2007 ISUZU KB P190 lock
[x] Cancel search: lockPage 5667 of 6020

9A-32 SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM
Service Precautions for SRS
Component Service
CAUTION: When fasteners are removed, always
reinstall them at the same location from which
they were removed. If a fastener needs to be
replaced, use the correct part number fastener fo
r
that application. If the correct part number
fastener is not available, a fastener of equal size
and strength (or stronger) may be used. Fasteners
that are not reused, and those requiring a thread
locking compound will be called out. The correct
torque value must be used when installing
fasteners that require it. If the above conditions
are not followed, parts or system damage could
result.
WARNING: WHEN PERFORMING SERVICE ON OR
AROUND SRS COMPONENTS OR SRS WIRING,
FOLLOW THE PROCEDURES LISTED BELOW TO
TEMPORARILY DISABLE THE SRS. FAILURE TO
FOLLOW PROCEDURES COULD RESULT IN
POSSIBLE AIR BAG DEPLOYMENT, PERSONAL
INJURY OR OTHERWISE UNNEEDED SRS
REPAIRS.
The SRS control unit in the Driver–Passenger SRS
can maintain sufficient voltage to cause a deployment
for up to 15 seconds after the ignition switch is turned
“OFF,” the battery is disconnected, or the fuse
powering the SRS control unit is removed.
Many of the service procedures require removal of the
“SRS” fuse, and disconnection of the air bag assembl
y
from the deployment loop to avoid an accidental
deployment. If the air bag assembly is disconnected
from the deployment loop as noted in the “Disabling
the SRS” procedure that follows, service can begin
immediately without waiting for the 15 second time
period to expire.
Disabling The SRS
Removal
Turn the ignition switch to “OFF” and turn the steering
wheel so that the vehicle's wheels are pointing straight
ahead.
1. Remove the SRS fuse “SRS” from the left dash side lower fuse block or disconnect the battery.
2. Disconnect the yellow connector at the base o
f
steering column.
3. Remove the glove box assembly; Refer to “Passenger air bag assembly replacement” in this
section.
4. Disconnect the passenger air bag assembly yello
w
connector behind the glove box assembly.
CAUTION: With the “SRS” fuse removed and the
ignition switch to “ON,” the “SRS” warning lamp
will be “ON.” This is normal operation and does
not indicate an SRS malfunction.
Enabling The SRS
Installation
Turn the ignition switch to “LOCK” and remove the
key.
1. Connect the yellow connector passenger air bag assembly.
2. Install the glove box assembly. Refer to “Passenger Air Bag Assembly Replacement” in
this section.
3. Connect the yellow connector at the base of the steering column.
4. Install the “AIR BAG” fuse “SRS” to the left dash side lower fuse block or connect the battery.
Turn the ignition switch to “ON” and verify that the
“SRS” warning lamp flashes seven times and then
turns to “LOCK”. If it does not operate as described,
perform the “SRS Diagnostic System Check” in this
section.
Handling / Installation / Diagnosis
1. Air bag assembly should not be subjected to
temperatures above 65 °C (150 °F).
2.
Air bag assembly, and SRS control unit should not
be used if they have been dropped from a height
of 100 centimeters (3.28 feet) or more.
3. W hen a SRS control unit is replaced, it must be oriented with the arrow on the SRS control unit
pointing toward the front of the vehicle. It is ver
y
important for the SRS control unit to be located flat
on the mounting surface, parallel to the vehicle
datum line. It is important that the SRS control unit
mounting surface is free of any dirt or other foreign
material.
4. Do not apply power to the SRS unless all components are connected or a diagnostic chart
requests it, as this will set a diagnostic trouble
code.
5. The “SRS Diagnostic System Check” must be the starting point of any SRS diagnostics. The “SRS
Diagnostic System Check” will verify proper “SRS”
warning lamp operation and will lead you to the
correct chart to diagnose any SRS malfunctions.
Bypassing these procedures may result in
extended diagnostic time, incorrect diagnosis, and
incorrect parts replacements.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX TO MODEL INDEXISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 5668 of 6020
SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM 9A-33
Inspections Required After An Accident
CAUTION: Certain SRS components must be
replaced after a frontal crash involving air bag
deployment.
