2007 ISUZU KB P190 width
[x] Cancel search: widthPage 3794 of 6020

Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–8
1 General Information
1.1 Introduction
This Section covers the electrical diagnostic for the 4L60E automatic transmission when mated to a V6 engine.
1.2 General Description
The 4L60E automatic transmission incorporates electronic controls that utilise a transmission control module (TCM) to
control shift points through:
• the 1-2 and 2-3 shift solenoid valves,
• the 3-2 downshift solenoid valve,
• a torque converter clutch (TCC) solenoid valve,
• apply and release through the TCC pulse width modulated (PW M) solenoid valve, and
• line pressure through the pressure control (PC) solenoid valve.
Electrical signals from various sensors provide information to the TCM about the following:
• vehicle speed,
• throttle position,
• engine coolant temperature,
• transmission fluid temperature,
• gear range selector position,
• engine speed,
• converter turbine speed, and
• engine load braking and operating mode.
The TCM uses this information to determine the precise moment to upshift or downshift, apply or release the TCC and
what fluid pressure is needed to apply the clutches. This type of control provides consistent and precise shift points and
shift quality based on the operating conditions of the vehicle.
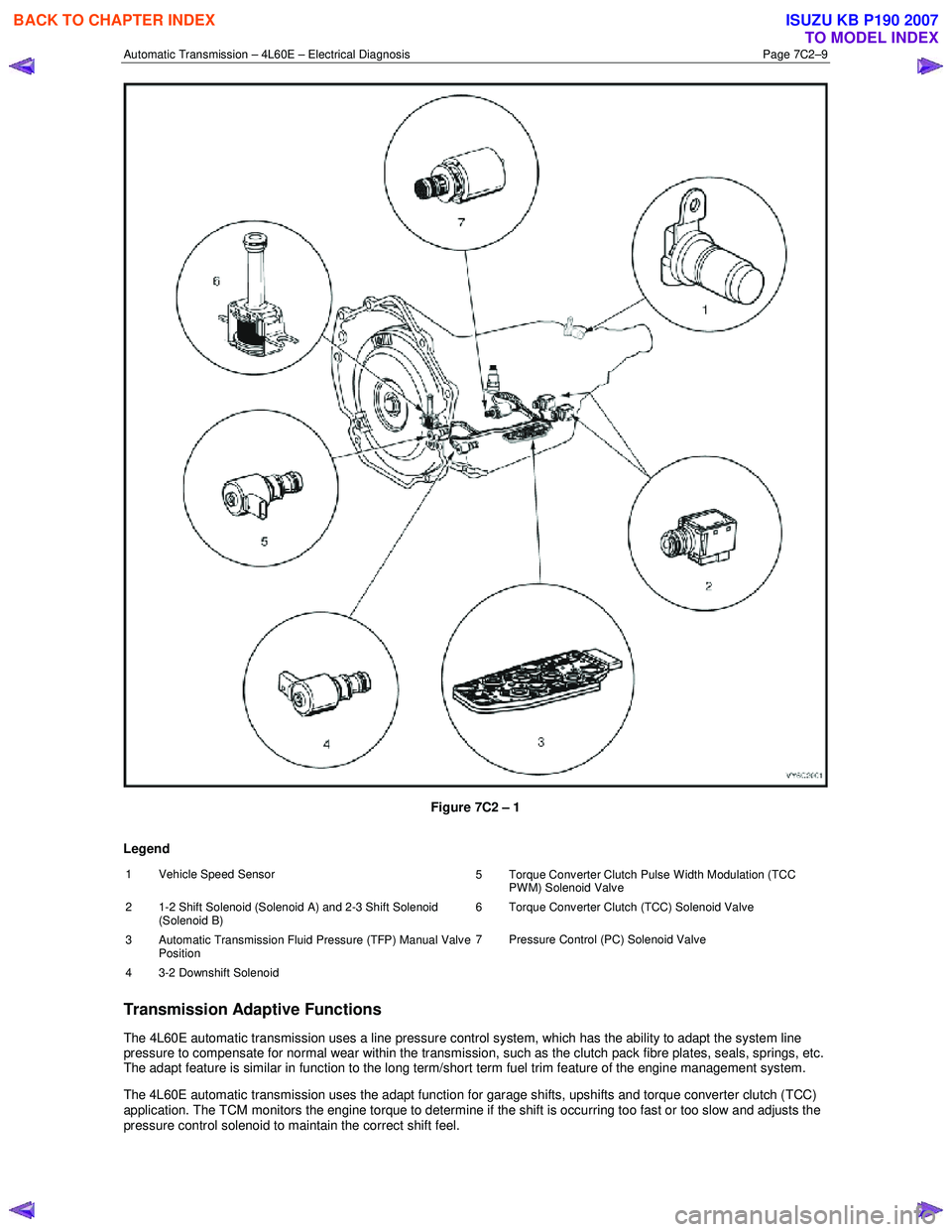
Figure 7C2 – 1 shows the location of the internal electronic components in the transmission.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3795 of 6020
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–9
Figure 7C2 – 1
Legend
1 Vehicle Speed Sensor 5 Torque Converter Clutch Pulse Width Modulation (TCC
PWM) Solenoid Valve
2 1-2 Shift Solenoid (Solenoid A) and 2-3 Shift Solenoid (Solenoid B) 6 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Solenoid Valve
3
Automatic Transmission Fluid Pressure (TFP) Manual Valve
Position 7 Pressure Control (PC) Solenoid Valve
4 3-2 Downshift Solenoid
Transmission Adaptive Functions
The 4L60E automatic transmission uses a line pressure control system, which has the ability to adapt the system line
pressure to compensate for normal wear within the transmission, such as the clutch pack fibre plates, seals, springs, etc.
