2007 ISUZU KB P190 Electrical
[x] Cancel search: ElectricalPage 3652 of 6020
Battery Page 6D1-3–12
9 Lock the doors and activate the theft deterrent system to arm the vehicle.
10 If the multimeter contains fuses, check they are serviceable.
Test Procedure
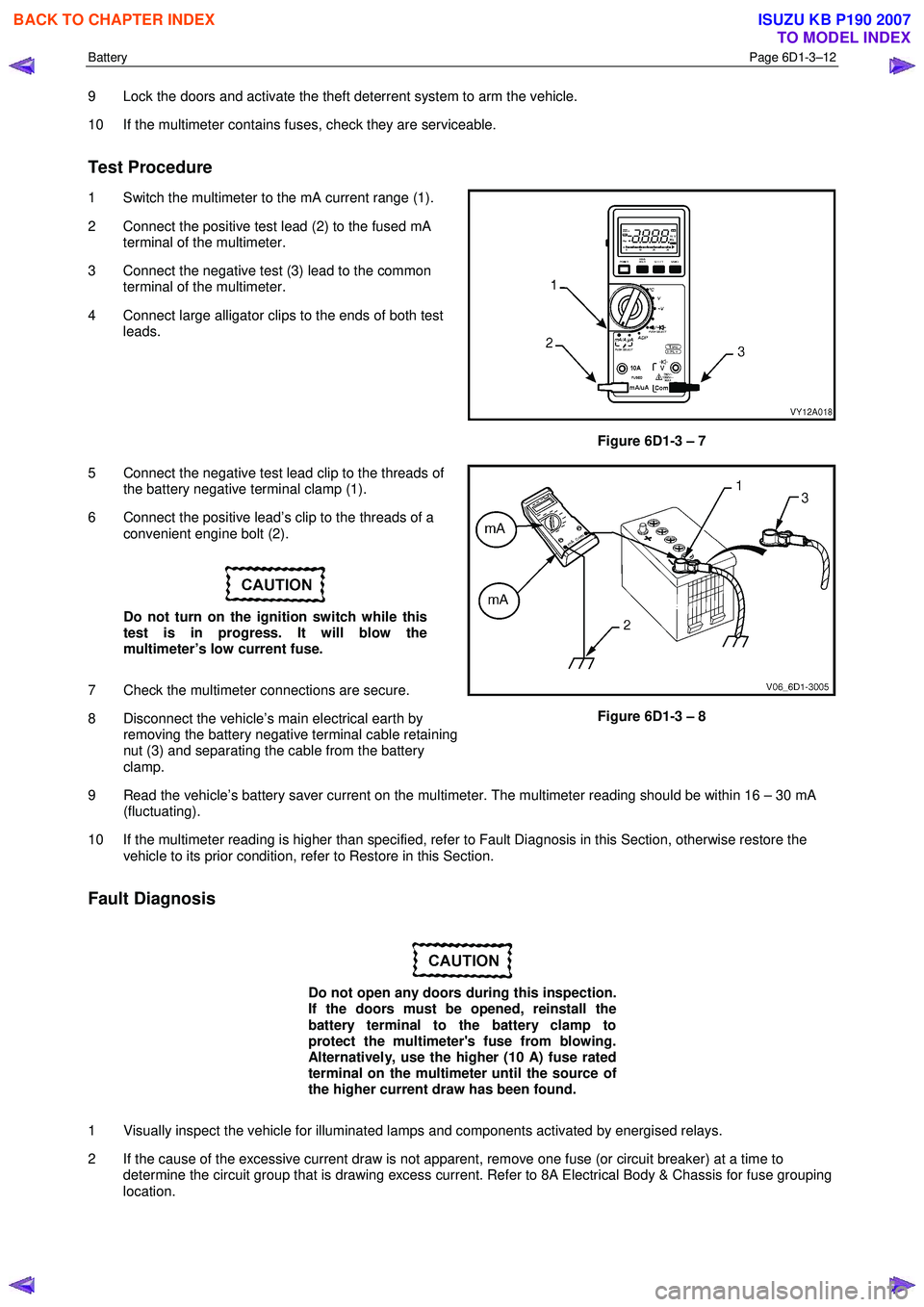
1 Switch the multimeter to the mA current range (1).
2 Connect the positive test lead (2) to the fused mA terminal of the multimeter.
3 Connect the negative test (3) lead to the common terminal of the multimeter.
4 Connect large alligator clips to the ends of both test leads.
Figure 6D1-3 – 7
5 Connect the negative test lead clip to the threads of the battery negative terminal clamp (1).
6 Connect the positive lead’s clip to the threads of a convenient engine bolt (2).
Do not turn on the ignition switch while this
test is in progress. It will blow the
multimeter’s low current fuse.
