2006 SUZUKI SX4 meter
[x] Cancel search: meterPage 14 of 1556
![SUZUKI SX4 2006 1.G Service Workshop Manual Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 00-7 Precautions:
Precautions in Servicing 4WD ModelS6RW0D0000014
CAUTION!
• Never perform any of the following [A], [B]
and [C] types of SUZUKI SX4 2006 1.G Service Workshop Manual Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 00-7 Precautions:
Precautions in Servicing 4WD ModelS6RW0D0000014
CAUTION!
• Never perform any of the following [A], [B]
and [C] types of](/manual-img/20/7612/w960_7612-13.png)
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 00-7 Precautions:
Precautions in Servicing 4WD ModelS6RW0D0000014
CAUTION!
• Never perform any of the following [A], [B]
and [C] types of service work.
If it is performed while 4WD-auto mode or
4WD-lock mode is selected, front wheels
(or rear wheels) drive rear wheels (or front
wheels) and vehicle accident, drivetrain
damage and personal injury may result.
Also, if it is performed while 2WD mode is
selected, the coupling may be damaged
because of the difference in revolution
speed between front wheels and rear
wheels.
• When testing with 2-wheel chassis
dynamometer or speedometer tester, be
sure to select 4WD system to 4WD-auto
mode or 4WD-lock mode and use 2-wheel
free roller together or make the vehicle as
front wheel drive by removing propeller
shaft.• When testing with 2-wheel brake tester, be
sure to observe the following instructions.
Otherwise, drivetrain damage and personal
injury may result.
– Shift transaxle to N (Neutral) position.
– Select 4WD system to 2WD mode.
– Run engine at specified idle speed.
– Rotate wheels (tires) by brake tester at
vehicle speed below 5 km/h (3 mile/h).
– Do not rotate wheels (tires) for 1 min. or
more.
• When using On-vehicle type wheel
balancing equipment (1), be sure to select
4WD system to 4WD-auto mode or 4WD-
lock mode and jack up all four wheels, off
the ground completely and support vehicle
with safety stands (2).
Be careful of other wheels, which will
rotate at the same time.
Using it with 2WD mode may damage
coupling.
• This vehicle should be towed under one of
the following conditions:
– With all wheels on a flatbed truck.
– With all wheels on the ground.
Precautions for Catalytic ConverterS6RW0D0000004
For vehicles equipped with a catalytic converter, use
only unleaded gasoline and be careful not to let a large
amount of unburned gasoline enter the converter or it
can be damaged.
• Conduct a spark jump test only when necessary,
make it as short as possible, and do not open the
throttle.
• Conduct engine compression checks within the
shortest possible time.
• Avoid situations which can result in engine misfire
(e.g. starting the engine when the fuel tank is nearly
empty.)[A]: Testing with 2-wheel chassis dynamometer or speedometer tester.
[B]: Driving front wheels, which are jacked up.
[C]: Towing under the condition where either front or rear wheels can not
rotate.
[A]
[B]
[C]
I3RH0A000004-03
I3RH01010062-01
Page 16 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 00-9 Precautions:
• When connecting connectors, also hold connectors
and put them together until they lock securely (a click
is heard).
• When installing the wiring harness, fix it with clamps
so that no slack is left.
• When installing vehicle parts, be careful so that the
wiring harness is not interfered with or caught by any
other part.
• To avoid damage to the harness, protect its part which
may contact against a part forming a sharp angle by
winding tape or the like around it.• Be careful not to touch the electrical terminals of parts
which use microcomputers (e.g. electronic control unit
like as ECM, PCM, P/S controller, etc.). The static
electricity from your body can damage these parts.
• Never connect any tester (voltmeter, ohmmeter, or
whatever) to electronic control unit when its coupler is
disconnected. Attempt to do it may cause damage to
it.
• Never connect an ohmmeter to electronic control unit
with its coupler connected to it. Attempt to do it may
cause damage to electronic control unit and sensors.
• Be sure to use a specified voltmeter / ohmmeter.
Otherwise, accurate measurements may not be
obtained or personal injury may result. If not specified,
use a voltmeter with high impedance (M Ω/V
minimum) or a digital type voltmeter.
