2007 FORD FIESTA ESP
[x] Cancel search: ESPPage 855 of 1226

303-05-1 7 Accessory Drive 303-05-1 7
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
REFER to: Accessory Drive Belt Tensioner -
1.6L Duratorq-TDCi (DV) Diesel, Vehicles i With: Air Conditioning (303-05, Removal and
Installation).
REFER to: Accessory Drive Belt Tensioner
-
1.6L Duratorq-TDCi (DV) Diesel (303-05
Accessory Drive, Removal and lnstallation).
TEST the system for normal operation.
2. Detach the accessory drive belt in the area of
the accessory drive belt tensioner.
3. N0TE:The accessory drive belt tensioner
has a damping feature, which is usually a
friction device, therefore some friction within
the system is normal.
Using the correct tool, move the accessory drive
belt tensioner from its relaxed position through
its full stroke and back to the relaxed position
to make sure there is no excessive stick, grab
or bind, and to make sure there is tension on
the accessory drive belt tensioner spring.
4. Rotate the accessory drive belt tensioner pulley
and check for damage, freedom of rotation and
alignment. INSTALL a new accessory drive belt
tensioner as necessary.
Accessory Drive Belt Tensioner - Dynamic
Check
The accessory drive belt tensioner may be checked
dynamically as follows:
1. With the engine running, observe the accessory
drive belt tensioner movement. The accessory
drive belt tensioner should move (respond)
when the engine is accelerated rapidly or when
the
A/C clutch cycles ON and OFF (the degree
of movement can be up to 4 mm). If the
accessory drive belt tensioner movement is not
constant without engine acceleration or
A/C
clutch cycling, a pulley or shaft is possibly bent,
out of round, or the damping mechanism inside
the accessory drive belt tensioner may be
damaged. INSTALL a new accessory drive belt
tensioner as necessary.
REFER to: Accessory Drive Belt Tensioner
-
1.6L Duratorq-TDCi (DV) Diesel, Vehicles
With: Air Conditioning (303-05, Removal and
Installation).
REFER to: Accessory Drive Belt Tensioner -
1.6L Duratorq-TDCi (DV) Diesel (303-05
Accessory Drive, Removal and lnstallation).
( :I. REFER to: Accessory Drive Belt Tensioner - TEST the system for normal operation.
1.6L Duratorq-TDCi (DV) Diesel, Vehicles
2. Excessive accessory drive belt rideout (uneven
With: Air Conditioning (303-05, Removal and
depth of grooves in the accessory drive belt)
Installation). may cause excessive accessory drive belt
REFER to: Accessory Drive Belt Tensioner
- tensioner movement. Check the condition by
1.6L Duratorq-TDCi (DV) Diesel (303-05
installing a new accessory drive belt.
Accessory Drive, Removal and
installation). . REFER to: Accessory Drive Belt - 1.3~
TEST the system for normal operation. Duratec-8V (Rocam) (303-05 Accessory
Drive,
5. If the accessory drive belt tensioner meets the
above criteria, proceed to test the accessory
drive belt tensioner dynamically. If the accessory
drive belt tensioner does not meet the above
criteria, INSTALL a new accessory drive belt
tensioner.
REFER to: Accessory Drive Belt Tensioner
-
1.6L Duratorq-TDCi (DV) Diesel, Vehicles
With: Air Conditioning (303-05, Removal and
Installation).
REFER to: Accessory Drive Belt Tensioner
-
1.6L Duratorq-TDCi (DV) Diesel (303-05
Accessory Drive, Removal and Installation).
TEST the system for normal operation. Removal and Installation).
REFER to: Accessory Drive Belt
- 1.4L
Duratorq-TDCi (DV) Diesel (303-05 Accessory
Drive, Removal and Installation).
REFER to: Accessory Drive Belt - 1.6L
Duratorq-TDCi (DV) Diesel (303-05 Accessory
Drive, Removal and Installation).
REFER to: Accessory Drive Belt
- 2.OL
Duratec-H E (M 14) (303-05 Accessory Drive,
Removal and Installation).
TEST the system for normal operation.
