2007 ISUZU KB P190 sensor
[x] Cancel search: sensorPage 3339 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–61
• DTCs P0341, P0342, P0343, ran and passed:
• The engine is running.
• The ECM has learned the camshafts position.
DTC P0016
Run continuously once the following conditions are met.
• DTCs P0335, P0336, P0338, P0341, P0342 and P0343 ran and passed:
• The calculated engine oil temperature is less than 95 °C.
• The engine coolant temperature is 20 – 90 °C.
• The engine is running for greater than 5 seconds.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0008
The ECM detects that both camshafts on bank 1 of the engine are misaligned with the crankshaft.
DTC P0009
The ECM detects that both camshafts on bank 2 of the engine are misaligned with the crankshaft.
DTC P0016
The ECM detects the following deviation in the correlation between the camshaft position and the crankshaft position for
greater than 10 minutes:
• a camshaft position is too advanced in relationship to the crankshaft, or
• a camshaft position is too retarded in relationship to the crankshaft.
Conditions for Clearing DTC
The CKP / CMP sensor correlation DTCs are Type B DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes in this Section, for
action taken when Type B DTCs set and conditions for clearing Type B DTCs.
Additional Information
• Refer to 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the CMP system operation.
• Inspect the engine for recent engine mechanical repairs. Incorrect camshaft, camshaft actuator or timing chain
installation will trigger these DTCs.
• The engine oil condition has a major impact on the operation of the camshaft actuator.
• A low oil level may set these DTCs.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical -
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section, for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
3 A fault condition in any of the listed sensors will trigger these DTCs.
5 Incorrect camshaft, camshaft actuator or timing chain installation will trigger these DTCs.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3340 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–62
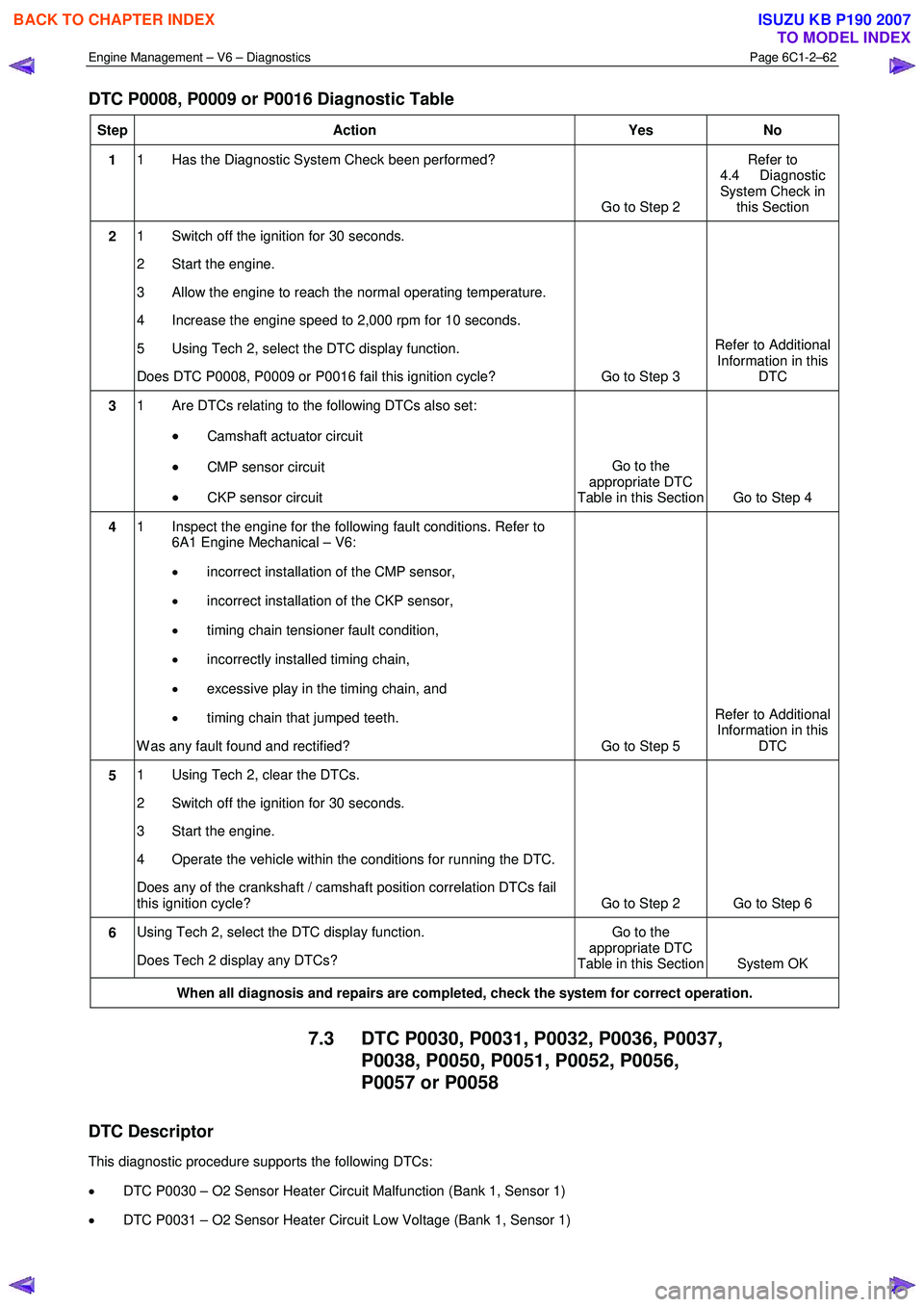
DTC P0008, P0009 or P0016 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.4 Diagnostic
System Check in this Section
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Start the engine.
3 Allow the engine to reach the normal operating temperature.
4 Increase the engine speed to 2,000 rpm for 10 seconds.
5 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0008, P0009 or P0016 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3 Refer to Additional
Information in this DTC
3 1 Are DTCs relating to the following DTCs also set:
• Camshaft actuator circuit
• CMP sensor circuit
• CKP sensor circuit Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table in this Section Go to Step 4
