2007 ISUZU KB P190 engine
[x] Cancel search: enginePage 3001 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–224
Page 6A1–224
Valve Guide Measurement
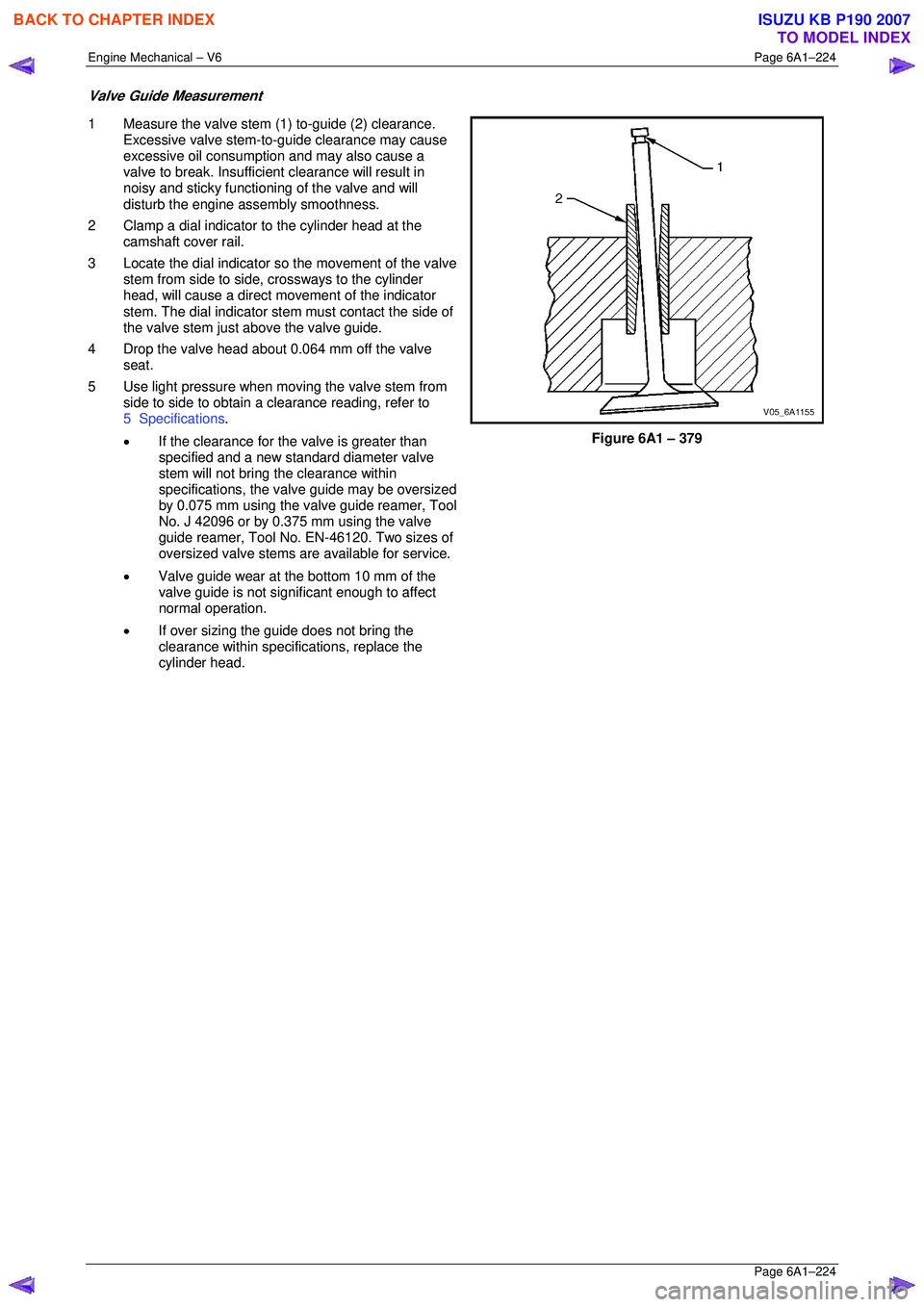
1 Measure the valve stem (1) to-guide (2) clearance.
Excessive valve stem-to-guide clearance may cause
excessive oil consumption and may also cause a
valve to break. Insufficient clearance will result in
noisy and sticky functioning of the valve and will
disturb the engine assembly smoothness.
2 Clamp a dial indicator to the cylinder head at the camshaft cover rail.
3 Locate the dial indicator so the movement of the valve
stem from side to side, crossways to the cylinder
head, will cause a direct mo vement of the indicator
stem. The dial indicator stem must contact the side of
the valve stem just above the valve guide.
4 Drop the valve head about 0.064 mm off the valve seat.
5 Use light pressure when moving the valve stem from side to side to obtain a clearance reading, refer to
5 Specifications .
• If the clearance for the valve is greater than
specified and a new st andard diameter valve
stem will not bring the clearance within
specifications, the valv e guide may be oversized
by 0.075 mm using the valve guide reamer, Tool
No. J 42096 or by 0.375 mm using the valve
guide reamer, Tool No. EN-46120. Two sizes of
oversized valve stems are available for service.
• Valve guide wear at the bottom 10 mm of the
valve guide is not significant enough to affect
normal operation.
• If over sizing the guide does not bring the
clearance within specif ications, replace the
cylinder head.
