2007 ISUZU KB P190 check engine light
[x] Cancel search: check engine lightPage 3448 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–170
Step Action Yes
No
7 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs? Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table in this Section System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
7.46 DTC P2096 or P2098
DTC Descriptors
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P2096 Post Catalyst O2 Sensor Fuel Trim Below Lower Limit (Bank 1)
• DTC P2098 Post Catalyst O2 Sensor Fuel Trim Below Lower Limit (Bank 2)
Circuit Description
The wide band heated oxygen sensor 1 measures the amount of oxygen in the exhaust system and provides more
information than the switching style HO2S2. The wide band sensor consists of an oxygen sensing cell, an oxygen
pumping cell, and a heater. The exhaust gas sample passes through a diffusion gap between the sensing cell and the
pumping cell. The engine control module (ECM) supplies a voltage to the HO2S and uses this voltage as a reference to
the amount of oxygen in the exhaust system. An electronic circuit within the ECM controls the pump current through the
oxygen pumping cell, maintaining a constant voltage in the oxygen sensing cell. The ECM monitors the voltage variation
in the sensing cell and attempts to keep the voltage constant by increasing or decreasing the amount of current flow, or
oxygen ion flow, to the pumping cell. By measuring the amount of current required to maintain the voltage in the sensing
cell, the ECM can determine the concentration of oxygen in the exhaust. The HO2S voltage is displayed as a lambda
value. A lambda value of 1 is equal to a stoichiometric air fuel ratio of 14.7:1. Under normal operating conditions, the
lambda value will remain around 1. W hen the fuel system is lean, the oxygen level will be high and the lambda signal
will be high or more than 1. W hen the fuel system is rich, the oxygen level will be low, and the lambda signal will be low
or less than 1. The ECM uses this information to maintain the correct air / fuel ratio.
Fuel trim biasing is used by the ECM to keep the post catalyst HO2S voltage within a range of 580 – 665 mV as
possible. This allows optimal catalyst efficiency under light load conditions, such as at idle or a steady cruise. The ECM
constantly monitors how lean or rich the fuel trim bias is commanded. If the ECM detects that the fuel trim bias is
commanded lean for more than a calibrated amount, DTC P2096 or P2098 sets.
Conditions for Running the DTC
• Before the ECM can report DTC P2096 or P2098 failed, DTCs P0030, P0031, P0032, P0041, P0050, P0051,
P0052, P0101, P0131, P0132, P0135, P0137, P0138, P0140, P0141, P0151, P0152, P0155, P0157, P0158,
P0160, P0161, P2231, P2234, P2237, P2240, P2243, P2247, P2251, P2254, P2270, P2271, P2273, P2626, and
P2629 must run and pass.
• The engine is operating for more than 2 seconds.
• The post catalyst fuel trim control is enabled.
• The front and rear HO2S are in Closed Loop.
• DTCs P2096and P2098 run continuously once the above conditions are met for more than 40 seconds.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
The post catalyst fuel trim correction factor is biased lean by more than 3 percent of the HO2S lambda value for more
than 4 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
• The ECM activates the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL) on the second consecutive ignition cycle that the
diagnostic runs and fails.
• The ECM records the operating conditions at the time the diagnostic fails. The first time the diagnostic fails, the
control module stores this information in the Failure Records. If the diagnostic reports a failure on the second
consecutive ignition cycle, the control module records the operating conditions at the time of the failure. The
control module writes the operating conditions to the Freeze Frame and updates the Failure Records.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3586 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations Page 6C1-3–62
6 Special Tools
Tool Number Illustration Description Tool Classification
7000086i
Tech 2 scan tool
Used for diagnosis of vehicle electrical
systems.
Previously released. Mandatory
3588
Digital Multimeter
Previously released as j 39200, 3545
GM. Available
J 35616
Connector Test Adaptor Kit
Used when carrying out electrical
diagnostic circuit checks.
Previously released. Desirable
J 34142-a
Un-powered Test Lamp
Previously released as CT-40-C and
also commercially available.
Must have a current draw less than
0.3 A. Mandatory
J 34730-2C
Injector Test Light
Used to check for power and the
control circuit of the fuel injector, for
proper operation.
Also previously released as
ST- 8329 Mandatory
J 39021 Fuel Injector Coil / Balance Tester
Used in conjunction with a DMM for
testing the fuel injector coil windings
and for injector balance testing.
