2007 ISUZU KB P190 engine coolant
[x] Cancel search: engine coolantPage 3199 of 6020

Engine Cooling – V6 Engine Page 6B1–64
5 Specifications
General
Coolant Filler Cap Pressure Rating .............................................................................120 kPa
Cooling System Capacity
Automatic Transmission ........................................................................................ 9.9 litres
Manual Transmission .......................................................................................... 10.3 litres
Coolant Corrosion Inhibitor Quantity W hen Refilling System Automatic Transmission Models......................................................................... 5 litres
Manual Transmission Models .......................................................................... 5.2 litres
NOTE
DEX-COOL® long life coolant or equivalent such
as Extended Life Anti-freeze Coolant, conforming
to GM Specification 6277M, must be used when
changing coolant.
Thermostat Type...............................................................................................Power element (wax pellet)
Start to Open at ......................................................................................................... 82 ± 2 ° C
Fully Open at .......................................................................................................... 95° C ma x.
Coolant Pump
Type........................................................................................................................ Cen trifugal
Drive ................................................................................................ Multi-Vee Serpentine Belt
Bearing Type .................................................................................... Double Row Ball Bearing
Radiator
Core type ......................................................................................... Aluminium crossflow core
Overall width ................................................................................................................ 66 4 mm
Core width.................................................................................................................... 5 10 mm
Overall height............................................................................................................... 60 2 mm
Core height .................................................................................................................. 51 2 mm
Core thickness ............................................................................................................... 27 mm
Plastic Tanks .............................................................................. Nylon 6.6 (30% Glass Filled)
Radiator Hoses Lower Upper
Number ............................................................................... One............................. One
Type................................................................................ Moulded ...................... Moulded
Inside diameter ................................................................. 34 mm ........................ 34 mm
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3201 of 6020

Engine Cooling – V6 Engine Page 6B1–66
6 Torque Wrench Specifications
N.m
Coolant Outlet housing to Engine Outlet Attaching Bolts............................... 10
Coolant Pump to Front Cover Attaching Bolts ............................................... 10
Coolant Pump Pulley Attaching Bolts ............................................................ 12
Coolant Inlet Pipe to Thermostat Housing Attaching Bolt .............................. 23
Fan Motor Assembly to Shroud Attaching Screws .......................................... 5
Heater Pipe Assembly to Thermostat Housing Attaching Bolts ..................... 10
Heater Pipe Assembly to Cylinder Head Attaching Bolt ................................ 35
Thermostat Housing to Engine Block Attaching Bolts.................................... 10
Rear Engine Harness .................................................................................... 15
Engine Harness Ground Terminal ................................................................. 12
Coolant Inlet Pipe To Engine Block Bolt ........................................................ 25
Transmission Cooler Lines Bracket .............................................................. 23
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3202 of 6020
Engine Cooling – V6 Engine Page 6B1–67
7 Special Tools
Tool number Illustration Description Classification
AU505
Coolant Tester
Used for testing the coolant
concentration level.
Previously released. Mandatory
AU525
Quick Connect Release Tool
Used to release the quick connect
fittings on automatic transmission fluid
cooler lines at the radiator end, when
fitted.
Previously released. Mandatory
BT3373–F
Belt Tension Gauge
Used when checking drive and
accessory belt tension and
adjustments.
Previously released. Desirable
J 26568 Refractometer
Used for testing coolant concentration
level.
Previously released, as AU 435. Mandatory
J28431–B Fluid Dye
Available in 24 x 1-ounce bottles.
Used in conjunction with a black light
such as J42220 to locate the source
of various fluid leaks.
Previously released. Desirable
J42220 Black Light, Leak Detection Lamp
Used with dye, J28431–B to locate the
source of various vehicle fluid leaks.