• When taking measurements at electrical connectors
using a tester probe, be sure to insert the probe (2)
from the wire harness side (backside) of the
connector (1).
I2RH01010041-01
I2RH01010042-01
I2RH01010043-01
I2RH01010044-01
I3RM0A000004-01
I2RH01010046-01
Page 17 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Precautions: 00-10
• When connecting meter probe (2) from terminal side
of coupler (1) because it can’t be connected from
harness side, use extra care not to bend male
terminal of coupler of force its female terminal open
for connection.
In case of such coupler as shown connect probe as
shown to avoid opening female terminal.
Never connect probe where male terminal is
supposed to fit.
• When checking connection of terminals, check its
male half for bend and female half for excessive
opening and both for locking (looseness), corrosion,
dust, etc.
• Before measuring voltage at each terminal, check to
make sure that battery voltage is 11 V or higher. Such
terminal voltage check at low battery voltage will lead
to erroneous diagnosis.Air Bag WarningS6RW0D0000008
WARNING!
For vehicles equipped with Supplemental
Restraint (Air Bag) System:
• Service on and around the air bag system
components or wiring must be performed
only by an authorized SUZUKI dealer. Refer
to “Air Bag System Components, Wiring
and Connectors Location in Section 8B” in
order to confirm whether you are
performing service on or near the air bag
system components or wiring. Please
observe all WARNINGS in Air Bag System
section and “Precautions on Service and
Diagnosis of Air Bag System in Section
8B” before performing service on or
around the air bag system components or
wiring. Failure to follow WARNINGS could
result in unintentional activation of the
system or could render the system
inoperative. Either of these two conditions
may result in severe injury.
• Technical service work must be started at
least 90 seconds after the ignition switch is
turned to the LOCK position and the
negative cable is disconnected from the
battery. Otherwise, the system may be
activated by reserve energy in the Sensing
and Diagnostic Module (SDM).
Air Bag System Service WarningS6RW0D0000009
WARNING!
• Service on or around the air bag system
components or wiring must be performed
only by an authorized SUZUKI dealer.
Please observe all WARNINGS in Air Bag
System section and “Precautions on
Service and Diagnosis of Air Bag System
in Section 8B” before performing service