In all types of accidents regardless of “Air Bag”
deployment, visually inspect all of the following
components and replace as required:
– Driver air bag assembly
– Passenger air bag assembly
– Steering wheel
– SRS coil assembly
– Steering column
– Knee bolster and instrument panel mounting attachments
– Driver seat and belt
– Passenger seat and belt
– SRS control unit
The SRS control unit should always be checked
according to “SRS Control Unit Replacement
Guidelines.”
CAUTION: Refer to “SRS control unit Replacement
Guidelines” below for important information on
SRS control unit replacement in both deployment
and non–deployment crashes.
Inspect the SRS coil assembly wiring and the steering
wheel for any sign of scorching, melting, or damage
due to excessive heat. If the coil assembly wire o
r
steering wheel is damaged, replace them. The
steering column and wheel must be dimensionall
y
checked to determine if they are damaged. Refer to
“steering wheel” in this manual.
Never use SRS parts from another vehicle. This does
not include remanufactured parts purchased from an
authorized ISUZU/GM Retailer; they may be used fo
r
SRS repairs.
Do not attempt to repair the SRS control unit, the SRS
harness, the SRS coil assembly, the air bag assembly,
the steering wheel, or the steering column. Service o
f
these items is replacement only. Verify replacement
part numbers.
CAUTION: Proper operation of the SRS control
unit and the supplemental restraint system (SRS)
requires that any repairs to the vehicle structure
return it to its original production configuration.
SRS Connectors
CAUTION: The special yellow color connectors are
used for the supplemental restraint system-air bag
circuit. When removing the cable harness, do not
pull the cables otherwise cable disconnection may
occur. When connecting the SRS connector, insert
the connector completely. Imperfect locking may
cause malfunction of the SRS circuit.
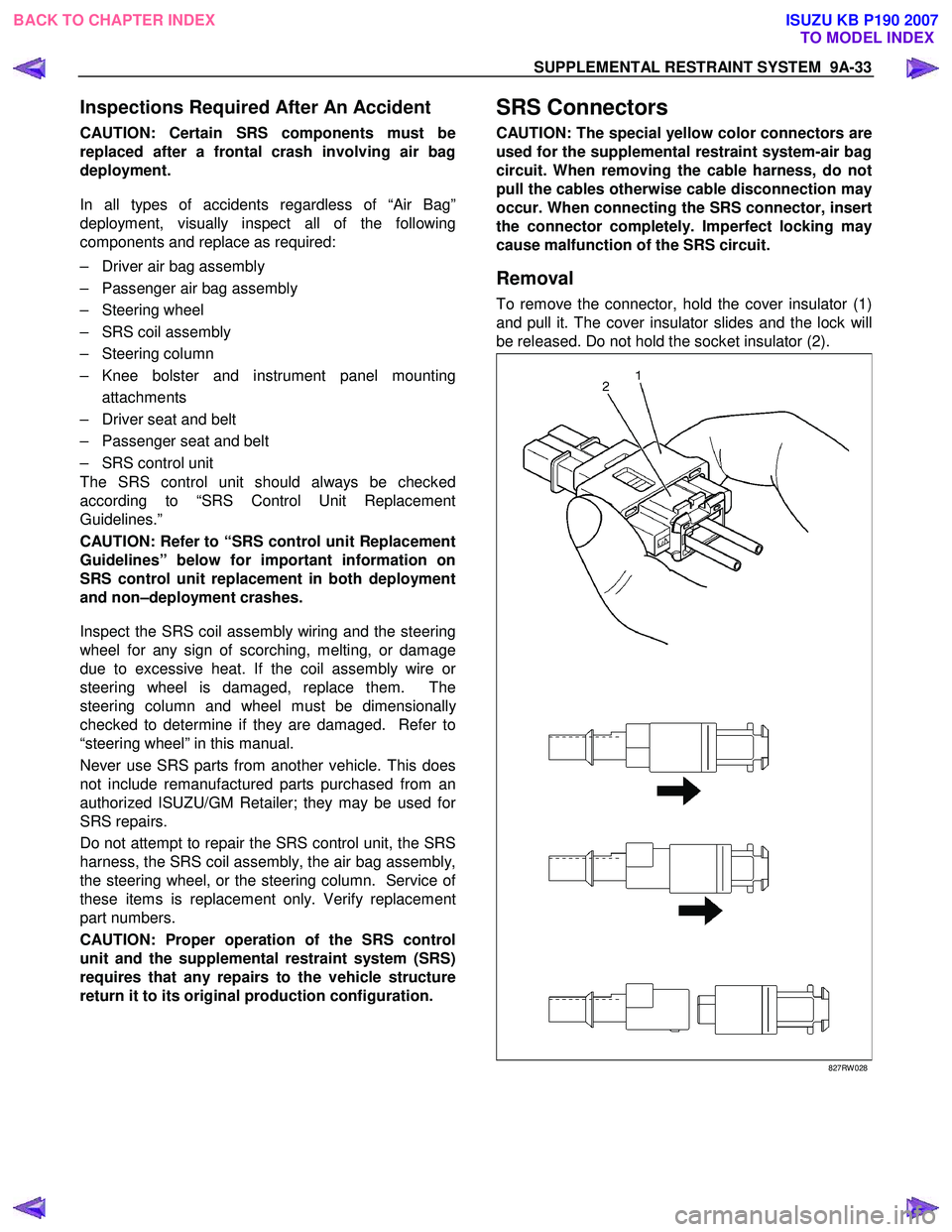
Removal
To remove the connector, hold the cover insulator (1)
and pull it. The cover insulator slides and the lock will
be released. Do not hold the socket insulator (2).