Previously released. Desirable
N/A Cooling System Pressure Tester
Previously released. Commercially available. Mandatory
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3244 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – General Information Page 6C1-1–2
3.9 Serial Data Communication System ................................................................................................................... 17
3.10 Self Diagnostics System ..................................................................................................................................... 17
3.11 Service Programming System ..................................................................................................... ....................... 17
3.12 Immobiliser System ............................................................................................................................................. 18
4 Component Description and Operation ............................................................................................ .19
4.1 A/C Refrigerant Pressure Sensor ....................................................................................................................... 19
4.2 Brake Pedal Switch Assembly ............................................................................................................................ 19
Stop Lamp and Initial Brake Apply Switch ....................................................................................... ................. 19
Stop Lamp Switch ............................................................................................................................................ 19
Initial Brake Apply Switch ..................................................................................................... ............................ 19
4.3 Barometric Pressure Sensor..................................................................................................... .......................... 20
4.4 Camshaft Position Sensor .................................................................................................................................. 20
4.5 Crankshaft Position Sensor ................................................................................................................................ 21
4.6 Clutch Pedal Switch Assembly – Manual Vehicles Only ............................................................................ ...... 22
4.7 Engine Control Module........................................................................................................................................ 22
4.8 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor .............................................................................................. ................... 23
4.9 Electric Cooling Fans .......................................................................................................................................... 23
4.10 Engine Oil Level and Temperature Sensor ........................................................................................ ................ 24
Engine Oil Temperature Sensor ......................................................................................................................... 24
Engine Oil Level Sensor ...................................................................................................................................... 25
4.11 Engine Oil Pressure Sensor..................................................................................................... ........................... 25
4.12 Fuel Injectors........................................................................................................................................................ 26
4.13 Fuel Rail Assembly ............................................................................................................. ................................. 27
4.14 Heated Oxygen Sensors .......................................................................................................... ............................ 27
LSF 4.2 Two-step Planar Heated Oxygen Sensors .................................................................................. ......... 27
LSU 4.2 Wide-band Planar Heated Oxygen Sensors ................................................................................. ....... 29
4.15 Ignition Coil and Spark Plug ............................................................................................................................... 31
4.16 Intake Air Temperature Sensor .................................................................................................. ......................... 32
4.17 Knock Sensor ....................................................................................................................................................... 32
4.18 Mass Air Flow Sensor........................................................................................................... ............................... 33
Air Intake System ................................................................................................................................................. 33
Mass Air Flow Sensor........................................................................................................... ............................... 33
Construction ..................................................................................................................................................... 34
Operation ......................................................................................................................................................... 34
5 Abbreviations and Glossary of Terms ............................................................................................ ...35
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3246 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – General Information Page 6C1-1–4
ADR 37/01 (Petrol) 2.1 0.26 2 0.63 Not Applicable
ADR 79/01 (Petrol,
LPG, CNG) 2.3 0.2 2 0.15 0.05
1.3 Warning Caution and Notes
This Section contains various W ARNINGS, CAUTIONS and NOTE statements that you must observe carefully to reduce
the risk of death or injury during service, repair procedures or vehicle operation. Incorrect service or repair procedures
may damage the vehicle or cause operational faults. W ARNINGS, CAUTION and NOTE statements are not exhaustive.
GM Holden LTD can not possibly warn of all the potentially hazardous consequences of failure to follow these
instructions.
Definition of WARNING, CAUTION and NOTE Statements
Diagnosis and repair procedures in this Section contain both general and specific W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE
statements. GM Holden LTD is dedicated to the presentation of service information that helps the technician to diagnose
and repair the systems necessary for proper operation of the vehicle. Certain procedures may present a hazard to the
technician if they are not followed in the recommended manner. W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE statements are
designed to help prevent these hazards from occurring, but not all hazards can be foreseen.
WARNING defined
A W ARNING statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in death or injury. A W ARNING statement alerts you to take necessary action or not to take a
prohibited action. If a W ARNING statement is ignored, the following consequences may occur:
• Death or injury to the technician or other personnel working on the vehicle,
• Death or injury to other people in or near the workplace area, and / or
• Death or injury to the driver / or passenger(s) of the vehicle or other people, if the vehicle has been improperly
repaired.