Figure 6A1 – 379
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3002 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–225
Page 6A1–225
Valve Spring Inspection and Measurement
Inspection Procedure
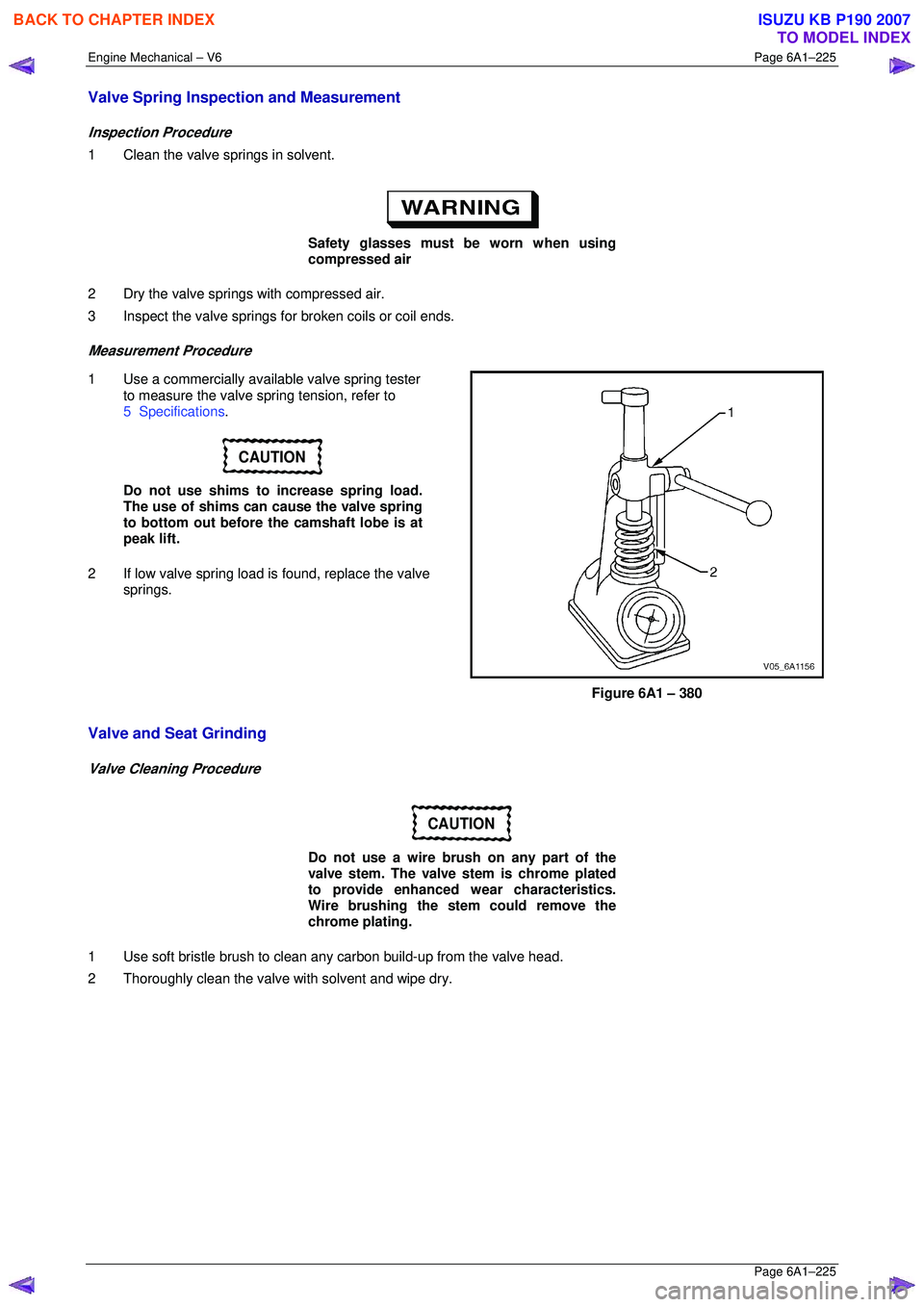
1 Clean the valve springs in solvent.
Safety glasses must be worn when using
compressed air
2 Dry the valve springs with compressed air.
3 Inspect the valve springs for broken coils or coil ends.
Measurement Procedure
1 Use a commercially available valve spring tester to measure the valve spring tension, refer to
5 Specifications .
CAUTION
Do not use shims to increase spring load.
The use of shims can cause the valve spring
to bottom out before the camshaft lobe is at
peak lift.
2 If low valve spring load is found, replace the valve springs.
Figure 6A1 – 380
Valve and Seat Grinding
Valve Cleaning Procedure
CAUTION
Do not use a wire brush on any part of the
valve stem. The valve stem is chrome plated
to provide enhanced wear characteristics.
Wire brushing the stem could remove the
chrome plating.
