2007 ISUZU KB P190 wiring diagram
[x] Cancel search: wiring diagramPage 3354 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–76
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0116
The ECM detects the engine coolant temperature sensor value is 10°C less than the minimum calculated engine
temperature.
DTC P0117
The ECM detects the engine coolant temperature is greater than 140 °C for longer than 3 seconds.
DTC P0118
The ECM detects the engine coolant temperature is less than -39 °C for longer than 3 seconds.
DTC P0125
The ECM determines the calculated engine temperature by measuring the amount of airflow into the engine. This DTC
sets if the ECM detects the actual ECT sensor is not within 10ºC of the calculated engine temperature for approximately
2 – 5 minutes.
DTC P1258
The ECM detects the engine coolant temperature is greater than 131 °C for longer than 2 seconds.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The ECT sensor DTCs are Type B DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes in this Section, for action taken when a
Type B DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type B DTC.
Additional Information
• Refer to 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the ECT sensor operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
• DTCs P0116, P0117, P0118 and P0125 diagnostic table is developed with the assumption the engine cooling
system is functioning correctly. Therefore, rectify any engine cooling system fault conditions before proceeding
with this diagnostic table.
• Test the ECT sensor using the ECT Temperature vs. Resistance in 6C1-3 Engine Management –V6 – Service
Operations. If the engine has sat overnight, the ECT sensor should display within 3 °C of the IAT sensor values.
W hen the engine is first started, the ECT should rise steadily to about 90 °C then stabilise when thermostat opens.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical -
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section, for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
2 A fault condition in the engine cooling system may trigger these DTCs.
7 The ECT sensor low reference circuit is shared with other components. DTC P0118 may set if the shared low reference circuit is shorted to voltage. Test the low reference circuit of all components that share this circuit to find
the source of the fault condition.
DTC P0116, P0117, P0118, P0125 and P1258 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.4 Diagnostic
System Check in this Section
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3355 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–77
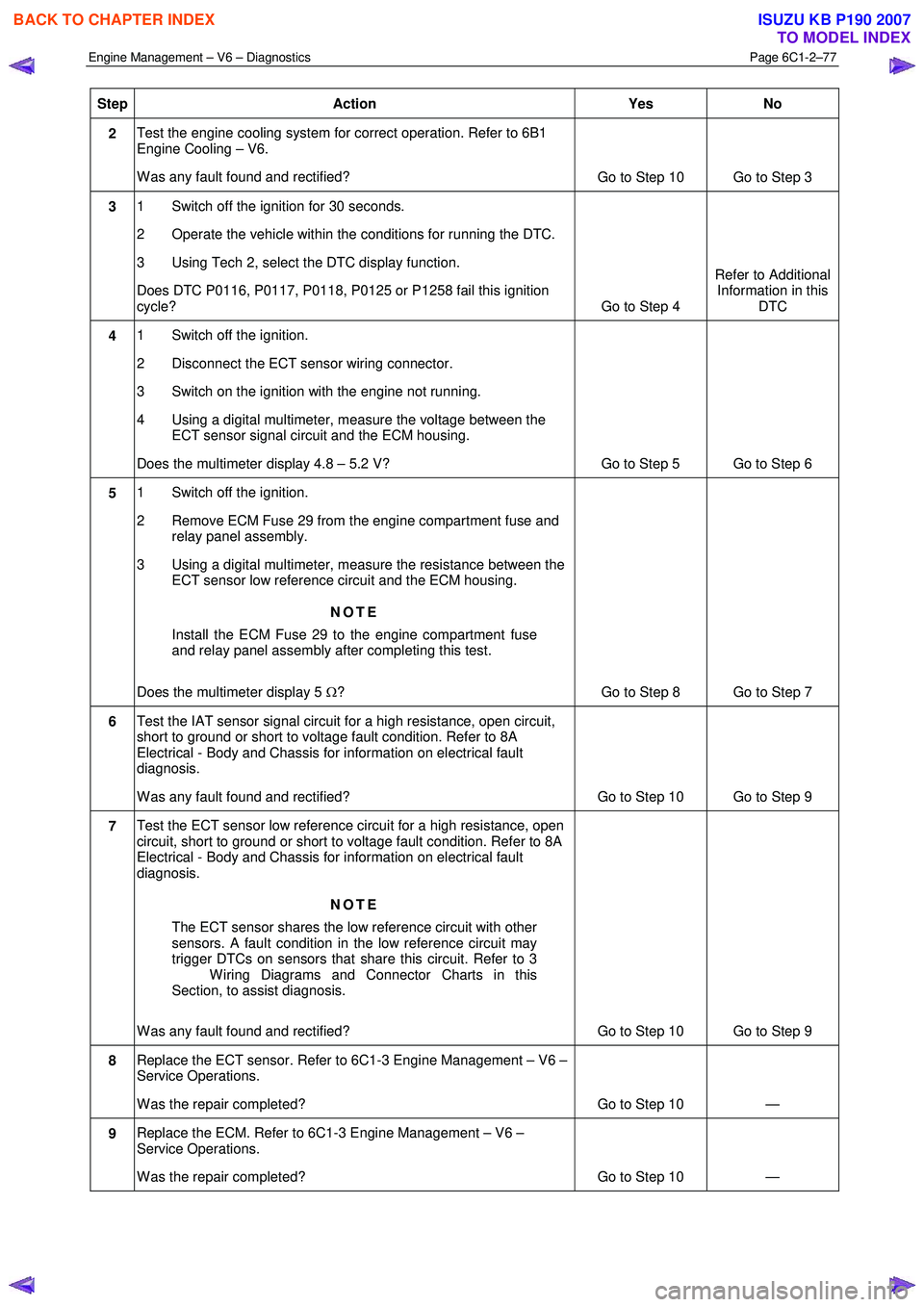
Step Action Yes No
2 Test the engine cooling system for correct operation. Refer to 6B1
Engine Cooling – V6.
W as any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 3
3 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0116, P0117, P0118, P0125 or P1258 fail this ignition