2006.0 Fiesta 12/2006 G346263en
procarmanuals.com
Page 940 of 1226

Electronic Engine Controls
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
detected in either the STFT or LTFT, and it is still
present on a second trip, the MIL will be switched
on.
Heated Oxygen Sensor (H02S) Monitor (All except
vehicles with diesel engine)
This monitors the operation of the pre (upstream)
and post (downstream) catalytic converter
H02S
sensors. It will detect deviations in airlfuel ratios
(AFR) and sensor faults.
The
H02S will cause emission increase when its
response time increases too much. To diagnose
a sensor a period is measured and the number of
leanlrich transitions are counted. The sum of valid
periods is then calculated. To avoid
non-representative measurements, the period is
valid only if the
H02S has been below a low
threshold and above a high threshold between 2
consecutive leanlrich transitions.
A failure is
declared when the sum of the measured periods
exceeds the sum of the corresponding limit (held
within the PCM) and the MIL is illuminated.
Catalytic Converter Efficiency Monitor (All except
vehicles with diesel engine)
The efficiency of a catalytic converter is measured
by its ability to store and later release oxygen to
convert harmful gases. The efficiency is reduced
if the converter becomes contaminated as it ages,
and at high gas flow rates, because the exhaust
gas does not remain in the converter long enough
to complete the conversion process. switches
over or until the end of a delay. If this
delay expires or the sensor does not switch, the
sensor is treated as failed.
Combustion Noise Monitor (Vehicles with common
rail fuel injection)
In diesel variants, the Combustion Noise Monitor
is used to trim the fuel injection pulse lengths. Each
fuel injector has an associated set of correction
data that is determined during a production end of
line test. The Combustion Noise Monitor is used
to determine how the fuel injector characteristic
changes from this initial calibration over the life of
the fuel injector.
EGR Monitor (Vehicles with diesel engine)
The functionality of the EGR system is checked by
comparing either the MAP sensor output or EGR
valve lift potentiometer output (depending upon
application) with expected values.
Diagnostic Requirements
Vehicles equipped with EOBD, can be diagnosed
using the WDS. In order for the EOBD system to
be invoked, a number of criteria must be met. After
any repair, which could affect emissions, a trip must
be carried out on the vehicle, to make sure that
engine management system operates correctly.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
The MIL is located in the instrument cluster and is
fitted to alert the driver to the fact that an abnormal
This monitor checks for the oxygen storage condition
has developed in the engine management
capacity (OSC) of the catalytic converter. During system,
that is having an adverse effect on
a controlled period, the catalyst monitor sensor emissions.
In cases of misfires which are likely to
signal is analyzed to evaluate the OSC of the cause
catalytic converter damage, it is switched
catalyst. It represents the quantity of oxygen that on immediately.
With all other faults it will illuminate
is really used for the oxidation-reduction reaction continuously
from the second trip after the condition
by the catalytic converter If a fault has occurred occurred.
Under normal operation it should
with the catalyst monitor sensor during the catalyst illuminate
at key-on and go out almost as soon as
diagnosis, a sensor diagnosis is carried out. During the
engine is started.
the controlled diagnosis phase, the catalyst monitor
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) sensor activity is measured and is compared to the
OSC of the catalyst. If this activity is high (low The
DTCs given
by the PCM are standardized,
0SC)theMILwillbeilluminated.Ifthroughoutthe whichmeansthatgenericscantoolscanread
controlled phase, repeated several times, the results from
all vehicles.
downstream sensor output has not moved, the
closed loop mode is delayed in order to test the
sensor. If the catalyst monitor sensor is set to rich,
the injection time is forced to lean and conversely
if the downstream sensor is set to lean, the
injection time is forced to rich until the sensor
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G384566en
procarmanuals.com
Page 942 of 1226

303-1 4-1 8 Electronic Engine Controls 303-1 4-1 8
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
I PO123 I TP sensor circuit I high input I
MIL Code
PO119
PO 1 22
I PO130 I H02S circuit open circuit I
Description
ECT intermittent failure
Throttle position
(TP) sensor circuit 1 low input
I PO131 I H02S circuit low voltage I
pol34 r- HO~S IOW amplitude I
PO1 32
PO1 33
I PO136 I Catalyst monitor sensor circuit open circuit I
H02S circuit high voltage
H02S circuit slow response
I PO137 I Catalyst monitor sensor circuit low voltage I
PO1 38
PO1 39
I PO172 I Fuel system error, rich limit I
Catalyst monitor sensor circuit high voltage
Catalyst monitor sensor circuit slow response
PO171
PO171
Fuel system error, lean limit
Fuel system error
, NOx emissions
PO172
PO201
I PO203 I Cylinder No. 3 - injector circuit open circuit I
Fuel system error, HClCO emissions
Cylinder No.