1 Use soft bristle brush to clean any carbon build-up from the valve head.
2 Thoroughly clean the valve with solvent and wipe dry.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3003 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–226
Page 6A1–226
Valve Visual Inspection Procedure
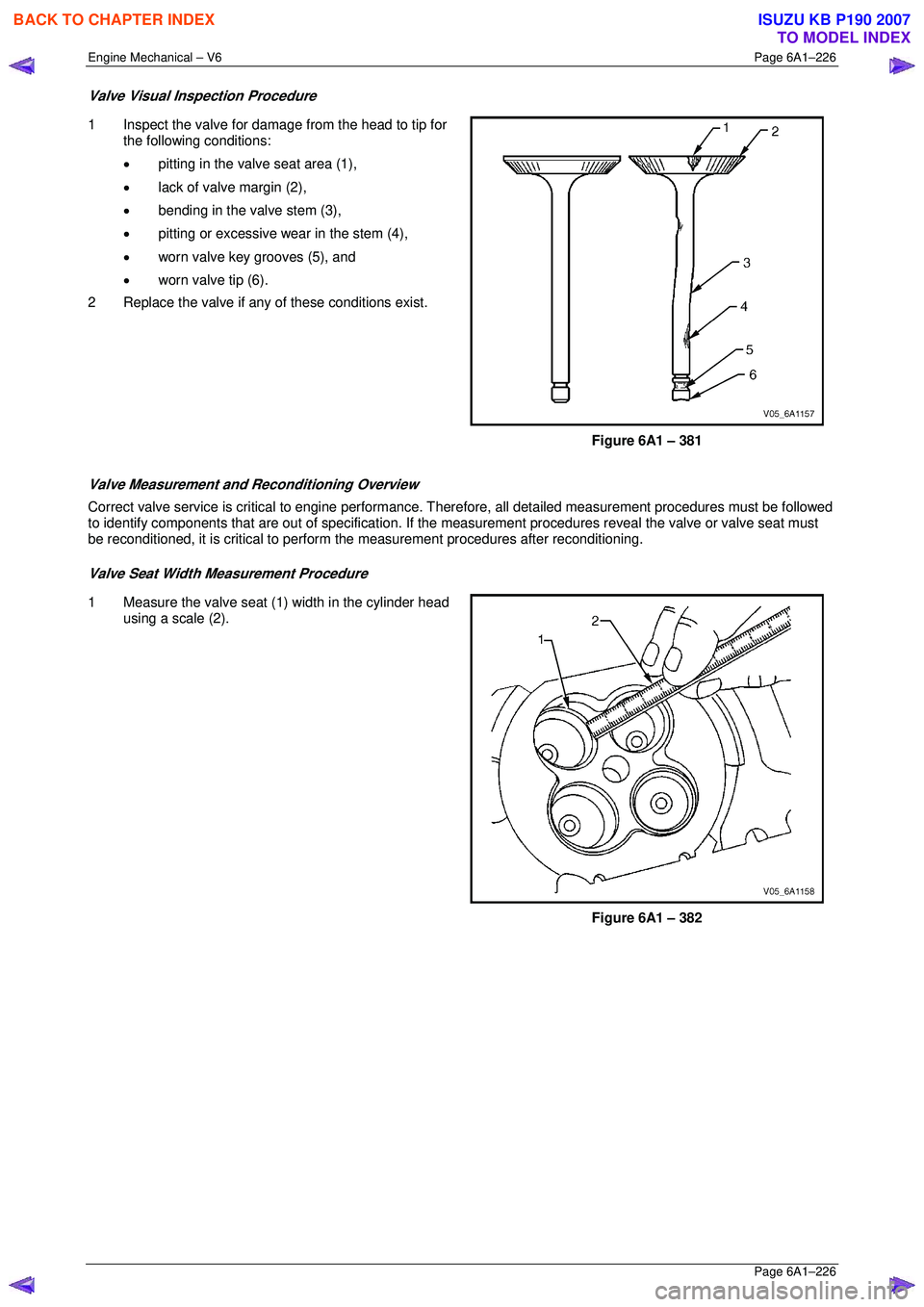
1 Inspect the valve for damage from the head to tip for
the following conditions:
• pitting in the valve seat area (1),
• lack of valve margin (2),
• bending in the valve stem (3),
• pitting or excessive wear in the stem (4),
• worn valve key grooves (5), and
• worn valve tip (6).
2 Replace the valve if any of these conditions exist.
Figure 6A1 – 381
Valve Measurement and Reconditioning Overview
Correct valve service is critical to engine performance. Therefore, all detailed measurement procedures must be followed
to identify components that are out of specification. If the measurement procedures reveal t he valve or valve seat must
be reconditioned, it is critical to perform t he measurement procedures after reconditioning.
Valve Seat Width Measurement Procedure
1 Measure the valve seat (1) width in the cylinder head
using a scale (2).
