2007 ISUZU KB P190 boot
[x] Cancel search: bootPage 742 of 6020

BRAKES 5C-43
3. Dust seal; Piston
• Apply grease to piston groove and dust seal boot.
1) Make sure a piston and its groove area are free from dust.
2) Use 0.5g to apply grease to groove area thoroughly using a brush or finger.
Make sure color of groove changes as shown bello
w
after apply grease.
3) After assembling a dust seal boot to the piston, apply
1.5g to contact area of the piston and the dust seal boot
as shown in the picture bellow.
4. Piston
Apply clean brake fluid to the piston, and attach the caliper.
W hen inserting the piston into the cylinder, use finger pressure
only. Do not use a mallet or other impact tool, since damage to
the cylinder wall or ring seal can result.
The movement of a caliper piston into a caliper bore should be
smooth and even. If a caliper piston is frozen or difficult to
move to the bottom, the caliper requires overhaul o
r
replacement.
RTW 35CSH000701
W hen not entering with a finger, insert a discarded inner brake
pad (2) or block of wood in front of the pistons. Using 2 large
C-clamps (1) installed over the body of the caliper (3) and
against the brake pad or block of wood, slowly move the
pistons evenly into the bores.
Insert the dust seal ring into the dust seal.
CAUTION:
Pistons made of plastic material.
Do not hit the piston with a hammer etc. and don’t grasp
the face of the piston with pliers.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 744 of 6020

BRAKES 5C-45
REAR DRUM BRAKE ASSEMBLY
DISASSEMBLY
First, disassemble the brake drum. Then disassemble the rear brake assembly.
Refer to the “REAR AXLE” section for the brake drum disassembly procedure.
RTW 75CMF001001
MAJOR COMPONENTS
Disassembly Steps
1. Spring; adjuster
2. Ring; Adjuster lever
3. Lever; adjuster
▲ 4. Spring; Shoe hold
5. Pin; Shoe hold
▲ 6. Spring; Shoe to shoe, lower
7. Adjuster assembly
8. Spring; shoe to shoe, upper
9. Shoe; leading
10. Shoe; trailing
11. Spring; lever return
12. Retainer
13. W asher; lever
14. Lever; parking
15. Bolt; wheel cylinder
16. W heel cylinder assembly
17. Cover
18. Back plate
MINOR COMPONENTS
Disassembly Steps
Wheel Cylinder Assembly
19. Piston assembly
20. Cup; piston
21. Boot; piston
22. Return spring
23. Cap; bleeder
24. Bleeder
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 747 of 6020

5C-48 BRAKES
REASSEMBLY
RTW 75CMF000601
MINOR COMPONENTS
Reassembly Steps
Wheel cylinder Assembly
▲ 1. Piston assembly
2. Cup; piston
3. Return spring
4. Boot; piston
▲ 5. Bleeder
6. Cap; bleeder
MAJOR COMPONENTS
Reassembly Steps
7. Back plate
8. Cover
▲ 9. W heel cylinder assembly
▲ 10. Bolt; wheel cylinder
▲ 11. Shoe; leading
▲ 12. Lever; parking
▲ 13. W asher; lever
▲ 14. Retainer
15. Spring; lever return
▲
16. Shoe; trailing
▲ 17. Spring; shoe to shoe, upper
▲ 18. Adjuster assembly
19. Spring; shoe to shoe; lower
▲ 20. Lever; adjuster
▲ 21. Ring; Adjuster lever
▲ 22. Spring; shoe hold
▲ 23. Pin; shoe hold
24. Spring; adjuster
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 748 of 6020

BRAKES 5C-49
Important Operations
Note:
• W ash the disassembled parts in clean brake fluid.
• Use compressed air to clean the ports.
• Protect the disassembled part surfaces from contamination
by dust and other foreign material.
• Before reassembly, check the part surfaces fo
r
contamination with dust or other foreign material.
• Be sure to replace the designated parts with new ones.
1. Piston Assembly
Install new piston cups on each piston so that the flared end of
the cups are turned to the inboard side of the pistons.
Attach the return spring and the boot to the piston.
Be sure to use new piston cup and boot.
RTW 55CSH000201
•
Apply brake fluid to the pistons and the inner face of the
boots.
• Note the direction of piston cup (1).
• Apply rubber grease to the boots (2) as shown in the
illustration.
