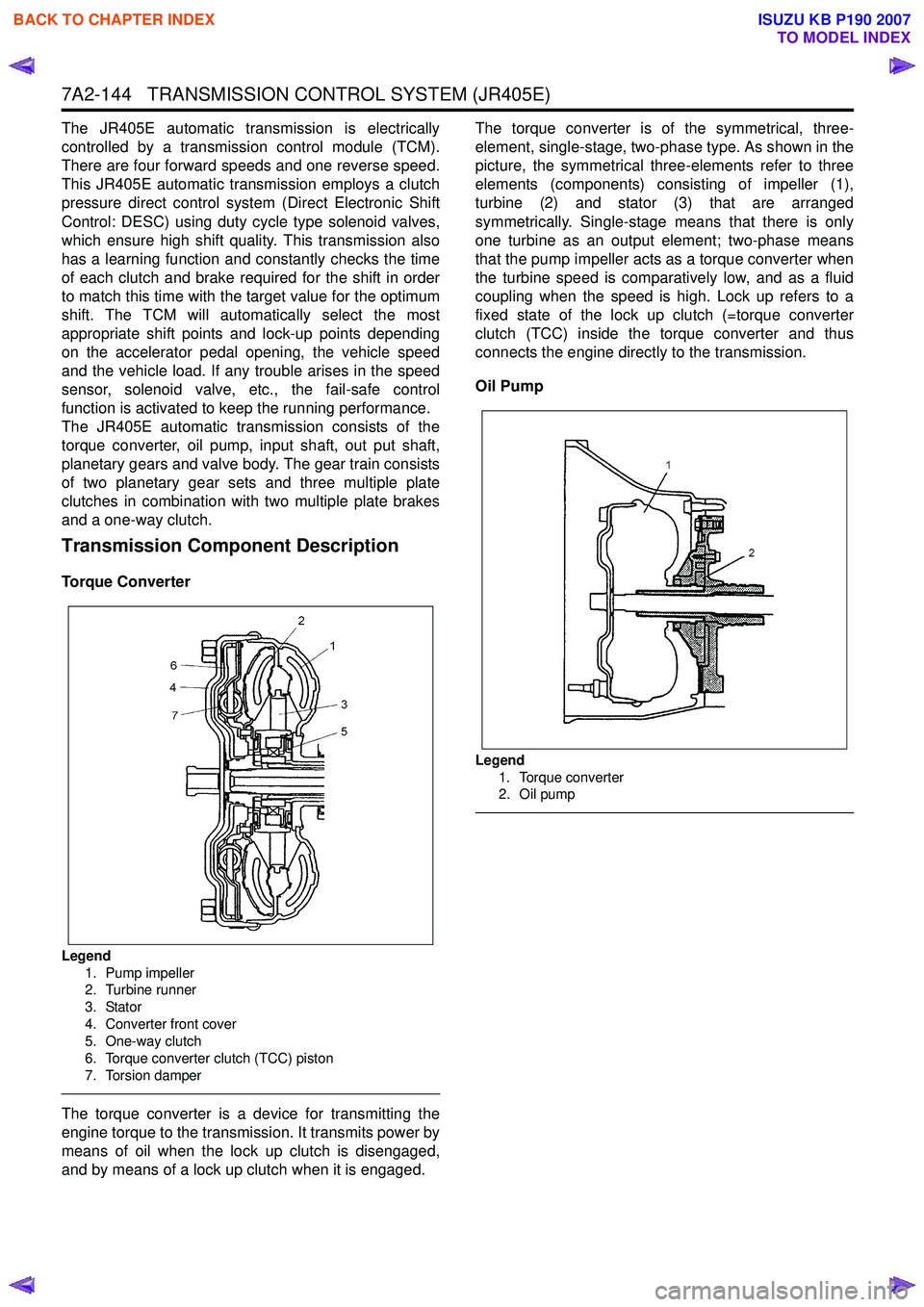
Torque Converter
Legend
1. Pump impeller
2. Turbine runner
3. Stator
4. Converter front cover
5. One-way clutch
6. Torque converter clutch (TCC) piston
7. Torsion damper
The torque converter is a device for transmitting the
engine torque to the transmission. It transmits power by
means of oil when the lock up clutch is disengaged,
and by means of a lock up clutch when it is engaged. The torque converter is of the symmetrical, three-
element, single-stage, two-phase type. As shown in the
picture, the symmetrical three-elements refer to three
elements (components) consisting of impeller (1),
turbine (2) and stator (3) that are arranged
symmetrically. Single-stage means that there is only
one turbine as an output element; two-phase means
that the pump impeller acts as a torque converter when
the turbine speed is comparatively low, and as a fluid
coupling when the speed is high. Lock up refers to a
fixed state of the lock up clutch (=torque converter
clutch (TCC) inside the torque converter and thus
connects the engine directly to the transmission.