The adapt feature is similar in function to the long term/short term fuel trim feature of the engine management system.
The 4L60E automatic transmission uses the adapt function for garage shifts, upshifts and torque converter clutch (TCC)
application. The TCM monitors the engine torque to determine if the shift is occurring too fast or too slow and adjusts the
pressure control solenoid to maintain the correct shift feel.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3797 of 6020

Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–11
Figure 7C2 – 2
The TCM is an electronic control module receiving input or providing output to control the operation of the 4L60E
automatic transmission.
The TCM receives the following inputs from the engine control module (ECM):
• engine speed and torque values,
• engine intake air temperature (IAT), accelerator pedal position (APP) information,
• engine coolant temperature (ECT),
• driver selected shift mode, and
• air-conditioning (A/C) status.
The ECM provides this data to the TCM through the databus.
Other TCM inputs are:
• battery and ignition voltage,
• brake switch status,
• transmission fluid temperature (TFT), and
vehicle speed sensor (VSS).
The TCM provides the following outputs to control the automatic transmission:
• shift solenoids to control transmission shifting,
• torque converter clutch (TCC) pulse width modulated (PW M) solenoid operation to control the apply and release of
the torque converter clutch assembly, and
• pressure control (PC) solenoid to regulate the transmission line pressure.
Other TCM outputs provided to the ECM / PIM are:
• MIL illumination request,
• vehicle speed,
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3843 of 6020
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–57
Step Action Yes No
3 Test the stop lamp switch assembly, refer to 8B Cruise Control.
Is the stop lamp switch assembly serviceable? Go to Step 4 Replace the stop
lamp switch assembly
4 1 Disconnect connector C-96 from the TCM.
2 Using a multimeter set to measure voltage, probe between harness connector C-96 pin 42 and a known ground.
3 Press the brake pedal.
Does the multimeter display battery voltage? Go to Step 5 Repair or replace
affected circuit
Go to Step 6
5 Replace the TCM, refer to 7C4 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E –
On-vehicle Servicing.
Did you complete the replacement? Go to Step 6 —
6 Perform the following procedure to verify the repair:
1 On Tech 2 select: Diagnostic Trouble Codes / Clear Engine & Transmission
DTCs.
2 Follow the instructions on Tech 2 and clear any DTCs.
3 Operate the vehicle under the following conditions:
• Turn on the ignition, with the engine off for at least
2 seconds.
• Start the vehicle and idle for 5 seconds.
• Drive in D4 from 0 – 60 km/h then brake, eight times in one
ignition cycle.
4 On Tech 2 select:
Diagnostic Trouble Codes / Read DTC Information.
Has DTC P0724 set? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 7
7 On Tech 2 select:
Diagnostic Trouble Codes / Read DTC Information.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs you have not diagnosed? Refer to
4.8 Diagnostic Trouble Code List System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the
system for correct operation.
4.18 DTC P0741 – Torque Converter Clutch
System – Stuck Off
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC P0741 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) System - Stuck Off.
Circuit Description
The torque converter clutch (TCC) solenoid valve is a normally-open exhaust valve that is used with the torque converter
clutch pulse width modulation (TCC PWM) solenoid valve to control fluid acting on the converter clutch apply valve. The
TCC solenoid valve attaches to the transmission case assembly extending into the pump cover. W hen grounded by the
transmission control module (TCM), the TCC solenoid valve stops converter signal oil from exhausting. This causes
converter signal oil pressure to increase and move the converter clutch apply valve against spring force and into the
apply position. In this position, release fluid is open to an exhaust port and converter feed fluid fills the apply fluid circu it.
The converter feed fluid applies the TCC. When the TCM no longer provides a ground path, the TCC solenoid valve de-
energizes and apply fluid exhausts, releasing the TCC.
