2007 ISUZU KB P190 check transmission fluid
[x] Cancel search: check transmission fluidPage 4402 of 6020
7A2-118 TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E)
J1: Transmission Fluid Leaks from Breather
J2: Transmission Fluid Leaks Between Engine and Converter Housing
J3: Transmission Fluid Leaks Between Converter Housing and Transmission Case
J4: Transmission Fluid Leaks Between Transmission Case and Extension Housing
J3: Transmission Fluid Leaks from Oil Pan
J3: Transmission Fluid Leaks from Manual Shaft Oil Seal
J3: Transmission Fluid Leaks from Oil Cooler Pipe Joint
Z1: Transmission Overheat
Transmission Fluid Checks Inspect the transmission fluid for the following conditions. If the transmission
fluid is extremely blacked, contaminated or smells burnt, slipping of clutch is
suspected.
• Low quantity
• Contamination
• Smell
Control Valve Body Checks Inspect the valve body for the following conditions.
• Faulty operation
• Sticking spool valve
• Sticking TCC solenoid valve. Perform function check. Refer to On- Vehicle Service section.
• Clogged hydraulic circuit
Sensor Checks Inspect the TFT sensor. Use the Temperature vs. Resistance table to test
the TFT sensor at various temperature levels to evaluate the possibility of a
skewed sensor.
Checks
Action
Checks Action
Definition:
Transmission fluid leaks from breather.
Diagnosis Hints Transmission fluid quantity is excessively high.
Checks Action
Definition:
Transmission fluid leaks between engine and converter housing.
Transmission fluid leaks between converter housing and transmission case.
Transmission fluid leaks between transmission case and extension housing.
Transmission fluid leaks from oil pan.
Transmission fluid leaks from manual shaft oil seal.
Transmission fluid leaks from oil cooler pipe joint.
Diagnosis Hints Faulty oil seal or contact surface is suspected.
Checks Action
Definition:
Smells burnt or smoke from transmission.
Diagnosis Hints • Transmission fluid quantity is excessively high.
• Slipping of the clutch is suspected. Gear ratio error DTC might be set.
• Clogged oil cooler.
• Faulty operation of oil pump.
• Faulty torque converter clutch (TCC) piston.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4403 of 6020
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E) 7A2-119
Z2: Mode Lamp (Power Drive or 3rd Start) Does Not Turn On
Z3: Mode Lamp (Power Drive or 3rd Start) Does Not Turn Off
Z4: A/T Oil Temperature Lamp Turns On
Z5: Selector Lever Feeling is Faulty
Z6: Poor Fuel Consumption
Checks Action
Definition:
Mode lamp on the instrument panel (IP) cluster does not turn ON even though the switch is ON.
Diagnosis Hints • Faulty mode switch circuit.
• Faulty mode switch.
• Faulty lamp control circuit.
• Faulty IP cluster.
Checks Action
Definition:
Mode lamp on the instrument panel cluster does not turn OFF even though the switch is OFF.
Diagnosis Hints • Faulty mode switch circuit.
• Faulty mode switch.
• Faulty lamp control circuit.
• Faulty IP cluster.
Checks Action
Definition:
A/T oil temperature lamp turns On sometimes.
Diagnosis Hints • If the fluid temperature increases to 135°C (275 °F), the TCM illuminates
A/T Oil Temp lamp on the instrument panel cluster. When the fluid
temperature deceases below 125 °C (257 °F), the lamp goes off.
• When the vehicle is stuck in the mud or continues to accelerate under overload, transmission fluid temperature increases and lamp may be
turned On.
• If the lamp is On under usual conditions, following causes are suspected. - Transmission fluid level has increased for some fault. Refer to category No. “Z1: Transmission Overheat”.
- Skewed transmission fluid temperature (TFT) sensor.
Checks Action
Definition:
Selector lever feeling is faulty.
Diagnosis Hints • Inspect the selector lever cable for misadjusting or disordering.
