2007 ISUZU KB P190 check engine light
[x] Cancel search: check engine lightPage 3154 of 6020
Engine Cooling – V6 Engine Page 6B1–19
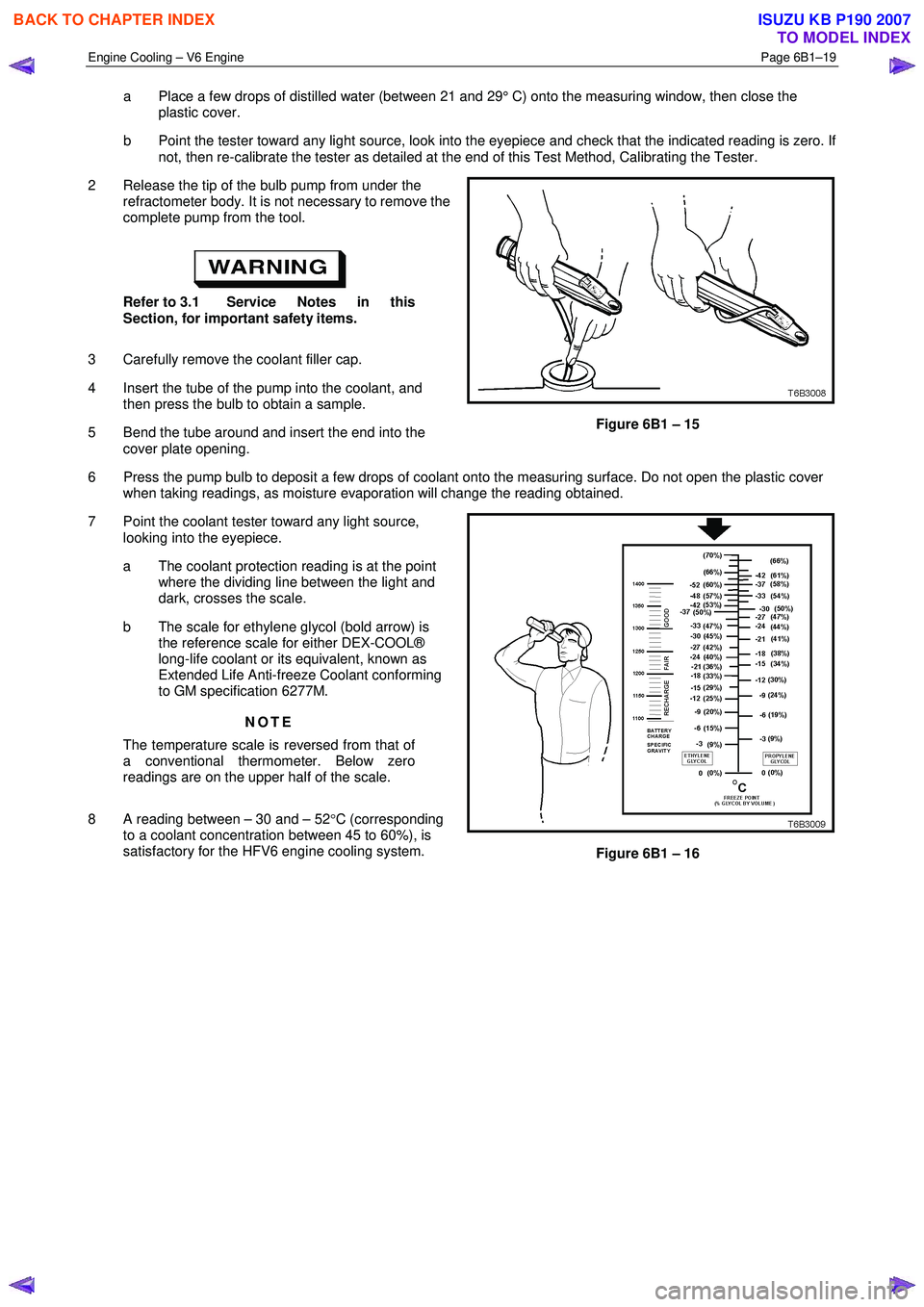
a Place a few drops of distilled water (between 21 and 29° C) onto the measuring window, then close the
plastic cover.
b Point the tester toward any light source, look into the eyepiece and check that the indicated reading is zero. If not, then re-calibrate the tester as detailed at the end of this Test Method, Calibrating the Tester.