4 1 Inspect the engine for the following fault conditions. Refer to
6A1 Engine Mechanical – V6:
• incorrect installation of the CMP sensor,
• incorrect installation of the CKP sensor,
• timing chain tensioner fault condition,
• incorrectly installed timing chain,
• excessive play in the timing chain, and
• timing chain that jumped teeth.
W as any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 5 Refer to Additional
Information in this DTC
5 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the crankshaft / camshaft position correlation DTCs fail
this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 6
6 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs? Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table in this Section System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
7.3 DTC P0030, P0031, P0032, P0036, P0037,
P0038, P0050, P0051, P0052, P0056,
P0057 or P0058
DTC Descriptor
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0030 – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
• DTC P0031 – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3341 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–63
• DTC P0032 – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
• DTC P0036 – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 2)
• DTC P0037 – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 2)
• DTC P0038 – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 2)
• DTC P0050 – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2, Sensor 1)
• DTC P0051 – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 2, Sensor 1)
• DTC P0052 – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Voltage (Bank 2, Sensor 1)
• DTC P0056 – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2, Sensor 2)
• DTC P0057 – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 2, Sensor 2)
• DTC P0058 – O2 Sensor Heater Circuit High Voltage (Bank 2, Sensor 2)
Circuit Description
The engine control relay applies positive voltage to the heater ignition voltage circuits of the HO2S. The ECM applies a
pulse width modulated (PW M) ground to the heater control circuit of the HO2S through a device within the ECM called a
driver, to control the HO2S rate of heating.
The driver has a feedback circuit that is pulled-up when the voltage is approximately 3.3 V. The ECM monitors the driver
feedback circuit to determine if the control circuit is open, shorted to ground or shorted to a positive voltage.
An HO2S heater control circuit DTC sets if the ECM detects a high resistance, open circuit, short to ground or short to
voltage fault condition in the HO2S heater control circuit.
Conditions for Running the DTC
Runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
• Engine speed is greater than 80 rpm
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0030, P0036, P0050 or P0056
The ECM detects an open circuit fault condition in the HO2S heater control circuit when the HO2S heater is commanded
off.