827RW 028
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX TO MODEL INDEXISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 5669 of 6020
9A-34 SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM
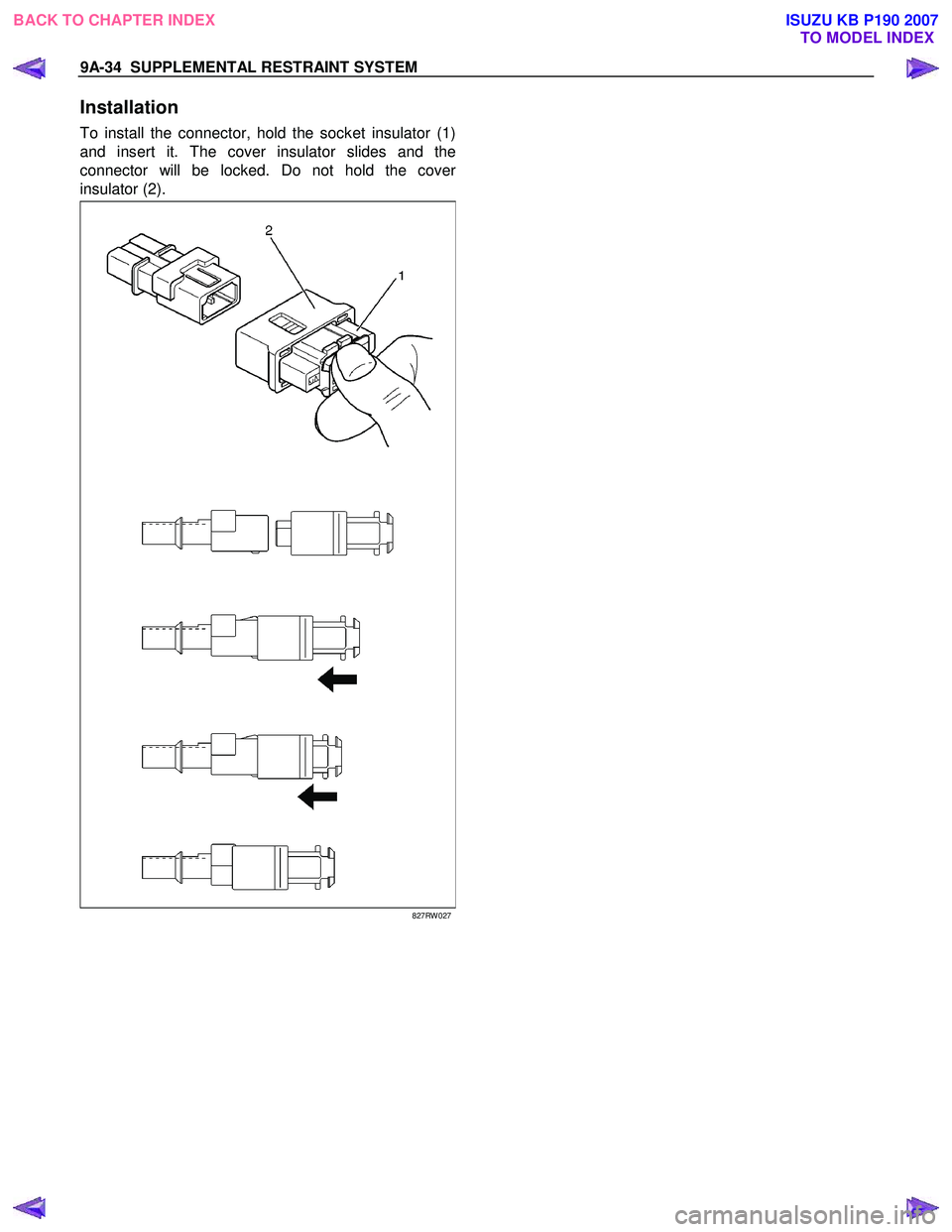
Installation
To install the connector, hold the socket insulator (1)
and insert it. The cover insulator slides and the
connector will be locked. Do not hold the cove
r
insulator (2).