on or around the air bag system
components or wiring. Failure to follow
WARNINGS could result in unintended
activation of the system or could render
the system inoperative. Either of these two
conditions may result in severe injury.
• The procedures in the air bag system
section must be followed in the order
listed to disable the air bag system
temporarily and prevent false DTCs from
setting. Failure to follow procedures could
result in possible activation of the air bag
system, personal injury or otherwise
unneeded air bag system repairs.
I2RH01010047-01
I2RH01010048-01
Page 19 of 1556
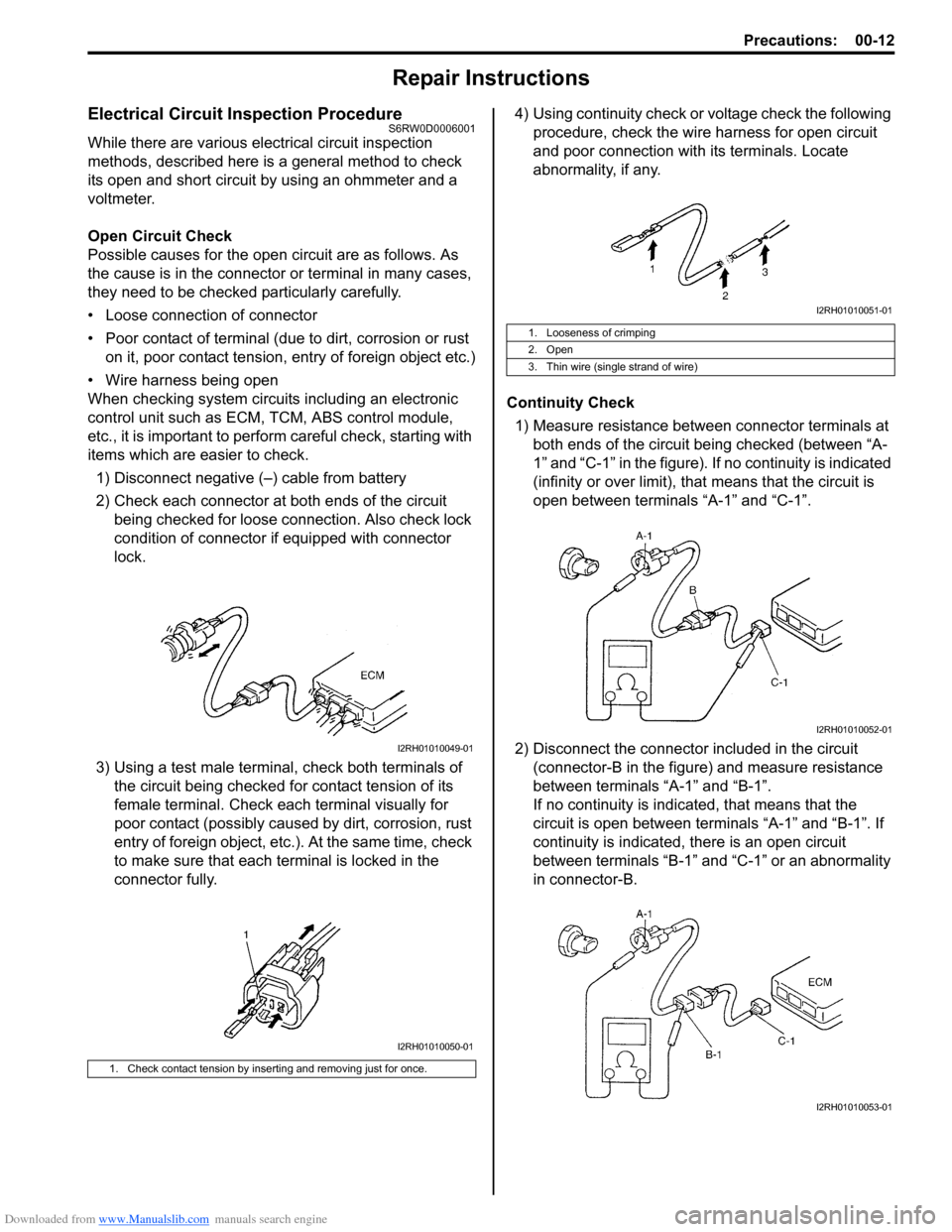
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Precautions: 00-12
Repair Instructions
Electrical Circuit Inspection ProcedureS6RW0D0006001
While there are various electrical circuit inspection
methods, described here is a general method to check
its open and short circuit by using an ohmmeter and a
voltmeter.
Open Circuit Check
Possible causes for the open circuit are as follows. As
the cause is in the connector or terminal in many cases,
they need to be checked particularly carefully.
• Loose connection of connector
• Poor contact of terminal (due to dirt, corrosion or rust
on it, poor contact tension, entry of foreign object etc.)
• Wire harness being open
When checking system circuits including an electronic
control unit such as ECM, TCM, ABS control module,
etc., it is important to perform careful check, starting with
items which are easier to check.
1) Disconnect negative (–) cable from battery
2) Check each connector at both ends of the circuit
being checked for loose connection. Also check lock
condition of connector if equipped with connector
lock.
3) Using a test male terminal, check both terminals of
the circuit being checked for contact tension of its
female terminal. Check each terminal visually for
poor contact (possibly caused by dirt, corrosion, rust
entry of foreign object, etc.). At the same time, check
to make sure that each terminal is locked in the
connector fully.4) Using continuity check or voltage check the following
procedure, check the wire harness for open circuit
and poor connection with its terminals. Locate
abnormality, if any.
Continuity Check
1) Measure resistance between connector terminals at
both ends of the circuit being checked (between “A-
1” and “C-1” in the figure). If no continuity is indicated
(infinity or over limit), that means that the circuit is
open between terminals “A-1” and “C-1”.