cycle? Go to Step 4 Refer to Additional
Information in this DTC
4 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Disconnect the ECT sensor wiring connector.
3 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
4 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the ECT sensor signal circuit and the ECM housing.
Does the multimeter display 4.8 – 5.2 V? Go to Step 5 Go to Step 6
5 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Remove ECM Fuse 29 from the engine compartment fuse and relay panel assembly.
3 Using a digital multimeter, measure the resistance between the ECT sensor low reference circuit and the ECM housing.
NOTE
Install the ECM Fuse 29 to the engine compartment fuse
and relay panel assembly after completing this test.
Does the multimeter display 5 Ω? Go to Step 8 Go to Step 7
6 Test the IAT sensor signal circuit for a high resistance, open circuit,
short to ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer to 8A
Electrical - Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault
diagnosis.
W as any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 9
7 Test the ECT sensor low reference circuit for a high resistance, open
circuit, short to ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer to 8A
Electrical - Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault
diagnosis.
NOTE
The ECT sensor shares the low reference circuit with other
sensors. A fault condition in the low reference circuit may
trigger DTCs on sensors that share this circuit. Refer to 3
W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this
Section, to assist diagnosis.
W as any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 9
8 Replace the ECT sensor. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
W as the repair completed? Go to Step 10 —
9 Replace the ECM. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
W as the repair completed? Go to Step 10 —
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3357 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–79
• The TP sensor 2 signal voltage is 0.15 – 4.8 V.
DTC P0222 runs continuously once the following conditions are met:
• The battery voltage is greater than 7 V.
• The ignition is switched on.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0121
The following conditions exist:
• The TP sensor 1 signal voltage and the TP sensor 2 signal voltage have a difference of greater than 9 percent.
• The TP sensor signal voltage has a difference of greater than 9 percent from the calculated TP sensor signal
voltage.
DTC P0122
The ECM detects the TP sensor 1 signal voltage is less than 0.18 volt.
DTC P0123
The ECM detects the TP sensor 1 signal voltage is greater than 4.6 V.
DTC P0221
The following conditions exist:
• The TP sensor 2 signal voltage and the TP sensor 1 signal voltage have a difference of greater than 9 percent.
• The TP sensor 2 signal voltage has a difference of greater than 9 percent from the calculated TP sensor signal
voltage.
