2007 ISUZU KB P190 engine
[x] Cancel search: enginePage 3602 of 6020

Charging System – V6 Page 6D1-1-15
4 Major Service Operations
4.1 Generator
Remove
Refer to 1.2 WARNING, CAUTION and NOTES
before disconnecting the battery.
1 Disconnect the battery ground lead P-5. Refer to 8A Electrical Body and Chassis.
2 Insert a ½ inch drive socket bar into the tensioner arm and rotate the tensioner arm clockwise.
3 Remove the drive belt from the generator pulley and release the tensioner. Refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical – V6 for further details as required.
4 Pull the battery harness cap back from generator terminal P-9 (3), remove the nut (4) and remove the
positive lead (2) from the generator (5).
5 Disengage the connector retaining clip and remove the connector E-4, (1) from the generator.
Figure 6D1-1 4
6 Remove the three bolts (1, 2, 4) retaining the generator (3) to the generator bracket.
7 Remove the generator assembly from the vehicle.
Figure 6D1-1 5
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3603 of 6020

Charging System – V6 Page 6D1-1-16
Reinstall
Reinstallation of the generator is the reverse of the removal procedure, noting the following:
1 Tighten all fasteners to the correct torque specification.
2 Reconnect the battery ground lead.
3 Start the engine.
4 Check the generator warning indicator operation.
5 Check the drive belt is correctly routed and aligned.
6 Check the generator output. Refer to 3.3 On-vehicle Testing.
7 Check the voltage regulator operation. Refer to 3.3 On-vehicle Testing.
8 Turn the ignition switch off.
Generator mounting bolts ........................... (1) 58.0 Nm
Generator mounting bolts ........................... (2) 58.0 Nm
Generator mounting bolts ........................... (4) 58.0 Nm
Battery harness to P-9 pin B nut
torque specification ...................................7.1 – 13.3 Nm
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3604 of 6020
Charging System – V6 Page 6D1-1-17
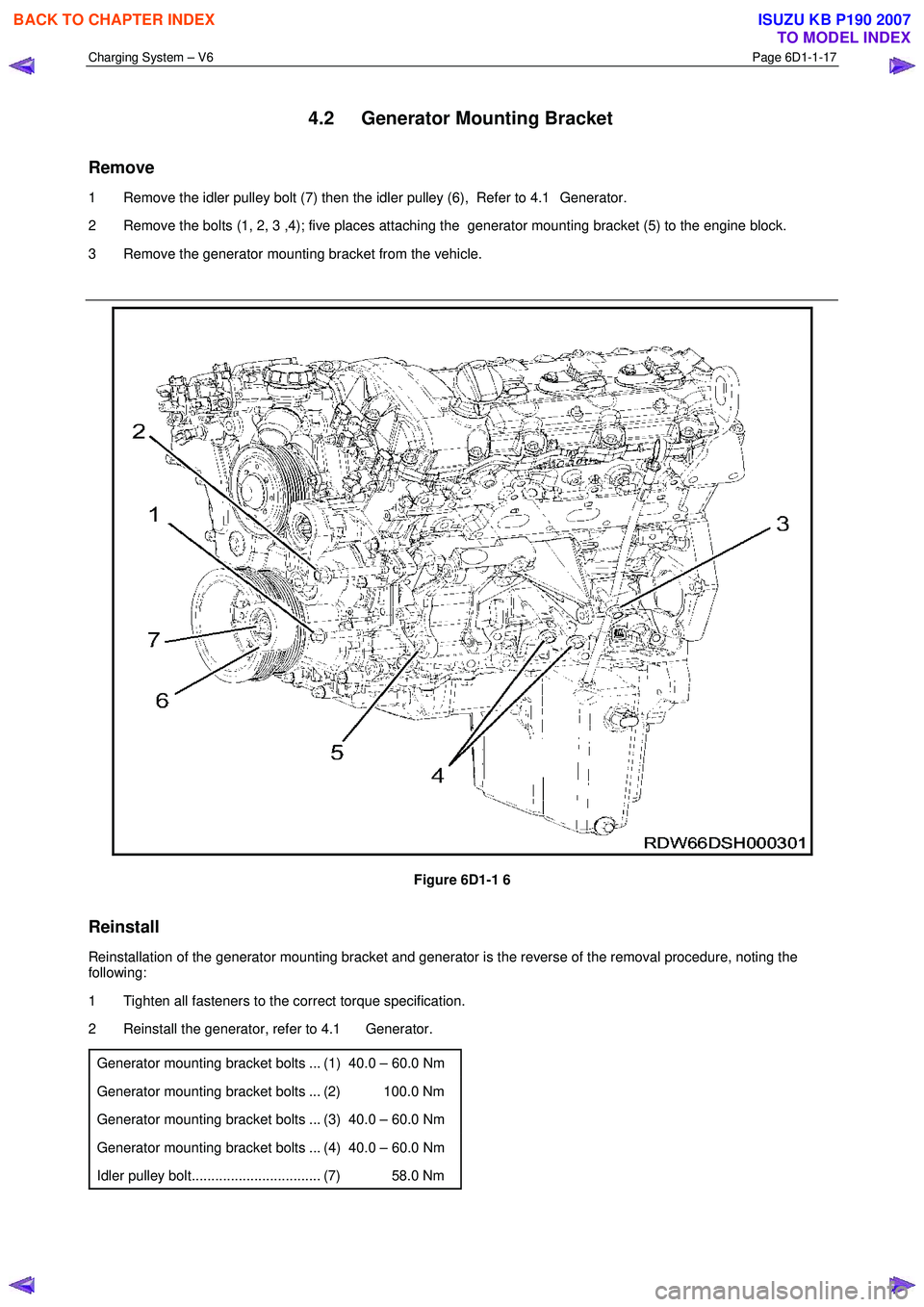
4.2 Generator Mounting Bracket
Remove
1 Remove the idler pulley bolt (7) then the idler pulley (6), Refer to 4.1 Generator.
2 Remove the bolts (1, 2, 3 ,4); five places attaching the generator mounting bracket (5) to the engine block.
3 Remove the generator mounting bracket from the vehicle.
Figure 6D1-1 6
Reinstall
Reinstallation of the generator mounting bracket and generator is the reverse of the removal procedure, noting the
following:
1 Tighten all fasteners to the correct torque specification.