2) Disconnect the connector included in the circuit
(connector-B in the figure) and measure resistance
between terminals “A-1” and “B-1”.
If no continuity is indicated, that means that the
circuit is open between terminals “A-1” and “B-1”. If
continuity is indicated, there is an open circuit
between terminals “B-1” and “C-1” or an abnormality
in connector-B.
1. Check contact tension by inserting and removing just for once.
I2RH01010049-01
I2RH01010050-01
1. Looseness of crimping
2. Open
3. Thin wire (single strand of wire)
I2RH01010051-01
I2RH01010052-01
I2RH01010053-01
Page 24 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 0A-1 General Information:
General Information
General Information
General Description
AbbreviationsS6RW0D0101001
A:
ABDC: After Bottom Dead Center
ABS: Anti-lock Brake System
AC: Alternating Current
A/C: Air Conditioning
A-ELR: Automatic-Emergency Locking Retractor
A/F: Air Fuel Mixture Ratio
ALR: Automatic Locking Retractor
API: American Petroleum Institute
APP sensor: Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor
A/T: Automatic Transmission, Automatic Transaxle
AT D C : After Top Dead Center
ATF: Automatic Transmission Fluid, Automatic
Transaxle Fluid
B:
B+: Battery Positive Voltage
BBDC: Before Bottom Dead Center
BCM: Body Electrical Control Module
BTDC: Before Top Dead Center
C:
CAN: Controller Area Network
CKT: Circuit
CKP Sensor: Crankshaft Position Sensor
CMP Sensor: Camshaft Position Sensor
CO: Carbon Monoxide
CPP Switch: Clutch Pedal Position Switch (Clutch
Switch, Clutch Start Switch)
CPU: Central Processing Unit
CRS: Child Restraint System
D:
DC: Direct Current
DLC: Data Link Connector (Assembly Line Diag. Link,
ALDL, Serial Data Link, SDL)
DOHC: Double Over Head Camshaft
DOJ: Double Offset Joint
DRL: Daytime Running Light
DTC: Diagnostic Trouble Code (Diagnostic Code)
E:
EBCM: Electronic Brake Control Module, ABS Control
Module
EBD: Electronic Brake Force Distribution
ECM: Engine Control Module
ECT Sensor: Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
(Water Temp. Sensor, WTS)
EFE Heater: Early Fuel Evaporation Heater (Positive
Temperature Coefficient, PTC Heater)
EGR: Exhaust Gas Recirculation
EGRT Sensor: EGR Temperature Sensor (Recirculated
Exhaust Gas Temp. Sensor, REGTS)
EPS: Electronic Power Steering
EVAP: Evaporative Emission
EVAP Canister: Evaporative Emission Canister
(Charcoal Canister)F:
4WD: 4 Wheel Drive
G:
GEN: Generator
GND: Ground
GPS: Global Positioning System
H:
HAVC: Heating, Ventilating and Air Conditioning
HC: Hydrocarbons
HO2S: Heated Oxygen Sensor
I:
IAC Valve: Idle Air Control Valve (Idle Speed Control
Solenoid Valve, ISC Solenoid Valve)
IAT Sensor: Intake Air Temperature Sensor (Air
temperature Sensor, ATS)
ICM: Immobilizer Control Module
IG: Ignition
ISC Actuator: Idle Speed Control Actuator
L:
LH: Left Hand
LHD: Left Hand Drive vehicle
LSPV: Load Sensing Proportioning Valve
M:
MAF Sensor: Mass Air Flow Sensor (Air Flow Sensor,
AFS, Air Flow Meter, AFM)
MAP Sensor: Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor
(Pressure Sensor, PS)
Max: Maximum
MFI: Multiport Fuel Injection (Multipoint Fuel Injection)
Min: Minimum
MIL: Malfunction Indicator Lamp (“SERVICE ENGINE
SOON” Light)
M/T: Manual Transmission, Manual Transaxle
N:
NOx: Nitrogen Oxides
O:
OBD: On-Board Diagnostic System (Self-Diagnosis
Function)
O/D: Overdrive
OHC: Over Head Camshaft
O2S: Oxygen Sensor
P:
PCM: Powertrain Control Module
PCV: Positive Crankcase Ventilation
PNP: Park / Neutral Position
P/S: Power Steering
PSP Switch: Power Steering Pressure Switch (P/S
Pressure Switch)
R:
RH: Right Hand
RHD: Right Hand Drive vehicle
Page 26 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 0A-3 General Information:
There are two kinds of colored wire used in this vehicle. One is single-colored wire and the other is dual-colored
(striped) wire.