DTC P0222
The ECM detects the TP sensor 2 signal voltage is less than 0.16 volt.
DTC P0223
The ECM detects the TP sensor 2 signal voltage is greater than 4.8 V.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
DTCs P0121, P0122, P0123, P0221, P0222 are P0223 are Type B DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes in
this Section, for action taken when a Type B DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type B DTCs.
Additional Information
• Refer to 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the TP sensor operation.
• The ECM defaults to a reduced power mode if there is a fault condition in the TP sensor circuits for the entire
ignition cycle, even if the fault condition is corrected.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
• The TP sensors share a common 5 V reference circuit, test for a fault condition in the 5 V reference circuit if both
DTCs P0122 and P0222 are set.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical -
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section, for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3364 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–86
DTC P2243 and P2247
The ECM detects the internal HO2S signal voltage is not 0.2 – 4.7 V.
DTC P2270 and P2272
W hen the ECM detects the HO2S 2 is less than 650 mV for 100 seconds, the ECM enriches the fuel mixture up to 30
percent for 10 seconds. This DTC sets if the ECM detects the HO2S 2 is still less than 650 mV.
DTC P2271 and P2273
W hen the ECM detects the HO2S 2 is greater than 650 mV for 100 seconds, the ECM leans the fuel mixture up to -7
percent for 10 seconds. If this signal voltage is still greater than 650 mV, the ECM tests the HO2S at the next decel fuel
cut-off. This DTC sets if the ECM detects the HO2S 2 signal voltage is greater than 200 mV after 4 seconds in decel fuel
cu-off mode.
DTC P2297 and P2298
The ECM detects the internal HO2S 1 signal voltage is greater than 3.7 V for longer than 10 seconds.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The HO2S reference circuit DTCs are Type B DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes in this Section, for action
taken when Type B DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type B DTCs.
Additional Information
• Refer to 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the HO2S system operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
• The HO2S must be tightened correctly. A loose HO2S will trigger these DTCs.
• A fault condition in the fuel delivery system, air intake system or exhaust system may trigger these DTCs.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical -
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section, for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
DTC P0130 to P0132, P0135 to P0138, P0140, P0141, P0150 to P0152, P0155, P0157, P0158,
P0160, P0161, P2243, P2247, P2270 to P2273, P2297 or P2298 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1
Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed? Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.4 Diagnostic
System Check in this Section
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Start the engine.
3 Allow the engine to reach the normal operating temperature.
4 Increase the engine speed to 2,000 rpm for 10 seconds or operate the vehicle within the conditions for setting the DTC.
5 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0130, P0131, P0132, P0135, P0137, P0138, P0140,
P0141, P0150, P0151, P0152, P0155, P0160, P0161, P2243, P2247,
P2270, P2271, P2272, P2273, P2297 or P2298 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3 Refer to Additional