2 Release the tip of the bulb pump from under the refractometer body. It is not necessary to remove the
complete pump from the tool.
Refer to 3.1 Service Notes in this
Section, for important safety items.
3 Carefully remove the coolant filler cap.
4 Insert the tube of the pump into the coolant, and then press the bulb to obtain a sample.
5 Bend the tube around and insert the end into the cover plate opening.
Figure 6B1 – 15
6 Press the pump bulb to deposit a few drops of coolant onto the measuring surface. Do not open the plastic cover when taking readings, as moisture evaporation will change the reading obtained.
7 Point the coolant tester toward any light source, looking into the eyepiece.
a The coolant protection reading is at the point where the dividing line between the light and
dark, crosses the scale.
b The scale for ethylene glycol (bold arrow) is the reference scale for either DEX-COOL®
long-life coolant or its equivalent, known as
Extended Life Anti-freeze Coolant conforming
to GM specification 6277M.
NOTE
The temperature scale is reversed from that of
a conventional thermometer. Below zero
readings are on the upper half of the scale.
8 A reading between – 30 and – 52 °C (corresponding
to a coolant concentration between 45 to 60%), is
satisfactory for the HFV6 engine cooling system.
Figure 6B1 – 16
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3168 of 6020
Engine Cooling – V6 Engine Page 6B1–33
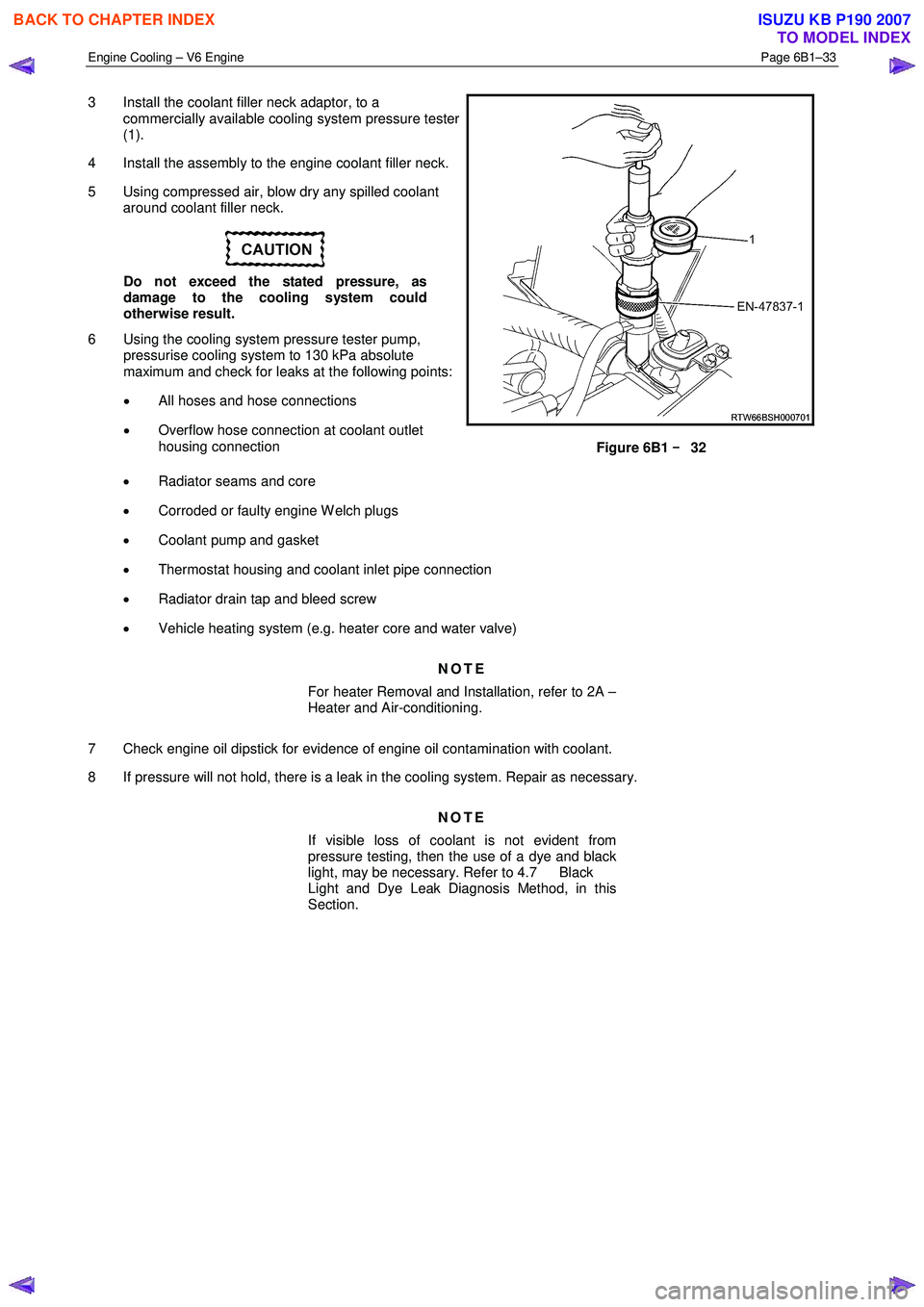
3 Install the coolant filler neck adaptor, to a
commercially available cooling system pressure tester
(1).
4 Install the assembly to the engine coolant filler neck.
5 Using compressed air, blow dry any spilled coolant around coolant filler neck.
Do not exceed the stated pressure, as
damage to the cooling system could
otherwise result.
6 Using the cooling system pressure tester pump, pressurise cooling system to 130 kPa absolute
maximum and check for leaks at the following points:
• All hoses and hose connections
• Overflow hose connection at coolant outlet