DTC P0031, P0037, P0051 or P0057
The ECM detects a short to ground fault condition in the HO2S heater control circuit when the HO2S heater is
commanded off.
DTC P0032, P0038, P0052 or P0058
The ECM detects a short to voltage fault condition in the HO2S heater control circuit for five seconds when the HO2S
heater is commanded on.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The HO2S heater control circuit DTCs are Type B DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes in this Section, for
action taken when Type B DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type B DTCs.
Additional Information
• Refer to 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the HO2S system operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
• A faulty HO2S heater element may cause an open heater circuit condition. This fault may be intermittent or only
show up after the sensor has operated for a period.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3342 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–64
• Inspect the HO2S wiring harness for contact with the exhaust system.
• The front and the rear HO2Ss have a separate fuse connection. If both front or both the rear DTCs are set, the
appropriate HO2S ignition voltage circuit may be open.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical -
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section, for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
Test Description
The following number refers to the step number in the diagnostic table:
4 The ECM monitors the driver feedback circuit to determine if the heater control circuit is open, shorted to ground or shorted to a positive voltage. If the voltage is outside the specified range, there is a fault condition with the heater
control circuit.
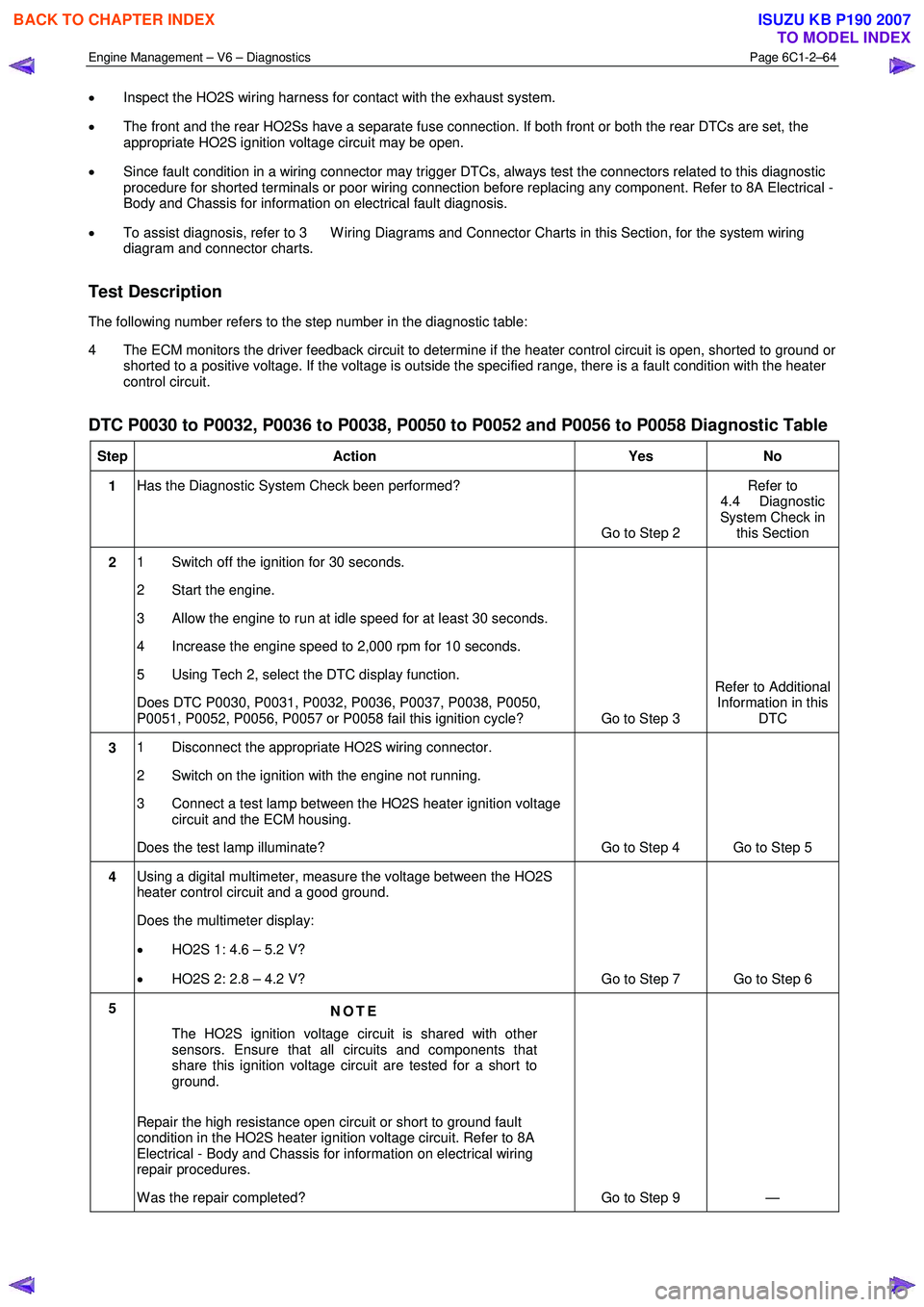
DTC P0030 to P0032, P0036 to P0038, P0050 to P0052 and P0056 to P0058 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.4 Diagnostic
System Check in this Section
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Start the engine.