2 Reinstall the generator, refer to 4.1 Generator.
Generator mounting bracket bolts ... (1) 40.0 – 60.0 Nm
Generator mounting bracket bolts ... (2) 100.0 Nm
Generator mounting bracket bolts ... (3) 40.0 – 60.0 Nm
Generator mounting bracket bolts ... (4) 40.0 – 60.0 Nm
Idler pulley bolt................................. (7) 58.0 Nm
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3605 of 6020
Charging System – V6 Page 6D1-1-18
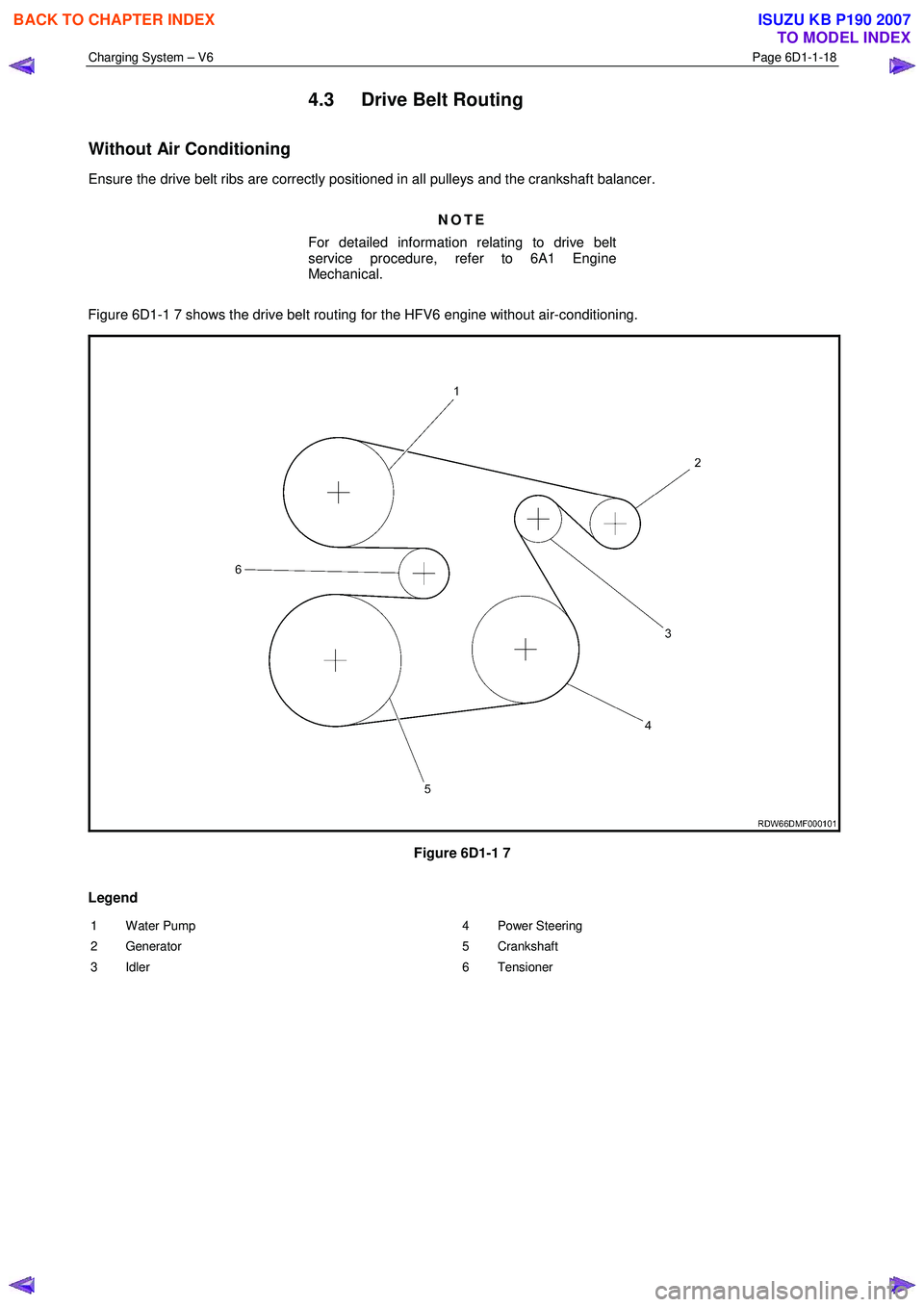
4.3 Drive Belt Routing
Without Air Conditioning
Ensure the drive belt ribs are correctly positioned in all pulleys and the crankshaft balancer.
NOTE
For detailed information relating to drive belt
service procedure, refer to 6A1 Engine
Mechanical.
Figure 6D1-1 7 shows the drive belt routing for the HFV6 engine without air-conditioning.
Figure 6D1-1 7
Legend
1 Water Pump
2 Generator
3 Idler 4 Power Steering
5 Crankshaft
6 Tensioner
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3609 of 6020

Starting System – V6 Page 6D1-2–1
6D1-2
Starting System – V6
ATTENTION
Before performing any service operation or other procedure described in this Section, refer to 1.1
WARNING, CAUTION and NOTES for correct workshop practices with regard to safety and/or property
damage.