Figure 6A1 – 382
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3004 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–227
Page 6A1–227
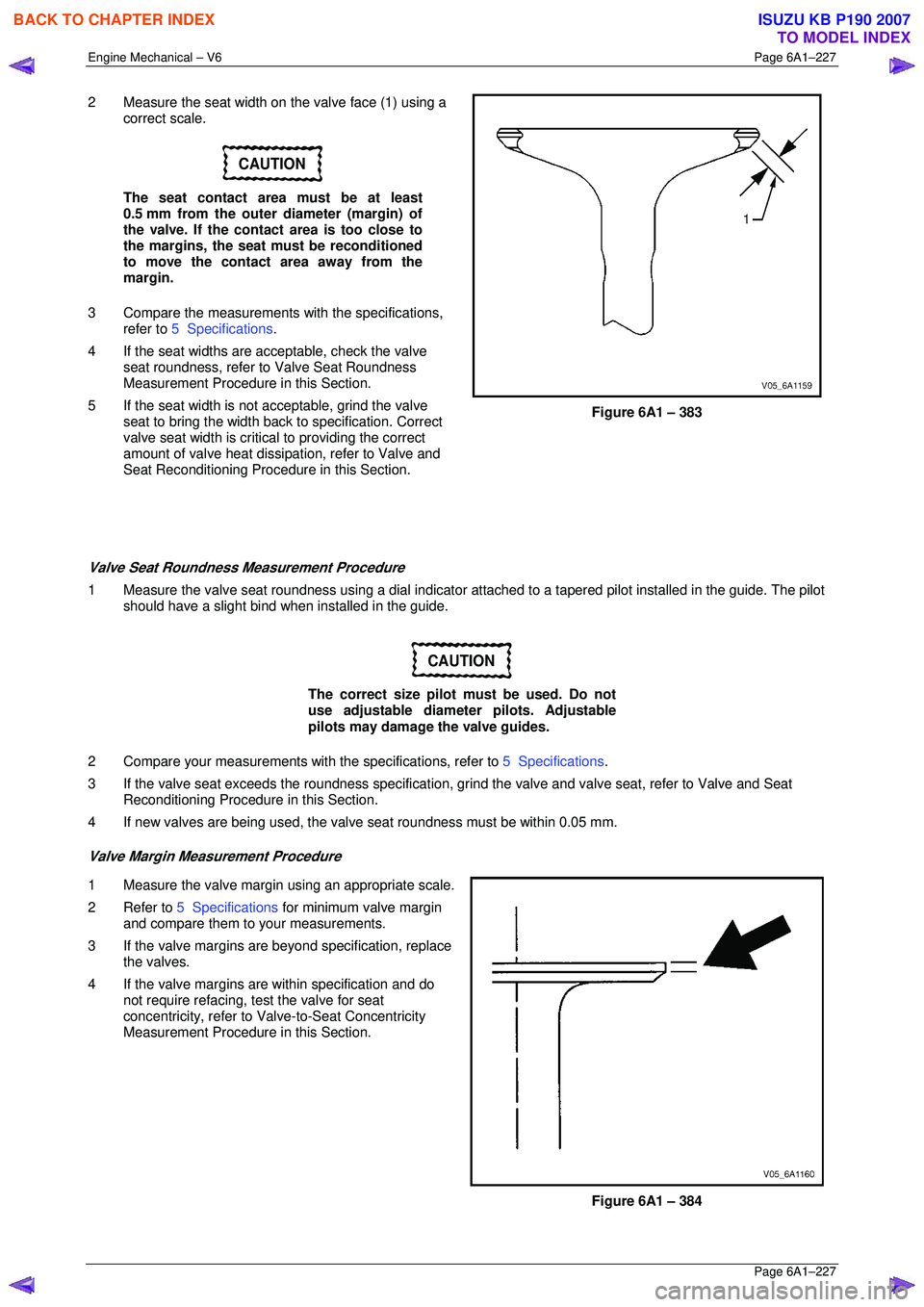
2 Measure the seat width on the valve face (1) using a
correct scale.
CAUTION
The seat contact area must be at least
0.5 mm from the outer diameter (margin) of
the valve. If the contact area is too close to
the margins, the seat must be reconditioned
to move the contact area away from the
margin.
3 Compare the measurements with the specifications,
refer to 5 Specifications .
4 If the seat widths are a cceptable, check the valve
seat roundness, refer to Valve Seat Roundness
Measurement Procedure in this Section.
5 If the seat width is not acceptable, grind the valve
seat to bring the width back to specification. Correct
valve seat width is critical to providing the correct
amount of valve heat dissipat ion, refer to Valve and
Seat Reconditioning Procedure in this Section.
Figure 6A1 – 383
Valve Seat Roundness Measurement Procedure
1 Measure the valve seat roundness using a dial indicator a ttached to a tapered pilot installed in the guide. The pilot
should have a slight bind w hen installed in the guide.
CAUTION
The correct size pilot must be used. Do not
use adjustable diameter pilots. Adjustable
pilots may damage the valve guides.
2 Compare your measurements with the specifications, refer to 5 Specifications.
3 If the valve seat exceeds the roundne ss specification, grind the valve and valve seat, refer to Valve and Seat
Reconditioning Procedure in this Section.
4 If new valves are being used, the valv e seat roundness must be within 0.05 mm.
Valve Margin Measurement Procedure
1 Measure the valve margin using an appropriate scale.
2 Refer to 5 Specifications for minimum valve margin
and compare them to your measurements.
3 If the valve margins are beyond specification, replace the valves.
4 If the valve margins are within specification and do not require refacing, test the valve for seat
concentricity, refer to Valve-to-Seat Concentricity
Measurement Procedure in this Section.