7 Check the multimeter connections are secure.
8 Disconnect the vehicle’s main electrical earth by removing the battery negative terminal cable retaining
nut (3) and separating the cable from the battery
clamp.
Figure 6D1-3 – 8
9 Read the vehicle’s battery saver current on the multimeter. The multimeter reading should be within 16 – 30 mA (fluctuating).
10 If the multimeter reading is higher than specified, refer to Fault Diagnosis in this Section, otherwise restore the vehicle to its prior condition, refer to Restore in this Section.
Fault Diagnosis
Do not open any doors during this inspection.
If the doors must be opened, reinstall the
battery terminal to the battery clamp to
protect the multimeter's fuse from blowing.
Alternatively, use the higher (10 A) fuse rated
terminal on the multimeter until the source of
the higher current draw has been found.
1 Visually inspect the vehicle for illuminated lamps and components activated by energised relays.
2 If the cause of the excessive current draw is not apparent, remove one fuse (or circuit breaker) at a time to determine the circuit group that is drawing excess current. Refer to 8A Electrical Body & Chassis for fuse grouping
location.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3653 of 6020

Battery Page 6D1-3–13
3 W hen the circuit group is determined, install the fuse / circuit breaker and identify the specific circuit within this
group that is drawing the excess current. Disconnect the wiring harness connectors in this circuit group one at a
time. Refer to 8A Electrical Body & Chassis.
4 W hen the cause is disconnected, the multimeter reading should drop to the correct reading as outlined in Step 9 of the Test Procedure in this Section.
5 If required, remove the components in this circuit one at a time to determine the cause of the excessive standing current. Refer to 8A Electrical Body & Chassis.
6 Repair the fault, refer to 8A Electrical Body & Chassis.
7 Ensure any fuses, circuit breakers and connectors that have been removed are secure.
Restore
1 Reconnect the electrical earth cable to the battery terminal and tighten the nut to the correct torque specification.
Battery terminal nut
torque specification .....................................2.0 – 5.0 Nm
2 Disconnect the multimeter connections.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3656 of 6020

Battery Page 6D1-3–16
NOTE
Charging a battery at higher current rates can
significantly reduce the life of the battery.
Charge Rate Initial Current Maximum Time Required
Slow charge 4 A 24 hours
Fast charge 35 A 2 hours
6 After a few minutes, check the colour and specific gravity of the electrolyte. Refer to 3.3 Hydrometer Test.
7 Monitor the electrolyte temperature while the battery is charging. If the electrolyte temperature reaches 55 °C:
a switch the charging current off,
b allow the battery to cool,
c reduce the charging current, and
d restart charging the battery.
NOTE
For the best results, charge the battery with the
electrolyte and plates at room temperature. An
extremely cold battery may not appear to accept
current for several hours after starting the battery
charger. If the battery does not appear to accept
charge after several hours replace the battery.
8 For slow charging check the voltage and specific gravity each hour or more regularly for fast charging. Stop the charging when there is no change in voltage or electrolyte specific gravity over three checks.
9 If the battery was fast charged connect the battery to a slow-charger for a few hours to bring the battery to the fully charged condition. Ensure the last few hours of charge do not exceed 1 A.
10 Tighten the filler caps. Ensure they are secure.
11 Install the battery in the vehicle. Refer to 4.1 Battery.
4.3 Emergency Jump Starting Procedure
Safety Precautions
• Read and obey the general safety precautions for working with batteries, refer to 2 Safety Precautions.
• Do not allow the vehicles to touch each other during the jump starting procedure.
• Ensure the assisting vehicle battery has the same voltage rating and connects negative to ground. If this is not the
case, serious injury and damage to electrical equipment can result.