Oil Pump
Legend 1. Torque converter
2. Oil pump
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4431 of 6020
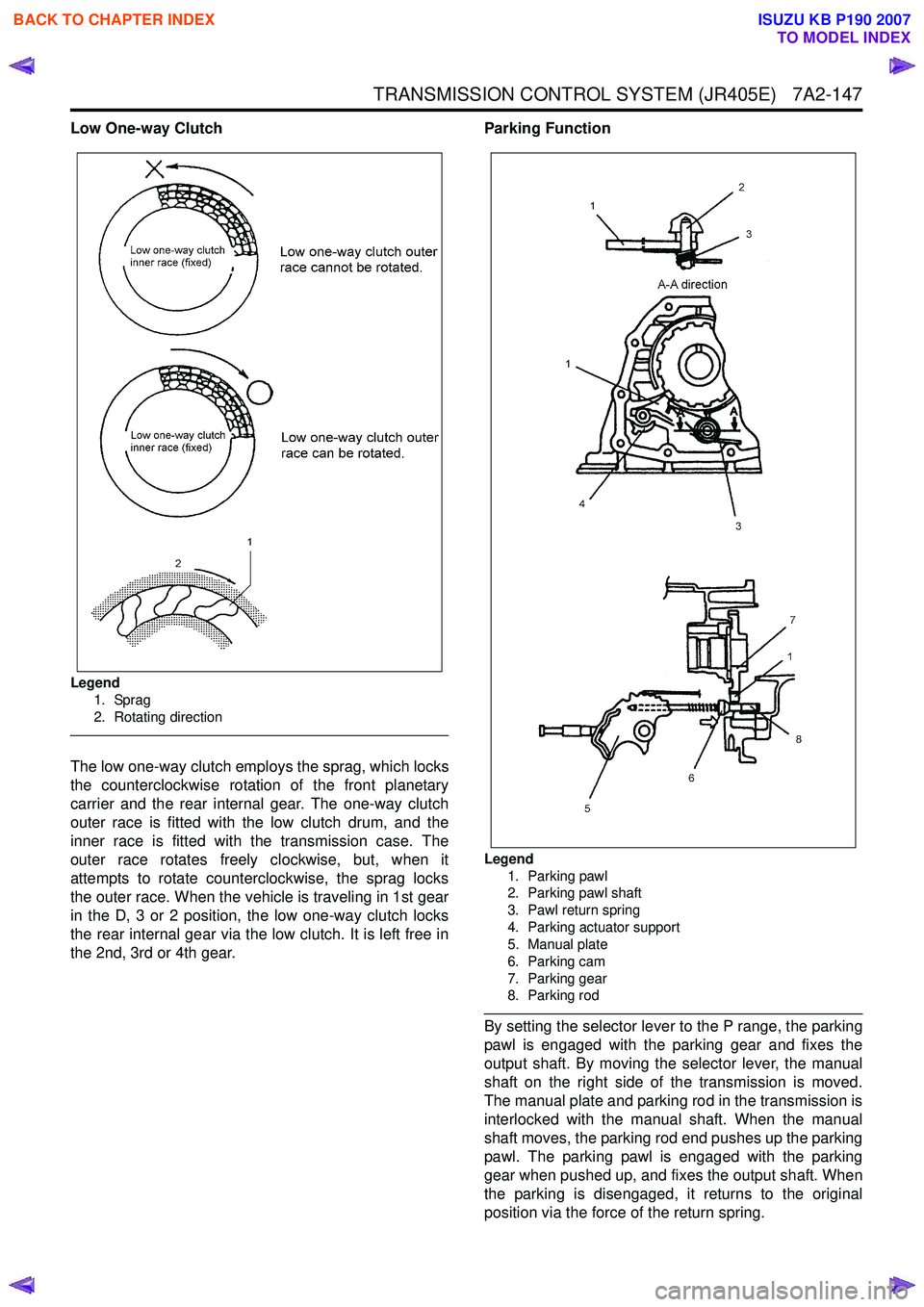
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E) 7A2-147
Low One-way Clutch
Legend1. Sprag
2. Rotating direction
The low one-way clutch employs the sprag, which locks
the counterclockwise rotation of the front planetary
carrier and the rear internal gear. The one-way clutch
outer race is fitted with the low clutch drum, and the
inner race is fitted with the transmission case. The
outer race rotates freely clockwise, but, when it
attempts to rotate counterclockwise, the sprag locks
the outer race. When the vehicle is traveling in 1st gear
in the D, 3 or 2 position, the low one-way clutch locks
the rear internal gear via the low clutch. It is left free in
the 2nd, 3rd or 4th gear. Parking Function
Legend
1. Parking pawl
2. Parking pawl shaft
3. Pawl return spring
4. Parking actuator support
5. Manual plate
6. Parking cam
7. Parking gear
8. Parking rod
By setting the selector lever to the P range, the parking
pawl is engaged with the parking gear and fixes the
output shaft. By moving the selector lever, the manual
shaft on the right side of the transmission is moved.
The manual plate and parking rod in the transmission is
interlocked with the manual shaft. When the manual
shaft moves, the parking rod end pushes up the parking
pawl. The parking pawl is engaged with the parking
gear when pushed up, and fixes the output shaft. When
the parking is disengaged, it returns to the original
position via the force of the return spring.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4441 of 6020
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E) 7A2-157
Down Slope Mode
Condition for setting the down slope mode shift map;
All of the following conditions are met:
• Brake pedal switch is depressed
• Accelerator pedal is released
• Vehicle speed is more than 60 km/h (36 MPH)
• Increment of vehicle speed is more than 1 km/h (1 MPH) per second
• Selector lever is D or 3 range
Condition for canceling the down slope mode shift map;
Either of the following condition is met:
• Accelerator pedal is depressed
• Selector lever is other than D or 3 range Power Drive Mode
When the power drive switch is ON, the TCM switches
shift map to the power drive mode map and performs
gearshift control from 1st to 4th to gain more
acceleration compared with normal mode.
Up Slope Mode
Up slope reasoning value is calculated from the
averaged accelerator pedal angle and the averaged
acceleration. Otherwise, up slope reasoning value is
calculated from the vehicle speed. The TCM selects a
up slope mode when the former is bigger than the
latter.