3 Allow the engine to run at idle speed for at least 30 seconds.
4 Increase the engine speed to 2,000 rpm for 10 seconds.
5 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0030, P0031, P0032, P0036, P0037, P0038, P0050,
P0051, P0052, P0056, P0057 or P0058 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3 Refer to Additional
Information in this DTC
3 1 Disconnect the appropriate HO2S wiring connector.
2 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
3 Connect a test lamp between the HO2S heater ignition voltage circuit and the ECM housing.
Does the test lamp illuminate? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 5
4 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the HO2S
heater control circuit and a good ground.
Does the multimeter display:
• HO2S 1: 4.6 – 5.2 V?
• HO2S 2: 2.8 – 4.2 V? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 6
5
NOTE
The HO2S ignition voltage circuit is shared with other
sensors. Ensure that all circuits and components that
share this ignition voltage circuit are tested for a short to
ground.
Repair the high resistance open circuit or short to ground fault
condition in the HO2S heater ignition voltage circuit. Refer to 8A
Electrical - Body and Chassis for information on electrical wiring
repair procedures.
W as the repair completed? Go to Step 9 —
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3343 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–65
Step Action Yes No
6 Test the HO2S heater control circuit for a high resistance, open
circuit, short to ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer to 8A
Electrical - Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault
diagnosis.
W as any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
7 Replace the appropriate HO2S. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management
– V6 – Service Operations.
W as the repair completed? Go to Step 9 —
8 Replace the ECM. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
W as the repair completed? Go to Step 9 —
9 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the HO2S heater control circuit DTCs fail this ignition
cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 10
10 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs? Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table in this Section System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
7.4 DTC P0040 or P0041
DTC Descriptor
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0040 – O2 Sensor Signals Not Plausible (Bank 1, Sensor 1 & Bank 2, Sensor 1)
• DTC P0041 – O2 Sensor Signals Not Plausible (Bank 1, Sensor 2 & Bank 2, Sensor 2)
Circuit Description
The engine control relay applies positive voltage to the heater ignition voltage circuits of the HO2S. The ECM applies a
pulse width modulated (PW M) ground to the heater control circuit of the HO2S through a device within the ECM called a
driver, to control the HO2S rate of heating.
The ECM applies a voltage of approximately 450 mV between the reference signal circuit and low reference circuit of the
HO2S while the sensor temperature is less than the operating range.
Once the HO2S reaches operating temperature, the sensor varies this reference signal voltage, which constantly
fluctuates between the high voltage output and the low voltage output.
• The low voltage output is 0 – 450 mV, which occurs if the air fuel mixture is lean.
• The high voltage output is 450 – 1,000 mV, which occurs if the air fuel mixture is rich.
The ECM monitors, stores and evaluates the HO2S voltage fluctuation information to determine the level of oxygen
concentration in the exhaust.
An HO2S signal not plausible or wire connector swapped DTC sets if the ECM detects the HO2S signal voltages are
heading in the opposite direction of what was commanded.