I - injector circuit open circuit
PO202
I PO204 I Cylinder No. 4 - injector circuit open circuit I
Cylinder No. 2 - injector circuit open circuit
-1 TP sensor circuit 2 low input I
1 PO223 1 TP sensor circuit 2 high input I
I PO231 I Fuel pump input low voltage I
PO232
PO261
Fuel pump input high voltage
Cylinder No.
1 - injector circuit low voltage
PO262
PO264
1 PO267 1 Cylinder No. 3 - injector circuit low voltage I
Cylinder No. 1 - injector circuit high voltage
Cylinder No.
2 - injector circuit low voltage
PO265
1 PO268 1 Cylinder No. 3 - injector circuit high voltage I
-- -
Cylinder No. 2 - injector circuit high voltage I
I . PO270 I Cylinder No. 4 - injector circuit low voltage I
PO271
PO300
Cylinder No. 4 - injector circuit high voltage
Random misfire detected
PO301
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G384566en
Cylinder No. 1 misfire detected
PO302
-- -
Cylinder No. 2 misfire detected
procarmanuals.com
Page 945 of 1226

303-1 4-21 Electronic Engine Controls 303-1 4-21
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
lnspection and Verification
MIL Code
U0121
U0122
U0155
B1213
B1600
B1601
B1602
B1681
B2103
B2139
B2141
B2431
U2510
1. Verify the customer concern by operating the
( I system.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of mechanical
or electrical damage. Description
CAN missing frame from ABS
CAN missing frame from ESP
CAN missing frame from HEC
Number of Passive Anti-Theft System (PATS) programmed keys is below minimum
PATS ignition key transponder signal is not received
PATS received incorrect key-code from ignition key transponder
PATS received invalid format of key-code from ignition key transponder
PATS transceiver module signal is not received
PATS immobilizer antenna not connected
PATS immobilizer challenge response doesn't match
PATS immobilizer no PCM-ID transferred
PATS immobilizer transponder programming failure
PATS immobilizer problem with messages on data link
Visual Inspection Chart
Mechanical
I Electrical
- Sensors
- Actuators - Wiring harness
- Electrical
connector(s)
- Powertrain control
module (PCM)
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported
concern is found, correct the cause (if possible)
before proceeding to the next step.
4. If the cause is not visually evident, verify the
symptom and refer to WDS or equivalent scan
tool for further diagnostics.