Figure 6A1 – 384
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3005 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–228
Page 6A1–228
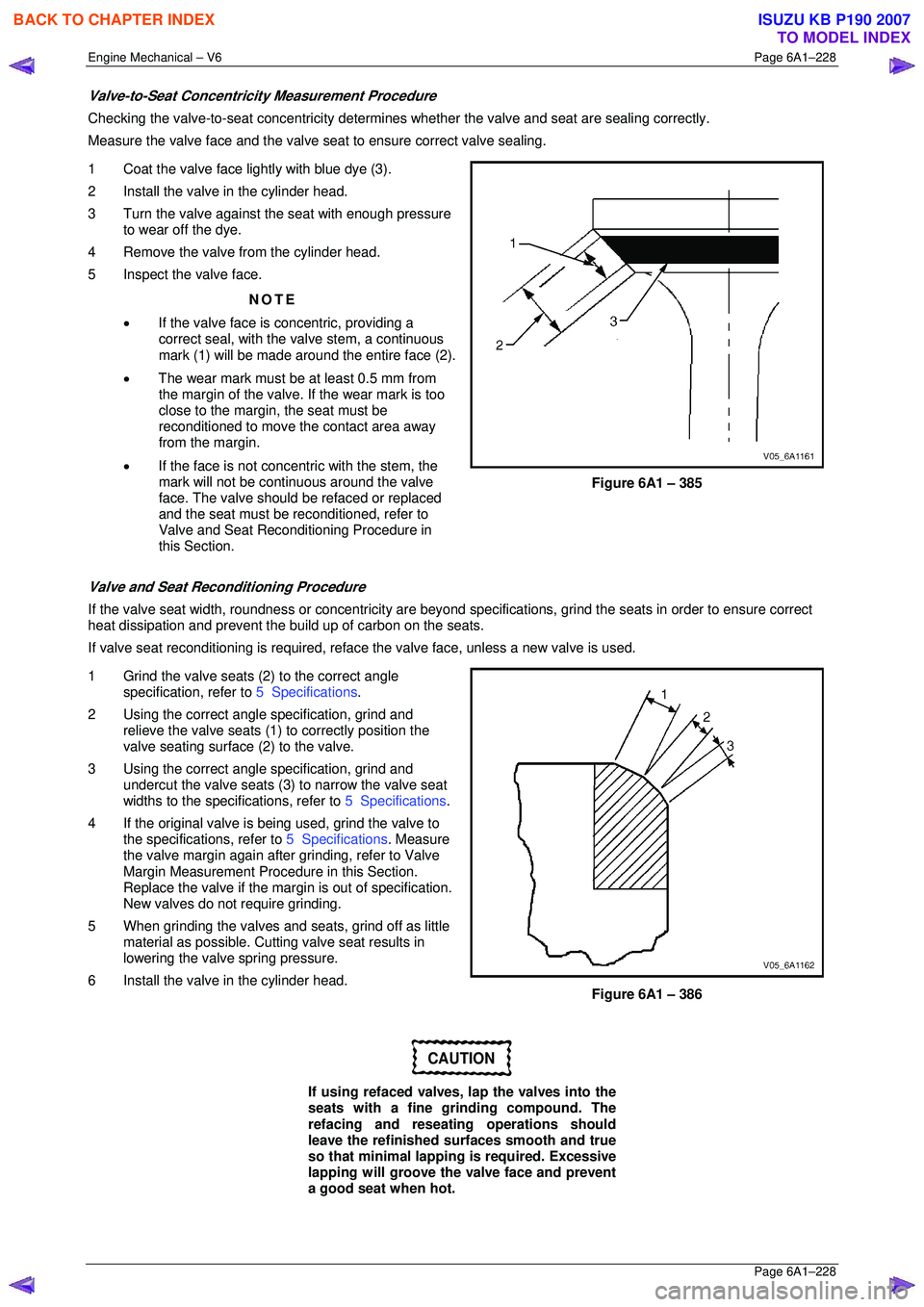
Valve-to-Seat Concentricity Measurement Procedure
Checking the valve-to-seat concentricity determines whether the valve and seat are sealing correctly.
Measure the valve face and the valve s eat to ensure correct valve sealing.
1 Coat the valve face lightly with blue dye (3).
2 Install the valve in the cylinder head.
3 Turn the valve against the seat with enough pressure to wear off the dye.
4 Remove the valve from the cylinder head.
5 Inspect the valve face.
NOTE
• If the valve face is concentric, providing a
correct seal, with the valve stem, a continuous
mark (1) will be made around the entire face (2).
• The wear mark must be at least 0.5 mm from
the margin of the valve. If the wear mark is too
close to the margin, the seat must be
reconditioned to move the contact area away
from the margin.
• If the face is not concentric with the stem, the
mark will not be continuous around the valve
face. The valve should be refaced or replaced
and the seat must be reconditioned, refer to
Valve and Seat Reconditioning Procedure in
this Section.
Figure 6A1 – 385
Valve and Seat Reconditioning Procedure
If the valve seat width, roundness or conc entricity are beyond specifications, grind the seats in order to ensure correct
heat dissipation and prevent the bu ild up of carbon on the seats.
If valve seat reconditioning is required, reface the valve face, unless a new valve is used.
1 Grind the valve seats (2) to the correct angle specification, refer to 5 Specifications.
2 Using the correct angle specification, grind and
relieve the valve seats (1) to correctly position the
valve seating surface (2) to the valve.
3 Using the correct angle specification, grind and
undercut the valve seats (3) to narrow the valve seat
widths to the specifications, refer to 5 Specifications.
4 If the original valve is being used, grind the valve to the specifications, refer to 5 Specifications. Measure
the valve margin again after grinding, refer to Valve
Margin Measurement Procedure in this Section.