Information in this DTC
3 Are DTCs relating to the heater circuit of the O2 sensor, also set?
(e.g. P0030, P0031, P0032, P0036, P0037, P0038, P0050, P0051,
P0052, P0056, P0057 or P0058) Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table in this Section Go to Step 4
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3367 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–89
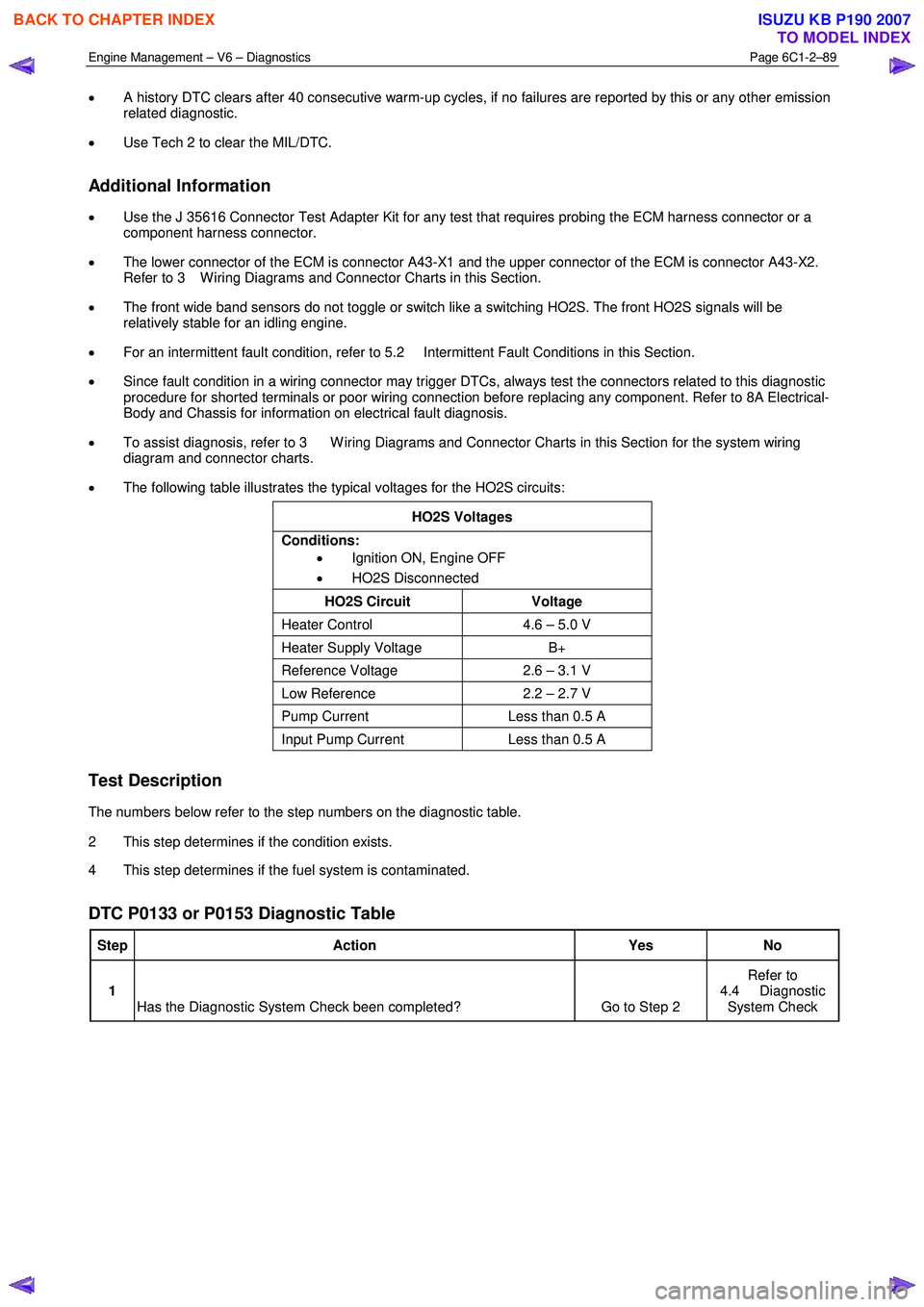
• A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive warm-up cycles, if no failures are reported by this or any other emission
related diagnostic.
• Use Tech 2 to clear the MIL/DTC.
Additional Information
• Use the J 35616 Connector Test Adapter Kit for any test that requires probing the ECM harness connector or a
component harness connector.
• The lower connector of the ECM is connector A43-X1 and the upper connector of the ECM is connector A43-X2.
Refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section.
• The front wide band sensors do not toggle or switch like a switching HO2S. The front HO2S signals will be
relatively stable for an idling engine.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical-
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
• The following table illustrates the typical voltages for the HO2S circuits:
HO2S Voltages
Conditions: • Ignition ON, Engine OFF
• HO2S Disconnected
HO2S Circuit Voltage
Heater Control 4.6 – 5.0 V
Heater Supply Voltage B+
Reference Voltage 2.6 – 3.1 V
Low Reference 2.2 – 2.7 V
Pump Current Less than 0.5 A
Input Pump Current Less than 0.5 A
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
2 This step determines if the condition exists.
4 This step determines if the fuel system is contaminated.
DTC P0133 or P0153 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1
Has the Diagnostic System Check been completed? Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.4 Diagnostic System Check
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3374 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–96
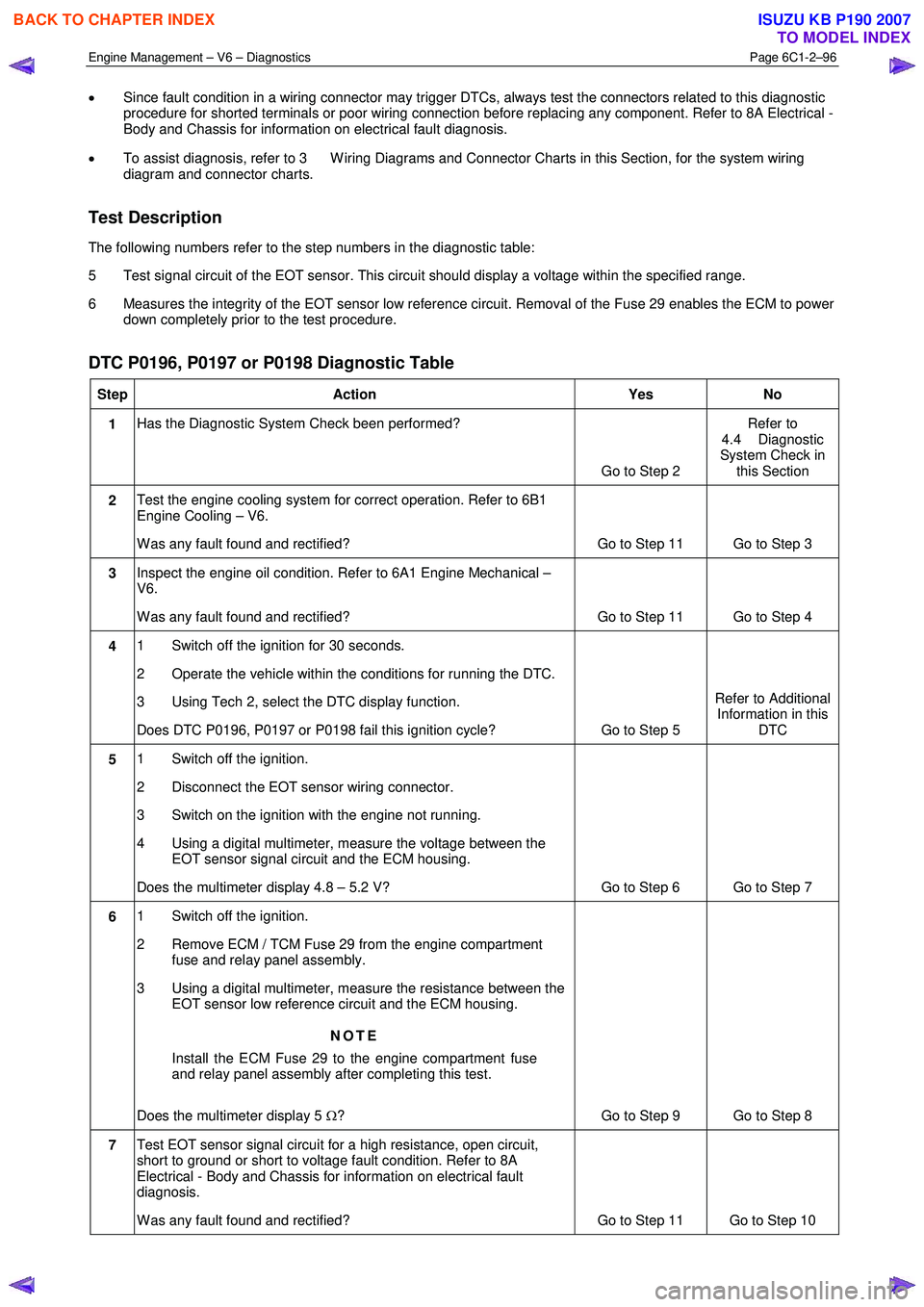
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical -
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section, for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
5 Test signal circuit of the EOT sensor. This circuit should display a voltage within the specified range.
6 Measures the integrity of the EOT sensor low reference circuit. Removal of the Fuse 29 enables the ECM to power down completely prior to the test procedure.