CAUTION defined
A CAUTION statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in damage to or destruction of equipment, or corruption of data. If a CAUTION statement is ignored,
the following consequences may occur:
• Damage to the vehicle,
• Unnecessary vehicle repairs or component replacement,
• Faulty operation or performance of any system or component being repaired,
• Damage to any system or components which depend on the proper operation of the system or component being
repaired,
• Faulty operation or performance of any systems or components which depend on the proper operation or
performance of the system or component under repair,
• Damage to fasteners, basic tools or special tools and / or
• Leakage of coolant, lubricant or other vital fluids.
NOTE defined
A NOTE statement immediately precedes or follows an operating procedure, maintenance practice or condition that
requires highlighting. A NOTE statement also emphasises necessary characteristics of a diagnostic or repair procedure.
A NOTE statement is designed to:
• Clarify a procedure,
• Present additional information for accomplishing a procedure,
• Give insight into the reasons for performing a procedure in the recommended manner, and / or
• Present information that gives the technician the benefit of past experience in accomplishing a procedure with
greater ease.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3249 of 6020
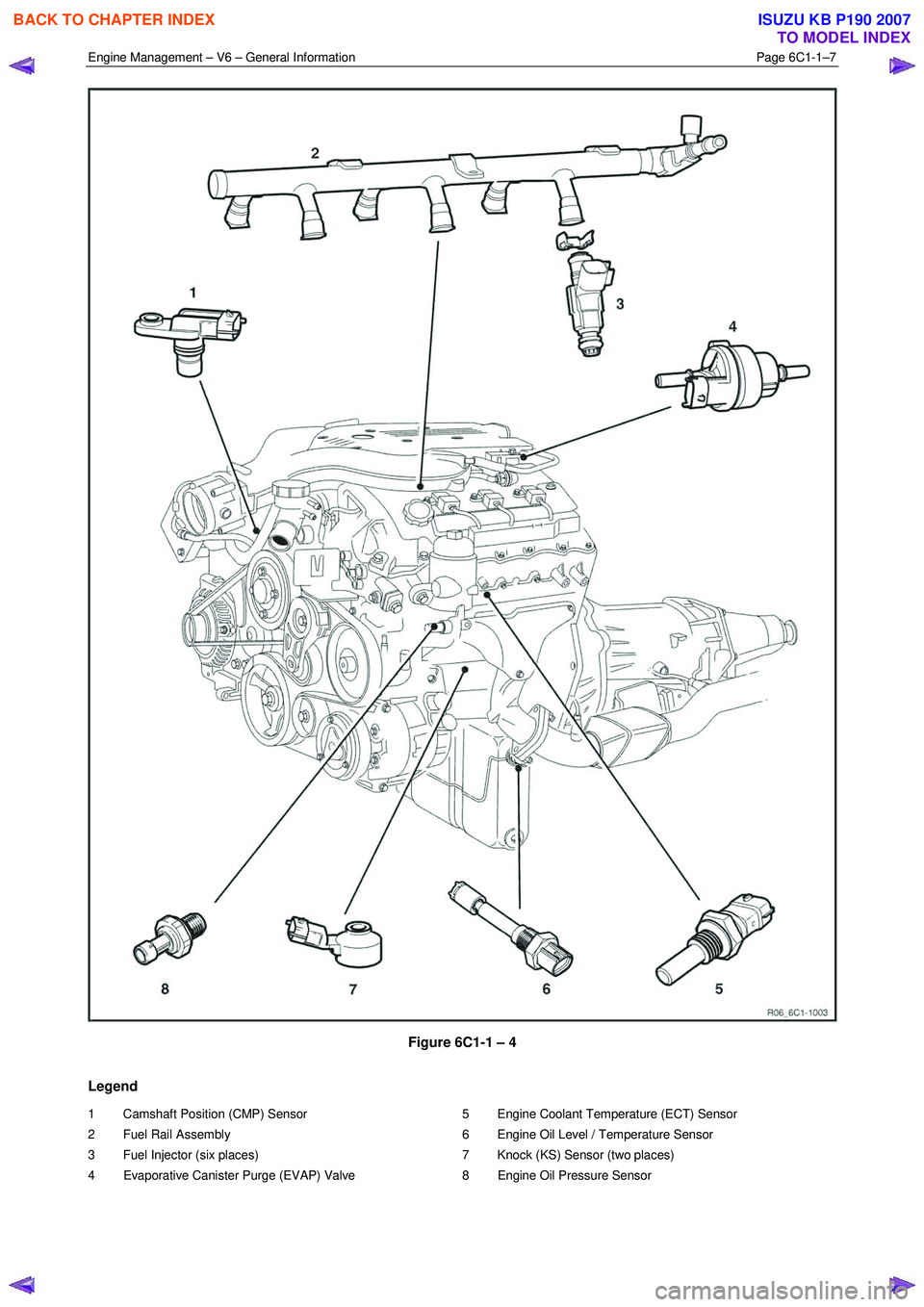
Engine Management – V6 – General Information Page 6C1-1–7
Figure 6C1-1 – 4
Legend
1 Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor
2 Fuel Rail Assembly
3 Fuel Injector (six places)
4 Evaporative Canister Purge (EVAP) Valve 5 Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor
6 Engine Oil Level / Temperature Sensor
7 Knock (KS) Sensor (two places)
8 Engine Oil Pressure Sensor
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3253 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – General Information Page 6C1-1–11
3.2 Air / Fuel Control System
The engine control module (ECM) controls the amount of air and fuel delivered into each of the engine cylinders. Based
on the various ECM inputs, the ECM switches to the following air / fuel control system mode to provide the optimum air /