Replace the valve if the margin is out of specification.
New valves do not require grinding.
5 When grinding the valves and seats, grind off as little material as possible. Cutti ng valve seat results in
lowering the valve spring pressure.
6 Install the valve in the cylinder head.
Figure 6A1 – 386
CAUTION
If using refaced valves, lap the valves into the
seats with a fine grinding compound. The
refacing and reseati ng operations should
leave the refinished surfaces smooth and true
so that minimal lapping is required. Excessive
lapping will groove the valve face and prevent
a good seat when hot.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3006 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–229
Page 6A1–229
NOTE
• Clean any remaining lapping compound from
the valve and seat with solvent and
compressed air prior to final assembly.
• If fitting new valves, do not lap the valves
under any condition.
7 After obtaining the correct valve seat width in the cylinder head, measure the valve stem height, refer to Valve
Stem Height Measurement Pr ocedure in this Section.
8 If the valve stem height is acceptabl e, test the seats for concentricity, refer to Valve-to-Seat Concentricity
Measurement Procedure in this Section.
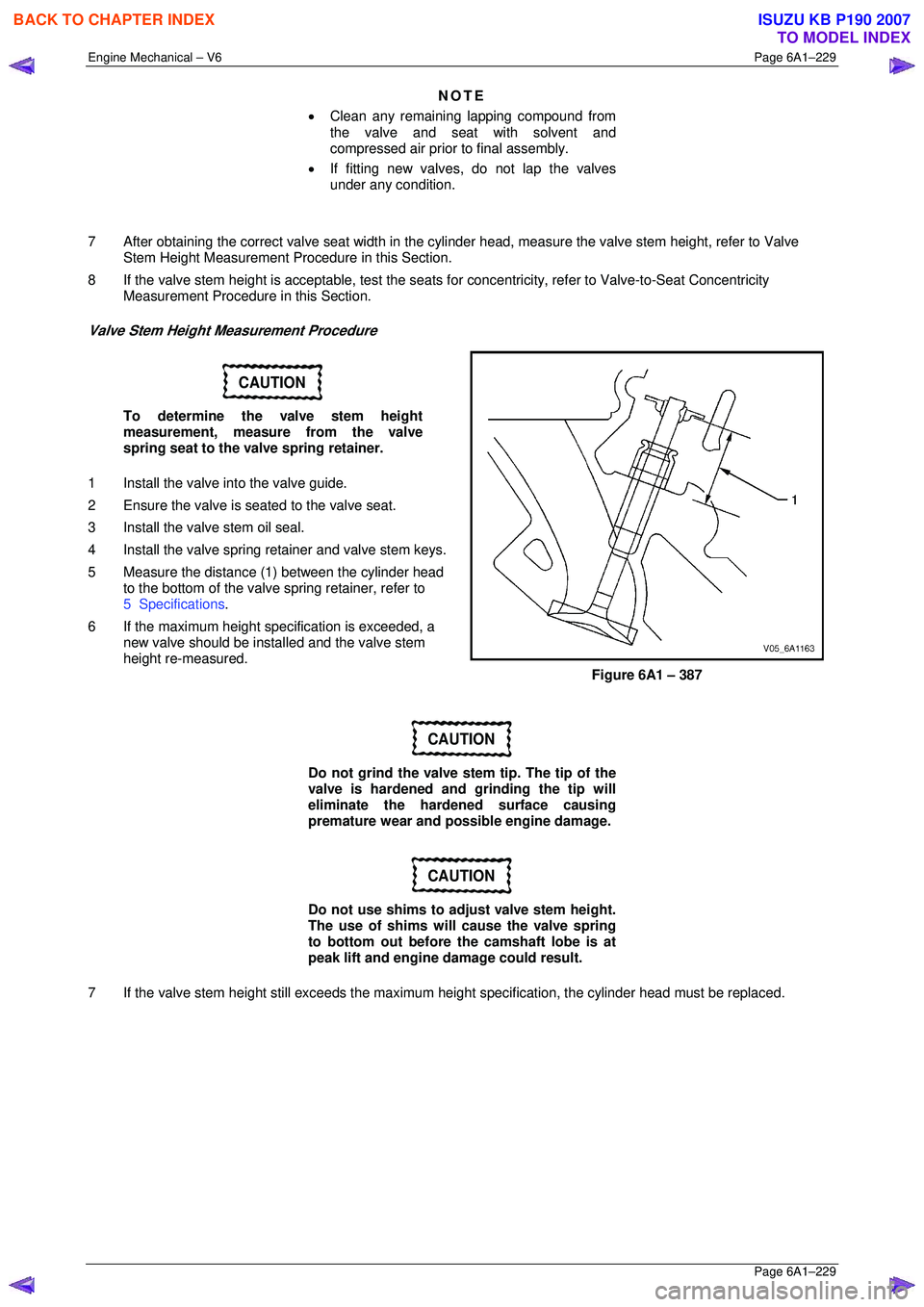
Valve Stem Height Measurement Procedure
CAUTION
To determine the valve stem height
measurement, measure from the valve
spring seat to the valve spring retainer.