- -
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G384566en
procarmanuals.com
Page 968 of 1226
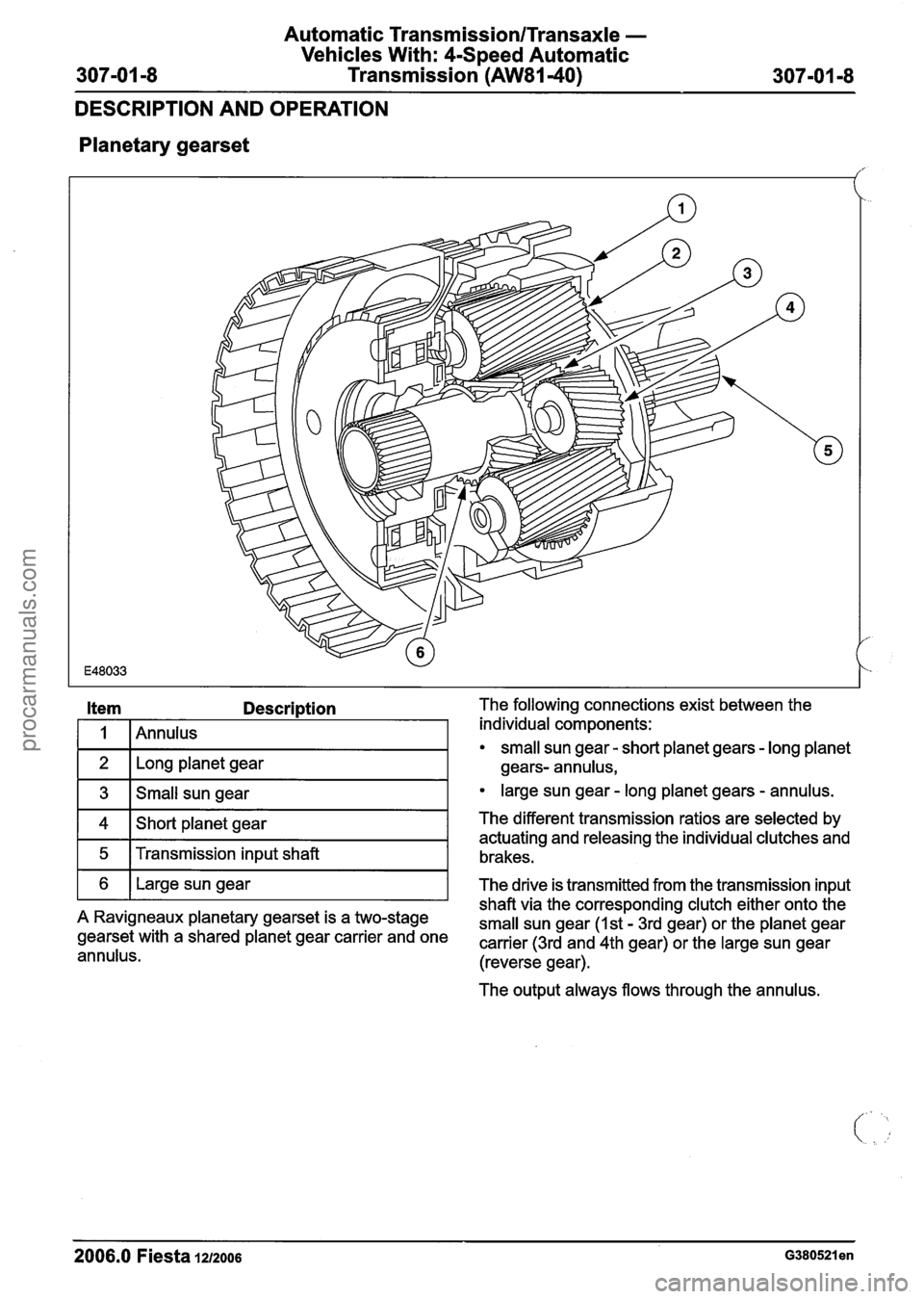
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle -
Vehicles With: 4-Speed Automatic
Transmission
(AW81-40) 307-01 -8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Planetary
gearset
Description The following connections exist between the
/ individual components:
small sun gear - short planet gears - long planet
Long planet gear gears- annulus,
3 Small sun gear large sun gear - long planet gears - annulus.
4
5
The output always flows through the annulus.
6
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 ~380521 en
Short planet gear
Transmission input shaft The different transmission ratios
are selected by
actuating and releasing the individual clutches and
brakes.
shaft via the corresponding clutch either onto the
A Ravigneaux planetary gearset is a two-stage
small sun gear (1st - 3rd gear) or the planet gear gearset with a shared planet gear carrier and one carrier (3rd and 4th gear) or the large sun gear annulus. (reverse gear).
Large sun gear
The drive is transmitted from the transmission input
procarmanuals.com
Page 991 of 1226

Automatic TransmissionlTransaxle -
Vehicles With: 4-Speed Automatic
307-01 -31 Transmission (AW81-40) 307-01 -31
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
The transmission control unit determines hill climb
mode or trailer operation from the change in throttle
; valve position supplied by the PCM in relation to
the acceleration of the vehicle.