Additional Information
• Refer to 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the HO2S system operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3344 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–66
• The HO2S must be tightened correctly. A loose HO2S will trigger these DTCs.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical -
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section, for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
Conditions for Running the DTC
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
• The engine is running.
• The O2 Sensors are in closed loop.
• The ECM is commanding the HO2Ss fuel trim.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ECM detects the HO2S signal voltages are heading in the opposite direction of what was commanded.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The HO2S signal not plausible DTCs are Type B DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes in this Section, for
action taken when Type B DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type B DTCs.
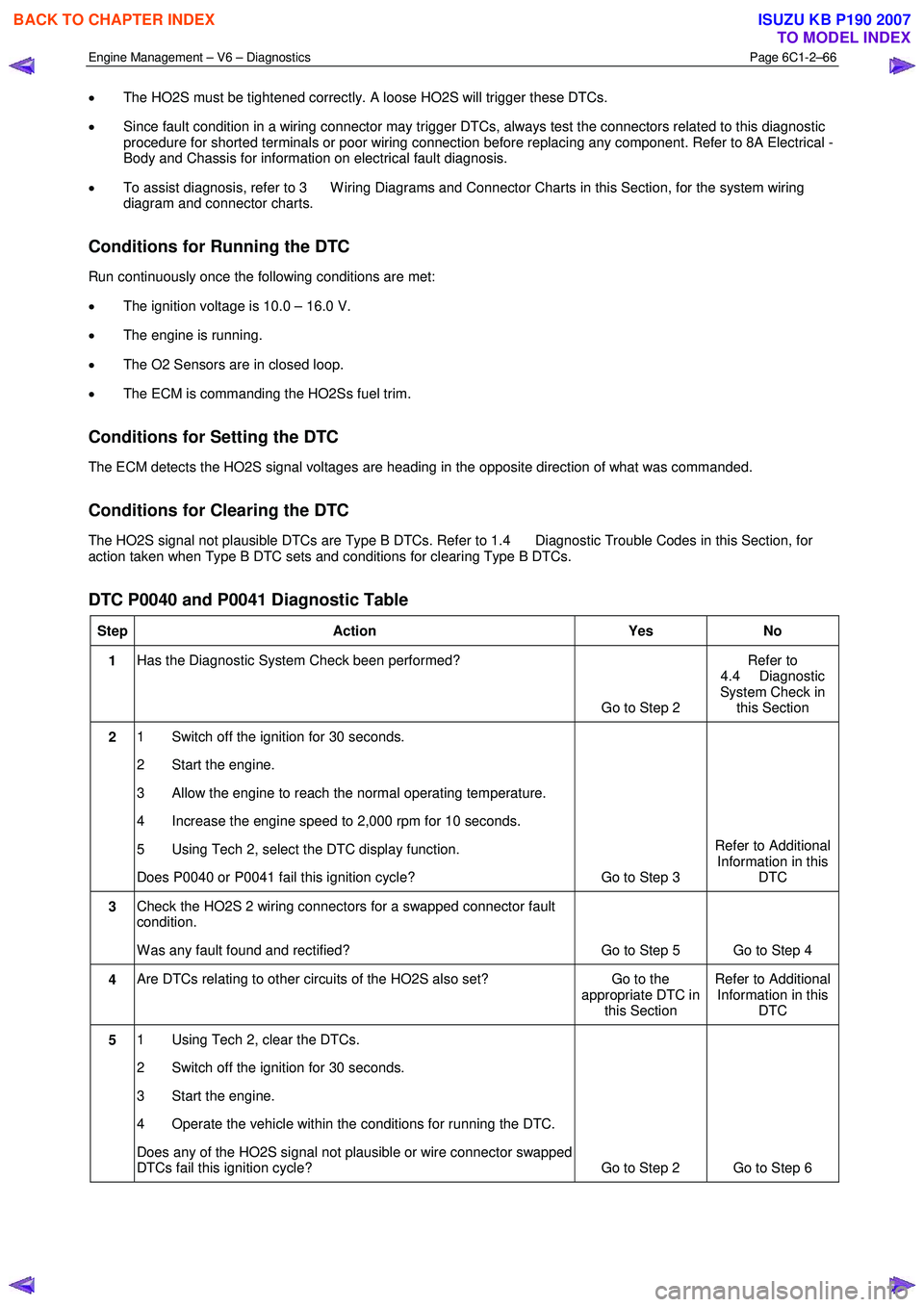
DTC P0040 and P0041 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.4 Diagnostic
System Check in this Section
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Start the engine.