• Faulty manual plate.
Checks Action
Definition:
Poor fuel consumption.
Diagnosis Hints The same causes as in category No. “C1 - C8: Engine Race Up (Slipping)” are
suspected.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4404 of 6020
7A2-120 TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E)
Z7: Shift Indicator is Faulty
Z8: Transmission Fluid is Splashed During Running
Z9: Abnormal Smell
Z10: Transmission Fluid Quantity is Low or High
Z11: Abnormal Transmission Fluid Pressure
Checks Action
Definition:
Shift indicator does not change even though the selector lever is moved.
Diagnosis Hints Inspect the transmission range switch and selector lever cable for
misadjusting or disordering. Refer to On-Vehicle Service section.
Checks Action
Definition:
Transmission Fluid is splashed during running.
Diagnosis Hints Transmission fluid quantity is excessively high.
Checks Action
Definition:
Abnormal smell.
Diagnosis Hints A trouble in the transmission main unit.
Checks Action
Definition:
Transmission fluid quantity is low or high.
Diagnosis Hints • If the fluid level is high, level check might be performed at low
temperature.
• If the fluid level is low, fluid leak is suspected.
Checks Action
Definition:
Transmission fluid pressure (TFP) is low or high.
Diagnosis Hints • Faulty pressure control (PC) solenoid valve or hydraulic circuits.
• If pressure is low, faulty oil pump is suspected.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4405 of 6020
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E) 7A2-121
Test Instructions
Line Pressure Test
