2007 ISUZU KB P190 relay
[x] Cancel search: relayPage 1983 of 6020
6E-366 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
The EGR valve is mounted on the intake manifold. The
ECM controls the EGR valve opening based on the
engine running condition. The ECM controls the EGR
valve by controlling the solenoid. The solenoid is
controlled based on pulse width modulation (PWM)
signal sent from the ECM. A duty ratio change 0% to
appropriate percentage is EGR valve lift control. To
open the valve, duty ratio is increased. To close the
valve, duty ratio becomes small.
The EGR valve position is detected by the position
sensor, and relayed to the ECM. The position sensor
provides a signal to the ECM on the signal circuit,
which is relative to the position changes of the EGR
valve. The ECM should detect a low signal voltage at a
small lift amount or closed position. The ECM should
detect high signal voltage at a large lift amount.
Intake Throttle Valve
The intake throttle valve is located on the intake
manifold inlet. The ECM controls the intake throttle
valve opening based on the engine running condition.
The ECM controls the intake throttle valve by
controlling the solenoid. The solenoid is controlled
based on pulse width modulation (PWM) signal sent
from the ECM. A duty ratio change 0% to appropriate
percentage is intake throttle valve opening angle
control. To open the valve, duty ratio is increased. To
close the valve, duty ratio becomes small.
The intake throttle valve position is detected by the
position sensor, and relayed to the ECM. The position
sensor provides a signal to the ECM on the signal