3 Allow the engine to reach the normal operating temperature.
4 Increase the engine speed to 2,000 rpm for 10 seconds.
5 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does P0040 or P0041 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3 Refer to Additional
Information in this DTC
3 Check the HO2S 2 wiring connectors for a swapped connector fault
condition.
W as any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 5 Go to Step 4
4 Are DTCs relating to other circuits of the HO2S also set? Go to the
appropriate DTC in this Section Refer to Additional
Information in this DTC
5 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the HO2S signal not plausible or wire connector swapped
DTCs fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 6
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3345 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–67
Step Action Yes No
6 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs? Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table in this Section System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
7.5 DTC P0053 or P0059
DTC Descriptor
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0053 – O2 Sensor Heater Resistance Range / Performance (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
• DTC P0059 – O2 Sensor Heater Resistance Range / Performance (Bank 2, Sensor 1)
Circuit Description
The engine control relay applies positive voltage to the heater ignition voltage circuits of the HO2S. The ECM applies a
pulse width modulated (PW M) ground to the heater control circuit of the HO2S through a device within the ECM called a
driver, to control the HO2S rate of heating.
The ECM maintains the voltage between the reference signal circuit and low reference circuit of the HO2S 1 to about
450 mV by increasing or decreasing the oxygen content in the HO2S diffusion gap. To achieve this, the ECM controls
the current applied to the oxygen pumping cell in the HO2S.
• If the air / fuel mixture in the exhaust is balanced (lambda = 1), the oxygen pumping cell current is zero.
• If the exhaust gas in the HO2S 1 diffusion gap is lean, the ECM applies a positive current to the oxygen pumping
cell to discharge oxygen from the diffusion gap.
• If the exhaust gas in the HO2S 1 diffusion gap is rich, the ECM applies a negative current to the oxygen pumping
cell to draw oxygen into the diffusion gap.
The pumping current required to maintain the HO2S 1 signal circuit voltage to about 450 mV is proportional to the level
of oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas. The ECM monitors and evaluates the oxygen pumping current to determine
the level of oxygen concentration in the exhaust.
An HO2S internal heater resistance performance DTC sets if the ECM detects an internal fault condition in the ECM
HO2S heater circuit.
Conditions for Running the DTC
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• DTCs P0030, P0031, P0032, P0101, P0121, P012, P0123, P0131, P0132, P0133, P0221, P0222, P0223, P0336,
P0338, P2237, P2243 and P2626 ran and passed.
• The calculated exhaust temperature is greater than 400ºC.
• The engine does not misfire.
• The ignition voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V.
• The HO2S is commanded on.