Previously released Mandatory
J 44602 Injector Test Adapter
Mandatory
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3597 of 6020

Charging System – V6 Page 6D1-1-10
3 Minor Service Operations
3.1 Safety Precautions
Observe the following precautions. Failure to observe these precautions will result in serious damage to the generator.
• Only use the generator and voltage regulator in a negative ground system.
• Always refer to 1.2 W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTES before disconnecting the battery.
• W hen installing a battery, fit the positive (+) cable to the battery before fitting the negative cable.
• W hen a slave battery is used for starting purposes, ensure that both batteries are connected in parallel. That is,
positive terminals connected and negative terminals connected.
• Only use jumper leads that have surge protection.
• Disconnect both battery cables when charging the battery. This isolates the generator from the battery and from
the external charging equipment.
• Do not operate the generator within an open circuit or without a battery in the circuit.
• Do not disconnect the battery while the generator is running.
• Do not attempt to polarise the generator.
• Do not connect generator connector E-4 pin 1 to 12 V (the battery or ignition circuits).
• Some battery powered timing lights can produce high transient voltages when connected or disconnected.
Only disconnect or connect timing lights when the engine is switched off.
Ensure the generator connector E-4 pin 1 has
a maximum sinking current of 50mA.
3.2 Maintenance
Regular Checks
Check the following at regular intervals:
• generator terminals – for corrosion and loose connections,
• wiring – for continuity and damaged insulation,
• mounting bolts – for tightness,
• drive belt – for alignment and wear, and
• drive pulley – for damage and warping.
NOTE
The drive-belt adjustment for the engine
ancillaries (i.e. generator and water pump) is
provided by a spring-loaded tensioner. Therefore,
the drive belt does not require manual
adjustment.
Lubrication
High tolerance bearings are used in this generator. If the bearings are removed during the generator disassembly, new
bearings must be installed to restore the generator to original specification. The ball bearings supporting the rotor shaft
are pre-lubricated and sealed. Do not attempt to lubricate these during servicing.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3651 of 6020
Battery Page 6D1-3–11
b W ait 15 seconds for the battery to recover.
8 If possible, set the selector to 50% of rapid discharge current (or three times the 20 hour discharge rate).
9 Apply the load test for 10 seconds and record the battery voltage. If one cell is faulty it will gas excessively or overheat. This indicates a faulty battery.
10 Recharge the battery if the voltage is at or below the minimum voltage specified by the HRD manufacturer (or 9.6 V).