circuit, which is relative to the position changes of the
intake throttle valve. The ECM should detect a low
signal voltage at a small opening amount or closed
position. The ECM should detect high signal voltage at
a large opening amount.Turbocharger Description
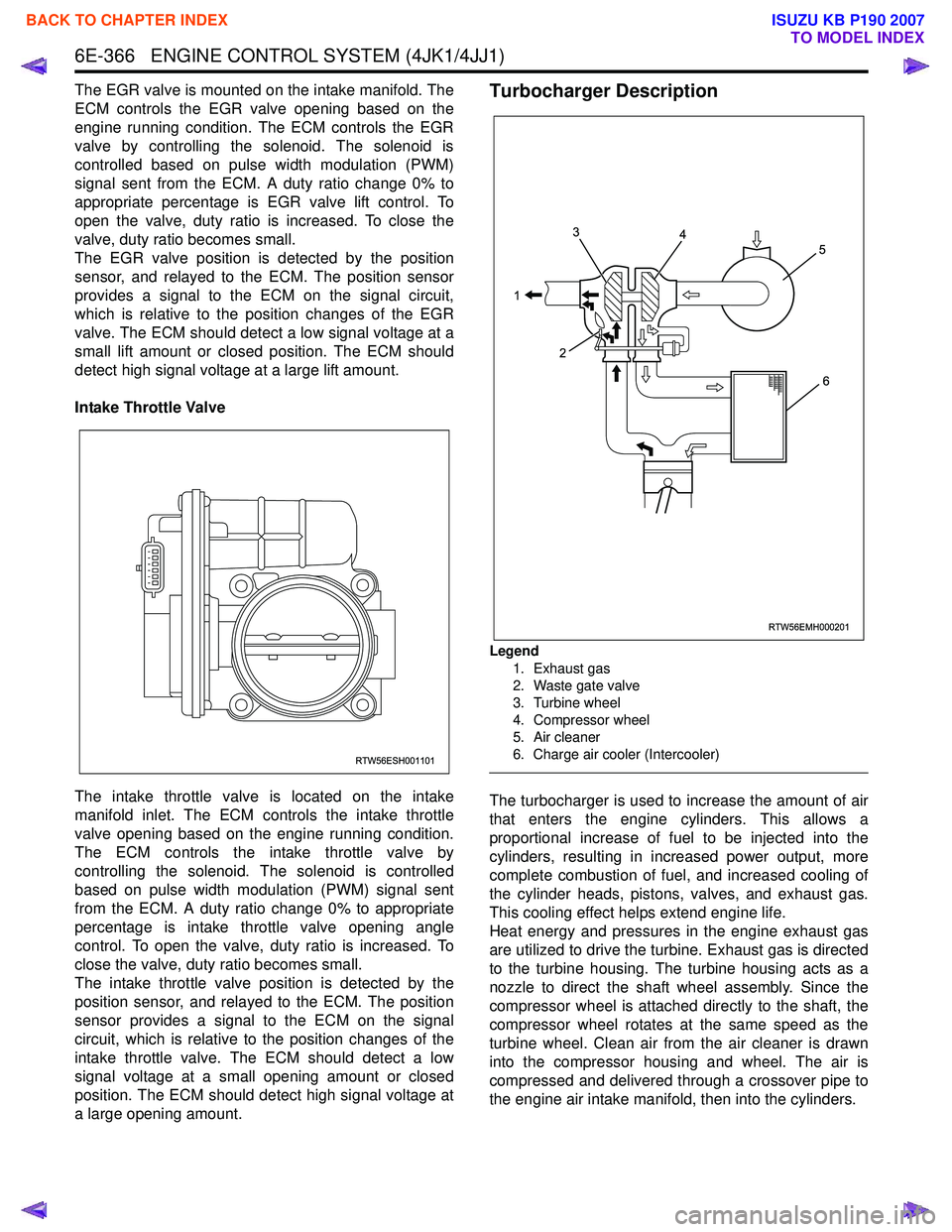
Legend
1. Exhaust gas
2. Waste gate valve
3. Turbine wheel
4. Compressor wheel
5. Air cleaner
6. Charge air cooler (Intercooler)
The turbocharger is used to increase the amount of air
that enters the engine cylinders. This allows a
proportional increase of fuel to be injected into the
cylinders, resulting in increased power output, more
complete combustion of fuel, and increased cooling of
the cylinder heads, pistons, valves, and exhaust gas.
This cooling effect helps extend engine life.
Heat energy and pressures in the engine exhaust gas
are utilized to drive the turbine. Exhaust gas is directed
to the turbine housing. The turbine housing acts as a
nozzle to direct the shaft wheel assembly. Since the
compressor wheel is attached directly to the shaft, the
compressor wheel rotates at the same speed as the
turbine wheel. Clean air from the air cleaner is drawn
into the compressor housing and wheel. The air is
compressed and delivered through a crossover pipe to
the engine air intake manifold, then into the cylinders.
RTW56ESH001101
RTW56EMH000201
1 3
2 4
5
6
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2003 of 6020
ENGINE DIAGNOSIS (C24SE) 6-3
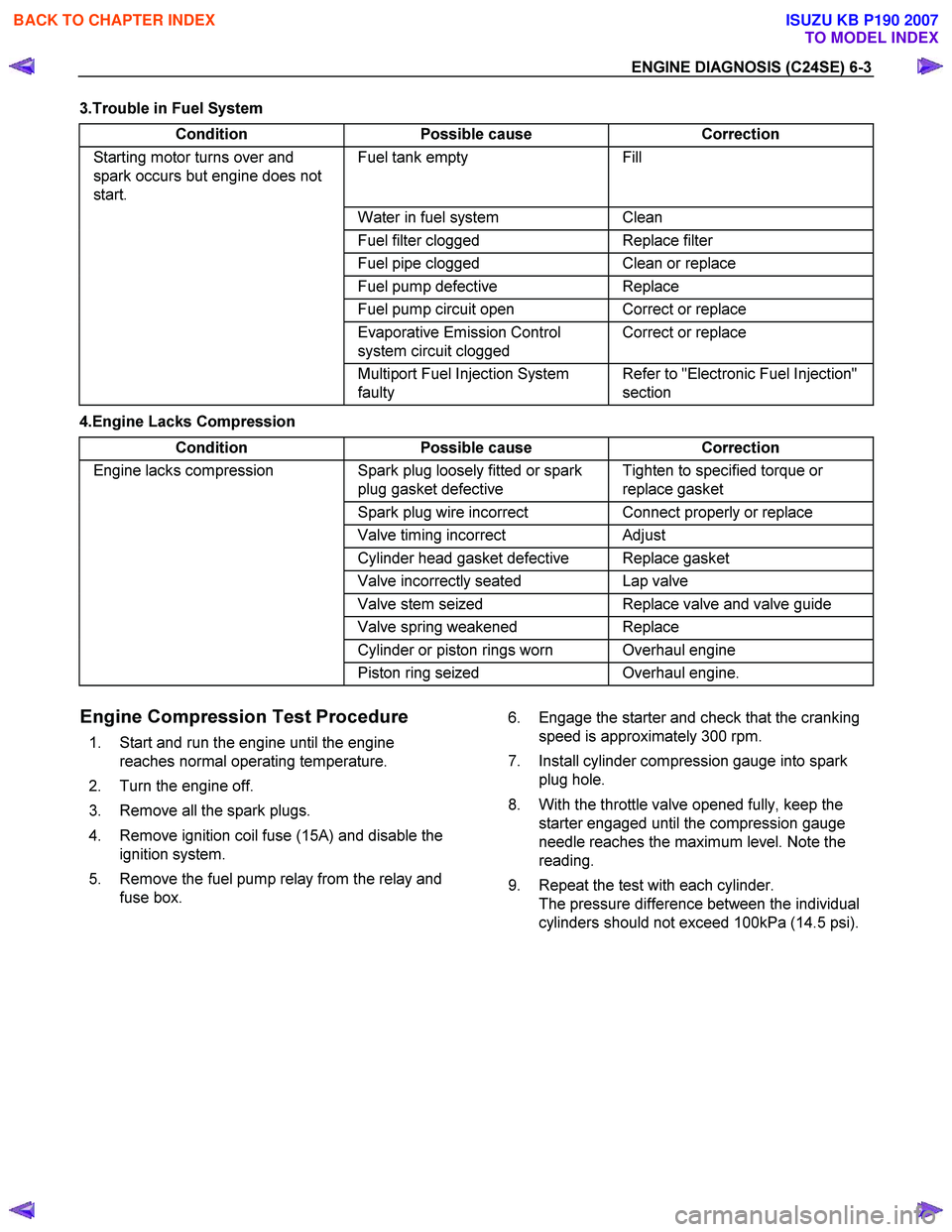
3.Trouble in Fuel System Condition Possible cause Correction
Starting motor turns over and