housing connection
Figure 6B1 –
––
–
32
• Radiator seams and core
• Corroded or faulty engine W elch plugs
• Coolant pump and gasket
• Thermostat housing and coolant inlet pipe connection
• Radiator drain tap and bleed screw
• Vehicle heating system (e.g. heater core and water valve)
NOTE
For heater Removal and Installation, refer to 2A –
Heater and Air-conditioning.
7 Check engine oil dipstick for evidence of engine oil contamination with coolant.
8 If pressure will not hold, there is a leak in the cooling system. Repair as necessary.
NOTE
If visible loss of coolant is not evident from
pressure testing, then the use of a dye and black
light, may be necessary. Refer to 4.7 Black
Light and Dye Leak Diagnosis Method, in this
Section.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3198 of 6020

Engine Cooling – V6 Engine Page 6B1–63
4.5 Problems Not Requiring Disassembly of
Cooling System
1 Large obstructions blocking radiator or condenser airflow.
• Auxiliary oil coolers
• License plate
• Obstruction of radiator grille, for example, driving lights or mud
2 Loose, damaged or missing air chute side panels.
3 Missing or damaged air baffle.
4 Cracked or loose coolant recovery system hose.
5 Leaking heater component such as the heater core or water valve.
4.6 Problems Requiring Disassembly of Cooling System
1 Damaged cooling fan or faulty motor operation.
2 Pressure test cooling system.
3 Defective coolant pump.
• Eroded or broken impeller vanes
• Failed bearing or seal – check for shaft or bearing end play
4 Internally blocked radiator core.
5 Obstruction of coolant recovery system.
6 Internal system leaks.
• Head gaskets
• Cracked cylinder block
• Engine front cover
• Intake manifold gaskets
7 Blocked coolant passages in cylinder heads or block – remove cylinder heads and check.
4.7 Black Light and Dye Leak Diagnosis Method
It is strongly recommended that this diagnostic method be used to diagnose fluid leaks. This method is a proven and
reliable method that identifies the specific leak source.