827RW 027
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX TO MODEL INDEXISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 5678 of 6020
SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM 9A-43
Pretensioner Seat Belt (If so equipped)
Service Precaution
WARNING: WHEN PERFORMING SERVICE ON OR
AROUND THE PRETENSIONER SEAT BELT OR
THE PRETENSIONER SEAT BELT WIRING,
FOLLOW THE PROCEDURES LISTED BELOW TO
TEMPORARILY DISABLE THE PRETENSIONER
SEAT BELT.
FAILURE TO FOLLOW PROCEDURES COULD
RESULT IN POSSIBLE THE PRETENSIONER SEAT
BELT DEPLOYMENT, PERSONAL INJURY OR
OTHERWISE UNNEEDED THE PRETENSIONER
SEAT BELT REPAIR.
AS A PRECAUTION, WEAR GLOVES AND SAFETY
GLASSES WHEN PERFORMING THE
PRETENSIONER SEAT BELT. WHEN DEPLOY
A
LIVE PRETENSIONER SEAT BELT AT OUTSIDE
THE
VEHICLE, DEPLOYMENT HARNESS SHALL
REMAIN SHORTED AND NOT BE CONNECTED TO
A POWER SOURCE UNTIL THE PRETENSIONER
SEAT BELT IS TO BE DEPLOYED. THE
PRETENSIONER SEAT BELT WILL IMMEDIATELY
DEPLOY WHEN A POWER SOURCE IS
CONNECTED TO IT. CONNECTING THE
DEPLOYMENT HARNESS SHOULED ALWAYS BE
THE FINAL STEP IN THE PRETENSIONER SEAT
BELT DEPLOYMENT PROCEDURE. FAILURE TO
FOLLOW PROCEDURES IN THE ORDER LISTED
COULD RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY.
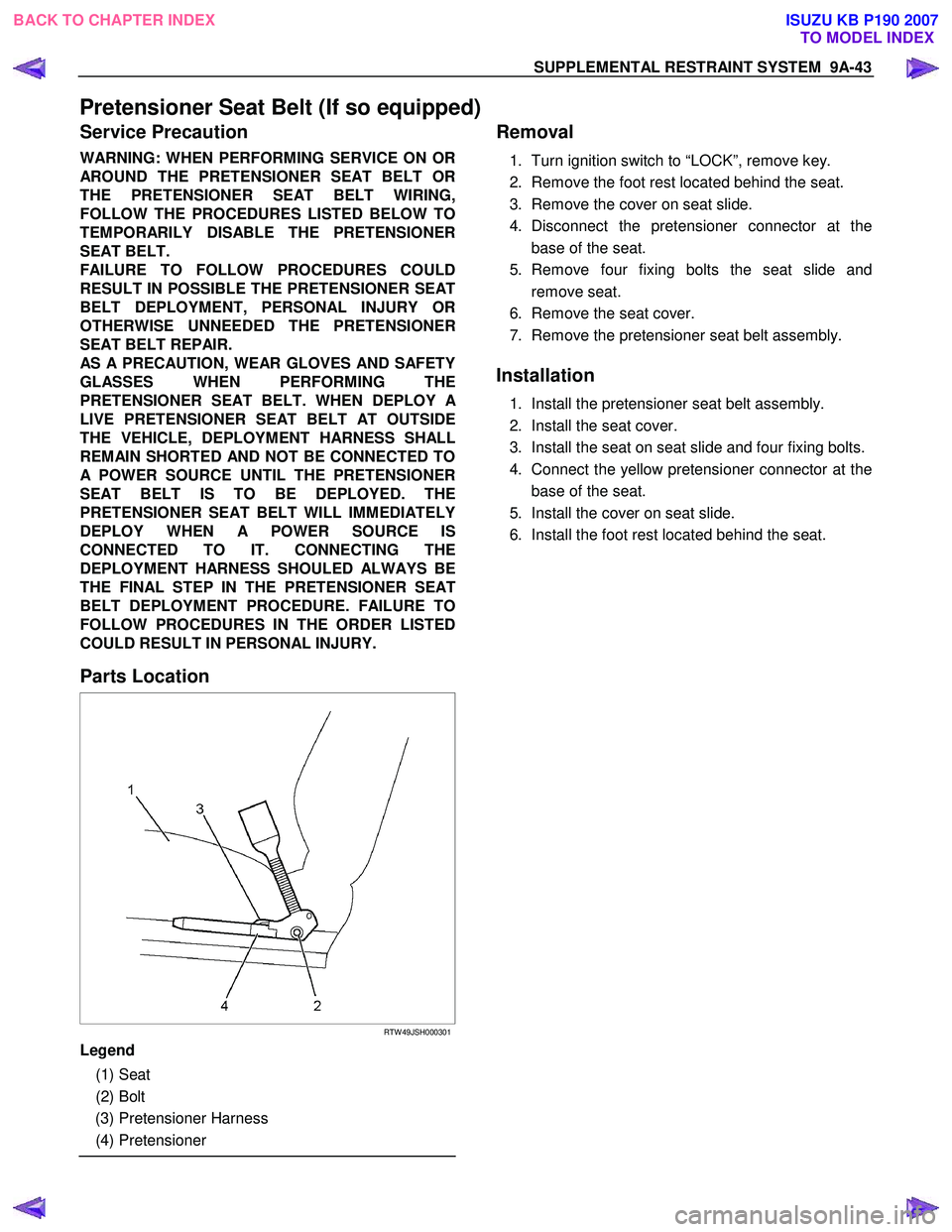
Parts Location
RTW 49JSH000301
Legend
(1) Seat
(2) Bolt
(3) Pretensioner Harness
(4) Pretensioner
Removal
1. Turn ignition switch to “LOCK”, remove key.
2. Remove the foot rest located behind the seat.
3. Remove the cover on seat slide.
4. Disconnect the pretensioner connector at the base of the seat.
5. Remove four fixing bolts the seat slide and remove seat.
6. Remove the seat cover.
7. Remove the pretensioner seat belt assembly.