When the TCM detects high torque converter slip when the TCC is commanded off, then DTC P0741 sets. DTC P0741 is
a type B DTC.
Refer to 2 W iring Diagrams and Connector Chart to aid in diagnosis.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3846 of 6020

Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–60
Step Action Yes No
4 Perform the following procedure to verify the repair:
1 On Tech 2 select: Diagnostic Trouble Codes / Clear Engine & Transmission
DTCs.
2 Follow the instructions on Tech 2 and clear any DTCs.
3 On Tech 2 select: Automatic Transmission / Data Display / Transmission Data.
4 Drive the vehicle in D4 with the TCC on and the throttle above 10%. Ensure Tech 2 displays TCC Slip Speed between -25 to
+25 RPM for 3 seconds.
5 On Tech 2 select:
Diagnostic Trouble Codes / Read DTC Information.
Has DTC P0741 set? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 5
5 On Tech 2 select:
Diagnostic Trouble Codes / Read DTC Information.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs you have not diagnosed? Refer to
4.8 Diagnostic Trouble Code List System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
4.19 DTC P0742 – Torque Converter Clutch
System – Stuck On
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC P0742 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) System – Stuck On.
Circuit Description
The torque converter clutch (TCC) solenoid valve is a normally-open exhaust valve that is used with the torque converter
clutch pulse width modulation (TCC PWM) solenoid valve to control fluid acting on the converter clutch apply valve. The
TCC solenoid valve attaches to the transmission case assembly extending into the pump cover. W hen grounded by the
transmission control module (TCM), the TCC solenoid valve stops converter signal oil from exhausting. This causes
converter signal oil pressure to increase and move the converter clutch apply valve against spring force and into the
apply position. In this position, release fluid is open to an exhaust port and converter feed fluid fills the apply fluid circu it.
The converter feed fluid applies the TCC. When the TCM no longer provides a ground path, the TCC solenoid valve de-
energizes and apply fluid exhausts, releasing the TCC.
W hen the TCM detects low torque converter slip when the TCC is commanded off, then DTC P0742 sets. DTC P0742 is
a type B DTC.
Refer to 2 W iring Diagrams and Connector Chart to aid in diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
• No DTCs P0722, P0723, P0741 P02763, P02764, P02769 or P02770.
• Ignition voltage is 8 – 18 V.
• The engine run time is greater than 5 seconds.
• The IMS range is D4.
• The transmission fluid temperature is 10 – 130°C.
• The engine speed is 500 – 6,500 r.p.m. for 5 seconds, then 800 – 4,400 r.p.m.
• The engine torque is 156 – 881 Nm.
• The throttle position is greater than 10 percent.
• The transmission is not in 1st gear and the gear ratio is 0.95:1 – 1.56:1.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3868 of 6020
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–82
Step Action Yes No
3 1 Connect Tech 2 to the DLC.
2 Turn on the ignition, with the engine off.
NOTE
Before clearing the DTC, use the Tech 2 Freeze
Frame/Failure Record to record the transmission
parameters at the time the DTC set. Using Tech 2 to clear
the DTC(s) erases the Freeze Frame/Failure Record
records from the TCM.
3 On Tech 2 select: Transmission / Automatic Transmission / Diagnostic
Trouble Codes / Freeze Frame.
4 Select the relevant DTC and note the parameters at the time of the DTC setting.
5 On Tech 2 select:
Diagnostic Trouble Codes / Clear Engine & Transmission
DTCs.
6 Follow the instructions on Tech 2 and clear the DTCs.
NOTE
It may be necessary to allow multiple TCC cycles to occur
to verify a slipping condition. It may also be necessary to
ensure the transmission is warm before performing this
step.
7 On Tech 2 select: Automatic Transmission / Data Display / Transmission Data.
8 Drive the vehicle in 4th gear with the TCC commanded on.
On Tech 2, while TCC Solenoid status is On, is the TCC Slip Speed
within 130 – 800 RPM for 7 seconds?
Go to Step 4 Refer to Diagnostic
Aids within this Section
4 1 Inspect the torque converter clutch (TCC) solenoid valve for the
following conditions:
• internal malfunction, such as sediment or damage, and
• damaged seals, refer to 7C4 Automatic Transmission –
4L60E – On-vehicle Servicing.
2 Inspect the torque converter clutch pulse width modulation (TCC PWM) solenoid valve for the following conditions:
• internal malfunction, such as sediment or damage, and
• damaged seals, refer to 7C4 Automatic Transmission –
4L60E – On-vehicle Servicing.