DTC P0196, P0197 or P0198 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.4 Diagnostic
System Check in this Section
2 Test the engine cooling system for correct operation. Refer to 6B1
Engine Cooling – V6.
W as any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 3
3 Inspect the engine oil condition. Refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical –
V6.
W as any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 4
4 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0196, P0197 or P0198 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 5 Refer to Additional
Information in this DTC
5 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Disconnect the EOT sensor wiring connector.
3 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
4 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the EOT sensor signal circuit and the ECM housing.
Does the multimeter display 4.8 – 5.2 V? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 7
6 1 Switch off the ignition.
2 Remove ECM / TCM Fuse 29 from the engine compartment fuse and relay panel assembly.
3 Using a digital multimeter, measure the resistance between the EOT sensor low reference circuit and the ECM housing.
NOTE
Install the ECM Fuse 29 to the engine compartment fuse
and relay panel assembly after completing this test.
Does the multimeter display 5 Ω? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 8
7 Test EOT sensor signal circuit for a high resistance, open circuit,
short to ground or short to voltage fault condition. Refer to 8A
Electrical - Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault
diagnosis.
W as any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 10
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3376 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–98
• DTC P0268 – Injector 3 Control Circuit High Voltage
• DTC P0270 – Injector 4 Control Circuit Low Voltage
• DTC P0271 – Injector 4 Control Circuit High Voltage
• DTC P0273 – Injector 5 Control Circuit Low Voltage
• DTC P0274 – Injector 5 Control Circuit High Voltage
• DTC P0276 – Injector 6 Control Circuit Low Voltage
• DTC P0277 – Injector 6 Control Circuit High Voltage
Circuit Description
The engine control relay applies ignition positive voltage to the fuel injector ignition circuit. The ECM applies a pulse
width modulated (PW M) ground to the injector control circuit through a device within the ECM called a driver to control
each fuel injector on time.
The driver has a feedback circuit that is pulled-up when the voltage is approximately 3.3 V. The ECM monitors the driver
feedback circuit to determine if the control circuit is open, shorted to ground or shorted to a positive voltage.
A fuel injector control circuit DTC sets if the ECM detects a fault condition in a fuel injector control circuit.
Conditions for Running the DTC
Run continuously once the following conditions are met:
• the battery voltage is 10.0 – 16.0 V, and
• engine speed is greater than 80 rpm
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P0201,P0202, P0203, P0204, P0205 or P0206
The ECM detects an open circuit fault condition in a fuel injector circuit.
DTC P0261, P0264, P0267, P0270, P0273 and P0276
The ECM detects a short to ground fault condition in the control circuit a fuel injector.
DTC P0262, P0265, P0268, P0271, P0274 and P0277
The ECM detects a short to voltage fault condition in the control circuit of a fuel injector.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The fuel injector control circuit DTCs are Type B DTCs. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes in this Section, for
action taken when Type B DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type B DTCs.
Additional Information
• Refer to 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the fuel injector operation.
• Using Tech 2, observe the appropriate fuel injector status parameter while wriggle testing related harness and
connectors. Tech 2 reading will change from Ok to Fault if there is an intermittent fault condition in the harness or
connector being tested.