spark occurs but engine does not
start. Fuel tank empty Fill
Water in fuel system Clean
Fuel filter clogged Replace filter
Fuel pipe clogged Clean or replace
Fuel pump defective Replace
Fuel pump circuit open Correct or replace
Evaporative Emission Control
system circuit clogged Correct or replace
Multiport Fuel Injection System
faulty Refer to "Electronic Fuel Injection"
section
4.Engine Lacks Compression
Condition Possible cause Correction
Engine lacks compression Spark plug loosely fitted or spark
plug gasket defective Tighten to specified torque or
replace gasket
Spark plug wire incorrect Connect properly or replace
Valve timing incorrect Adjust
Cylinder head gasket defective Replace gasket
Valve incorrectly seated Lap valve
Valve stem seized Replace valve and valve guide
Valve spring weakened Replace
Cylinder or piston rings worn Overhaul engine
Piston ring seized Overhaul engine.
Engine Compression Test Procedure
1. Start and run the engine until the engine
reaches normal operating temperature.
2. Turn the engine off.
3. Remove all the spark plugs.
4. Remove ignition coil fuse (15A) and disable the ignition system.
5. Remove the fuel pump relay from the relay and fuse box. 6. Engage the starter and check that the cranking
speed is approximately 300 rpm.
7. Install cylinder compression gauge into spark plug hole.
8. With the throttle valve opened fully, keep the starter engaged until the compression gauge
needle reaches the maximum level. Note the
reading.
9. Repeat the test with each cylinder. The pressure difference between the individual
cylinders should not exceed 100kPa (14.5 psi).