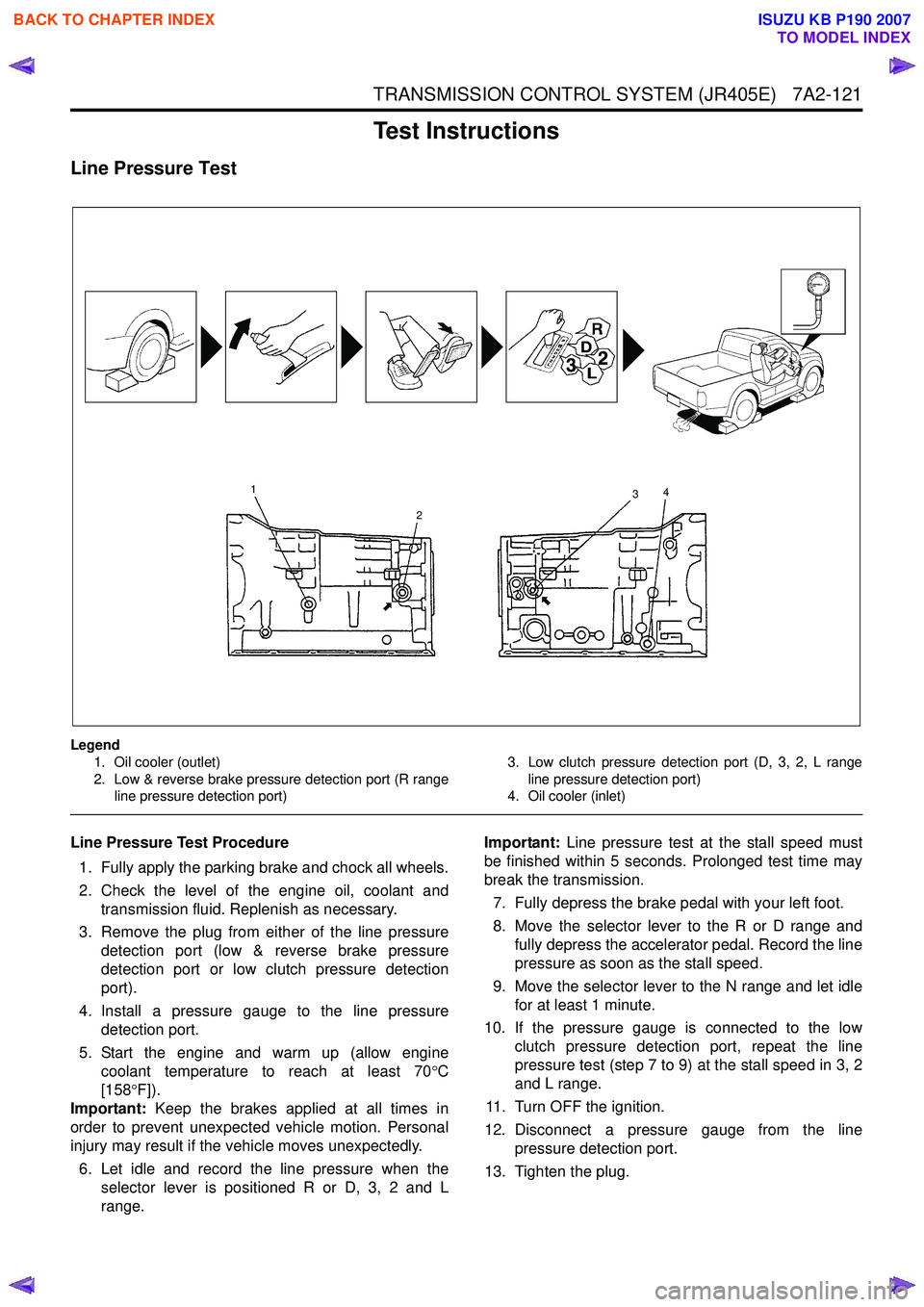
Legend1. Oil cooler (outlet)
2. Low & reverse brake pressure detection port (R range line pressure detection port) 3. Low clutch pressure detection port (D, 3, 2, L range
line pressure detection port)
4. Oil cooler (inlet)
Line Pressure Test Procedure
1. Fully apply the parking brake and chock all wheels.
2. Check the level of the engine oil, coolant and transmission fluid. Replenish as necessary.
3. Remove the plug from either of the line pressure detection port (low & reverse brake pressure
detection port or low clutch pressure detection
port).
4. Install a pressure gauge to the line pressure detection port.
5. Start the engine and warm up (allow engine coolant temperature to reach at least 70 °C
[158 °F]).
Important: Keep the brakes applied at all times in
order to prevent unexpected vehicle motion. Personal
injury may result if the vehicle moves unexpectedly.
6. Let idle and record the line pressure when the selector lever is positioned R or D, 3, 2 and L
range. Important:
Line pressure test at the stall speed must
be finished within 5 seconds. Prolonged test time may
break the transmission.
7. Fully depress the brake pedal with your left foot.
8. Move the selector lever to the R or D range and fully depress the accelerator pedal. Record the line
pressure as soon as the stall speed.
9. Move the selector lever to the N range and let idle for at least 1 minute.
10. If the pressure gauge is connected to the low clutch pressure detection port, repeat the line
pressure test (step 7 to 9) at the stall speed in 3, 2
and L range.