5. Bleeder
Torque N ⋅m (kgf ⋅m/Ib ⋅in)
6 - 8 (0.6 – 0.8 / 52 - 69)
9. Wheel Cylinder Assembly
10. Bolt; Wheel cylinder
Torque N ⋅m (kgf ⋅m/Ib ⋅in)
14 - 18 (1.4 – 1.8 / 122 - 156)
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3273 of 6020
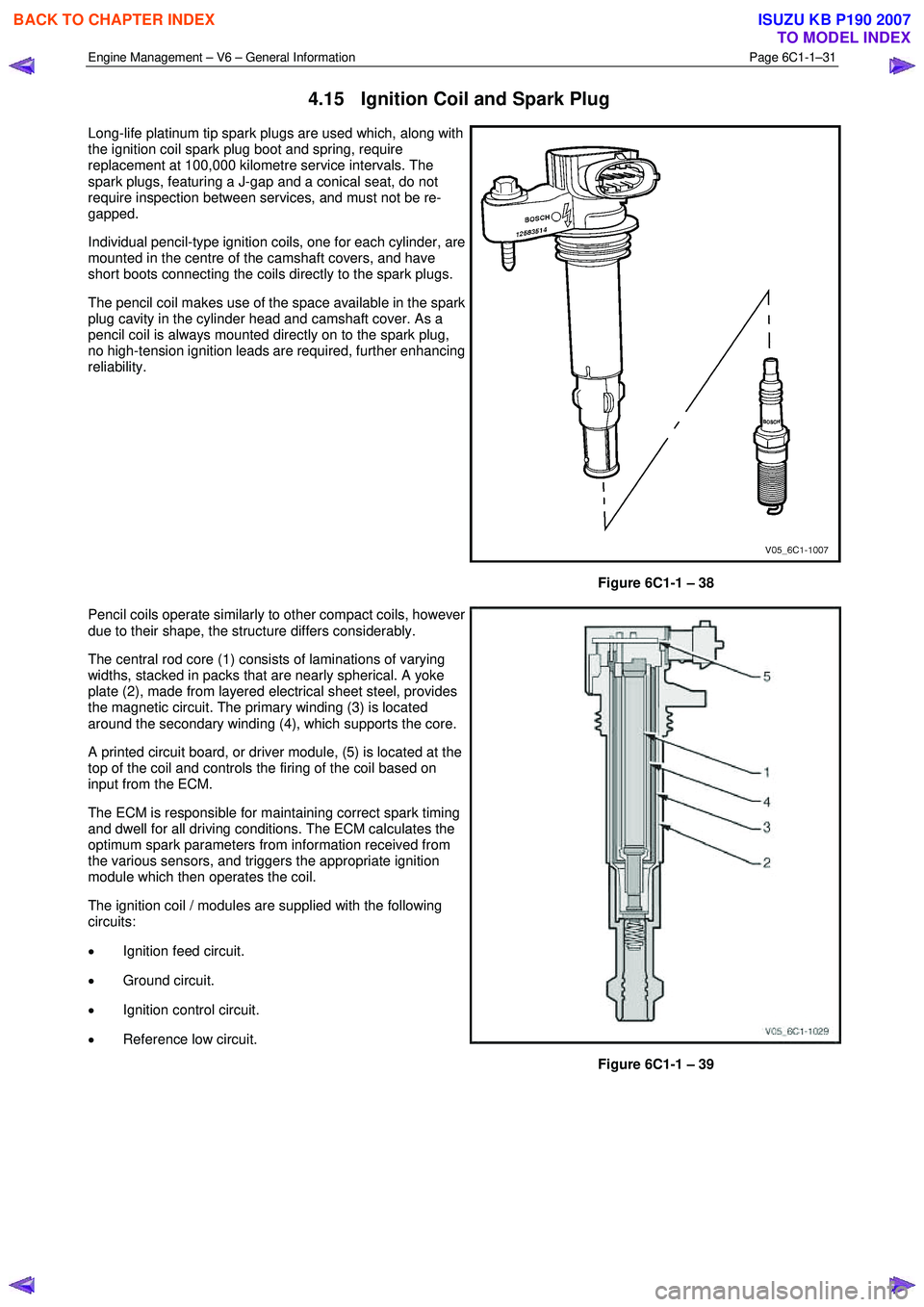
Engine Management – V6 – General Information Page 6C1-1–31
4.15 Ignition Coil and Spark Plug
Long-life platinum tip spark plugs are used which, along with
the ignition coil spark plug boot and spring, require
replacement at 100,000 kilometre service intervals. The
spark plugs, featuring a J-gap and a conical seat, do not
require inspection between services, and must not be re-
gapped.