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2004 of 6020
6-4 ENGINE DIAGNOSIS (C24SE)
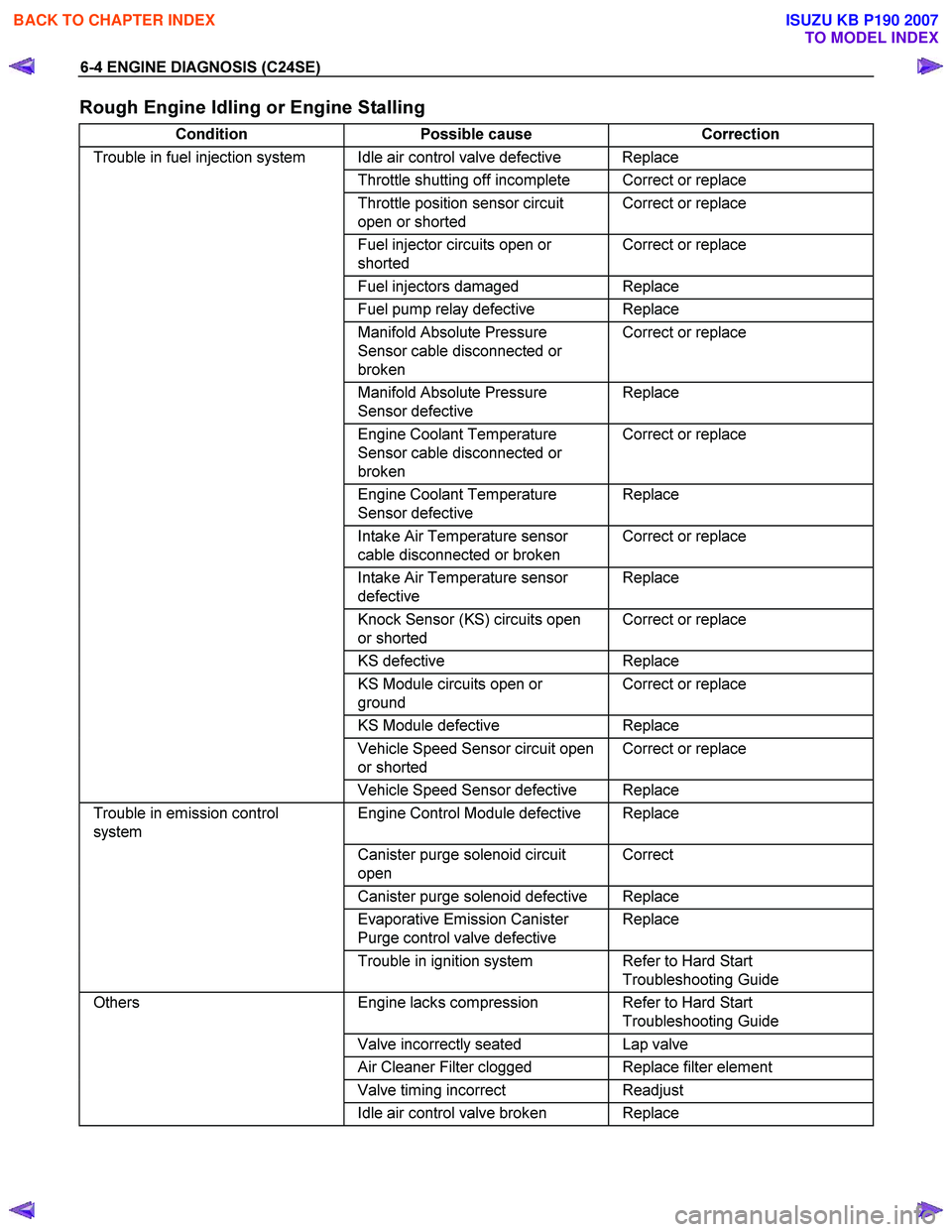
Rough Engine Idling or Engine Stalling
Condition Possible cause Correction
Trouble in fuel injection system Idle air control valve defective Replace
Throttle shutting off incomplete Correct or replace
Throttle position sensor circuit
open or shorted Correct or replace
Fuel injector circuits open or
shorted Correct or replace
Fuel injectors damaged Replace
Fuel pump relay defective Replace
Manifold Absolute Pressure
Sensor cable disconnected or
broken Correct or replace
Manifold Absolute Pressure
Sensor defective Replace
Engine Coolant Temperature
Sensor cable disconnected or
broken Correct or replace
Engine Coolant Temperature
Sensor defective Replace
Intake Air Temperature sensor
cable disconnected or broken Correct or replace
Intake Air Temperature sensor
defective Replace
Knock Sensor (KS) circuits open
or shorted Correct or replace
KS
defective Replace
KS Module circuits open or
ground Correct or replace
KS Module defective Replace
Vehicle Speed Sensor circuit open
or shorted Correct or replace
Vehicle Speed Sensor defective Replace
Trouble in emission control
system Engine Control Module defective Replace
Canister purge solenoid circuit
open Correct
Canister purge solenoid defective Replace
Evaporative Emission Canister
Purge control valve defective Replace
Trouble in ignition system Refer to Hard Start
Troubleshooting Guide
Others Engine lacks compression Refer to Hard Start
Troubleshooting Guide
Valve incorrectly seated Lap valve
Air Cleaner Filter clogged Replace filter element
Valve timing incorrect Readjust
Idle air control valve broken Replace
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2011 of 6020
ENGINE DIAGNOSIS (C24SE) 6-11
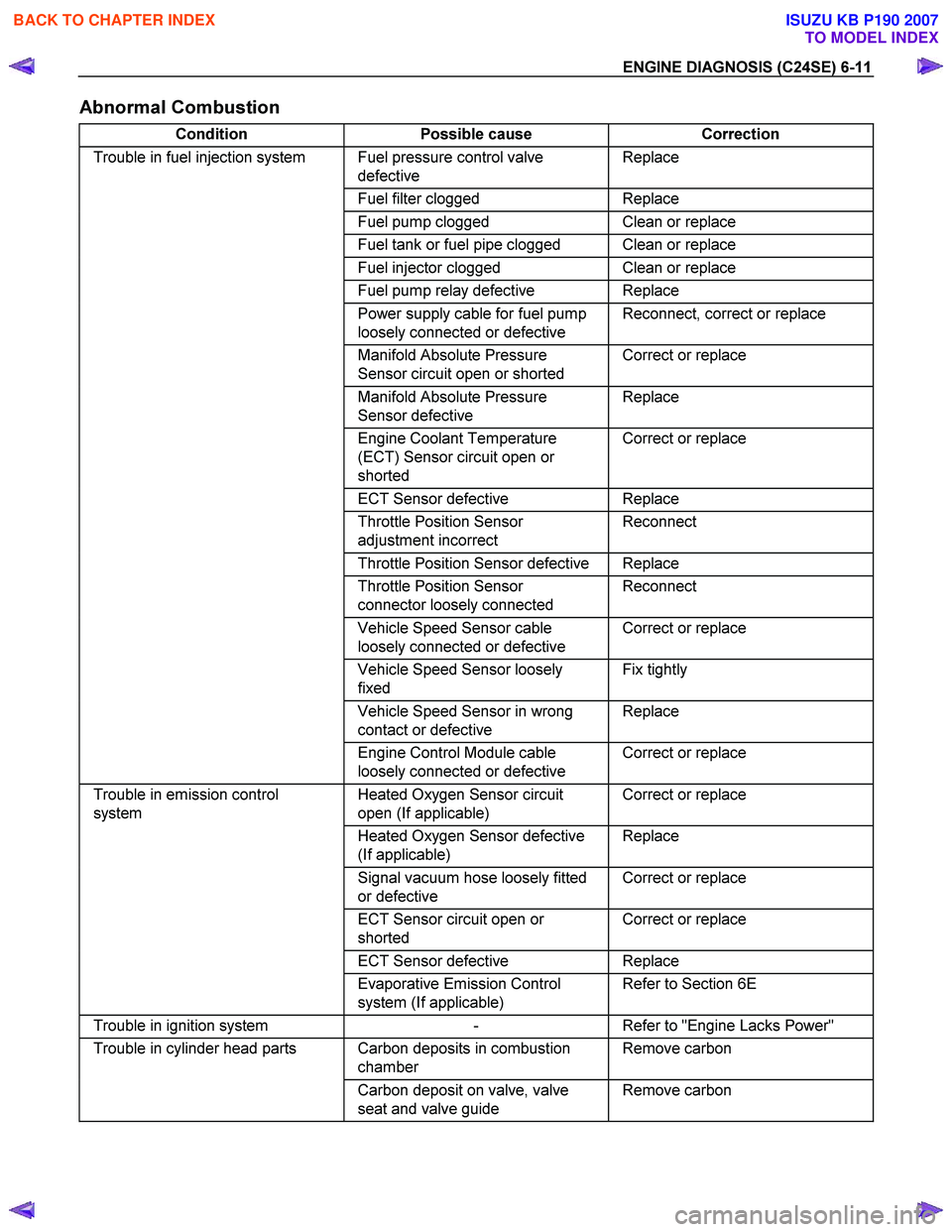
Abnormal Combustion
Condition Possible cause Correction
Trouble in fuel injection system Fuel pressure control valve
defective Replace
Fuel filter clogged Replace
Fuel pump clogged Clean or replace
Fuel tank or fuel pipe clogged Clean or replace
Fuel injector clogged Clean or replace