The black light kit can be used for the leak detection of a number of fluids, when used with the appropriate tracer dye.
Examples are: Coolant, Engine Oil, Automatic Transmission Fluid and Air Conditioning Refrigerant (R134A).
The following is a summary of the steps involved in detecting a cooling system fluid leak using black light and dye:
1 Pour specified amount of dye into the cooling system via the coolant filler cap on the outlet housing. Refer 3.1 Service Notes in this Section.
2 Road test the vehicle under normal operating conditions.
3 Direct the light towards the suspect area. The fluid leak will appear as a brightly coloured path leading from the source.
4 Repair fluid leak and recheck to ensure that leak has been rectified.
5 Refer to the manufacturer’s directions when using this method.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3202 of 6020
Engine Cooling – V6 Engine Page 6B1–67
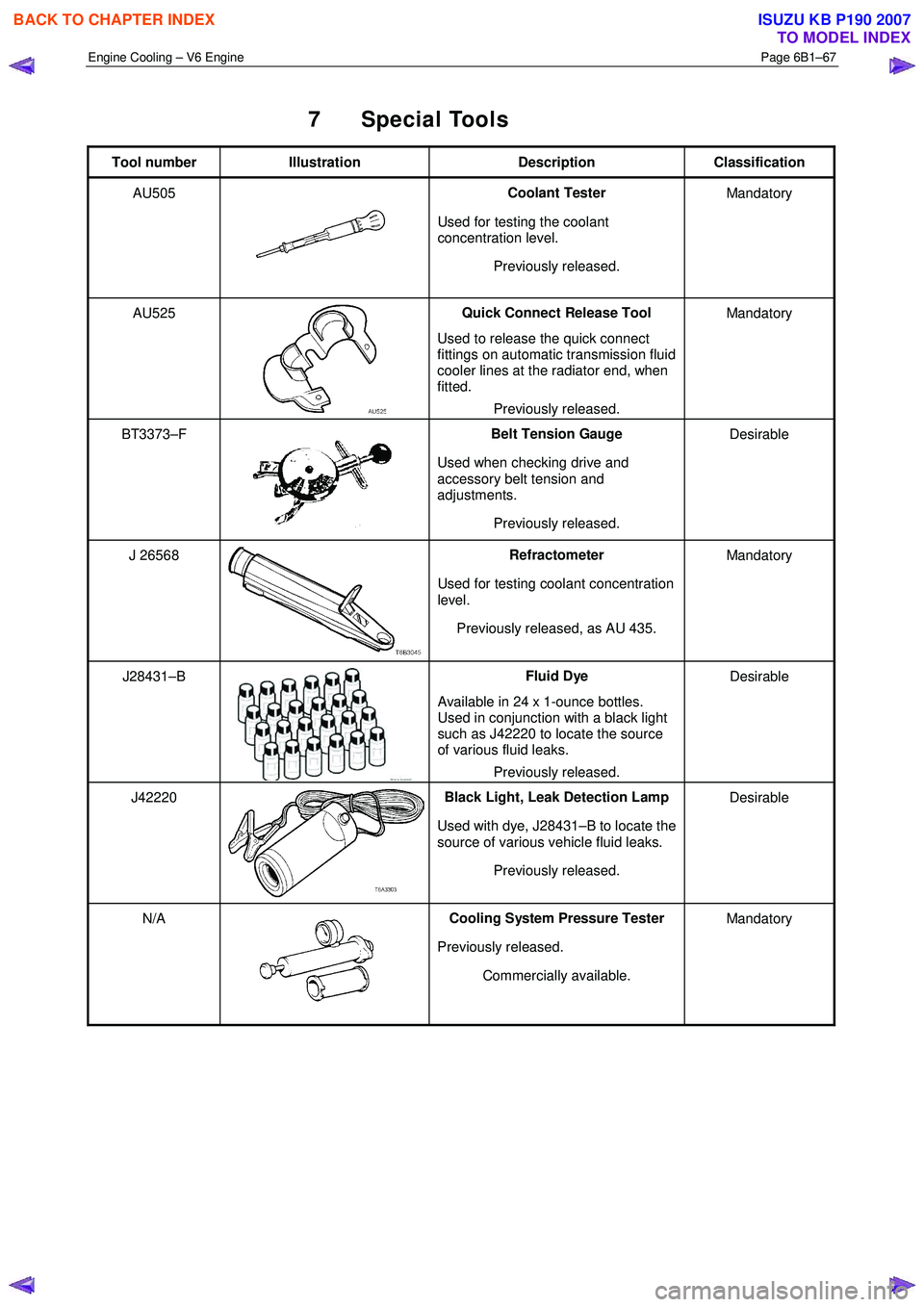
7 Special Tools
Tool number Illustration Description Classification
AU505
Coolant Tester
Used for testing the coolant
concentration level.