1 Install the valve into the valve guide.
2 Ensure the valve is seated to the valve seat.
3 Install the valve stem oil seal.
4 Install the valve spring retainer and valve stem keys.
5 Measure the distance (1 ) between the cylinder head
to the bottom of the valve spring retainer, refer to
5 Specifications .
6 If the maximum height spec ification is exceeded, a
new valve should be installed and the valve stem
height re-measured.
Figure 6A1 – 387
CAUTION
Do not grind the valve stem tip. The tip of the
valve is hardened and grinding the tip will
eliminate the hardened surface causing
premature wear and possible engine damage.
CAUTION
Do not use shims to adjust valve stem height.
The use of shims will cause the valve spring
to bottom out before the camshaft lobe is at
peak lift and engine damage could result.
7 If the valve stem height still exceeds the maximum height specification, the cylinder head must be replaced.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3007 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–230
Page 6A1–230
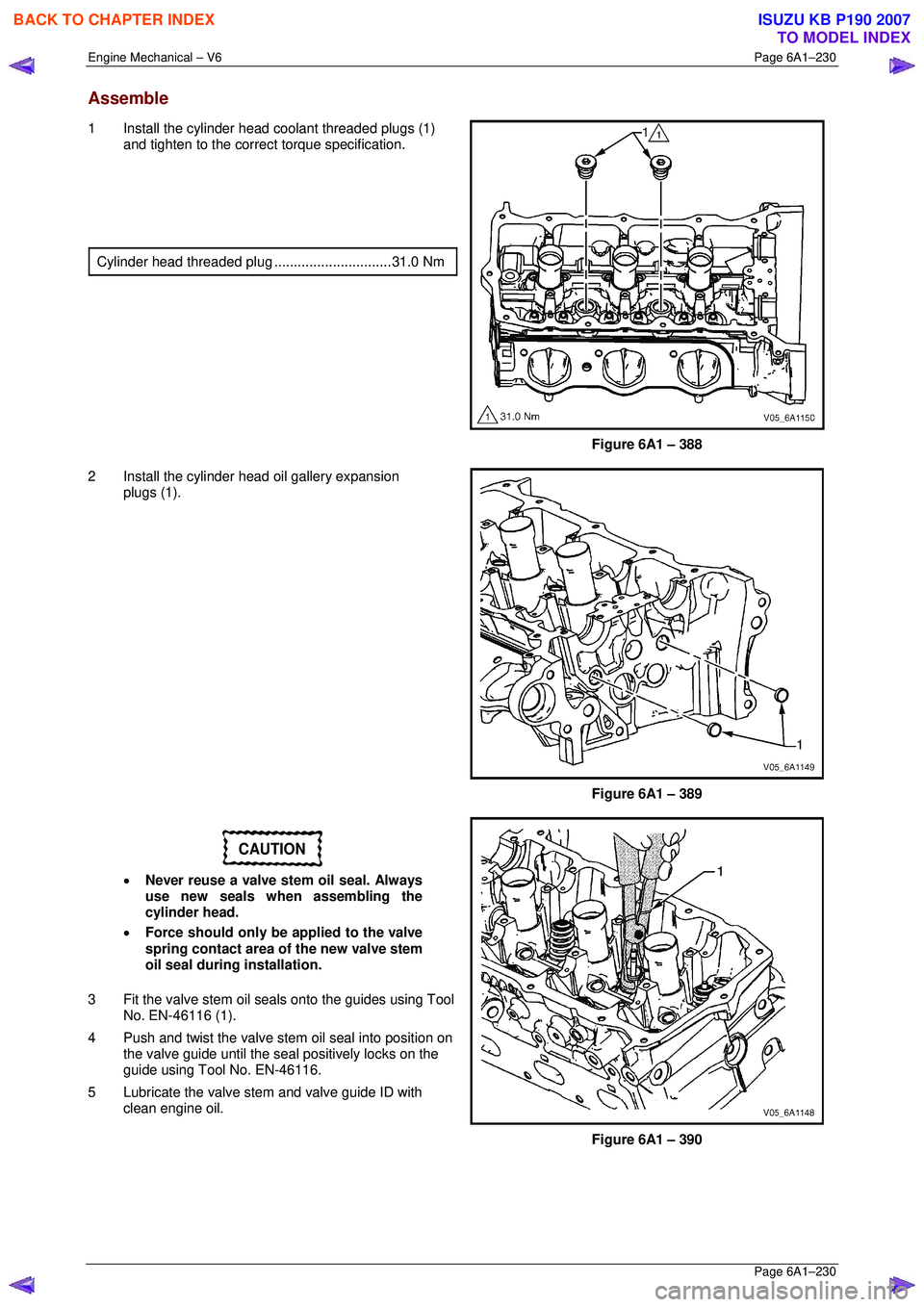
Assemble
1 Install the cylinder head coolant threaded plugs (1)
and tighten to the correct torque specification.
Cylinder head thre aded plug .............................. 31.0 Nm
Figure 6A1 – 388
2 Install the cylinder head oil gallery expansion plugs (1).
Figure 6A1 – 389
CAUTION
• Never reuse a valve stem oil seal. Always
use new seals when assembling the
cylinder head.
• Force should only be applied to the valve
spring contact area of the new valve stem
oil seal during installation.
3 Fit the valve stem oil seal s onto the guides using Tool
No. EN-46116 (1).
4 Push and twist the valve stem oil seal into position on the valve guide until the s eal positively locks on the
guide using Tool No. EN-46116.
