2007 ISUZU KB P190 maintenance schedule
[x] Cancel search: maintenance schedulePage 2124 of 6020

6C-6 ENGINE FUEL (C24SE)
Fuel Filter
Inspection
1. Replace the fuel filter if the fuel leaks from fuel filter
body or if the fuel filter body itself is damaged.
2. Replace the filter if it is clogged with dirt o
r
sediment.
Installation
1. Install the filter to holder from fuel tank front side.
NOTE: Attend direction of fuel filter. (1) to engine side
(2) to fuel tank side.
NOTE: Verify to hang holder hook to fuel filter.
RTW 36CSH000301
2. Connect the quick connector from the fuel tube to
the fuel filter.
NOTE: Pull of the left checker into the fuel pipe.
NOTE: Refer to “Fuel Tube/Quick Connector Fittings” in
this section when performing any repairs.
3. Tighten fuel filler cap until at least one click are heard.
4. Connect the battery ground cable.
Inspection
After installation, start engine and check for fuel
leakage.
In–Tank Fuel Filter
The filter is located on the lower end of fuel pickup tube
in the fuel tank. It prevents dirt from entering the fuel
pipe and also stops water unless the filter is completel
y
submerged in the water. It is a selfcleaning type, not
requiring scheduled maintenance. Excess water and
sediment in the tank restricts fuel supply to the engine,
resulting in engine stoppage. In such a case, the tank
must be cleaned thoroughly.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2224 of 6020
6E–54 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION FOR ELECTRIC
IGNITION SYSTEM
The engine use two ignition coils, one per two cylinders.
A two wire connector provides a battery voltage primary
supply through the ignition fuse.
The ignition control spark timing is the ECM’s method of
controlling the spark advance and the ignition dwell.
The ignition control spark advance and the ignition dwell
are calculated by the ECM using the following inputs.
• Engine speed
• Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor
• Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor
• Throttle position sensor
• Vehicle speed sensor
• ECM and ignition system supply voltage
Ignition coil works to generate only the secondary
voltage be receiving the primary voltage from ECM.
The primary voltage is generated at the coil driver
located in the ECM. The coil driver generate the primary
voltage based on the crankshaft position signal. In
accordance with the crankshaft position signal, ignition
coil driver determines the adequate ignition timing and
also cylinder number to ignite.
Ignition timing is determined the coolant temperature,
intake air temperature, engine speed, engine load,
knock sensor signal, etc.
Spark Plug
Although worn or dirty spark plugs may give satisfactory
operation at idling speed, they frequently fail at higher
engine speeds. Faulty spark plugs may cause poor fuel
economy, power loss, loss of speed, hard starting and
generally poor engine performance. Follow the
scheduled maintenance service recommendations to
ensure satisfactory spark plug performance. Refer to
Maintenance and Lubrication .
Normal spark plug operation will result in brown to
grayish-tan deposits appearing on the insulator portion
of the spark plug. A small amount of red-brown, yellow,
and white powdery material may also be present on the
insulator tip around the center electrode. These
deposits are normal combustion by-products of fuels
and lubricating oils with additives. Some electrode wear
will also occur. Engines which are not running properly
are often referred to as “misfiring.” This means the
ignition spark is not igniting the air/fuel mixture at the
proper time. While other ignition and fuel system causes
must also be considered, possible causes include
ignition system conditions which allow the spark voltage
to reach ground in some other manner than by jumping
across the air gap at the tip of the spark plug, leaving
the air/fuel mixture unburned. Misfiring may also occur
when the tip of the spark plug becomes overheated and
ignites the mixture before the spark jumps. This is
referred to as “pre-ignition.”
Spark plugs may also misfire due to fouling, excessive
gap, or a cracked or broken insulator. If misfiring occurs before the recommended replacement interval, locate
and correct the cause.
Carbon fouling of the spark plug is indicated by dry,
black carbon (soot) deposits on the portion of the spark
plug in the cylinder. Excessive idling and slow speeds
under light engine loads can keep the spark plug
temperatures so low that these deposits are not burned
off. Very rich fuel mixtures or poor ignition system output
may also be the cause. Refer to DTC P1167.
Oil fouling of the spark plug is indicated by wet oily
deposits on the portion of the spark plug in the cylinder,
usually with little electrode wear. This may be caused by
oil during break-in of new or newly overhauled engines.