1 General Information ............................................................................................................ ...................3
1.1 WARNING, CAUTION and NOTES .................................................................................................... ................... 3
Definition of WARNING, CAUTION and NOTE Statements ............................................................................. .... 3
WARNING defined ............................................................................................................................................. 3
CAUTION defined .............................................................................................................................................. 3
NOTE defined..................................................................................................................................................... 3
1.2 Components .......................................................................................................................................................... 4
Starting System Components ............................................................................................................................... 4
Starter Motor and Solenoid Switch Components................................................................................... ............. 4
Solenoid Switch.................................................................................................................................................. 4
Planetary Drive Train.......................................................................................................... ................................ 4
Armature ............................................................................................................................................................ 4
Brushes .............................................................................................................................................................. 4
1.3 System Operation .................................................................................................................................................. 5
Operation ...................................................................................................................... ..................................... 5
Sequence of Operation .......................................................................................................... ............................ 6
2 Diagnostics .............................................................................................................................................7
2.1 Diagnostic General Information............................................................................................................................ 7
Basic Diagnostic Tools Required ......................................................................................................................... 7
2.2 Tech 2 Data List ............................................................................................................... ...................................... 7
2.3 Diagnostic Systems Check ....................................................................................................... ............................ 7
2.4 Wiring Diagram ...................................................................................................................................................... 8
2.5 Starting System Inoperative / Malfunctioning ................................................................................... ................ 10
Circuit Description ............................................................................................................................................ 10
Diagnostic Table Notes ......................................................................................................... ........................... 10
Diagnostic Table............................................................................................................................................... 10
Diagnostic Table – Slow Cranking, Solenoid Clicks or Chatters.................................................................. ..... 14
3 Minor Service Operations ....................................................................................................................15
3.1 Safety Precautions............................................................................................................................................... 15
3.2 Maintenance ......................................................................................................................................................... 15
Regular Checks ................................................................................................................. ................................... 15
3.3 On-Vehicle Testing ............................................................................................................. ................................. 15
Engine Compartment Relay And Fuse Panel ........................................................................................ ........... 16
Bad Connection Test ........................................................................................................................................ 16
Starter Motor Ground Test ...................................................................................................... ......................... 17
Switching Circuit Test ....................................................................................................................................... 17
Cranking Voltage Test .......................................................................................................... ............................ 18
Current Draw Test ............................................................................................................................................ 18
4 Major Service Operations ....................................................................................................................19
4.1 Starter Motor ........................................................................................................................................................ 19
Remove ................................................................................................................................................................. 19
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3611 of 6020

Starting System – V6 Page 6D1-2–3
1 General Information
All HFV6 engines are fitted with a Mitsubishi starter motor. This consists of a solenoid switch on a DC motor. The motor
has permanent magnet excitation, which has the advantage of low weight a with high output torque and is visually
identifiable by the absence of pole-shoe retaining screws.
The starter motor does not have field coil windings or pole shoes. These parts have been replaced by six permanent
magnets that are held in the pole housing by clips. The positive brushes are now part of the brush plate assembly.
The solenoid switch is the only component of the starter motor assembly that is serviced separately. If any other parts
require replacement, the starter motor must be replaced.
1.1 WARNING, CAUTION and NOTES
This Section contains various W ARNINGS, CAUTIONS and NOTE statements that you must observe carefully to reduce
the risk of death or injury during service, repair procedures or vehicle operation. Incorrect service or repair procedures
may damage the vehicle or cause operational faults. W ARNINGS, CAUTION and NOTE statements are not exhaustive.
HOLDEN LTD can not possibly warn of all the potentially hazardous consequences of failure to follow these instructions.
Definition of WARNING, CAUTION and NOTE Statements
Diagnosis and repair procedures in this Section contain both general and specific W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE
statements. HOLDEN LTD is dedicated to the presentation of service information that helps the technician to diagnose
and repair the systems necessary for proper operation of the vehicle. Certain procedures may present a hazard to the
technician if they are not followed in the recommended manner. W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE statements are
designed to help prevent these hazards from occurring, but not all hazards can be foreseen.