Depending on the driving resistance, the
transmission control unit chooses between two
gearshift maps which have been specially
programmed for this purpose and in which the shift
timings are again chosen as a function of the
accelerator pedal position and the vehicle speed..
Hill descent mode
The hill descent mode is used to take better
advantage of engine braking during hill descents.
A 'hill descent' situation is recognised by the
transmission control unit if the vehicle is
accelerating without operation of the accelerator
pedal.
If in addition the brake is also depressed then the
transmission control unit automatically shifts back
from 4th into 3rd gear.
( ' Cold start mode
In order to reach operating temperature as quickly
as possible under low ambient temperatures,
gearshifts into 4th gear and engagement of the
torque converter clutch (TCC) are suppressed if
one of the following conditions is met:
Transmission fluid temperature below +20 "C
Coolant temperature below - 40°C
The following are actuated: SSA shift solenoid valve,
SSB shift solenoid valve,
Shift solenoid valve, TCC.
Overheating protection mode
The overheating protection mode serves to protect
the transmission against overheating and the
serious damage that this can cause.
If the transmission fluid temperature reaches a
temperature of around 135
"C, the transmission
control employs a shift pattern designed to prevent
a further increase in the transmission fluid
temperature. When
the transmission fluid temperature drops
back below approx. 125
"C, the transmission
control exits the overheating protection mode.
The MIL warning lamp is actuated by the
transmission control unit if the transmission fluid
temperature reaches approximately 140
"C.
The MIL warning lamp goes out again when the
transmission fluid temperature drops back to below
around 130
"C.
Main line pressure control
In order to ensure the highest possible efficiency
of the automatic transmission and to limit the power
losses from the fluid pump, the main line pressure
is adapted accordingly by the main regulating valve
as a function of the accelerator pedal position
(driver torque demand) and the selector lever
position.
This is influenced by the following variables:
Accelerator pedal position and actuation
Selector lever position
The following are actuated:
Main 'regulating valve
Engagement of the TCC
The TCC is engaged in 3rd and 4th gear depending
on the current driving situation.
Engagement is controlled in accordance with the
shift map stored in the control unit.
This is influenced by the following variables:
Accelerator pedal position and actuation,
Vehicle speed,
Selector lever position,
Transmission fluid temperature,
Coolant temperature.
The following are actuated:
Shift solenoid valve, TCC.
Torque reduction during gearshifts
In order to improve the quality of gearshifts and to
avoid gearshift judder, the engine torque is reduced
by the PCM in response to a request from the
transmission control unit during gearshifts.
The engine torque is also reduced during
engagement and disengagement of the TCC.
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G380530en
procarmanuals.com
Page 992 of 1226

Automatic Transmission/Transaxle -
Vehicles With: 4-Speed Automatic
307-01 -32 Transmission
(AW81-40) 307-01 -32
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
This is influenced by the following variables:
Engine speed,
Engine load,
Transmission input speed,
Vehicle speed.
The following are actuated:
PCM (torque reduction request signal via the
CAN databus).
Pressure control during gearshifts
In order to ensure that the engagement of the
clutches and brakes is as judder-free as possible,
the main line pressure is reduced during gearshifts.
This is influenced by the following variables:
Enginespeed,
Engine load,
Transmission input speed,
Vehicle speed.
The following are actuated:
Main regulating valve.
Shift timing adaptation during upshifts
In order to ensure that the engagement of the
clutches and brakes is as judder-free as possible,
the timing of the gearshift processes is monitored
during upshifts.
In the event of any discrepancy from the target
values, the main line pressure is adapted
accordingly during the next gearshift.
The shift timing adaptation during upshifts is only
active at transmission fluid temperatures between
50
"C and 120 "C.
This is influenced by the following variables:
Engine load,
Accelerator pedal position,
Transmission input speed,
Vehicle speed,
Transmission fluid temperature,
Selector lever position.
The following are actuated:
Main regulating valve.
Shift timing adaptation during shifts from
3rd to 4th gear
The shift from 3rd gear into 4th gear is the only
gearshift during which a clutch is disengaged and
a brake is engaged simultaneously.