Previously released. Mandatory
AU525
Quick Connect Release Tool
Used to release the quick connect
fittings on automatic transmission fluid
cooler lines at the radiator end, when
fitted.
Previously released. Mandatory
BT3373–F
Belt Tension Gauge
Used when checking drive and
accessory belt tension and
adjustments.
Previously released. Desirable
J 26568 Refractometer
Used for testing coolant concentration
level.
Previously released, as AU 435. Mandatory
J28431–B Fluid Dye
Available in 24 x 1-ounce bottles.
Used in conjunction with a black light
such as J42220 to locate the source
of various fluid leaks.
Previously released. Desirable
J42220 Black Light, Leak Detection Lamp
Used with dye, J28431–B to locate the
source of various vehicle fluid leaks.
Previously released. Desirable
N/A Cooling System Pressure Tester
Previously released. Commercially available. Mandatory
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3277 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – General Information Page 6C1-1–35
5 Abbreviations and Glossary of
Te r m s
Abbreviations and terms used in this Section are listed below in alphabetical order with an explanation of the
abbreviation or term.
Abbreviation Description
A/C Air-conditioning
AC Alternating Current – An electrical current where the polarity is constantly changing between positive and
negative
A/F Air / Fuel (A/F Ratio)
Analogue Signal An electrical signal that constantly varies in voltage within a given parameter
Barometric Pressure Barometric absolute pressure (atmospheric pressure)
CAN Controller Area Network – A type of serial data for communication between electronic devices.
Catalytic Converter
A muffler-shaped device fitted in the exhaust system, usually close to the engine. Through chemical reaction,
a catalytic converter converts harmful gases produced by the combustion process such as HC, CO, and NOx,
into environmentally safe water vapour, carbon dioxide, and nitrogen.
CKT Circuit
Closed Loop A fuel control mode of operation that uses the signal from the exhaust oxygen sensor(s), to control the air / fuel
ratio precisely at a 14.7 to 1 ratio. This allows maximum efficiency of the catalytic converter.
CO Carbon Monoxide. One of the gases produced by the engine combustion process.
DC Direct Current
Digital Signal An electrical signal that is either on or off.
DLC
Data Link Connector. Used at the assembly plant to evaluate the engine management system. For service, it
allows the use of Tech 2 in performing system checks.
DLC Data Stream An output from the ECM initiated by Tech 2 and transmitted via the Data Link Connector(DLC).
DMM (10 M Ω) Digital Multimeter. A multipurpose meter that has capability of measuring voltage, current flow and resistance.
A digital multimeter has an input impedance of 10 M Ω (megohms), which means they draw very little power
from the device under test, they are very accurate and will not damage delicate electronic components
Driver An electronic device, usually a power transistor, that operates as an electrical switch.
DTC
Diagnostic Trouble Code. If a fault occurs in the engine management system, the ECM may set a four digit
diagnostic trouble code (DTC) which represents the fault condition. Tech 2 is used to interface with the ECM
and access the DTC(s). The ECM may also operate the malfunction indicator lamp in the instrument cluster.
Duty Cycle The time, in percentage, that a circuit is on versus off.