Installation
1. Install the pretensioner seat belt assembly.
2. Install the seat cover.
3. Install the seat on seat slide and four fixing bolts.
4. Connect the yellow pretensioner connector at the base of the seat.
5. Install the cover on seat slide.
6. Install the foot rest located behind the seat.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX TO MODEL INDEXISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 5684 of 6020

9A1-2 RESTRAINT CONTROL SYSTEM
Service Precaution
WARNING: THIS VEHICLE HAS A SUPPLEMENTAL
RESTRAINT SYSTEM (SRS). REFER TO THE SRS
COMPONENT AND WIRING LOCATION VIEW IN
ORDER TO DETERMINE WHETHER YOU ARE
PERFORMING A SERVICE ON OR NEAR THE SRS
COMPONENTS OR THE SRS WIRING. WHEN YOU
ARE PERFORMING A SERVICE ON OR NEAR THE
SRS COMPONENTS OR THE SRS WIRING, REFER
TO THE SRS SERVICE INFORMATION. FAILURE TO
FOLLOW WARNINGS COULD RESULT IN
POSSIBLE AIR BAG DEPLOYMENT, PERSONAL
INJURY, OR OTHERWISE UNNECESSARY SRS
SYSTEM REPAIRS.
CAUTION: Always use the correct fastener in the
proper location. When you replace a fastener, use
ONLY the exact part number for that application.
ISUZU/GM will call out those fasteners that require
a replacement after removal. ISUZU/GM will also
call out the fasteners that require thread lockers o
r
thread sealant. UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED,
do not use supplemental coatings (paints, greases,
or other corrosion inhibitors) on threaded fasteners
or fastener joint interfaces. Generally, such
coatings adversely affect the fastener torque and
the joint clamping force, and may damage the
fastener. When you install fasteners, use the
correct tightening sequence and specifications.