• Do not push or tow the vehicle to start it. Damage can result when unburnt fuel reaches the catalytic converter and
ignites.
• Do not start the vehicle using a fast charger.
• W hen using jumper leads, treat both the booster battery and the discharged battery with care.
• Do not allow sparks, flame or smoking near the battery.
• Ensure that metal tools or jumper cables do not simultaneously contact the battery positive terminal and any other
metal part of the vehicle.
Jump Starting Procedure
1 Position the assisting vehicle so the batteries of both vehicles are close together, refer to Figure 6D1-3 – 10.
2 Apply the park brake on both vehicles.
3 Ensure that P (park) is selected for automatic transmission and N (neutral) is selected for manual transmissions.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3657 of 6020

Battery Page 6D1-3–17
4 Turn off the ignition, lights and all other electrical loads.
5 Check the battery filler caps on both batteries are tight.
6 Place a wet cloth over the battery filler caps of each battery.
7 Attach one end of the red jumper cable to the positive terminal of the booster battery.
8 Attach the other end of the same cable to the positive terminal of the discharged battery.
9 Attach one end of the black jumper cable to the negative terminal of the booster battery.
10 Attach the other end to a solid stationary, metallic point on the engine of the disabled vehicle.
NOTE
Do not connect this end directly to the negative
post of the discharged battery.
Figure 6D1-3 – 10
Legend
Order of hook-up:
1 Booster vehicle, positive terminal
2 Disabled vehicle, positive terminal
3 Booster vehicle, negative terminal
4 Disabled vehicle, engine ground point Booster vehicle
Disabled vehicle
11 Ensure the jumper cables are not on or near drive pulleys, cooling fans or other points that will move when the engine is started.
12 Start the engine in the booster vehicle and run the engine at a moderate speed for a few minutes.
13 Start the engine in the disabled vehicle.
NOTE
If the engine in the disabled vehicle does not start
within 30 seconds, stop cranking the engine and
fix the cause. Refer to 3 Diagnosis.
14 W hen the engine starts, allow both engines to idle for approximately seven minutes. This allows the voltage levels in both vehicles to balance.
15 Leave the vehicles running and remove the jumper cables in the reverse sequence to attaching them. W hen removing each clamp, take care to ensure that it does not touch any other metal.
16 Discard the wet cloths covering the battery filler caps of both batteries.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3661 of 6020
Battery Page 6D1-3–21
7 Special Tools
Tool Number Illustration Description Tool Classification
KM609 Connector Test Adaptor Kit
Used when carrying out electrical diagnostic circuit checks.
Previously released. Desirable
J39200
Digital Multimeter
Must have at least 10 M Ω input
impedance and be capable of reading frequencies.
Previously released. Available
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3685 of 6020

Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–24
7 Diagnostics Starting Point
7.1 Diagnostic Requirements, Precautions
and Preliminary Checks
Basic Knowledge Required
A lack of basic understanding of electronics,
electrical wiring circuits and use of electrical
circuit testing tools when performing the PIM
diagnostic procedures could result in
incorrect diagnostic results or damage to
components.
In addition, understanding of the Engine Management System is essential to prevent misdiagnosis and component
damage. Refer to 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information.
Basic Diagnostic Tools Required
Use of incorrect electrical circuit diagnostic
tools when performing the PIM diagnostic
procedures could result in incorrect
diagnostic results or damage to components.
The following electrical circuit testing tools are required to perform the diagnostic procedures detailed in this Section:
• Tech 2.
• Test lamp, refer to 8A Electrical - Body and Chassis for further information.
• Digital multimeter with 10 M Ω impedance, refer to 8A Electrical - Body and Chassis for further information.
• Connector test adapter kit Tool No. J35616-A.
Diagnostic Precautions
In addition to the safety and precautionary
measures listed in 11.1 Safety and
Precautionary Measures, the following
diagnostic precautions must be observed
when performing any PIM diagnostic
procedure:
• Use only the test equipment specified in the diagnostic tables. Other test equipment may either give incorrect
results or damage serviceable components.
• Do not clear any DTCs unless instructed.
• The fault must be present when using the DTC Diagnostic Tables. Otherwise, misdiagnosis or replacement of
serviceable parts may occur.