ECT Sensor
Engine Coolant Temperature sensor. A device that provides a variable voltage to the ECM based on the
temperature of the engine coolant.
EEPROM Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory. A type of read only memory (ROM) that can be
electrically programmed, erased and reprogrammed using Tech 2. Also referred to as Flash Memory
EMI or Electrical
Noise An unwanted signal interfering with a required signal. A common example is the effect of high voltage power
lines on an AM radio.
Engine Braking A condition where the engine is used to slow the vehicle on closed throttle or low gear.
EPROM Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory. A type of Read Only Memory (ROM) that can be erased with
ultraviolet light and then reprogrammed.
ESD Electrostatic Discharge. The discharge of static electricity which has built up on an insulated material
EVAP
Evaporative emission control system. Used to prevent fuel vapours from the fuel tank from entering into the
atmosphere. The vapours are stored in a canister that contains an activated charcoal element. The fuel
vapours are purged from the canister into the manifold to be burned in the engine.
GM LAN General Motors Local Area Network - A type of serial data for communication between electronic devices.
Fuse
A thin metal strip which melts when excessive current flows through it, creating an open circuit and protecting
a circuit from damage.
HC Hydrocarbon. Result of unburned fuel produced by incomplete combustion.
Heavy Throttle Approximately 3/4 of accelerator pedal travel (75% throttle position)
IAT Sensor
Intake Air Temperature sensor. A device that provides a variable voltage to the ECM based on the
temperature of air entering the intake system.
Ideal Mixture The air / fuel ratio which provides the best performance, while maintaining maximum conversion of exhaust
emissions, typically 14.7 to 1 on spark ignition engines
IGN Ignition
Inputs Information from sensors (MAF, TP, etc.) and switches (A/C request, etc.) used by the ECM to determine how
to control its outputs.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3297 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–19
• Do not start the engine if the battery terminal is not properly secured to the battery.
• Do not disconnect or reconnect the following while the ignition is switched on or when the engine is running:
− Any engine management system component electrical wiring connector, or
− Battery terminal leads.
• Ensure the correct procedure for disconnecting and connecting engine management system electrical wiring
connectors is always followed. For information on the correct procedure for disconnecting and connecting specific
wiring connectors, refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
• Ensure that all wiring harness connectors are fitted correctly.
• W hen steam or pressure cleaning engines, do not direct the cleaning nozzle at engine management system
components.
• Do not clear any DTCs unless instructed.
• The fault must be present when using the diagnostic trouble code (DTC) diagnostic tables. Otherwise,
misdiagnosis or replacement of good parts may occur.
• Do not touch the ECM connector pins or soldered components on the ECM circuit board to prevent ECM
Electrostatic Discharge damage. Refer to 8A Electrical - Body and Chassis for information on Electrostatic
Discharge.
• Use only the test equipment specified in the diagnostic tables as other test equipment may give incorrect results or
damage good components.
• The ECM is designed to withstand normal current draw associated with vehicle operations. However, the following
fault conditions or incorrect test procedure may overload the ECM internal circuit and damage the ECM:
− A short to voltage fault condition in any of the ECM low reference circuits may cause internal ECM and / or
sensor damage. Therefore, any short to voltage fault condition in the ECM low reference circuits must be
rectified before replacing a faulty component.
− A short to ground fault condition in any of the ECM 5 V reference circuits may cause internal ECM and / or
sensor damage. Therefore, any short to ground fault condition in the ECM 5 V reference circuits must be
rectified before replacing a faulty component.
− W hen using a test lamp to test an electrical circuit, do not use any of the ECM low reference circuits or 5 V
reference circuits as a reference point. Otherwise, excessive current draw from the test lamp may damage
the ECM.
• Disregard DTCs that set while performing the following diagnostic Steps:
− Using Tech 2 actuator tests, or
− Disconnecting an engine management system sensor connector then switching on the ignition.
• After completing the required diagnostics and service operations, road test the vehicle to ensure correct engine
management system operation.
4.3 Preliminary Checks
The preliminary checks are a set of visual and physical checks or inspections that may quickly identify engine
management system fault condition.