Deposit fouling of the spark plug occurs when the
normal red-brown, yellow or white deposits of
combustion by-products become sufficient to cause
misfiring. In some cases, these deposits may melt and
form a shiny glaze on the insulator around the center
electrode. If the fouling is found in only one or two
cylinders, valve stem clearances or intake valve seals
may be allowing excess lubricating oil to enter the
cylinder, particularly if the deposits are heavier on the
side of the spark plug facing the intake valve.
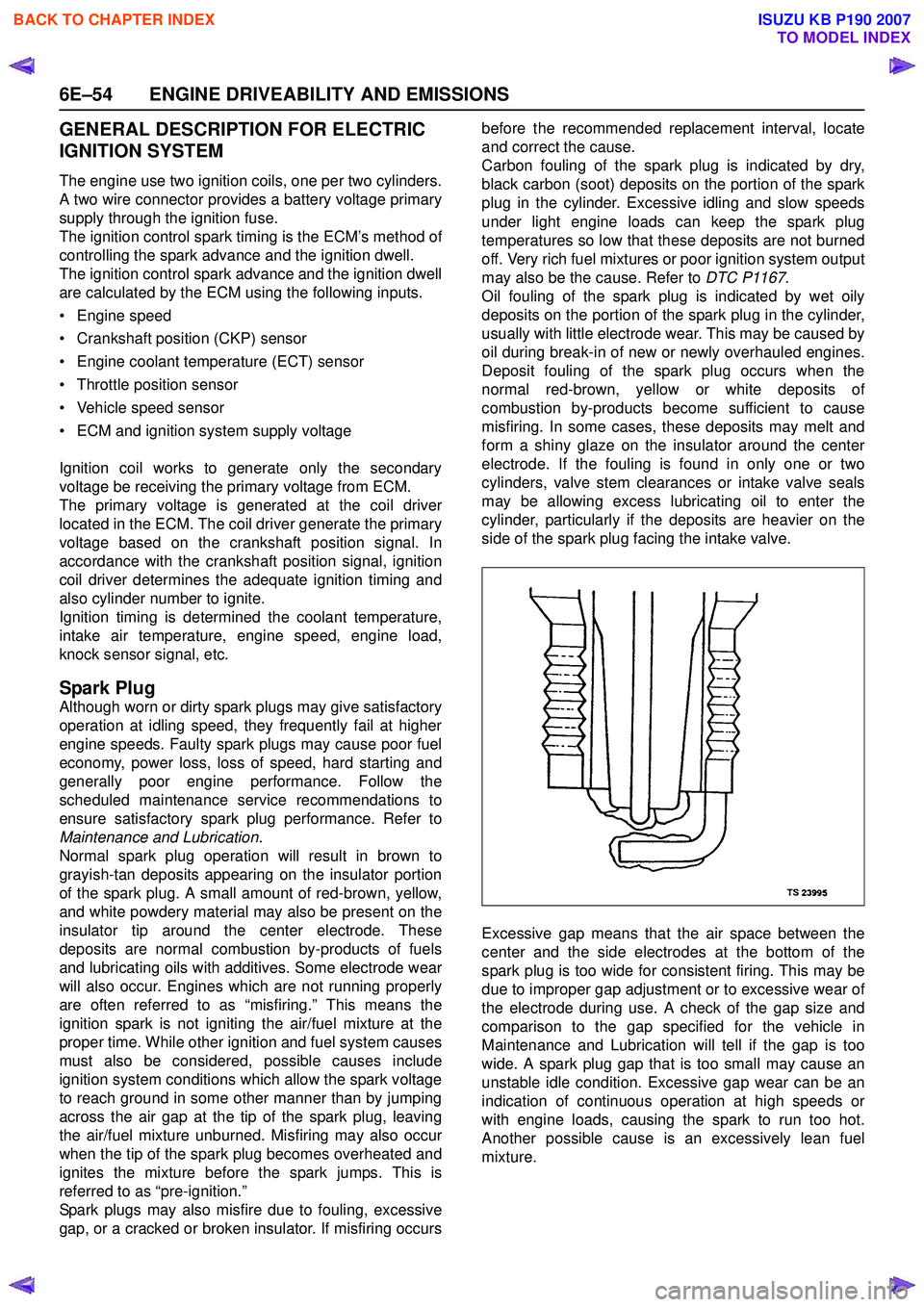
Excessive gap means that the air space between the
center and the side electrodes at the bottom of the
spark plug is too wide for consistent firing. This may be
due to improper gap adjustment or to excessive wear of
the electrode during use. A check of the gap size and
comparison to the gap specified for the vehicle in
Maintenance and Lubrication will tell if the gap is too
wide. A spark plug gap that is too small may cause an
unstable idle condition. Excessive gap wear can be an
indication of continuous operation at high speeds or
with engine loads, causing the spark to run too hot.