11. Turn OFF the ignition.
12. Disconnect a pressure gauge from the line pressure detection port.
13. Tighten the plug.
1
2 3
4
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4407 of 6020
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E) 7A2-123
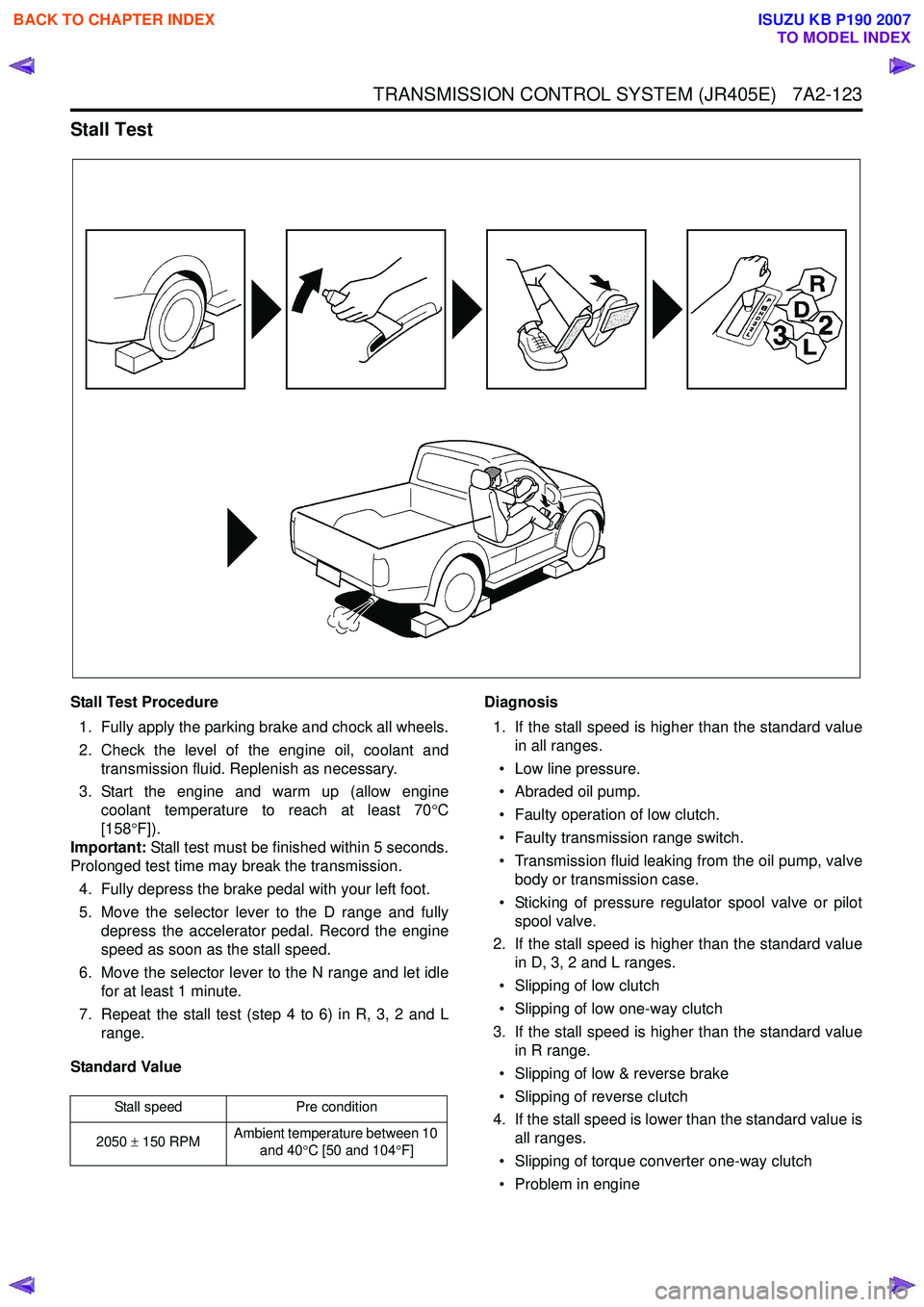
Stall Test
Stall Test Procedure1. Fully apply the parking brake and chock all wheels.
2. Check the level of the engine oil, coolant and transmission fluid. Replenish as necessary.
3. Start the engine and warm up (allow engine coolant temperature to reach at least 70 °C
[158 °F]).
Important: Stall test must be finished within 5 seconds.
Prolonged test time may break the transmission.
4. Fully depress the brake pedal with your left foot.
5. Move the selector lever to the D range and fully depress the accelerator pedal. Record the engine
speed as soon as the stall speed.
6. Move the selector lever to the N range and let idle for at least 1 minute.
7. Repeat the stall test (step 4 to 6) in R, 3, 2 and L range.
Standard Value Diagnosis
1. If the stall speed is higher than the standard value in all ranges.
• Low line pressure.
• Abraded oil pump.