• Refer to the appropriate Service Techlines for relevant information regarding the fault condition.
• Ensure the battery is fully charged.
• Inspect the battery connections for corrosion or a loose terminal.
• Ensure that all engine management system related fuses are serviceable.
• Inspect for incorrect aftermarket theft deterrent devices, lights or mobile phone installation.
• Ensure there is no speaker magnet positioned too close to any electronic module that contains relays.
• Inspect the engine wiring harness for proper connections, pinches or cuts.
• Ensure that all engine management related electrical wiring connectors are fitted correctly.
• Inspect the ECM ground connections for corrosion, loose terminal or incorrect position.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3301 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–23
• there is no Current DTC but a History DTC is stored.
Diagnostic Table
Checks Actions
Preliminary
• Perform the preliminary checks. Refer to 4.3 Preliminary Checks in this
Section.
• Gather information from the customer regarding the conditions that trigger the
intermittent fault such as:
• At what engine or ambient temperature range does the fault occur?
• Does the fault occur when operating aftermarket electrical equipment inside
the vehicle?
• Does the fault occur on rough roads or in wet road conditions?
• If the intermittent fault is a start and then stall condition, check the immobiliser
system. Refer to 11A Immobiliser.
Tech 2 Tests The following are lists of Tech 2 diagnostic tests that may be used to diagnose
intermittent faults:
• W riggle test the suspected wiring harness and connectors while observing Tech 2
operating parameters. If Tech 2 read-out fluctuates during this procedure, check
the tested wiring harness circuit for a loose connection.
• Observe the freeze frame / failure records for the suspected history DTC and then
operate the vehicle in the conditions that triggers the intermittent fault while an
assistant observes the suspected Tech 2 operating parameter data.
• Capture and store data in the snapshot mode when the fault occurs. The stored
data may be played back at a slower rate to aid diagnostics. Refer to Tech 2 User
Instructions for further information on the Snapshot function.
• Compare the engine operating parameters of the engine being diagnosed to the
engine operating parameters of a known good engine.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp The following conditions may cause an intermittent Malfunction Indicator Lamp fault with no DTC listed:
• Electromagnetic interference (EMI) caused by a faulty relay, ECM controlled
solenoid, switch or other external source.
• Incorrect installation of aftermarket electrical equipment such as the following:
• mobile phones,
• lights, or
• radio equipment.
• ECM grounds are loose.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3302 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–24
Checks Actions
Temperature Related Temperature related intermittent fault condition occurs only when the engine or ambient
temperature is hot, or only when it is cold.
• If the intermittent fault is heat related, review Tech 2 data in relationship to the
following:
• high ambient temperature,
• engine generated heat,
• circuit generated heat due to a poor electrical connection or high electrical
load, and
• higher than normal load conditions (towing, etc.).
• If the intermittent fault is related to cold ambient or engine temperature, review
Tech 2 data in relationship to the following:
• low ambient temperature, and
• the fault condition that occurs only on a cold start situation.
Additional Tests
• Incorrect installation of aftermarket electrical equipment such as the following:
• mobile phones,
• theft deterrent alarms,
• lights, or
• radio equipment.
• Electromagnetic interference (EMI) caused by a faulty relay, ECM controlled
solenoid or switch. The fault is triggered when the relay or solenoid is activated.
• Test the A/C compressor clutch and some relays that contain a clamping diode or
resistor for an open circuit.
• Test the generator for a faulty rectifier bridge that may allow the A/C noise into the
ECM electrical circuit.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
5.3 Backfire
Description
The air / fuel mixture in the intake manifold or in the exhaust system ignites which produces a loud popping noise.
Checks Actions
Preliminary Perform the Preliminary Checks. Refer to 4.3 Preliminary Checks in this
Section.
Sensor / System • Check the air intake system and crankcase for air leaks.
• Check the PCV System for correct operation. Refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical –
V6.
• Use Tech 2 to monitor the knock sensor system for excessive spark retard
activity. Check for items that cause spark retard activity.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007