• Perform the fuel injector coil test to help isolate an intermittent condition. Refer to 6.2 Fuel Injector Coil
Test in this Section.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical -
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section, for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3379 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–101
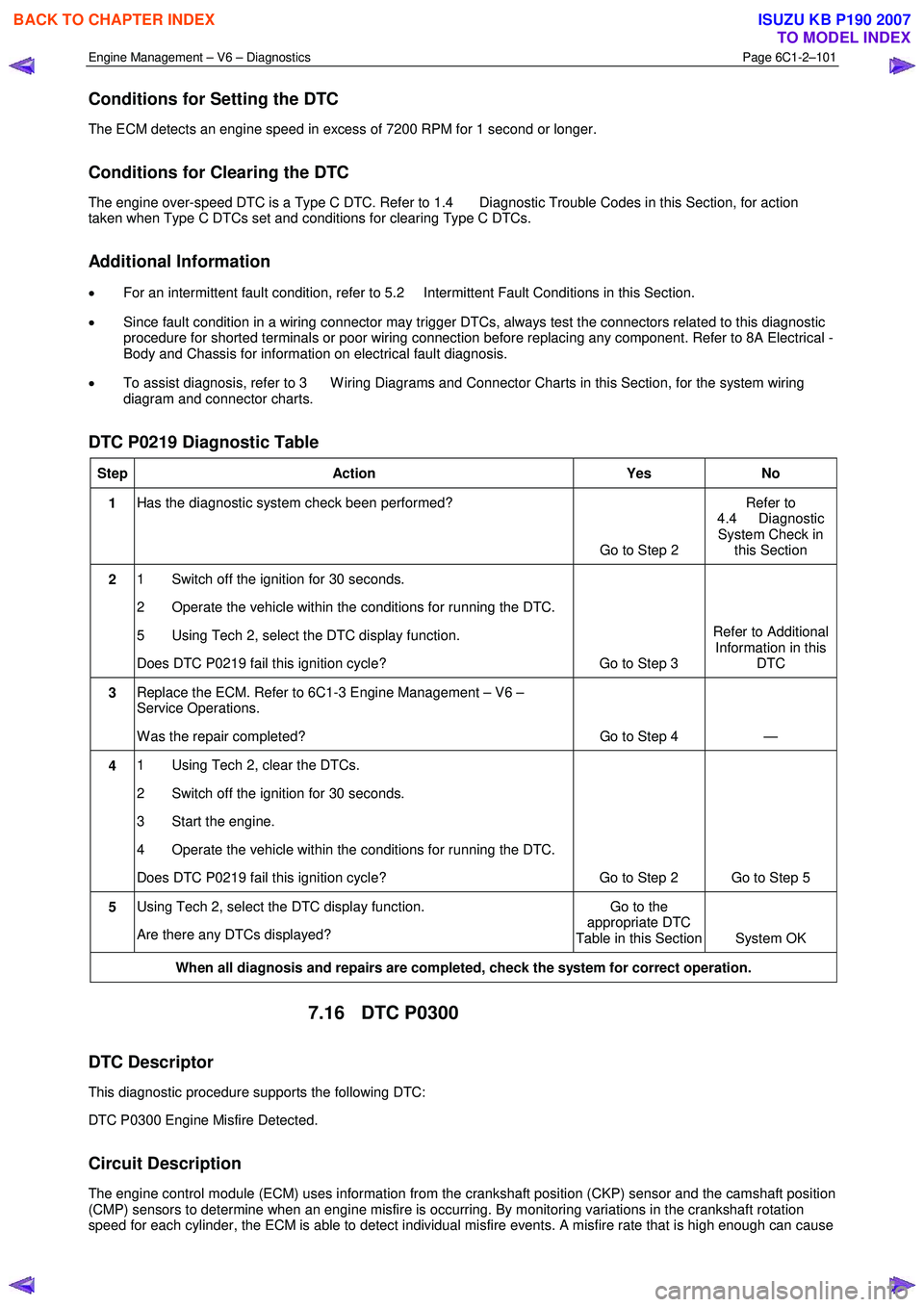
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The ECM detects an engine speed in excess of 7200 RPM for 1 second or longer.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
The engine over-speed DTC is a Type C DTC. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes in this Section, for action
taken when Type C DTCs set and conditions for clearing Type C DTCs.
Additional Information
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical -
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section, for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
DTC P0219 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the diagnostic system check been performed?
Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.4 Diagnostic System Check in this Section
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
5 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0219 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3 Refer to Additional
Information in this DTC
3 Replace the ECM. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
W as the repair completed? Go to Step 4 —
4 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does DTC P0219 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 5
5 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Are there any DTCs displayed? Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table in this Section System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
7.16 DTC P0300
DTC Descriptor
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTC:
DTC P0300 Engine Misfire Detected.
Circuit Description
The engine control module (ECM) uses information from the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor and the camshaft position
(CMP) sensors to determine when an engine misfire is occurring. By monitoring variations in the crankshaft rotation
speed for each cylinder, the ECM is able to detect individual misfire events. A misfire rate that is high enough can cause
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007