• Faulty operation of low clutch.
• Faulty transmission range switch.
• Transmission fluid leaking from the oil pump, valve body or transmission case.
• Sticking of pressure regulator spool valve or pilot spool valve.
2. If the stall speed is higher than the standard value in D, 3, 2 and L ranges.
• Slipping of low clutch
• Slipping of low one-way clutch
3. If the stall speed is higher than the standard value in R range.
• Slipping of low & reverse brake
• Slipping of reverse clutch
4. If the stall speed is lower than the standard value is all ranges.
• Slipping of torque converter one-way clutch
• Problem in engine
Stall speed Pre condition
2050 ± 150 RPM Ambient temperature between 10
and 40 °C [50 and 104 °F]
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4408 of 6020
7A2-124 TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E)
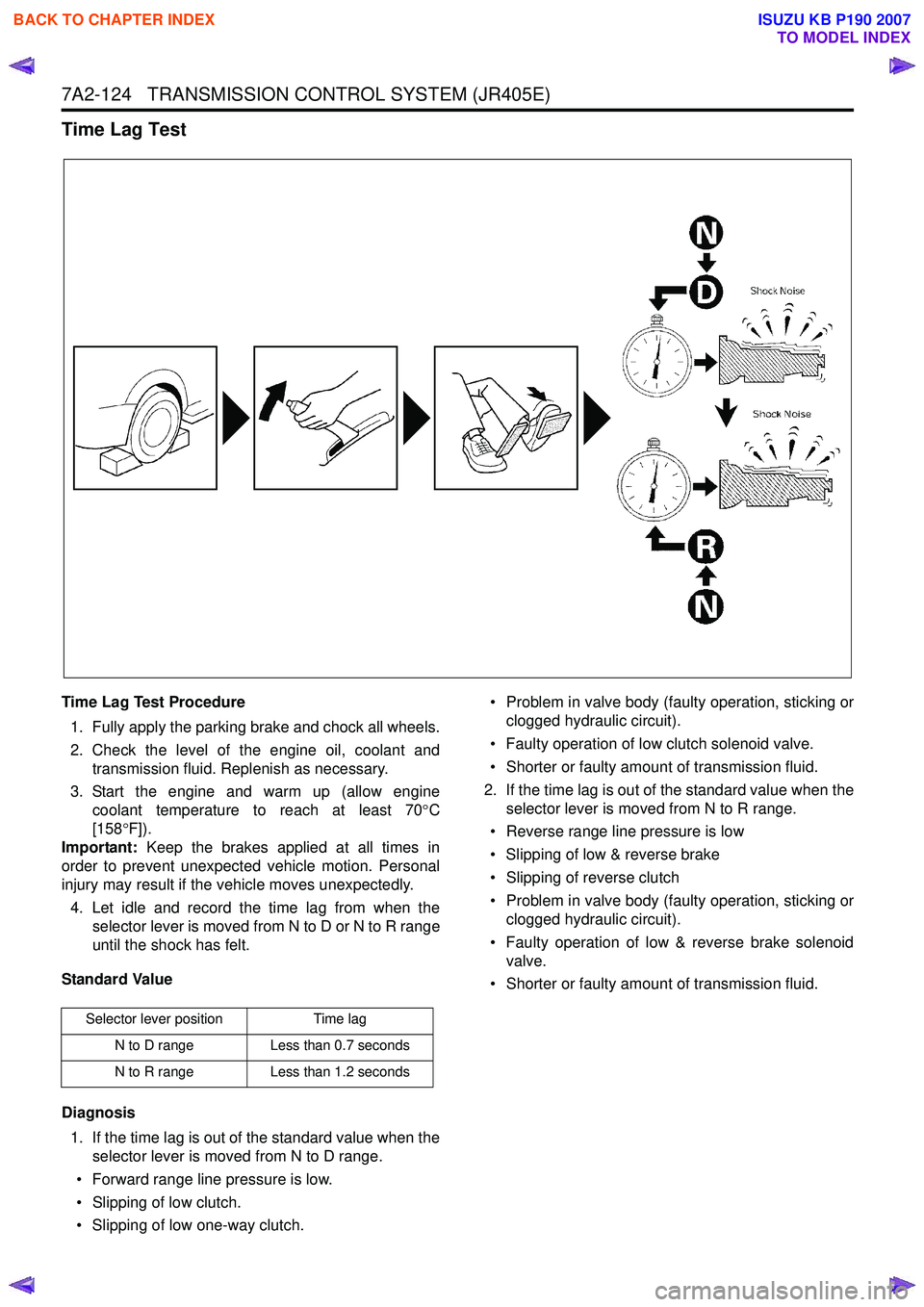
Time Lag Test
Time Lag Test Procedure1. Fully apply the parking brake and chock all wheels.