Following these instructions can help you avoid
damage to parts and systems.
DTC B0029 (Flash Code 29) Passenger pretensioner sqib Circuit High
Resistance ..................................................................................................................... ...............9A1-40
DTC B0031 (Flash Code 31) Passenger Pretensioner Squib Circuit Low
Resistance ..................................................................................................................... ...............9A1-43
DTC B0033 (Flash Code 33) Passenger Pretensi oner Squib Circuit Short to GND ................9A1-46
DTC B0034 (Flash Code 34) Passenger Pretensioner Squib Circuit Short to
Battery Voltage ................................................................................................................ .............9A1-49
DTC B0041 (Flash Code 41) Driver Pretension er Squib Circuit High Resistance...................9A1-51
DTC B0042 (Flash Code 42) Driver Pretensi oner Squib Circuit Low Resistance ...................9A1-54
DTC B0045 (Flash Code 45) Driver Pretensi oner Squib Circuit Short to GND ........................9A1-57
DTC B0046 (Flash Code 34) Driver Pretensioner Squib Circuit Short to Battery
Voltage ........................................................................................................................ ..................9A1-60
DTC B0051 (Flash Code 51) Air Bag Squi b Circuit Activated (Crash).....................................9A1-62
DTC B0052 (Flash Code 52) Pretensioner Squib Circuit Activated (Crash) ...........................9A1-64
DTC B0055 (Flash Code 55) Ve hicle Variant Missing ................................................................9A1-66
DTC B0061 (Flash Code 61) Warnin g Lamp Circuit Failure ......................................................9A1-68
DTC B0062 (Flash Code 62) Batt ery Voltage Too High ............................................................9A1-71
DTC B0063 (Flash Code 63) Batt ery Voltage Too Low .............................................................9A1-73
DTC B0071 (Flash Code 71) SRS Cont rol Unit Internal Fault....................................................9A1-75
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 5685 of 6020

RESTRAINT CONTROL SYSTEM 9A1-3
Diagnostic Information
CAUTION: When fasteners are removed, always
reinstall them at the same location from which they
were removed. If a fastener needs to be replaced,
use the correct part number fastener for that
application. If the correct part number fastener is
not available, a fastener of equal size and strength
(or stronger) may be used. Fasteners that are not
reused, and those requiring thread locking
compound, will be called out. The correct torque
value must be used when installing fasteners that
require it. If the above conditions are not followed,
parts or system damage could result.
Diagnostic Procedures
WARNING: TO AVOID DEPLOYMENT WHEN
TROUBLESHOOTING THE SRS, DO NOT USE
ELECTRICAL TEST EQUIPMENT SUCH AS
A
BATTERY-POWERED OR AC-POWERED
VOLTMETER, OHMMETER, ETC., OR ANY TYPE OF
ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT OTHER THAN THAT
SPECIFIED IN THIS MANUAL. DO NOT USE A NON-
POWERED, PROBE-TYPE TESTER.
INSTRUCTIONS IN THIS MANUAL MUST BE
FOLLOWED CAREFULLY, OTHERWISE PERSONAL
INJURY MAY RESULT.
The diagnostic procedures used in this section are
designed to aid in finding and repairing SRS problems.
Outlined below are the steps to find and repair SRS
problems quickly and effectively. Failure to carefull
y
follow these procedures may result in extended
diagnostic time, incorrect diagnosis and incorrect parts
replacement.
1. Perform The “SRS Diagnostic System Check”.
The “SRS Diagnostic System Check” should always be the starting point of any SRS diagnostics. The
“SRS Diagnostic System Check” checks for prope
r
“SRS” warning lamp operation and checks for SRS
trouble codes using both “Flash Code” and “Scan
Tool” Methods.
2. Refer To The Proper Diagnostic Chart As Directed By The “SRS Diagnostic System
Check”.
The “SRS Diagnostic System Check” will lead you to the correct chart to diagnose any SRS problems.
Bypassing these procedures may result in extended
diagnostic time, incorrect diagnosis and incorrect
parts replacement.
3. Repeat The “SRS Diagnostic System Check”
After Any Repair Or Diagnostic Procedures Has
Been Performed.
Performing the “SRS Diagnostic System Check” after all repairs or diagnostic procedures, will assure
that the repair has been made correctly and that no
other conditions exist.