Individual pencil-type ignition coils, one for each cylinder, are
mounted in the centre of the camshaft covers, and have
short boots connecting the coils directly to the spark plugs.
The pencil coil makes use of the space available in the spark
plug cavity in the cylinder head and camshaft cover. As a
pencil coil is always mounted directly on to the spark plug,
no high-tension ignition leads are required, further enhancing
reliability.
Figure 6C1-1 – 38
Pencil coils operate similarly to other compact coils, however
due to their shape, the structure differs considerably.
The central rod core (1) consists of laminations of varying
widths, stacked in packs that are nearly spherical. A yoke
plate (2), made from layered electrical sheet steel, provides
the magnetic circuit. The primary winding (3) is located
around the secondary winding (4), which supports the core.
A printed circuit board, or driver module, (5) is located at the
top of the coil and controls the firing of the coil based on
input from the ECM.
The ECM is responsible for maintaining correct spark timing
and dwell for all driving conditions. The ECM calculates the
optimum spark parameters from information received from
the various sensors, and triggers the appropriate ignition
module which then operates the coil.
The ignition coil / modules are supplied with the following
circuits:
• Ignition feed circuit.
• Ground circuit.
• Ignition control circuit.
• Reference low circuit.
Figure 6C1-1 – 39
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3384 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–106
− Damaged accessory drive belt
• For an intermittent condition, refer to 5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
• Since a fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this
diagnostic procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A
Electrical - Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section, for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
DTC P0301, P0302, P0303, P0304, P0305 or P0306 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1
Has the Diagnostic System Check been completed? Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.4 Diagnostic
System Check in this Section
2
W ere you sent here from DTC P0300? Go to Step 3 Go to 7.16
DTC P0300 in this Section
3 1 Ignition OFF.
2 Remove the ignition coil of the misfiring cylinder, but leave the electrical connector connected. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
3 Inspect the ignition coil boot for the following conditions:
− Holes.
− Tears.
− Carbon tracking.
− Oil contamination or water intrusion.
Did you find a condition with the ignition coil boot? Go to Step 12 Go to Step 4
4 1 Remove the fuel pump fuse from the under-hood fuse and relay
centre.
2 Install the J 26792 Spark Tester to the ignition coil boot and a good ground.
3 Crank the engine while observing J 26792.
Does the spark tester spark and is the spark consistent? Go to Step 5 Go to Electronic
Ignition System Diagnosis
5 1 Ignition OFF.
2 Remove the spark plug from the cylinder that indicated a misfire.
3 Inspect the spark plug. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