2. Check the level of the engine oil, coolant and transmission fluid. Replenish as necessary.
3. Start the engine and warm up (allow engine coolant temperature to reach at least 70 °C
[158 °F]).
Important: Keep the brakes applied at all times in
order to prevent unexpected vehicle motion. Personal
injury may result if the vehicle moves unexpectedly.
4. Let idle and record the time lag from when the selector lever is moved from N to D or N to R range
until the shock has felt.
Standard Value
Diagnosis 1. If the time lag is out of the standard value when the selector lever is moved from N to D range.
• Forward range line pressure is low.
• Slipping of low clutch.
• Slipping of low one-way clutch. • Problem in valve body (faulty operation, sticking or
clogged hydraulic circuit).
• Faulty operation of low clutch solenoid valve.
• Shorter or faulty amount of transmission fluid.
2. If the time lag is out of the standard value when the selector lever is moved from N to R range.
• Reverse range line pressure is low
• Slipping of low & reverse brake
• Slipping of reverse clutch
• Problem in valve body (faulty operation, sticking or clogged hydraulic circuit).
• Faulty operation of low & reverse brake solenoid valve.
• Shorter or faulty amount of transmission fluid.
Selector lever position Time lag
N to D range Less than 0.7 seconds
N to R range Less than 1.2 seconds
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4409 of 6020
TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E) 7A2-125
Road Test
Road Test Procedure
*1: Shifting at high vehicle speed, the transmission may
hold the gear position until vehicle speed gets down to
prevent engine overruning.
Notice: Perform this test at the normal transmission
fluid temperature between 50 to 80 °C (122 to 176 °F).
Drive the vehicle on level ground so as not to change to
up slope mode and down slope mode.
1. D range road test in normal and power drive mode. • Select into the D range and hold the accelerator pedal constant at the 50% and 100% accelerator
pedal position.
• 1 to 2, 2 to 3, 3 to 4 upshift and lock up should take place, and shift points should match those shown
in the shift speed chart.
• Also check to see that downshift is made from 4 to 3, 3 to 2 and 2 to 1 point is within the limits shown
in the shift speed chart.
2. 3 range road test in normal and power drive mode. • Select into the 3 range and hold the accelerator pedal constant at the 50% and 100% accelerator
pedal position.
• 1 to 2, 2 to 3 upshift and lock up should take place, and shift points should match those shown in the
shift speed chart.
• While running in the 3 range, does not upshift from 3 to 4.
3. 2 range road test in normal mode. • Select into the 2 range and hold the accelerator
pedal constant at the 50% and 100% accelerator
pedal position.
• 1 to 2 upshift should take place, and shift points should match those shown in the shift speed chart.
• While running in the 2 range, does not upshift from 2 to 3 or 3 to 4, and lock-up does not operate.
4. L range road test in normal mode.
• While running in the L range, does not upshift from 1 to 2, 2 to 3 or 3 to 4, and lock-up does not
operate.
5. R range road test. • Select into the R range and check for slipping.
6. P range road test. • Stop the vehicle on a grade and release the park brake after selecting into the P range. Then check
to see that the parking lock pawl holds the vehicle
in place.