WARNING defined
A W ARNING statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in death or injury. A W ARNING statement alerts you to take necessary action or not to take a
prohibited action. If a W ARNING statement is ignored, the following consequences may occur:
• Death or injury to the technician or other personnel working on the vehicle,
• Death or injury to other people in or near the workplace area, and / or
• Death or injury to the driver / or passenger(s) of the vehicle or other people, if the vehicle has been improperly
repaired.
CAUTION defined
A CAUTION statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in damage to or destruction of equipment, or corruption of data. If a CAUTION statement is ignored,
the following consequences may occur:
• Damage to the vehicle,
• Unnecessary vehicle repairs or component replacement,
• Faulty operation or performance of any system or component being repaired,
• Damage to any system or components which depend on the proper operation of the system or component being
repaired,
• Faulty operation or performance of any systems or components which depend on the proper operation or
performance of the system or component under repair,
• Damage to fasteners, basic tools or special tools and / or
• Leakage of coolant, lubricant or other vital fluids.
NOTE defined
A NOTE statement immediately precedes or follows an operating procedure, maintenance practice or condition that
requires highlighting. A NOTE statement also emphasises necessary characteristics of a diagnostic or repair procedure.
A NOTE statement is designed to:
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3612 of 6020

Starting System – V6 Page 6D1-2–4
• Clarify a procedure,
• Present additional information for accomplishing a procedure,
• Give insight into the reasons for performing a procedure in the recommended manner, and / or
Present information that gives the technician the benefit of past experience in accomplishing a procedure with greater
ease.
1.2 Components
Starting System Components
The main components of the starting system are:
• battery,
• wiring,
• ignition switch,
• theft deterrent engine crank inhibitor (a function of the theft deterrent system),
• park / neutral and back-up switch (on vehicles with 4 speed automatic transmission),
• engine control module (ECM),
• start relay,
• solenoid switch, and
• starter motor.
Starter Motor and Solenoid Switch Components
Solenoid Switch
The solenoid switch is used to activate the DC motor and has two windings; the pull-in winding and the hold-in winding.
The pull-in winding has heavier wire and is grounded through the DC motor winding and brushes. The hold-in winding is
grounded through the solenoid casing.
Planetary Drive Train
The planetary drive train consists of an internally toothed ring gear and three planetary gear wheels, which rotate on
sleeve bearings on the planetary drive shaft. The ring gear is keyed into the drive-end housing and is made from
high-grade polyamide with mineral additives.
W hen the starter motor operates, the armature turns the planetary gears inside the fixed planetary ring gear. This drives
the planetary shaft at a reduced speed ratio which turns the drive assembly. A fork lever in the drive-end housing forces
the drive assembly forward to engage with the flexplate / flywheel ring gear on the engine and transmit cranking torque.
An internal clutch allows the drive assembly pinion gear to rotate freely when the engine starts. This prevents the
armature from being driven at excessive speed by the engine.
Armature
The armature shaft is supported at each end by oil absorbent, sintered metal bushes; one in the commutator end shield
and one in the planetary drive shaft. The front end of the armature has a gear profile. This meshes with the three
planetary gear wheels. These in turn, mesh with the internal teeth of the ring gear.
