2006 SUZUKI SX4 Sensors
[x] Cancel search: SensorsPage 4 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine RECOMMENDATON OF GENUINE SUZUKI PARTS AND ACCESSORIES USE
SUZUKI strongly recommends the use of genuine SUZUKI parts* and accessories. Genuine SUZUKI parts and
accessories are built to the highest standards of quality and performance, and are designed to fit the vehicle’s
exact specifications.
A wide variety of non-genuine replacement parts and accessories for SUZUKI vehicles are currently available in
the market. Using these parts and accessories can affect the vehicle performance and shorten its useful life.
Therefore, installation of non-genuine SUZUKI parts and accessories is not covered under warranty.
Non-Genuine SUZUKI Parts and Accessories
Some parts and accessories may be approved by certain authorities in your country.
Some parts and accessories are sold as SUZUKI authorized replacement parts and accessories. Some genu-
ine SUZUKI parts and accessories are sold as re-use parts and accessories. These parts and accessories are
non-genuine Suzuki parts and accessories and use of these parts are not covered under warranty.
Re-use of Genuine SUZUKI Parts and Accessories
The resale or re-use of the following items which could give rise to safety hazards for users is expressly forbid-
den:
1) Airbag components and all other pyrotechnic items, including their components (e.g. cushion, control
devices and sensors)
2) Seatbelt system, including their components (e.g. webbing, buckles, and retractors)
The air bag and seat belt pretensioner components contain explosive chemicals. These components should be
removed and disposed of properly by SUZUKI authorized service shop or scrap yard to avoid unintended explo-
sion before scrapping.
*The parts remanufactured under SUZUKI's approval can be used as genuine SUZUKI parts in Europe.
Page 10 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 00-3 Precautions:
WARNING!
SDM
• For handling and storage of a SDM, select
a place where the ambient temperature
below 65 °C (150 °F), without high humidity
and away from electric noise.
• During service procedures, be very careful
when handling a Sensing and Diagnostic
Module (SDM). Never strike or jar the SDM.
• Never power up the air bag system when
the SDM is not rigidly attached to the
vehicle. All SDM and mounting bracket
fasteners must be carefully torqued and
the arrow must be pointing toward the
front of the vehicle to ensure proper
operation of the air bag system.
The SDM could be activated when powered
while not rigidly attached to the vehicle
which could cause deployment and result
in personal injury.
WARNING!
Driver and Passenger Seat Belt
Pretensioners
• For handling and storage of a live seat belt
pretensioner, select a place where the
ambient temperature below 65 °C (150 °F),
without high humidity and away from
electric noise.
• Never carry seat belt pretensioner by wire
or connector of pretensioner. When
placing a live seat belt pretensioner on the
workbench or some place like that, never
put something on seat belt pretensioner.
Otherwise, personal injury may result.
• Never dispose of live (inactivated) seat belt
pretensioners (drive and passenger). If
disposal is necessary, be sure to activate
them according to activation procedures
described in “Air Bag (Inflator) Module and
Seat Belt Pretensioner Disposal in Section
8B” before disposal.
• The seat belt pretensioner immediately
after activation is very hot. Wait for at least
half an hour to cool it off before
proceeding the work.
• With many service procedures, gloves and
safety glasses should be worn to prevent
any possible irritation of the skin or eyes.
• Even when the accident was light enough not to
cause air bags to activate, be sure to inspect system
parts and other related parts according to instructions
under “Repair and Inspection Required after Accident
in Section 8B”.
• When servicing parts other than air bag system, if
shocks may be applied to air bag system component
parts, remove those parts beforehand.
• When handling the air bag (inflator) modules (driver,
passenger, side and curtain), seat belt pretensioners
(driver and passenger), forward sensor, side sensors
or SDM, be careful not to drop it or apply an impact to
it. If an excessive impact was applied, never attempt
disassembly or repair but replace it with a new one.
• When grease, cleaning agent, oil, water, etc. has got
onto air bag (inflator) modules (driver, passenger, side
and curtain) or seat belt pretensioners (drive and
passenger), wipe off immediately with a dry cloth.
• Air bag wire harness is included in floor and
instrument panel wire harnesses. Air bag wire
harness branched off from floor and instrument panel
wire harnesses can be identified easily as it is covered
with a yellow protection tube and it has yellow
connectors. Be very careful when handling it.
• When an open in air bag wire harness, damaged wire
harness, connector or terminal is found, replace wire
harness, connectors and terminals as an assembly.
• Do not apply power to the air bag system unless all
components are connected or a diagnostic flow
requests it, as this will set a DTC.
• Never use air bag system component parts from
another vehicle.
• When using electric welding, be sure to disconnect all
air bag (inflator) module connectors and pretensioner
connectors from air bag wire harness respectively.
• Never expose air bag system component parts
directly to hot air (drying or baking the vehicle after
painting) or flames.
• WARNING / CAUTION labels are attached on each
part of air bag system components. Be sure to follow
the instructions.
• After vehicle is completely repaired, perform “Air Bag
Diagnostic System Check in Section 8B”.