fuel ratio under all engine operating conditions.
Starting Mode
W hen the ignition switch is moved to the START position and the engine begins to turn, a prime pulse may be injected to
speed starting. As soon as the ECM receives an input signal from the camshaft position (CMP) and crankshaft position
(CKP) sensor and determines which cylinder is in the firing stroke, the ECM applies a pulse width modulated (PW M)
ground to the injector control circuit. The ECM monitors mass air flow, intake air temperature, engine coolant
temperature, and throttle position to determine the required fuel injector on-time required for starting the engine.
Run Mode
The engine switches to run mode when the engine speed reaches 480 rpm after being started. The run mode has two
sub-modes called Open Loop and Closed Loop.
Open Loop Mode
The heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) does not produce a usable signal voltage output until it reaches operating
temperature. Therefore, while the HO2S is below its operating temperature, the ECM switches to open loop mode.
In open loop, the ECM ignores the signals from the HO2S and calculates the required injector pulse width based
primarily on inputs from the mass air flow (MAF), intake air temperature (IAT), and engine coolant temperature sensors.
The system will stay in the open loop mode until the HO2S produce a usable output.
Closed Loop Mode
Once the HO2S reaches operating temperature and starts producing its own signal voltage output, the ECM switches to
the closed loop mode.
In closed loop mode, the ECM initially calculates injector pulse width based on the same sensors used in open loop, and
additionally the ECM uses the oxygen sensor signals to modify and fine tune the fuel pulse width calculations to precisely
maintain the ideal 14.7 to 1 air / fuel ratio.
Acceleration Mode
The ECM monitors and calculates input signals from the accelerator pedal position (APP) and MAF sensor signals to
determine when the vehicle is being accelerated. If the ECM detects the accelerator pedal is depressed and there is a
demand for the vehicle to accelerate, the ECM switches to acceleration mode. In acceleration mode, the ECM increases
the fuel injector on-time to provide more fuel accordingly.