Brushes
A brush plate supports four commutator brushes. This plate is fixed to the commutator end shield with two retaining
screws. Two negative brushes are grounded to the pole housing. The two positive brushes are insulated from the pole
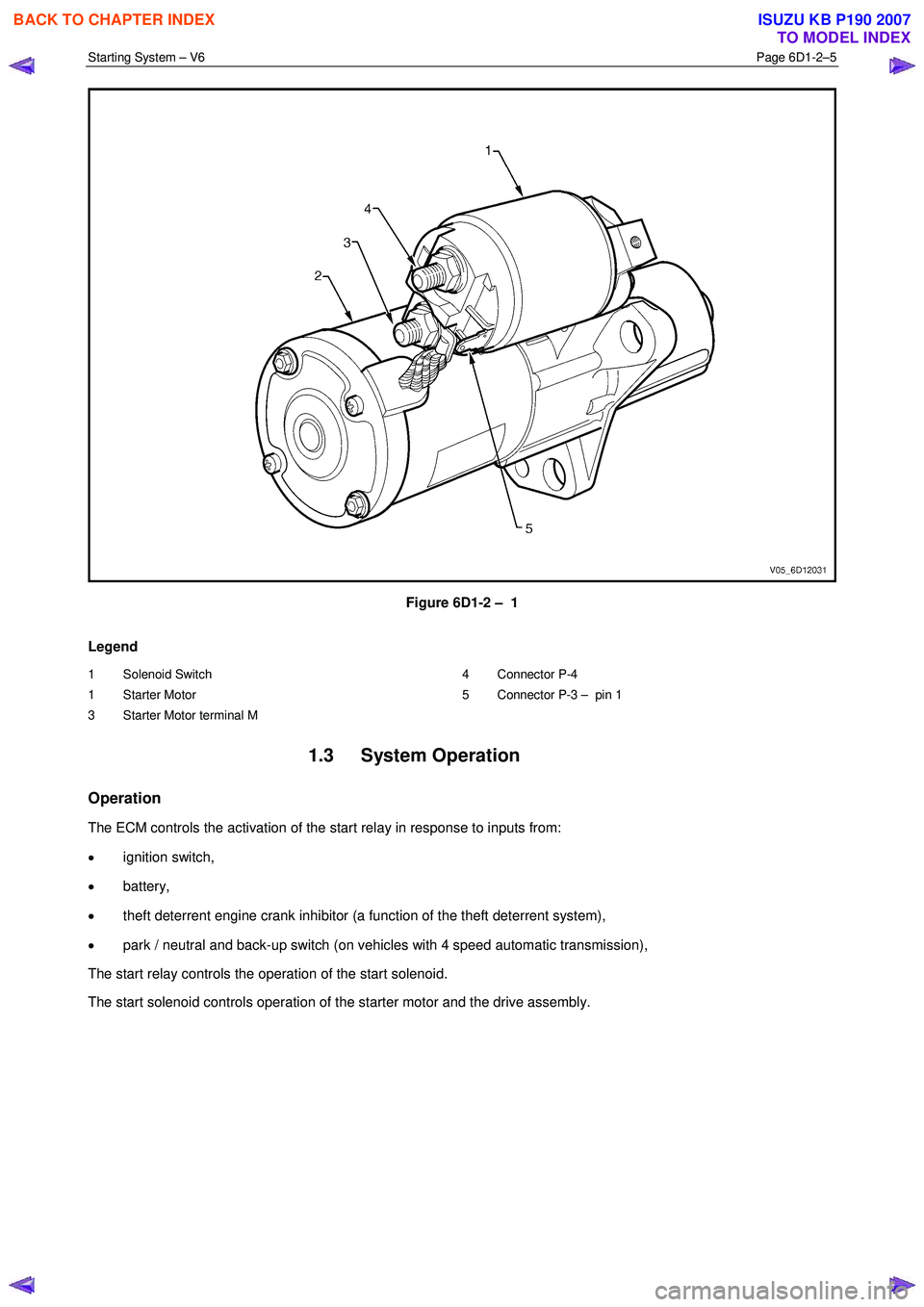
housing and connected to the solenoid switch M terminal, refer to Figure 6D1-2 – 1.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3613 of 6020
Starting System – V6 Page 6D1-2–5
Figure 6D1-2 – 1
Legend
1 Solenoid Switch
1 Starter Motor
3 Starter Motor terminal M 4 Connector P-4
5 Connector P-3 – pin 1
1.3 System Operation
Operation
The ECM controls the activation of the start relay in response to inputs from:
• ignition switch,
• battery,
• theft deterrent engine crank inhibitor (a function of the theft deterrent system),
• park / neutral and back-up switch (on vehicles with 4 speed automatic transmission),
The start relay controls the operation of the start solenoid.
The start solenoid controls operation of the starter motor and the drive assembly.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007