Fuel pump relay defective Replace
Power supply cable for fuel pump
loosely connected or defective Reconnect, correct or replace
Manifold Absolute Pressure
Sensor circuit open or shorted Correct or replace
Manifold Absolute Pressure
Sensor defective Replace
Engine Coolant Temperature
(ECT) Sensor circuit open or
shorted Correct or replace
ECT Sensor defective Replace
Throttle Position Sensor
adjustment incorrect Reconnect
Throttle Position Sensor defective Replace
Throttle Position Sensor
connector loosely connected Reconnect
Vehicle Speed Sensor cable
loosely connected or defective Correct or replace
Vehicle Speed Sensor loosely
fixed Fix tightly
Vehicle Speed Sensor in wrong
contact or defective Replace
Engine Control Module cable
loosely connected or defective Correct or replace
Trouble in emission control
system Heated Oxygen Sensor circuit
open (If applicable) Correct or replace
Heated Oxygen Sensor defective
(If applicable) Replace
Signal vacuum hose loosely fitted
or defective Correct or replace
ECT Sensor circuit open or
shorted Correct or replace
ECT Sensor defective Replace
Evaporative Emission Control
system (If applicable) Refer to Section 6E
Trouble in ignition system
- Refer to "Engine Lacks Power"
Trouble in cylinder head parts Carbon deposits in combustion
chamber Remove carbon
Carbon deposit on valve, valve
seat and valve guide Remove carbon
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2119 of 6020
ENGINE FUEL (C24SE) 6C-1
SECTION 6C
ENGINE FUEL (C24SE)
TABLE OF CONTENTS
General Description ............................................. 6C-2
Service Precaution ............................................... 6C-3
Fuel Metering ......................................................... 6C-4
Fuel Filter ................................................................ 6C-5
Removal ............................................................... 6C-5
Inspection ............................................................ 6C-6
Installation ........................................................... 6C-6
Inspection ............................................................ 6C-6