In order to control the synchronized switching of
the two components as exactly as possible, the
shifl timing solenoid valve is actuated accordingly.
In order to ensure that this particular gearshift is
performed as judder-free as possible throughout
the service life of the transmission, the gearshift is
monitored by the two rotational speed sensors and
the actuation of the shift timing solenoid valve is
adapted accordingly.
The shift timing adaptation for gearshifts from 3rd
gear into 4th gear is only active at transmission
fluid temperatures between 30
"C and 120 "C.
This is influenced by the following variables:
Engine load,
Accelerator pedal position,
Transmission input speed,
Vehicle speed,
Transmission fluid temperature,
Selector lever position.
The following are actuated:
Shift timing solenoid valve.
Shift timing adaptation during shifts from
4th to 3rd gear
The shift from 4th gear into 3rd gear is the only
gearshift during which a brake is disengaged and
a clutch is engaged simultaneously.
In order to control the engagement of the clutch as
precisely as possible, the main regulating valve is
actuated accordingly in order to build up the
actuating pressure at exactly the right time.
In order to ensure that this particular gearshift is
performed as judder-free as possible throughout
the service life of the transmission, the gearshift is
monitored by the two rotational speed sensors and
the actuation of the main regulating valve is
adapted accordingly.
The shift timing adaptation for gearshifts from 4th
-
gear into 3rd gear is only active at transmission (
fluid temperatures between 20 "C and 120 "C. .
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G380530en
procarmanuals.com
Page 993 of 1226

Automatic Transmission/Transaxle -
Vehicles With: 4Speed Automatic
307-01 -33 Transmission (AW81-40) 307-01 -33
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
This is influenced by the following variables: Vehicle
speed,
Engine load, Transmission fluid temperature.
Accelerator pedal position, The following are actuated:
Transmission input speed, SSA shift solenoid valve,
Vehicle speed,
Transmission fluid temperature,
Selector lever position.
The
following are actuated:
Main
regulating valve.
Reverse gear safety strategy
SSB shift solenoid valve.
Torque reduction when pulling away
In order to protect the clutches against excessively
high torque when pulling away, the PCM reduces
the engine torque in response to a request from
the transmission
control.
If the accelerator pedal is depressed while the
The transmission control unit prevents shifts into vehicle is pulling away, then the transmission reverse gear while the vehicle is driving forwards, control unit sends a corresponding signal as otherwise serious transmission damage can be requesting a torque reduction via the CAN databus. caused.
The reverse gear safety strategy is active when This
is influenced by the
following variables:
reverse gear is engaged with the selector lever at ' Selector lever position,
vehicle speeds in excess of 11 kmlh. Accelerator pedal position,
In this
case the transmission control unit actuates ' Engine speed,
the shift timing solenoid valve, as a result of which Transmission input speed,
the actuating pressure does not reach the reverse
. Vehicle speed. gear clutch or the reverse gear brake.
The following are actuated:
The reverse gear safety strategy is deactivated
PCM (torque reduction request signal via the
when the vehicle speed is below 9 kmlh. The
actuating pressure can then reach the reverse gear CAN
databus).
clutch and the reverse gear brake and the gearshift
into reverse gear is performed.
Selector lever positions
This is influenced by the following variables:
Vehicle speed,
Selector lever position.
The
following are actuated:
Shift timing solenoid valve.
Selector lever position "P"
No gear is engaged in selector lever position "P".
The parking
pawl is engaged manually via the
selector lever cable and the selector shaft.
Avoidance of gearshift judder during
engagement of a transmission range Selector
lever position "R"
In order to prevent gearshift judder when moving The reverse gear is eWaged in selector lever
the selector lever from N to D, the transmission position "R.
control unit initially shifts into
2nd gear instead of
1 st gear, and then immediately shifts back into I st
gear before the gearshift process is finished. Selector lever position "N"
This reduces the amount of gearshift judder during No gear is engaged in selector lever position WNW. engagement of a forward drive range.
The powertrain is not blocked. This is influenced by the following variables:
Selector lever position,
Accelerator pedal position,
Transmission input speed,
2006.0 Fiesta 1212006 G380530en
procarmanuals.com