Diagnostic Codes
The SRS control unit maintains a history record of all
diagnostic codes that have been detected since the
SRS codes were last cleared during service.
1. Active Codes - Faults that are presently detected in this ignition cycle. Active codes are stored in RAM
(Random Access Memory).
2. History Codes - All faults detected since the last time the history fault memory was cleared. History codes
are stored in the EEPROM. (Electronically Erasable
Programmable Read only Memory)
How To Read Trouble Codes
All codes (Active and history) can be read (or cleared)
by using a scan tool or equivalent.
If a PDT is not available, have the vehicle serviced by a
HOLDEN dealer.
How To Clear Trouble Codes
Trouble codes can only be cleared by using a Scan
Tool. If a “scan tool” is not available then inform the
owner of the stored codes and suggest that the codes
are cleared upon the next visit to a ISUZU/GM
dealership.
Scan Tool Diagnostics
A scan tool can be used to read current and history
codes and to clear all history codes after a repair is
complete. The scan tool must be updated to
communicate with the SRS through a replaceable
cartridge or a manufacturer's update before it can be
used for SRS diagnostics. To use the scan tool,
connect it to the DLC and turn the ignition switch “ON”.
Then follow the manufacturer's directions fo
r
communication with the SRS. The scan tool reads
serial data from the SRS control unit’s “Serial Data”
output (terminal 21) to the DLC (terminal 2).
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 5690 of 6020
9A1-8 RESTRAINT CONTROL SYSTEM
Circuit Description
W hen the ignition switch is first turned “ON”, “Ignition 1”
voltage is applied from the “SRS” fuse to the SRS
control unit at the “Ignition 1” input terminals “1”. The
SRS control unit responds by flashing the “SRS”
warning lamp seven times, while performing tests on
the SRS.
Notes On System Check Chart
1. The “SRS” warning lamp should flash seven times after the ignition is first turned “ON”.
2.
After the “SRS” warning lamp flashes seven times, it
should turn to “LOCK”
3. This test checks for the proper operation of the “Serial Data” line. This test will also determine
whether history diagnostic trouble codes are stored
and, if so, identify them.
4. Improper operation of the “SRS” warning lamp is indicated. This test differentiates between ‘a
warning lamp stays “ON” condition’ and ‘a warning
lamp does not come “ON” condition’.
5. This test checks for proper operation of the “Serial Data” line. This test will also identify the stored
diagnostic trouble codes and whether they are