• The engine is running at speed greater than 25 rpm
Conditions for Setting the DTC
There is an internal fault condition in the ECM HO2S heater circuit.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The HO2S internal heater resistance performance DTCs are Type B DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes in
this Section, for action taken when Type B DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type B DTCs.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3346 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–68
Additional Information
• Refer to 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the HO2S system operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
• The HO2S must be tightened correctly. A loose HO2S will trigger these DTCs.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical -
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section, for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
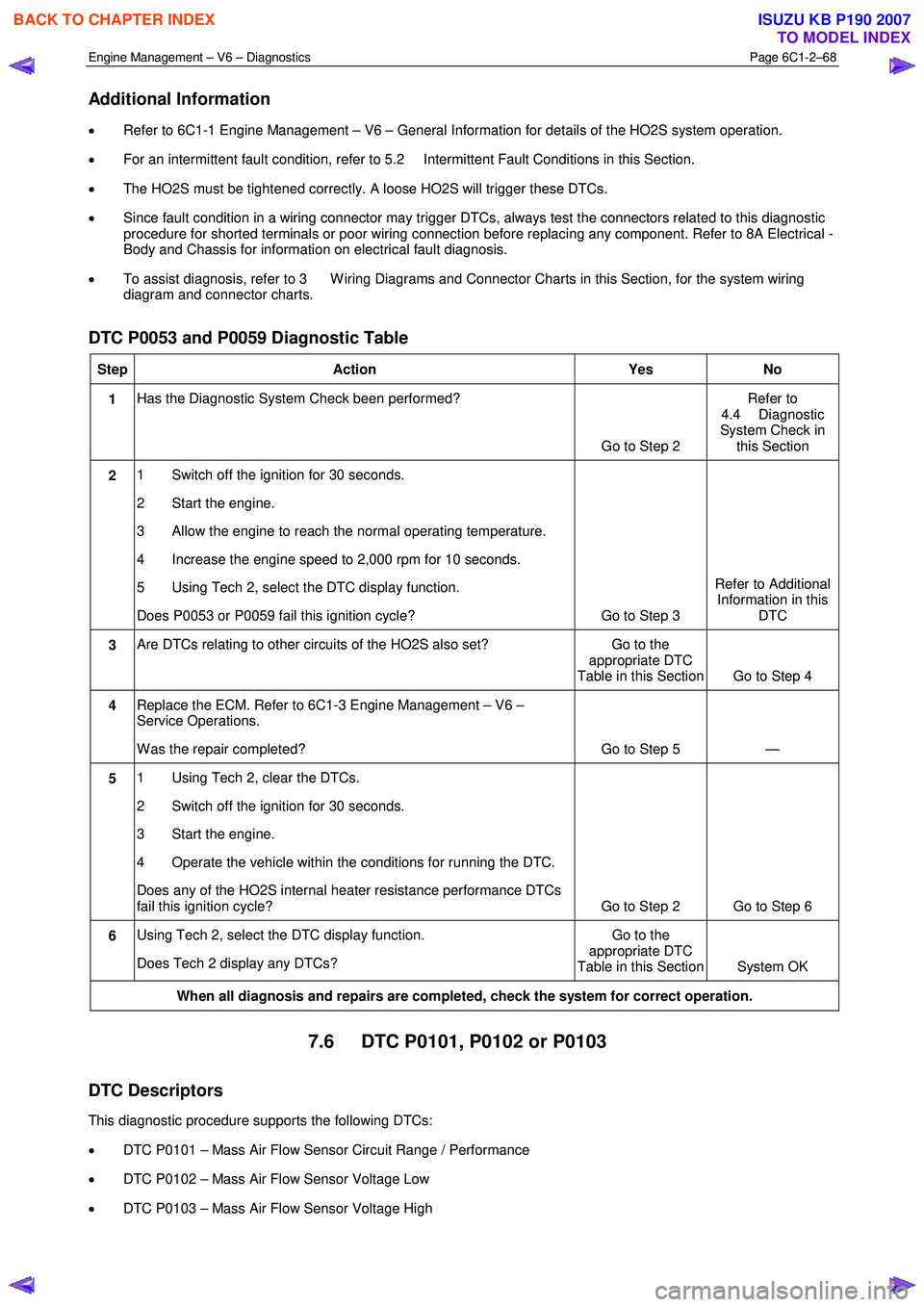
DTC P0053 and P0059 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.4 Diagnostic
System Check in this Section
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Start the engine.
3 Allow the engine to reach the normal operating temperature.
4 Increase the engine speed to 2,000 rpm for 10 seconds.
5 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does P0053 or P0059 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3 Refer to Additional
Information in this DTC
3 Are DTCs relating to other circuits of the HO2S also set? Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table in this Section Go to Step 4
4 Replace the ECM. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
W as the repair completed? Go to Step 5 —
5 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the HO2S internal heater resistance performance DTCs
fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 6
6 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs? Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table in this Section System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
7.6 DTC P0101, P0102 or P0103
DTC Descriptors
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P0101 – Mass Air Flow Sensor Circuit Range / Performance
• DTC P0102 – Mass Air Flow Sensor Voltage Low
• DTC P0103 – Mass Air Flow Sensor Voltage High
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007