11 Replace the battery if the voltage is below the minimum voltage specified by the HRD manufacturer (or below 9.6 V after the battery is charged and the test is repeated). Refer to 4.1 Battery.
12 Connect the battery positive terminal.
13 Connect the battery negative terminal.
Alternate Load Test
If HRD test equipment is not available, test the battery as follows:
1 Read and obey the safety precautions for working with batteries, refer to 2 Safety Precautions.
2 Ensure the state of the battery is at least 65% charged. Refer to 3.3 Hydrometer Test.
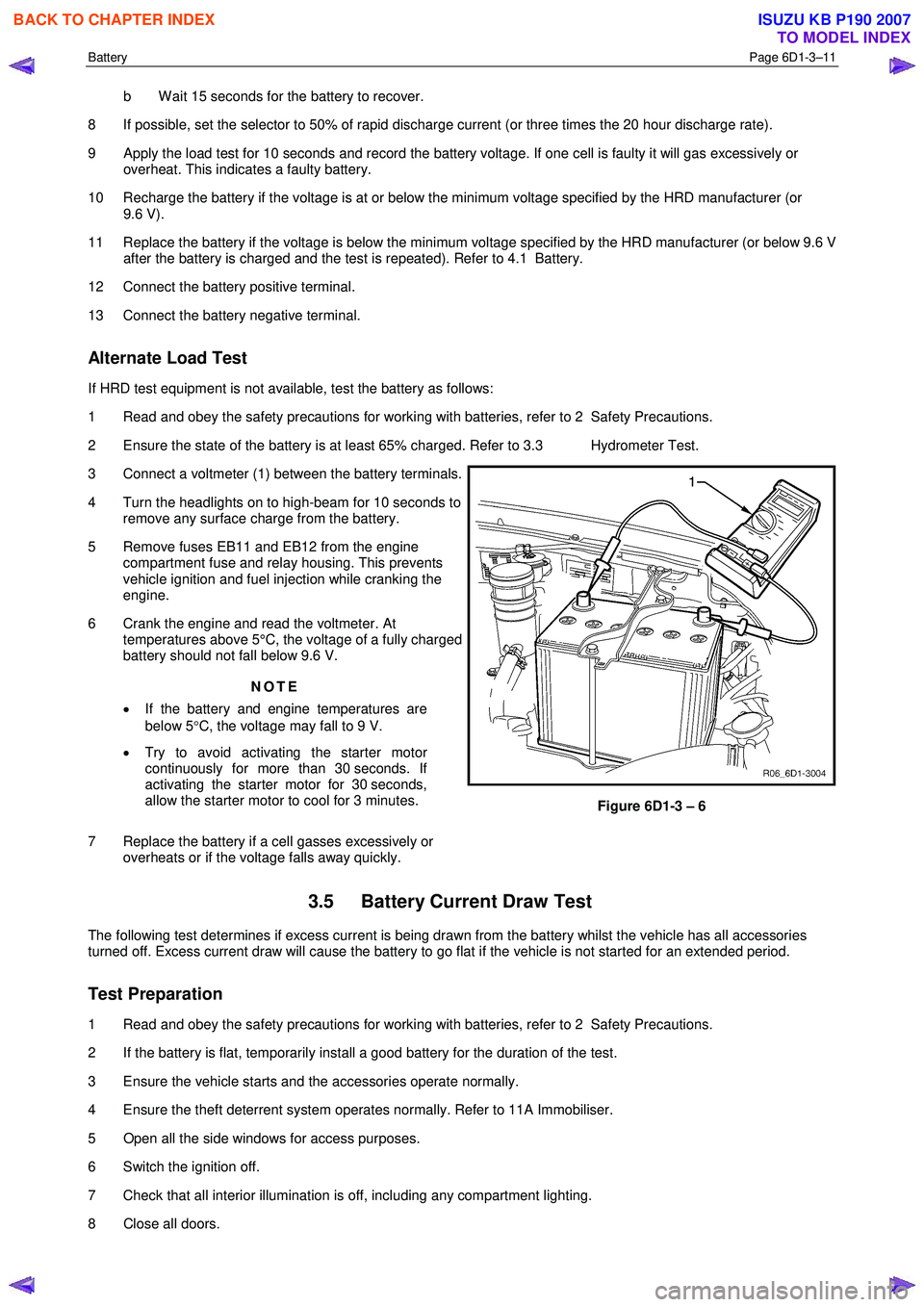
3 Connect a voltmeter (1) between the battery terminals.
4 Turn the headlights on to high-beam for 10 seconds to remove any surface charge from the battery.
5 Remove fuses EB11 and EB12 from the engine compartment fuse and relay housing. This prevents
vehicle ignition and fuel injection while cranking the
engine.
6 Crank the engine and read the voltmeter. At temperatures above 5°C, the voltage of a fully charged
battery should not fall below 9.6 V.
NOTE
• If the battery and engine temperatures are
below 5 °C, the voltage may fall to 9 V.
• Try to avoid activating the starter motor
continuously for more than 30 seconds. If
activating the starter motor for 30 seconds,
allow the starter motor to cool for 3 minutes.
7 Replace the battery if a cell gasses excessively or overheats or if the voltage falls away quickly.
Figure 6D1-3 – 6
3.5 Battery Current Draw Test
The following test determines if excess current is being drawn from the battery whilst the vehicle has all accessories
turned off. Excess current draw will cause the battery to go flat if the vehicle is not started for an extended period.
Test Preparation
1 Read and obey the safety precautions for working with batteries, refer to 2 Safety Precautions.
2 If the battery is flat, temporarily install a good battery for the duration of the test.
3 Ensure the vehicle starts and the accessories operate normally.
4 Ensure the theft deterrent system operates normally. Refer to 11A Immobiliser.
5 Open all the side windows for access purposes.
6 Switch the ignition off.
7 Check that all interior illumination is off, including any compartment lighting.
8 Close all doors.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3657 of 6020

Battery Page 6D1-3–17
4 Turn off the ignition, lights and all other electrical loads.
5 Check the battery filler caps on both batteries are tight.
6 Place a wet cloth over the battery filler caps of each battery.
7 Attach one end of the red jumper cable to the positive terminal of the booster battery.
8 Attach the other end of the same cable to the positive terminal of the discharged battery.
9 Attach one end of the black jumper cable to the negative terminal of the booster battery.
10 Attach the other end to a solid stationary, metallic point on the engine of the disabled vehicle.
NOTE
Do not connect this end directly to the negative
post of the discharged battery.