current or history.
Diagnostic Aids
The order in which diagnostic trouble codes are
diagnosed is very important. Failure to diagnose the
diagnostic trouble codes in the order specified ma
y
result in extended diagnostic time, incorrect diagnosis
and incorrect parts replacement.
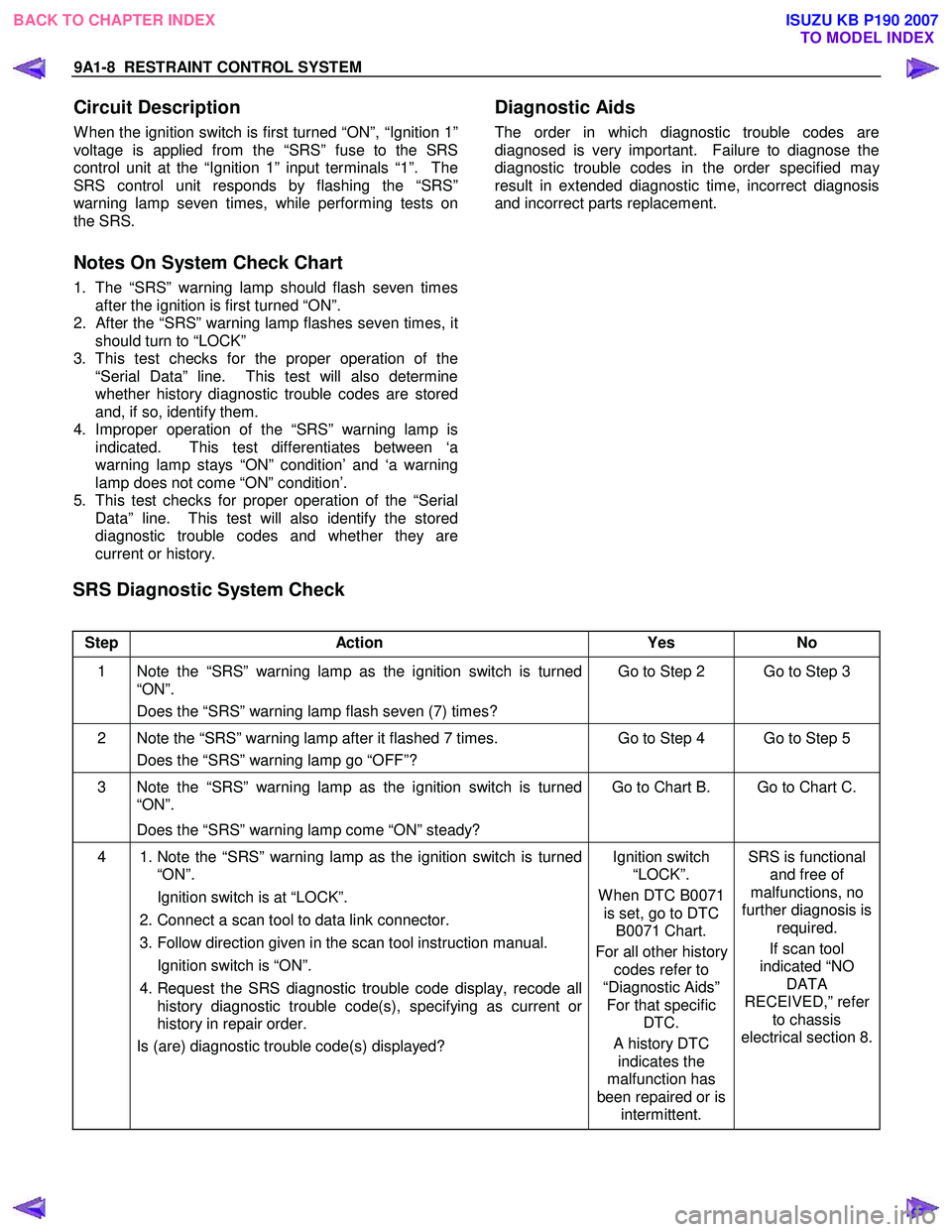
SRS Diagnostic System Check
Step Action Yes No
1 Note the “SRS” warning lamp as the ignition switch is turned
“ON”.
Does the “SRS” warning lamp flash seven (7) times? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 3
2 Note the “SRS” warning lamp after it flashed 7 times.
Does the “SRS” warning lamp go “OFF”? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 5
3 Note the “SRS” warning lamp as the ignition switch is turned
“ON”.
Does the “SRS” warning lamp come “ON” steady? Go to Chart B. Go to Chart C.
4
1. Note the “SRS” warning lamp as the ignition switch is turned
“ON”.
Ignition switch is at “LOCK”.
2. Connect a scan tool to data link connector.
3. Follow direction given in the scan tool instruction manual.
Ignition switch is “ON”.
4. Request the SRS diagnostic trouble code display, recode all
history diagnostic trouble code(s), specifying as current or
history in repair order.
Is (are) diagnostic trouble code(s) displayed?
Ignition switch
“LOCK”.
W hen DTC B0071 is set, go to DTC B0071 Chart.
For all other history codes refer to
“Diagnostic Aids” For that specific DTC.
A history DTC indicates the
malfunction has
been repaired or is intermittent. SRS is functional
and free of
malfunctions, no
further diagnosis is required.
If scan tool
indicated “NO DATA
RECEIVED,” refer to chassis
electrical section 8.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 5691 of 6020

RESTRAINT CONTROL SYSTEM 9A1-9
Step Action Yes No
5 1. Ignition switch is at “LOCK”.
2. Connect a scan tool to data link connector.
3. Follow directions as given in the scan tool instruction manual.
4. Ignition switch is “ON”.
5. Request the SRS diagnostic trouble code display, Recode all diagnostic trouble code(s), specifying as current or history in
repair order.
Is (are) diagnostic trouble code (s) displayed? Ignition switch
“LOCK”.
W hen the current DTC is set, go to applicable DTC chart.
And then if DTC B0019, B0025,
B0051, B0055 or
B0071 is set, go to these DTC chart first.
W hen only history
DTCs exist, refer to “Diagnostics Aids” for that specific DTC.
A history DTC indicates the
malfunction has
been repaired or is intermittent. If scan tool indicates
“No Data Received,” refer to chassis
electrical section 8.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007