Deceleration Mode
The ECM monitors and calculates input signals from the APP and MAF sensor signals to determine when the vehicle is
being decelerated. If the ECM detects the vehicle is decelerating, the ECM switches to deceleration mode. In
deceleration mode, the ECM decreases the fuel injector on-time, or disables the fuel injectors for short periods, to reduce
exhaust emissions and improve fuel economy.
Fuel Shut-off Mode
To protect the engine from damage or to improve the vehicle's driveability, the ECM switches to the fuel shut-off mode. In
fuel shut-off mode, the ECM performs the following:
• The ECM disables the six fuel injectors under the following conditions:
− Ignition off – to prevent engine dieseling,
− Ignition on but no ignition reference signal – prevents flooding or backfiring,
− At high engine speed – greater than the red line (rev limiter),
− At high vehicle speed – greater than the rated tire speed (vehicle speed limiter), or
− Extended high speed closed throttle coast-down – reduces engine emissions and increases engine braking.
• The ECM selectively disables the appropriate number of fuel injectors when torque management has been enabled.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3256 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – General Information Page 6C1-1–14
Throttle Body Relearn Procedure
The ECM stores values that include the lowest possible TP sensor positions (zero percent), the rest positions (seven
percent), and the spring return rate. These values will only be erased or overwritten if the ECM is reprogrammed or if a
throttle body relearn procedure is performed.
NOTE
If the battery has been disconnected, the ECM
performs a throttle body relearn procedure once
the battery has been reconnected and the ignition
turned on.
The ECM performs a throttle body relearn procedure anytime the ignition is turned on and the following conditions have
been met:
• The engine has been off for greater than 29 seconds,
• The engine speed is less than 40 rpm,
• The vehicle speed is 0 km/h,
• The engine coolant temperature (ECT) is 5 – 60°C; if Tech 2 is used to perform the relearn procedure, the ECT is
5 – 100°C,
• The intake air temperature (IAT) is greater than 5 – 60°C; if Tech 2 is used to perform the relearn procedure, the
IAT is 5 – 100°C,
• The APP sensor angle is less than 15 percent, and
• Ignition voltage is greater than 10 V.
The throttle body relearn procedure is performed 29 seconds after the ignition is turned on. The ECM commands the
throttle plate from the rest position (seven percent open) to full closed (zero percent), then to around 10 percent open.
This procedure takes about six – eight seconds. If any faults occur in the TAC system, a DTC sets. At the start of this
procedure, the Tech 2 TAC Learn Counter parameter should display 0, then count up to 11 after the procedure is
completed. If the counter did not start at 0, or if the counter did not end at 11, a fault has occurred and a DTC should set.
TAC System Default Actions / Reduce Power Modes
The ECM switches to the following reduce power modes if the ECM detects a fault condition in the TAC system:
• If an APP sensor circuit fault or TP sensor circuit fault is detected, the ECM limits engine torque so the vehicle
cannot reach speeds of greater than 100 km/h. The ECM remains in this reduce power mode during the entire
ignition cycle, even if the fault is corrected.
• If there is a fault condition with the throttle actuator control circuits, a throttle actuator command vs. actual position
fault, a return spring check fault, or a TP sensor one circuit fault, the ECM limits engine speed to 2500 rpm and
three – six fuel injectors are randomly disabled. At this time the reduce power indicator is commanded on. The
ECM remains in the reduce power mode during the entire ignition cycle even if the fault is corrected.
NOTE
If a TP sensor one or throttle actuator control
circuit fault is present at the time the vehicle is at
idle, with no accelerator pedal angle, the engine
may stall.
Forced Engine Shutdown
A further safety feature which is built into the TAC system is the ECM will initiate an engine shut down if, the ECM’s
internal monitoring functions detects a serious internal fault, the fuel injectors will be turned off.
3.6 Cruise Control System
The cruise control system integrates with the engine control module (ECM) through the powertrain interface module
(PIM), to control the electronic throttle actuator and maintain the vehicle at the speed set by the driver.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007