• Always use connector adapters such as those contained in connector test adapter kit Tool No. J35616-A to prevent
connector terminal damage.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3686 of 6020
Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–25
• Thorough inspection of the wiring circuits and connectors listed in the diagnostic procedures must be performed,
otherwise misdiagnosis may occur.
• Inspect the electrical circuitry or connector terminals that are suspected to be causing the complaint for the
following conditions:
• backed-out connector terminals,
• improper wiring connector mating,
• broken wiring connector locks,
• damaged connector terminals, and
• physical damage to the wiring harness.
• Before replacing a component, inspect its connector terminal for corrosion or deformation that may cause the fault
condition.
Preliminary Checks
The PIM preliminary check examines easily accessible components which may cause problems with the PIM. This visual
and physical inspection procedure may quickly identify the fault condition and eliminate the need for additional diagnosis.
• Refer to Service Techlines for relevant information regarding the fault condition.
• Ensure the battery is fully charged.
• Check the battery connections for corrosion or a loose terminal.
• Perform a visual and physical inspection of the following:
• PIM component wiring harness and terminals for proper connections, pinches or cuts, and
• PIM wiring harness routing which may be positioned very close to a high voltage or high current devices such
as aftermarket audio systems.
NOTE
High voltage or high current devices may induce
electrical noise on a circuit, which can interfere
with normal circuit operation.
• The PIM is sensitive to Electro Magnetic Interference (EMI). Check for incorrect aftermarket theft deterrent
devices, lights or mobile phone installations if an intermittent malfunction is suspected.
7.2 Diagnostic System Check
Step Action Yes No
1
Have you met the basic diagnostic requirements listed in the PIM
Diagnostic Starting Point?
Go to Step 2 Refer to
7.1 Diagnostic
Requirements,
Precautions and
Preliminary Checks
2 Have you read the Diagnostic Precautions?
Go to Step 3 Refer to
7.1 Diagnostic Requirements,
Precautions and
Preliminary Checks
3 Have you performed the Preliminary Checks?
Go to Step 4 Refer to
7.1 Diagnostic Requirements,
Precautions and
Preliminary Checks
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3688 of 6020
Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–27
7.3 Powertrain Interface Module – Module
Communication Check Failure
Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1
Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2 Refer to
7.2 Diagnostic System Check
2 Test the following PIM circuits for a high resistance, open circuit or
short to ground fault condition. Refer to 8A Electrical - Body and
Chassis for information on electrical diagnosis:
• 12 V battery supply circuit,
• 12 V ignition circuit, and
• ground circuit.
Has any fault been found and rectified? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 3
3 1 Disconnect the ECM harness connector.
2 Switch off the ignition for 10 seconds.
3 Using Tech 2, attempt to communicate with the PIM.
NOTE
Other DTCs may set when the ECM connector is
disconnected and the ignition is switched on. Disregard
DTCs that set under this condition on this DTC Table.
Does Tech 2 communicate with the PIM? Go to Step 4 For vehicles with
automatic
transmissions, go to
Step 5. For vehicles with manual
transmission go to Step 8
4 Replace the ECM. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Has the repair been completed? Go to Step 10 —
5 1 Disconnect the TCM harness connector.
2 Switch off the ignition for 10 seconds.
3 Using Tech 2, attempt to communicate with the PIM.
Does Tech 2 communicate with the PIM? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 8
6 Test serial data circuits between the TCM and ECM for a short to
voltage, short to ground or short together condition.
Has any fault been found and rectified? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 7
7 Replace the TCM. Refer to 7C4 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E –
On-vehicle Servicing.
Has the repair been completed? Go to Step 10 —
8 Test serial data circuits between the PIM and ECM for vehicles with
manual transmission, or between the PIM and TCM for vehicles with
automatic transmission for a high resistance or open circuit fault
condition. Refer to 8A Electrical - Body and Chassis for information on
wiring circuit testing and repair.
Has any fault been found and rectified? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 9
9 Replace the PIM. Refer to 11.2 Powertrain Interface Module.
Has the repair been completed? Go to Step 10 —
10 Using Tech 2, attempt to communicate with the PIM.
Does Tech 2 communicate with the PIM? Go to Step 11 Refer to
7.2 Diagnostic System Check
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007