Diagnosis 1. If there is no 1 to 2 upshift.• Faulty operation of 2-4 brake
• Faulty operation of 2-4 brake hydraulic circuits
• Sticking of 2-4 brake solenoid valve
• Refer to symptom diagnosis No. D1: Faulty Gear Shifting or DTC P0731 - P0734 Incorrect Gear
Ratio diagnosis.
2. If there is no 2 to 3 upshift.
• Faulty operation of high clutch
• Faulty operation of high clutch hydraulic circuits
• Sticking of high clutch solenoid valve
• Refer to symptom diagnosis No. D1: Faulty Gear Shifting or DTC P0731 - P0734 Incorrect Gear
Ratio diagnosis.
3. If there is no 3 to 4 upshift.
• Faulty operation of 2-4 brake
• Faulty operation of 2-4 brake hydraulic circuits
• Sticking of 2-4 brake solenoid valve
• Refer to symptom diagnosis No. D1: Faulty Gear Shifting or DTC P0731 - P0734 Incorrect Gear
Ratio diagnosis.
4. If there is no lock up in 2nd, 3rd and 4th. • Faulty operation of torque converter clutch (TCC) piston
• Faulty operation of lock up hydraulic circuit
• Sticking of TCC solenoid valve
• Refer to symptom diagnosis No. I1: No Lock-up
5. If there is no reverse. • Faulty operation of reverse clutch
• Faulty operation of reverse clutch hydraulic circuits
• Faulty operation of low & reverse brake hydraulic circuits
Selector lever
position GearshiftSelected gear
position
P
R
N
D
3
2
L 1st
2nd 3rd4th1st
2nd 3rd
4th(*1) 1st
2nd
3rd(*1) 4th(*1) 1st
2nd(*1) 3rd(*1)4th(*1)
Reverse
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 4428 of 6020
7A2-144 TRANSMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM (JR405E)
The JR405E automatic transmission is electrically
controlled by a transmission control module (TCM).
There are four forward speeds and one reverse speed.
This JR405E automatic transmission employs a clutch
pressure direct control system (Direct Electronic Shift
Control: DESC) using duty cycle type solenoid valves,
which ensure high shift quality. This transmission also
has a learning function and constantly checks the time
of each clutch and brake required for the shift in order
to match this time with the target value for the optimum
shift. The TCM will automatically select the most
appropriate shift points and lock-up points depending
on the accelerator pedal opening, the vehicle speed
and the vehicle load. If any trouble arises in the speed
sensor, solenoid valve, etc., the fail-safe control
function is activated to keep the running performance.
The JR405E automatic transmission consists of the
torque converter, oil pump, input shaft, out put shaft,
planetary gears and valve body. The gear train consists
of two planetary gear sets and three multiple plate
clutches in combination with two multiple plate brakes
and a one-way clutch.