Does the spark plug appear to be OK? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 6
6
Is the spark plug oil or coolant fouled? Inspect the spark
plugs. Go to 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations Go to Step 7
7 Is the spark plug gas fouled? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 9
8 Does the spark plug show any signs of being cracked, worn, or
incorrectly gap? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 9
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3563 of 6020
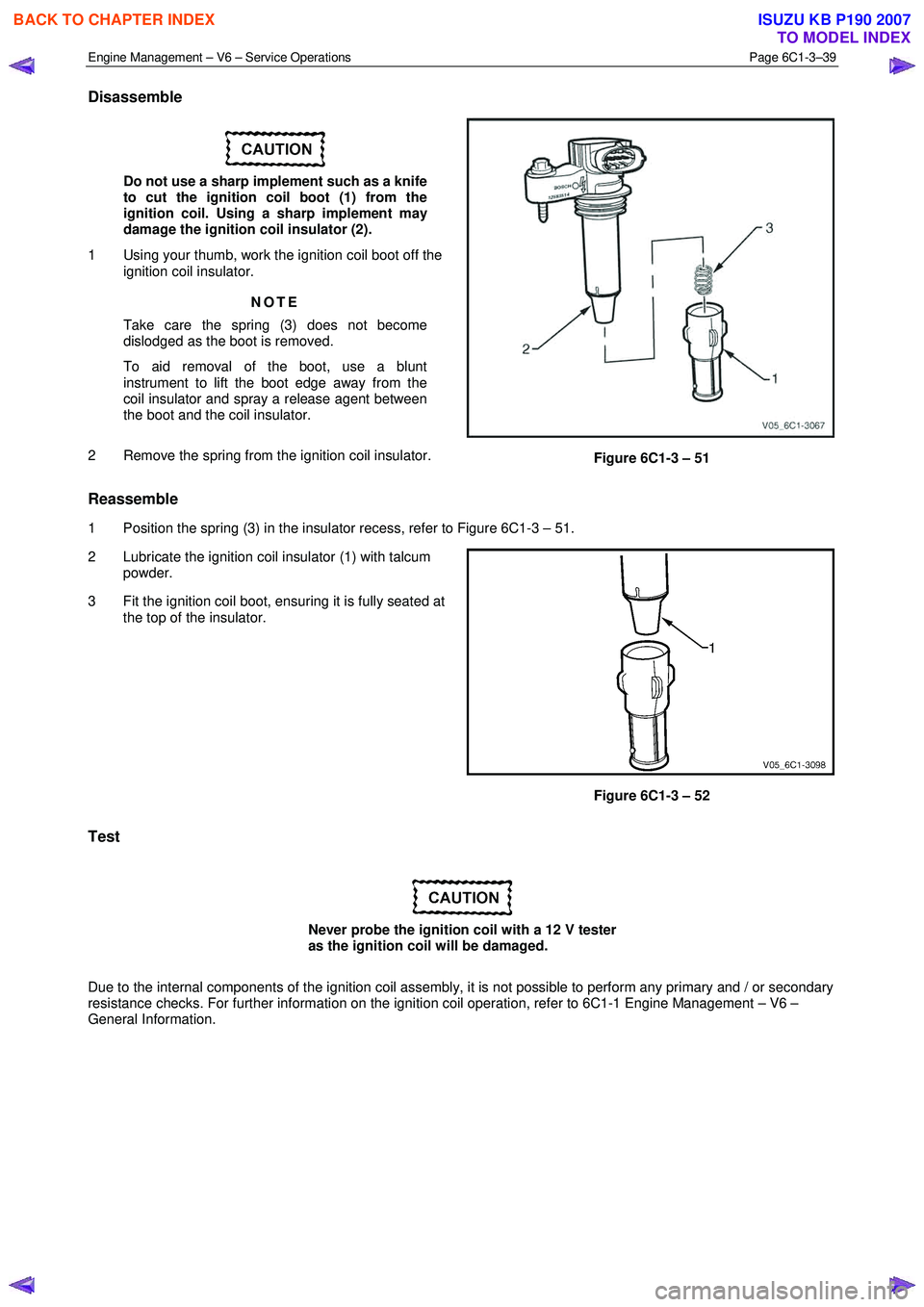
Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations Page 6C1-3–39
Disassemble
Do not use a sharp implement such as a knife
to cut the ignition coil boot (1) from the
ignition coil. Using a sharp implement may
damage the ignition coil insulator (2).
1 Using your thumb, work the ignition coil boot off the ignition coil insulator.
NOTE
Take care the spring (3) does not become
dislodged as the boot is removed.
To aid removal of the boot, use a blunt
instrument to lift the boot edge away from the
coil insulator and spray a release agent between
the boot and the coil insulator.
2 Remove the spring from the ignition coil insulator.
Figure 6C1-3 – 51
Reassemble
1 Position the spring (3) in the insulator recess, refer to Figure 6C1-3 – 51.
2 Lubricate the ignition coil insulator (1) with talcum powder.
3 Fit the ignition coil boot, ensuring it is fully seated at the top of the insulator.
Figure 6C1-3 – 52
Test
Never probe the ignition coil with a 12 V tester
as the ignition coil will be damaged.
Due to the internal components of the ignition coil assembly, it is not possible to perform any primary and / or secondary
resistance checks. For further information on the ignition coil operation, refer to 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 –
General Information.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3564 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations Page 6C1-3–40
Reinstall
Reinstallation of the ignition coil is the reverse of the removal procedure, noting the following:
1 Lubricate the ignition coil sealing rubber (1) with clean engine oil, and the inside of the ignition coil boot (2)
with talcum powder.
Figure 6C1-3 – 53
2 Reinstall the ignition coil by pushing down on the ignition coil to engage the sealing rubber in the camshaft cover.
Ensure the ignition coil is fully seated before
tightening the attaching bolt to the specified
torque.
3 Reinstall the ignition coil bolt and tighten to the correct torque specification. Ignition coil attaching bolt
torque specification ...................................7.0 – 11.0 Nm
4 Road test the vehicle and check for correct operation.
2.16 Intake Air Duct Assembly
Remove
1 Turn the ignition switch off.
2 Disconnect the crankcase ventilation hose (1) from the air intake duct (2).
3 Loosen the two air intake duct retaining clamps (3),
4 Pull the air intake duct away from the throttle body.
5 Pull the air intake duct away from the mass air flow sensor.
Figure 6C1-3 – 54
Reinstall
Reinstallation of the air intake duct is the reverse of the removal procedure, noting the following:
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007