Figure 6D1-3 – 10
Legend
Order of hook-up:
1 Booster vehicle, positive terminal
2 Disabled vehicle, positive terminal
3 Booster vehicle, negative terminal
4 Disabled vehicle, engine ground point Booster vehicle
Disabled vehicle
11 Ensure the jumper cables are not on or near drive pulleys, cooling fans or other points that will move when the engine is started.
12 Start the engine in the booster vehicle and run the engine at a moderate speed for a few minutes.
13 Start the engine in the disabled vehicle.
NOTE
If the engine in the disabled vehicle does not start
within 30 seconds, stop cranking the engine and
fix the cause. Refer to 3 Diagnosis.
14 W hen the engine starts, allow both engines to idle for approximately seven minutes. This allows the voltage levels in both vehicles to balance.
15 Leave the vehicles running and remove the jumper cables in the reverse sequence to attaching them. W hen removing each clamp, take care to ensure that it does not touch any other metal.
16 Discard the wet cloths covering the battery filler caps of both batteries.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3690 of 6020

Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–29
Intermittent Fault Conditions
8.1 Intermittent Conditions Diagnostic Table
Description
A fault condition is intermittent if one of the following conditions exists:
• The fault condition is not always present.
• The fault condition cannot be presently duplicated.
• There is no Current DTC but a History DTC is stored.
Diagnostic Table
Checks Actions
Preliminary
• Perform the Preliminary Checks, refer to 7.1 Diagnostic Requirements,
Precautions and Preliminary Checks.
• Gather information from the customer regarding the conditions that trigger the
intermittent fault such as:
• At what engine or ambient temperature range does the fault occur?
• Does the fault occur when operating aftermarket electrical equipment inside
the vehicle?
• Does the fault occur on rough roads or in wet road conditions?
• If the intermittent fault is a start and then stall condition, check immobiliser system.
Refer to 11A Immobiliser.
Harness / Connector Install Tech 2 and perform the Tech 2 Intermittent Fault Tests. Refer to 4.1 Diagnostic General Descriptions for information on Tech 2 ECU diagnostic
tests.
W arning Indicator The following conditions may cause an intermittent Malfunction Indicator Lamp fault with
no DTC listed:
• Electromagnetic Interference (EMI) caused by a faulty relay, ECM controlled
solenoid, switch or other external source.
• Incorrect installation of aftermarket electrical equipment such as the following:
• mobile phones,
• theft deterrent alarms,
• lights, or
• radio equipment.
• Loose PIM ground connections.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3691 of 6020
Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–30
Checks Actions
Temperature Related The Tech 2 Freeze Frame / Failure Records or Snapshot data may be used if applicable
to the fault condition. Refer to 4.1 Diagnostic General Descriptions for information on
Tech 2 ECU diagnostic tests.
• If the intermittent fault is heat related, review the Tech 2 data in relationship to the
following:
• high ambient temperature,
• underhood / engine generated heat,
• circuit generated heat due to a poor electrical connection or high electrical
load, and
• higher than normal load conditions (towing, etc.).
• If the intermittent fault is related to cold ambient or engine temperature, review the
Tech 2 data in relationship to the following:
• low ambient temperature, and
• the fault condition that occurs only on a cold start situation.
Additional Tests
• Check for incorrect installation of aftermarket electrical equipment such as the
following:
• mobile phones,
• theft deterrent alarms,
• lights, or
• radio equipment.
• Check for electromagnetic Interference (EMI) caused by a faulty relay, ECM
controlled solenoid or switch. The fault is triggered when the relay or solenoid is
activated.
• Check the A/C compressor clutch and some relays that contain a clamping diode
or resistor for an open circuit.