Another possible cause is an excessively lean fuel
mixture.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2237 of 6020

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–67
GENERAL SERVICE INFORMATION
Aftermarket Electrical and Vacuum
Equipment
Aftermarket (add-on) electrical and vacuum equipment
is defined as any equipment which connects to the
vehicle's electrical or vacuum systems that is installed
on a vehicle after it leaves the factory. No allowances
have been made in the vehicle design for this type of
equipment.
NOTE: No add-on vacuum equipment should be added
to this vehicle.
NOTE: Add-on electrical equipment must only be
connected to the vehicle's electrical system at the
battery (power and ground).
Add-on electrical equipment, even when installed to
these guidelines, may still cause the electric system to
malfunction. This may also include equipment not
connected to the vehicle electrical system such as
portable telephones and radios. Therefore, the first step
in diagnosing any electric problem is to eliminate all
aftermarket electrical equipment from the vehicle. After
this is done, if the problem still exists, it may be
diagnosed in the normal manner.
Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Electronic components used in the ECM are often
designed to carry very low voltage. Electronic
components are susceptible to damage caused by
electrostatic discharge. Less than 100 volts of static
electricity can cause damage to some electronic
components. By comparison, it takes as much as 4000
volts for a person to feel even the zap of a static
discharge.
There are several ways for a person to become
statically charged. The most common methods of
charging are by friction and induction.
• An example of charging by friction is a person sliding across a vehicle seat.
• Charge by induction occurs when a person with well- insulated shoes stands near a highly charged object
and momentarily touches ground. Charges of the
same polarity are drained off leaving the person
highly charged with the opposite polarity. Static
charges can cause damage, therefore it is important
to use care when handling and testing electronic
components. Non-OEM Parts
All of the OBD diagnostics have been calibrated to run
with OEM parts. Accordingly, if commercially sold
sensor or switch is installed, it makes a wrong diagnosis
and turns on the check engine lamp.
Aftermarket electronics, such as cellular phones,
stereos, and anti-theft devices, may radiate EMI into the
control system if they are improperly installed. This may
cause a false sensor reading and turn on the check
engine lamp.
Poor Vehicle Maintenance
The sensitivity of OBD diagnostics will cause the check
engine lamp to turn on if the vehicle is not maintained
properly. Restricted oil filters, fuel filters, and crankcase
deposits due to lack of oil changes or improper oil
viscosity can trigger actual vehicle faults that were not
previously monitored prior to OBD. Poor vehicle
maintenance can not be classified as a “non-vehicle
fault”, but with the sensitivity of OBD diagnostics,
vehicle maintenance schedules must be more closely
followed.
Related System Faults
Many of the OBD system diagnostics will not run if the
ECM detects a fault on a related system or component.
Visual/Physical Engine Compartment
Inspection
Perform a careful visual and physical engine
compartment inspection when performing any
diagnostic procedure or diagnosing the cause of an
emission test failure. This can often lead to repairing a
problem without further steps. Use the following
guidelines when performing a visual/physical
inspection:
• Inspect all vacuum hoses for punches, cuts, disconnects, and correct routing.
• Inspect hoses that are difficult to see behind other components.
• Inspect all wires in the engine compartment for proper connections, burned or chafed spots, pinched
wires, contact with sharp edges or contact with hot
exhaust manifolds or pipes.
Basic Knowledge of Tools Required
NOTE: Lack of basic knowledge of this powertrain
when performing diagnostic procedures could result in
an incorrect diagnosis or damage to powertrain
components. Do not attempt to diagnose a powertrain
problem without this basic knowledge.
A basic understanding of hand tools is necessary to
effectively use this section of the Service Manual.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007