The single-colored wire uses only one color symbol (i.e. “GRN”).
The dual-colored wire uses two color symbols (i.e. “GRN/YEL”). The first symbol represents the base color of the wire
(“GRN” in the figure) and the second symbol represents the color of the stripe (“YEL” in the figure).
Fasteners InformationS6RW0D0101004
Metric Fasteners
Most of the fasteners used for this vehicle are JIS-
defined and ISO-defined metric fasteners. When
replacing any fasteners, it is most important that
replacement fasteners be the correct diameter, thread
pitch and strength.
CAUTION!
Even when the nominal diameter (1) of thread
is the same, the thread pitch (2) or the width
across flats (3) may vary between ISO and
JIS. Refer to JIS-TO-ISO Main Fasteners
Comparison Table below for the difference.
Installing a mismatched bolt or nut will cause
damage to the thread.
Before installing, check the thread pitch for
correct matching and then tighten it by hand
temporarily. If it is tight, recheck the thread
pitch.
JIS-TO-ISO Main Fasteners Comparison TableFastener Strength Identification
Most commonly used metric fastener strength property
classes are 4T, 6.8, 7T, 8.8 and radial line with the class
identification embossed on the head of each bolt. Some
metric nuts will be marked with punch, 6 or 8 mark
strength identification on the nut face. Figure shows the
different strength markings.
When replacing metric fasteners, be careful to use bolts
and nuts of the same strength or greater than the original
fasteners (the same number marking or higher). It is
likewise important to select replacement fasteners of the
correct diameter and thread pitch. Correct replacement
bolts and nuts are available through the parts division.
Metric bolts: Identification class numbers or marks
correspond to bolt strength (increasing numbers
represent increasing strength).
I2RH01010010-01
Nominal diameter
M6 M8 M10 M12 M14
JISThread pitch 1.0 1.25 1.25 1.25 1.5
Width across flats1012141719
ISOThread pitch 1.0 1.25 1.5 1.5 1.5
Width across flats1013161821
I4RH0A010005-01
1. Nut strength identification
I5RH01010001-01
Page 27 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine General Information: 0A-4
Standard Tightening Torque
Each fastener should be tightened to the torque specified in each section. If no description or specification is provided,
refer to the following tightening torque chart for the applicable torque for each fastener. When a fastener of greater
strength than the original one is used, however, use the torque specified for the original fastener.
NOTE
• For the flanged bolt, flanged nut and self-lock nut of 4T and 7T strength, add 10% to the tightening
torque given in the following chart.
• The following chart is applicable only where the fastened parts are made of steel light alloy.