Transmission Component Description
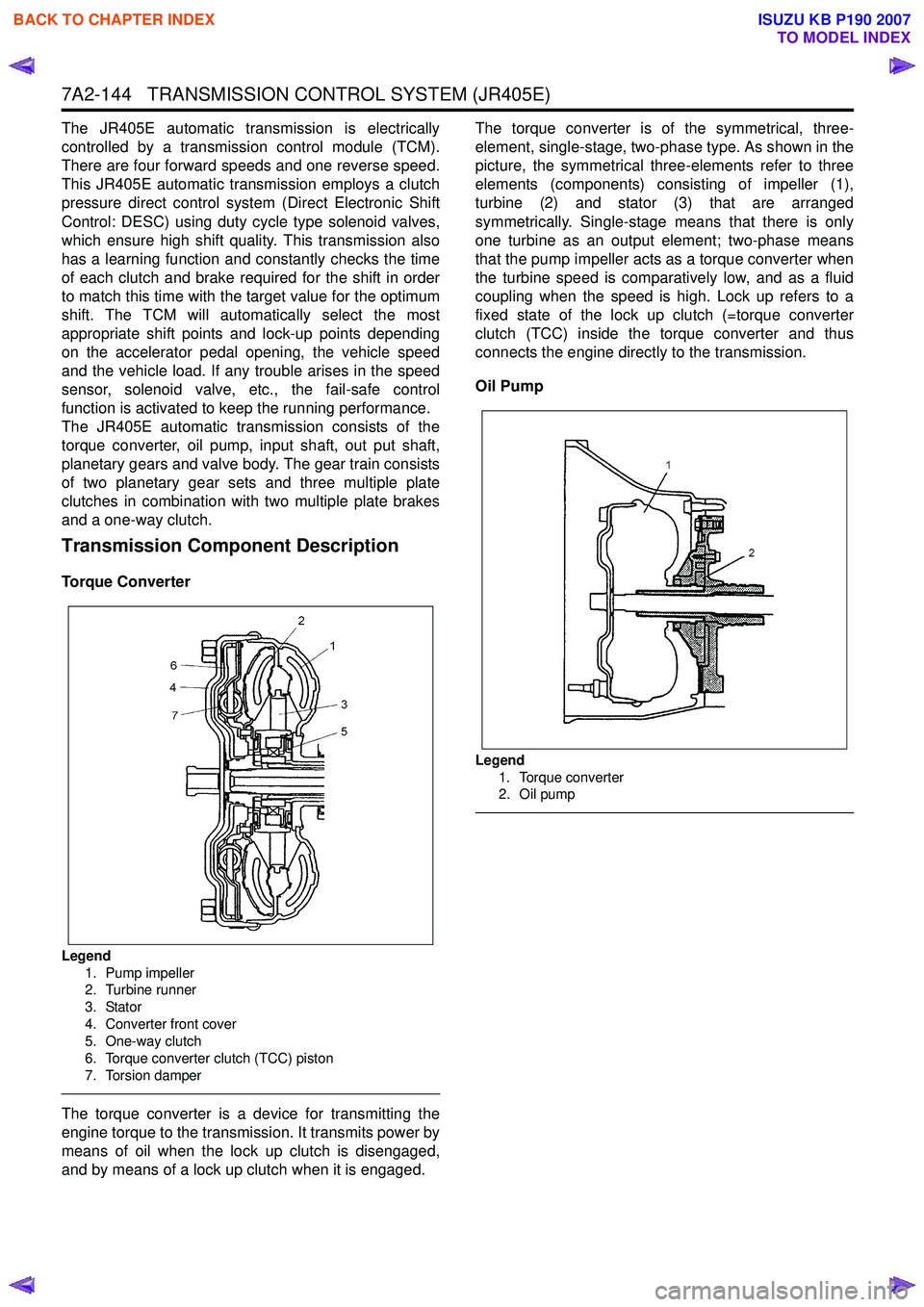
Torque Converter
Legend
1. Pump impeller
2. Turbine runner
3. Stator
4. Converter front cover
5. One-way clutch
6. Torque converter clutch (TCC) piston
7. Torsion damper
The torque converter is a device for transmitting the
engine torque to the transmission. It transmits power by
means of oil when the lock up clutch is disengaged,
and by means of a lock up clutch when it is engaged. The torque converter is of the symmetrical, three-
element, single-stage, two-phase type. As shown in the
picture, the symmetrical three-elements refer to three
elements (components) consisting of impeller (1),
turbine (2) and stator (3) that are arranged
symmetrically. Single-stage means that there is only
one turbine as an output element; two-phase means
that the pump impeller acts as a torque converter when
the turbine speed is comparatively low, and as a fluid
coupling when the speed is high. Lock up refers to a
fixed state of the lock up clutch (=torque converter
clutch (TCC) inside the torque converter and thus
connects the engine directly to the transmission.
Oil Pump
Legend 1. Torque converter
2. Oil pump
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007