Did you find and correct the condition? Go to Step 14 Go to Step 5
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3894 of 6020

Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–108
Step Action Yes No
13 On Tech 2 select:
Diagnostic Trouble Codes / Read DTC Information.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs you have not diagnosed? Refer to
4.8 Diagnostic Trouble Code List System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
4.33 DTC P2763 – Torque Converter Clutch
Pressure Control Solenoid Control
Circuit High Voltage
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC P2763 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Pressure Control (PC) Solenoid Control
Circuit High Voltage.
Circuit Description
The torque converter clutch pulse width modulation (TCC PW M) solenoid valve controls the fluid acting on the converter
clutch valve. The converter clutch valve controls the TCC application and release. The solenoid attaches to the control
valve body within the transmission. The solenoid receives voltage through ignition voltage circuit. The transmission
control module (TCM) controls the solenoid by providing a ground path on the TCC PW M solenoid valve control circuit.
Current flows through the solenoid coil according to the duty cycle, percentage of on and off time. The TCC PWM
solenoid valve provides a smooth engagement of the TCC by operating during a duty cycle percent of on time.
When the TCM detects a continuous short to voltage in the TCC PW M solenoid valve control circuit, then DTC P2763
sets. DTC P2763 is a type A DTC.
Refer to 2 W iring Diagrams and Connector Chart to aid in diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
• The system voltage is 8 – 18 V.
• The engine speed is 500 r.p.m. for 5 seconds.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P2763 sets if the TCM commands the solenoid on and the voltage feedback remains high, battery voltage.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
• The TCM requests the ECM to illuminate the MIL during the second consecutive trip in which the conditions for
setting the DTC are met.
• The TCM commands maximum line pressure.
• The TCM freezes transmission adaptive functions.
• The TCM inhibits TCC engagement.
• The TCM inhibits 4th gear if in hot mode.
• At the time of the first failure, the TCM records the operating conditions when the conditions for setting the DTC are
met. The TCM stores this information as a Failure Record.
• At the time of the second failure, the ECM records the operating conditions when the conditions for setting the DTC
are met. The ECM stores this information as a Freeze Frame.
• The TCM stores DTC P2763 in TCM history during the second consecutive trip in which the conditions for setting
the DTC are met.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
• The ECM turns off the MIL after the fourth consecutive drive trip in which the TCM does not send a MIL illumination
request.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3897 of 6020

Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–111
4.34 DTC P2764 – Torque Converter Clutch
Pressure Control Solenoid Control
Circuit Low Voltage
DTC Description
This diagnostic procedure supports DTC P2764 Torque Converter Clutch (TCC) Pressure Control (PC) Solenoid Control
Circuit Low Voltage.
Circuit Description
The torque converter clutch pulse width modulation (TCC PW M) solenoid valve controls the fluid acting on the converter
clutch valve. The converter clutch valve controls the TCC application and release. The solenoid attaches to the control
valve body within the transmission. The solenoid receives voltage through ignition voltage circuit. The transmission
control module (TCM) controls the solenoid by providing a ground path on the TCC PW M solenoid valve control circuit.
Current flows through the solenoid coil according to the duty cycle, percentage of on and off time. The TCC PWM
solenoid valve provides a smooth engagement of the TCC by operating during a duty cycle percent of on time.
W hen the TCM detects a continuous open or short to ground in the TCC PW M solenoid valve control circuit, then
DTC P2764 sets. DTC P2764 is a type A DTC.
Refer to 2 W iring Diagrams and Connector Chart to aid in diagnosis.
Conditions for Running the DTC
• The system voltage is 8 – 18 V.
• The engine speed is 500 r.p.m. for 5 seconds.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
DTC P2764 sets when either of the following conditions occurs for 5 seconds:
• The TCM detects an open in the TCC PWM shift solenoid valve circuit when the TCC PW M is commanded on.
• The TCM detects a short to ground in the TCC PWM shift solenoid valve circuit when the TCC PWM is
commanded on.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
• The TCM requests the ECM to illuminate the MIL during the second consecutive trip in which the Conditions for
Setting the DTC are met.
• The TCM commands maximum line pressure.
• The TCM freezes transmission adaptive functions.
• The TCM inhibits TCC engagement.
• The TCM inhibits 4th gear if in hot mode.
• At the time of the first failure, the TCM records the operating conditions when the conditions for setting the DTC are
met. The TCM stores this information as a Failure Record.
• At the time of the second failure, the ECM records the operating conditions when the conditions for setting the DTC
are met. The ECM stores this information as a Freeze Frame.
• The TCM stores DTC P2764 in TCM history during the second consecutive trip in which the conditions for setting
the DTC are met.
Conditions for Clearing the DTC
• The ECM turns off the MIL after the fourth consecutive drive trip in which the TCM does not send a MIL illumination
request.
• Tech 2 can clear the DTC.
• The TCM clears the DTC from TCM history if the vehicle completes 40 warm-up cycles without a non-emission
related diagnostic fault occurring.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007