In-Tank Fuel Filter ............................................. 6C-6
Fuel Pump Flow Test ........................................ 6C-7
Fuel Pump ............................................................... 6C-8
Fuel Pump and Associated Parts .................. 6C-8
Removal ............................................................... 6C-8
Installation ........................................................... 6C-9
Fuel Tube / Quick - Connector Fittings ........... 6C-10
Precautions ......................................................... 6C-10
Cautions During Work ...................................... 6C-10
Removal .............................................................. 6C-10
Reuse of Quick-Connector ............................. 6C-11
Assembling Advice ........................................... 6C-11
Fuel Pump Relay ................................................... 6C-12
General Description ......................................... 6C-12
Fuel Tank ................................................................ 6C-13
Fuel Tank and Associated Parts ................... 6C-13
Removal .............................................................. 6C-14
Installation .......................................................... 6C-14
Filler Neck .............................................................. 6C-15
Removal .............................................................. 6C-15
Installation .......................................................... 6C-15
Fuel Gauge Unit .................................................... 6C-15
Removal and Installation ................................ 6C-15
Fuel Filler Cap ....................................................... 6C-16
General Description ......................................... 6C-16
Inspection ........................................................... 6C-16
Main Data and Specifications ............................ 6C-17
Special Tool ........................................................ 6C-18
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2125 of 6020

ENGINE FUEL (C24SE) 6C-7
Fuel Pump Flow Test
If reduction of fuel supply is suspected, perform the
following checks.