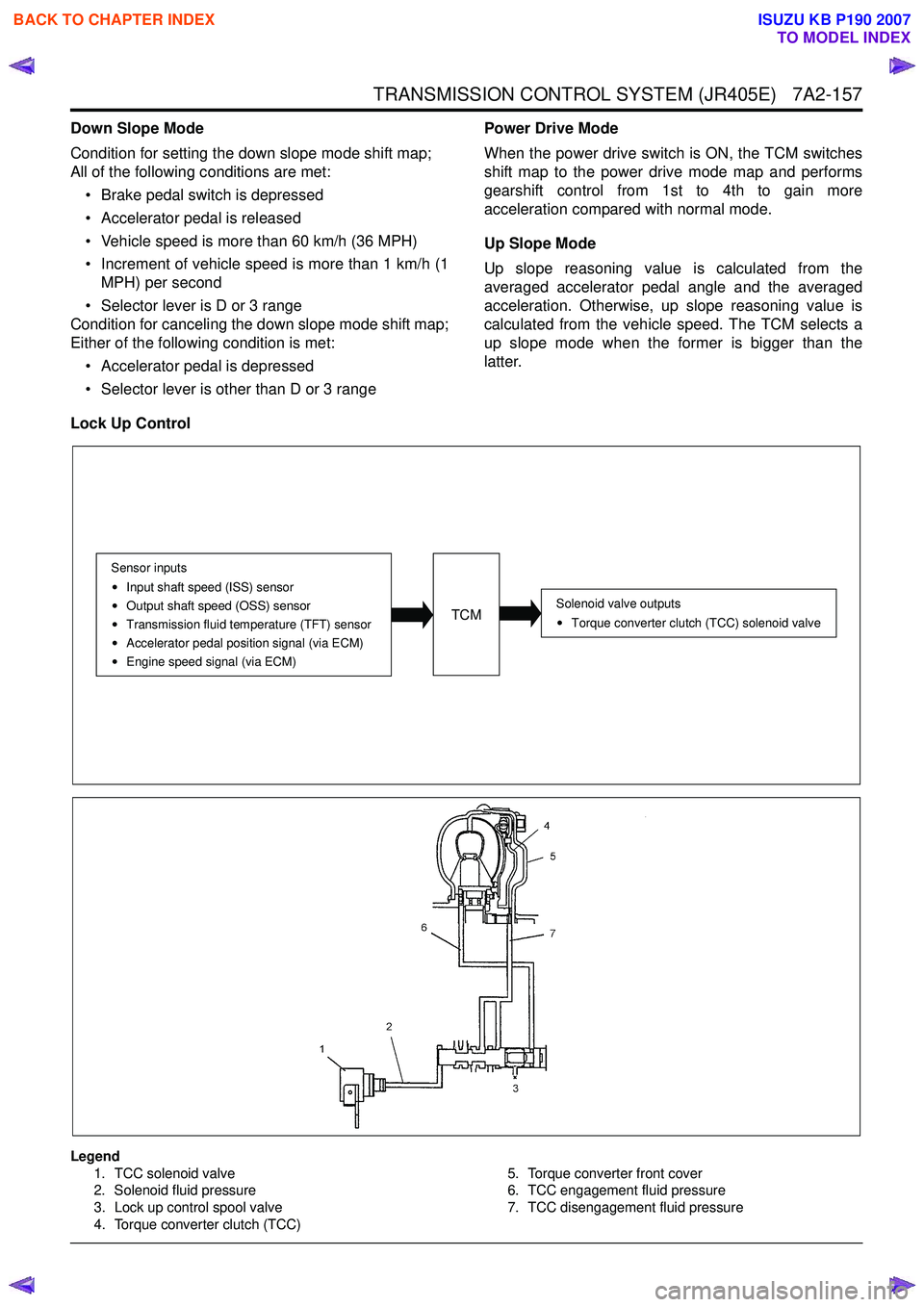
Lock Up Control
Legend 1. TCC solenoid valve
2. Solenoid fluid pressure
3. Lock up control spool valve
4. Torque converter clutch (TCC) 5. Torque converter front cover
6. TCC engagement fluid pressure
7. TCC disengagement fluid pressure
TCM
Sensor inputs
Input shaft speed (ISS) sensor
Output shaft speed (OSS) sensor
Transmission fluid temperature (TFT) sensor
Accelerator pedal position signal (via ECM)
Engine speed signal (via ECM)
Solenoid valve outputsTorque converter clutch (TCC) solenoid valve
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007