• Check the generator for a faulty rectifier bridge that may allow A/C noise into the
PIM electrical circuit.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the engine management system for correct operation.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3785 of 6020
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – General Information Page 7C1–25
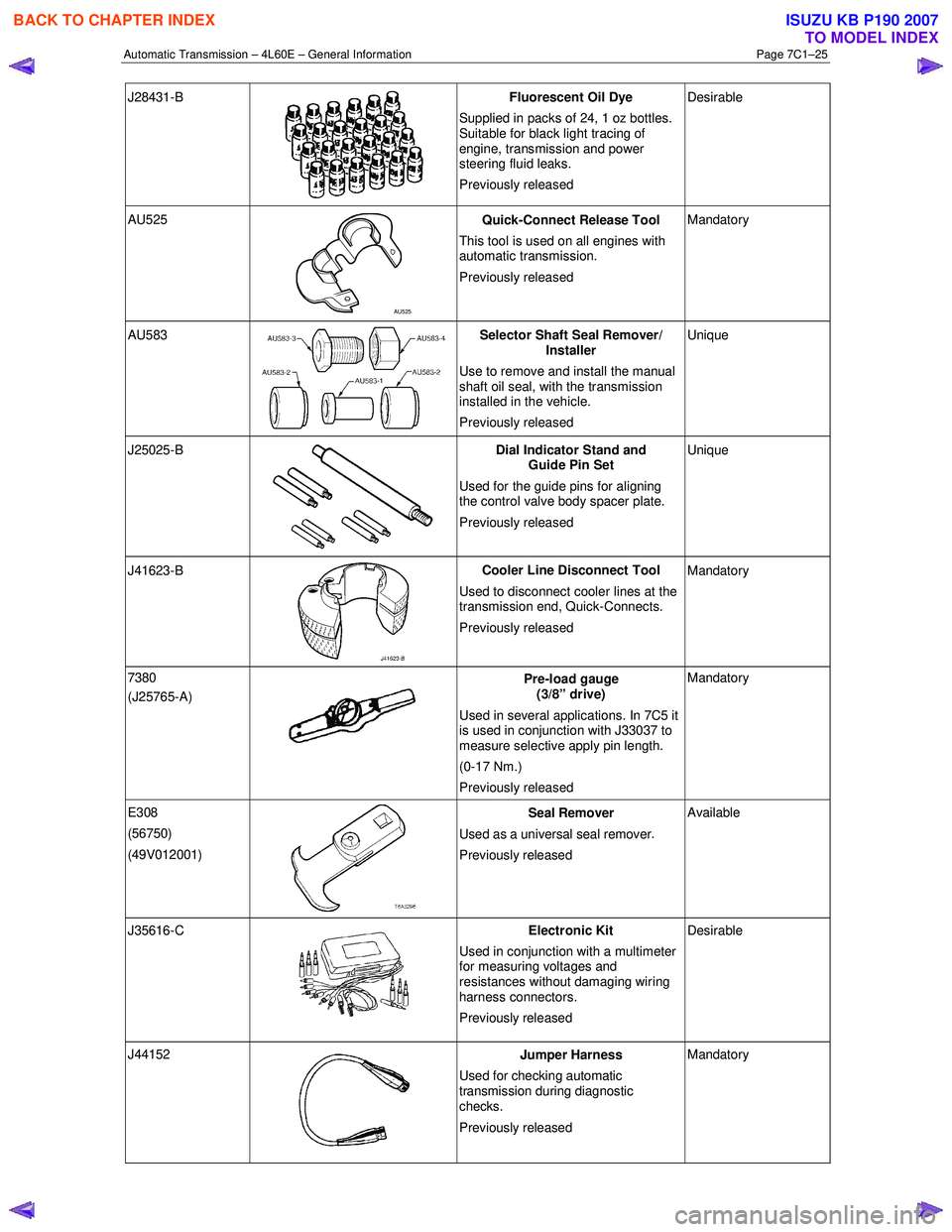
J28431-B
Fluorescent Oil Dye
Supplied in packs of 24, 1 oz bottles.
Suitable for black light tracing of
engine, transmission and power
steering fluid leaks.
Previously released Desirable
AU525
AU525 Quick-Connect Release Tool
This tool is used on all engines with
automatic transmission.
Previously released Mandatory
AU583 Selector Shaft Seal Remover/
Installer
Use to remove and install the manual
shaft oil seal, with the transmission
installed in the vehicle.
Previously released Unique
J25025-B
Dial Indicator Stand and
Guide Pin Set
Used for the guide pins for aligning
the control valve body spacer plate.
Previously released Unique
J41623-B
Cooler Line Disconnect Tool
Used to disconnect cooler lines at the
transmission end, Quick-Connects.
Previously released Mandatory
7380
(J25765-A)
Pre-load gauge
(3/8” drive)
Used in several applications. In 7C5 it
is used in conjunction with J33037 to
measure selective apply pin length.
(0-17 Nm.)
Previously released Mandatory
E308
(56750)
(49V012001)
Seal Remover
Used as a universal seal remover .
Previously released Available
J35616-C
Electronic Kit
Used in conjunction with a multimeter
for measuring voltages and
resistances without damaging wiring
harness connectors.
Previously released Desirable
J44152
Jumper Harness
Used for checking automatic
transmission during diagnostic
checks.
Previously released Mandatory
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007