Tightening torque chart
*:Self-lock nutStrength UnitThread diameter (Nominal diameter) (mm)
4 5 6 8 10 12 14 16 18
A equivalent of 4T strength fastener N⋅m 1.5 3.0 5.5 13 29 45 65 105 160
kgf-m 0.15 0.30 0.55 1.3 2.9 4.5 6.5 10.5 16
lb-ft 1.0 2.5 4.0 9.5 21.0 32.5 47.0 76.0 116.0
A equivalent of 6.8 strength fastener
without flangeN⋅m 2.4 4.7 8.4 20 42 80 125 193 280
kgf-m 0.24 0.47 0.84 2.0 4.2 8.0 12.5 19.3 28
lb-ft 2.0 3.5 6.0 14.5 30.5 58.0 90.5 139.5 202.5
A equivalent of 6.8 strength fastener
with flange
*: Self-lock nut (6 strength)N⋅m 2.4 4.9 8.8 21 44 84 133 203 298
kgf-m 0.24 0.49 0.88 2.1 4.4 8.4 13.3 20.3 29.8
lb-ft 2.0 3.5 6.5 15.5 32.0 61.0 96.5 147.0 215.5
A equivalent of 7T strength fastener N⋅m 2.3 4.5 10 23 50 85 135 210 240
kgf-m 0.23 0.45 1.0 2.3 5.0 8.5 13.5 21 24
lb-ft 2.0 3.5 7.5 17.0 36.5 61.5 98.0 152.0 174.0
A equivalent of 8.8 strength bolt (8
strength nut) without flangeN⋅m 3.1 6.3 11 27 56 105 168 258 373
kgf-m 0.31 0.63 1.1 2.7 5.6 10.5 16.8 25.8 37.3
lb-ft 2.5 4.5 8.0 19.5 40.5 76.0 121.5 187.0 270.0
A equivalent of 8.8 strength bolt (8
strength nut) with flangeN⋅m 3.2 6.5 12 29 59 113 175 270 395
kgf-m 0.32 0.65 1.2 2.9 5.9 11.3 17.5 27 39.5
lb-ft 2.5 5.0 9.0 21.0 43.0 82.0 126.5 195.5 286.0
I2RH01010012-01
I2RH01010013-01
I2RH01010014-01
I2RH01010015-01
I2RH01010016-01
I2RH01010017-01
Page 32 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 0B-1 Maintenance and Lubrication:
General Information
Maintenance and Lubrication
Precautions
Precautions for Maintenance and LubricationS6RW0D0200001
Air Bag Warning
Refer to “Air Bag Warning in Section 00”.
Scheduled Maintenance
Maintenance Schedule under Normal Driving ConditionsS6RW0D0205001
NOTE
• This interval should be judged by odometer reading or months, whichever comes first.
• This table includes service as scheduled up to 90,000 km (54,000 miles) mileage. Beyond 90,000 km
(54,000 miles), carry out the same services at the same intervals respectively.
IntervalKm (x 1,000) 15 30 45 60 75 90
Miles (x 1,000) 9 18 27 36 45 54
Months 12 24 36 48 60 72
Engine
Accessory drive belt (I: �), R: �))——I——R
Valve lash (clearance) (I: �))—I—I—I
Engine oil and oil filter (R: �)) RRRRRR
Engine coolant (R: �))——R——R
Exhaust system (I: �))—I—I—I
Ignition system
Spark plugs (R: �))When unleaded fuel is usedNickel Plug — — R — — R
Iridium Plug
(Highly recommended)Replace every 105,000 km (63,000
miles) or 84 months
When leaded fuel is used, refer to “Maintenance Recommended under Severe Driving
Conditions”.
Fuel system
Air cleaner filter (R: �), I: �))Paved-road I I R I I R
Dusty conditionsRefer to “Maintenance Recommended
under Severe Driving Conditions”.
Fuel lines and connections (I: �))—I—I—I
Fuel filter (see NOTE below) (R: �))Replace every 105,000 km (63,000
miles)
Fuel tank (I: �))——I——I
Emission control system
PCV valve (I: �)) ————— I
Fuel evaporative emission control system (I: �)) ————— I
Brake
Brake discs and pads (thickness, wear, damage) (I: �)) IIIIII
Brake drums and shoes (wear, damage) (I: �))—I—I—I
Brake hoses and pipes (leakage, damage, clamp) (I: �))—I—I—I
Brake fluid (R: �))—R—R—R
Brake lever and cable (damage, stroke, operation) (I: �))Inspect at first 15,000 km (9,000 miles
only)
Chassis and body
Clutch (fluid leakage, level) (I: �))—I—I—I
Tires (wear, damage, rotation) / wheels (damage) (I: �) / �)) IIIIII
Suspension system (tightness, damage, rattle, breakage) (I: �))—I—I—I
Steering system (tightness, damage, breakage, rattle) (I: �))—I—I—I
Drive shaft (axle) boots / Propeller shaft (4WD) (I: �)) (I: �))——I——I
Manual transaxle oil (leakage, level) (I: �) 1st 15,000 km only) (R: �))I—R——R