5 Lubricate the valve stem and valve guide ID with clean engine oil.
Figure 6A1 – 390
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3008 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–231
Page 6A1–231
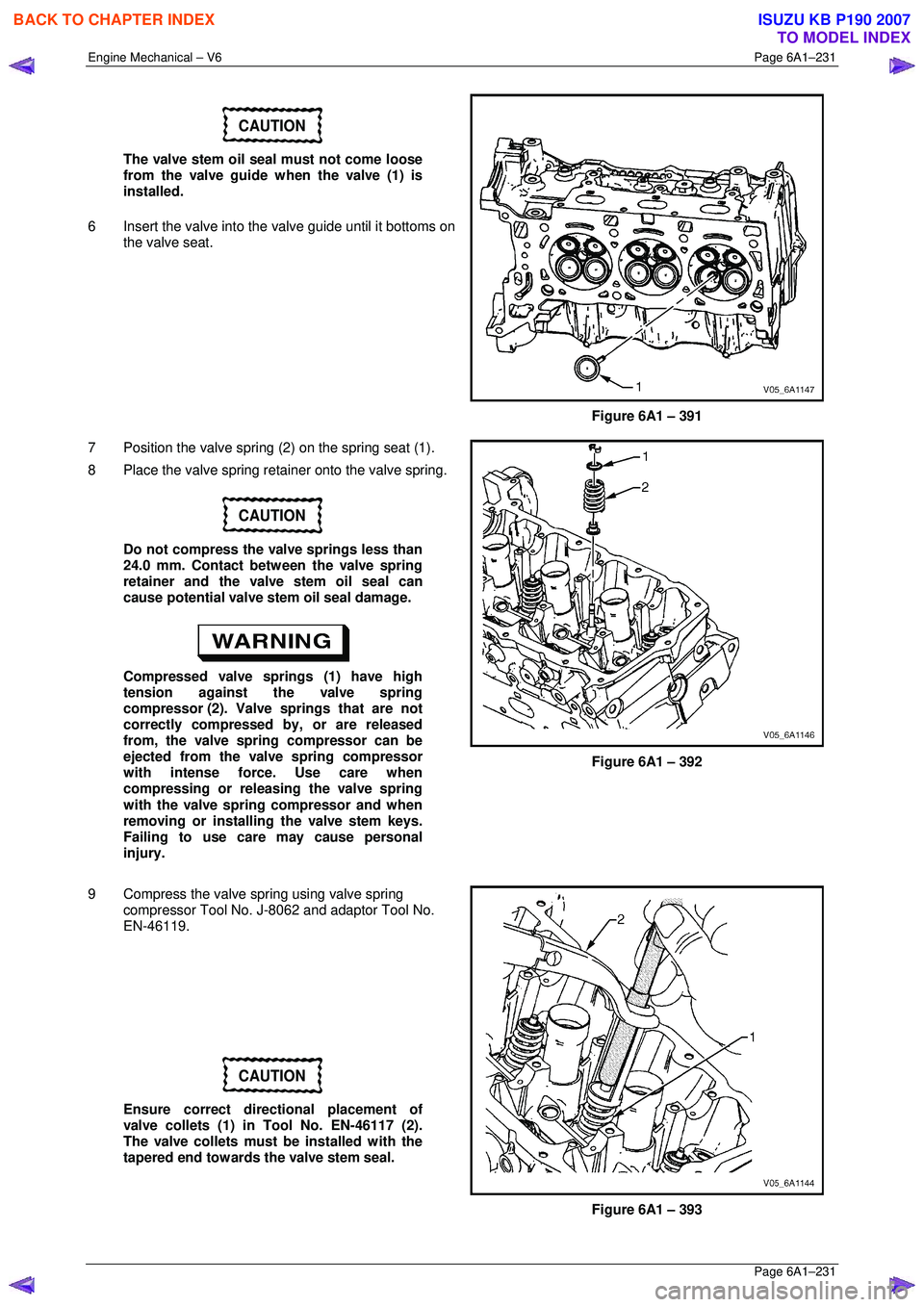
CAUTION
The valve stem oil seal must not come loose
from the valve guide when the valve (1) is
installed.
6 Insert the valve into the valve guide until it bottoms on
the valve seat.
Figure 6A1 – 391
7 Position the valve spring (2) on the spring seat (1).
8 Place the valve spring retainer onto the valve spring.
CAUTION
Do not compress the valve springs less than
24.0 mm. Contact between the valve spring
retainer and the valve stem oil seal can
cause potential valve stem oil seal damage.
Compressed valve springs (1) have high
tension against the valve spring
compressor (2). Valve springs that are not
correctly compressed by, or are released
from, the valve spring compressor can be
ejected from the valve spring compressor
with intense force. Use care when
compressing or releasing the valve spring
with the valve spring compressor and when
removing or installing the valve stem keys.
Failing to use care may cause personal
injury.
Figure 6A1 – 392
9 Compress the valve spring using valve spring compressor Tool No. J-8062 and adaptor Tool No.
EN-46119.
CAUTION
Ensure correct directional placement of
valve collets (1) in Tool No. EN-46117 (2).
The valve collets must be installed with the
tapered end towards the valve stem seal.
Figure 6A1 – 393
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007