1. Make sure that there is fuel in the tank.
2. W ith the engine running, check the fuel feed pipe and hose from fuel tank to injector for evidence o
f
leakage. Retighten, if pipe or hose connection is
loose. Also, check pipes and hoses for squashing
or clogging.
3. Insert the hose from fuel feed pipe into a clean container, and check for fuel pump flow rate.
4. Connect the pump relay terminals (2) with a jumper wire (1) as shown and start the fuel pump
to measure delivery.
RTW 36CSH000201
CAUTION: Never generate sparks when connecting
a jumper wire.
Delivery Delivery
15 seconds 0.38 liters minimum
If the measure value is out of standard, conduct the
pressure test.
Pressure test
For the pressure test to the fuel system, see Section 6E
“Fuel Control System".
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2130 of 6020

6C-12 ENGINE FUEL (C24SE)
Fuel Pump Relay
General Description
In order to control the fuel pump and sender assembly
(FPAS) operation, the FPAS relay is provided. W hen
the starter switch is turned to “ON" position, the FPAS
relay operates the FPAS for 2 seconds.
W hen it is turned to “START" position, the Engine
Control Module receives the reference pulse from the
Ignition Control Module and it operates the relay, again
causing the FPAS to feed fuel.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2150 of 6020
6D3-2 STARTING AND CHARGING SYSTEM
Starting System
General Description
Cranking Circuit
The cranking system consists of a battery, starter, starter
switch, starter relay, etc. These main components are
connected.
Starter
The cranking system employs a magnetic type reduction
starter in which the motor shaft is also used as a pinion shaft.
W hen the starter switch is turned on, the contacts of magnetic
switch are closed, and the armature rotates. At the same time,
the plunger is attracted, and the pinion is pushed forward by
the shift lever to mesh with the ring gear.
Then, the ring gear runs to start the engine. W hen the engine
starts and the starter switch is turned off, the plunger returns,
the pinion is disengaged from the ring gear, and the armature
stops rotation. W hen the engine speed is higher than the
pinion, the pinion idles, so that the armature is not driven.
Service Precaution
CAUTION:
Always use the correct fastener in the proper location.
When you replace a fastener, use ONLY the exact part
number for that application. ISUZU will call out those
fasteners that require a replacement after removal. ISUZU
will also call out the fasteners that require thread lockers
or thread sealant. UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED, do
not use supplemental coatings (Paints, greases, or other
corrosion inhibitors) on threaded fasteners or fastener
joint interfaces. Generally, such coatings adversely affect
the fastener torque and the joint clamping force, and may
damage the fastener. When you install fasteners, use the
correct tightening sequence and specifications. Following
these instructions can help you avoid damage to parts
and systems.
Diagnosis
Condition Possible cause Correction
Starter does not run Charging failure Repair charging system
Battery Failure Replace Battery
Terminal connection failure Repair or replace terminal connector
and/or wiring harness
Starter switch failure Repair or replace starter switch
Starter failure Repair or replace starter
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007