General PrecautionsS6RW0D0000002
The WARNING and CAUTION describe some general
precautions that you should observe when servicing a
vehicle. These general precautions apply to many of the
service procedures, and they will not necessarily be
repeated with each procedure to which they apply.
Page 16 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 00-9 Precautions:
• When connecting connectors, also hold connectors
and put them together until they lock securely (a click
is heard).
• When installing the wiring harness, fix it with clamps
so that no slack is left.
• When installing vehicle parts, be careful so that the
wiring harness is not interfered with or caught by any
other part.
• To avoid damage to the harness, protect its part which
may contact against a part forming a sharp angle by
winding tape or the like around it.• Be careful not to touch the electrical terminals of parts
which use microcomputers (e.g. electronic control unit
like as ECM, PCM, P/S controller, etc.). The static
electricity from your body can damage these parts.
• Never connect any tester (voltmeter, ohmmeter, or
whatever) to electronic control unit when its coupler is
disconnected. Attempt to do it may cause damage to
it.
• Never connect an ohmmeter to electronic control unit
with its coupler connected to it. Attempt to do it may
cause damage to electronic control unit and sensors.
• Be sure to use a specified voltmeter / ohmmeter.
Otherwise, accurate measurements may not be
obtained or personal injury may result. If not specified,
use a voltmeter with high impedance (M Ω/V
minimum) or a digital type voltmeter.
• When taking measurements at electrical connectors
using a tester probe, be sure to insert the probe (2)
from the wire harness side (backside) of the
connector (1).
I2RH01010041-01
I2RH01010042-01
I2RH01010043-01
I2RH01010044-01
I3RM0A000004-01
I2RH01010046-01
Page 52 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-2 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
• When checking ECM for DTC, keep in mind that DTC
is displayed on the scan tool as follows depending on
the scan tool used.
– SUZUKI scan tool displays DTC detected by ECM.
– CAN communication OBD generic scan tool
displays DTC detected by each of ECM and TCM
(for A/T model) simultaneously.
• Priorities for diagnosing troubles
If two or more DTCs are stored, proceed to the DTC
flow which has been detected earliest in the order and
follow the instruction in that flow.
If no instructions are given, troubleshoot DTCs
according to the following priorities.
a. DTCs other than DTC P0171 / P0172 (Fuel
system too lean / too rich), DTC P0300 / P0301 /
P0302 / P0303 / P0304 (Misfire detected) and
DTC P0401 / P0402 (EGR flow malfunction)
b. DTC P0171 / P0172 (Fuel system too lean / too
rich) and DTC P0401 / P0402 (EGR flow
malfunction)
c. DTC P0300 / P0301 / P0302 / P0303 / P0304
(Misfire detected)
• Be sure to read “Precautions for Electrical Circuit
Service in Section 00” before inspection and observe
what is written there.
• ECM replacement:
When substituting a known-good ECM, check for the
following conditions. Neglecting this check may cause
damage to a known-good ECM.
– Resistance value of all relays, actuators is as
specified respectively.
– MAP sensor, A/C refrigerant pressure sensor (if
equipped with A/C), accelerator pedal position
(APP) sensor and TP sensor are in good condition
and none of power circuits of these sensors is
shorted to ground.
• Communication of ECM, BCM, combination meter,
keyless start control module (if equipped with keyless
start control system), 4WD control module (if
equipped), TCM (for A/T model) and ABS control
module, is established by CAN (Controller Area
Network). (For more detail of CAN communication for
ECM, refer to “CAN Communication System
Description”). Therefore, handle CAN communication
line with care referring to “Precaution for CAN
Communication System in Section 00”.
• Immobilizer transponder code registration after
replacing ECM (Immobilizer model)
When ECM is replaced with new one or with another
one, make sure to register immobilizer transponder
code to ECM correctly according to “Procedure after
ECM Replacement in Section 10C”.Precautions for DTC TroubleshootingS6RW0D1100003
• Before performed trouble shooting, be sure to read
the “Precautions of ECM Circuit Inspection”.
• When measuring circuit voltage, resistance and/or
pulse signal at ECM connector, connect the special
tool to ECM and/or the ECM connectors referring to
“Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits”.
• Upon completion of inspection and repair work,
perform “DTC Confirmation Procedure” and confirm
that the trouble has been corrected.
Precautions of ECM Circuit InspectionS6RW0D1100004
• ECM connectors are waterproofed. Each terminal of
the ECM connectors is sealed up with the grommet.
Therefore, when measuring circuit voltage, resistance
and/or pulse signal at ECM connector, do not insert
the tester’s probe into the sealed terminal at the
harness side. When measuring circuit voltage,
resistance and/or pulse signal at ECM connector,
connect the special tool to the ECM connectors. And,
insert the tester’s probe into the special tool’s
connectors at the harness side, and then measure
voltage, resistance and/or pulse signal. Or, ECM and
its circuits may be damaged by water.
• Wire colors of the special tool’s connectors are
different from the ones of the ECM connectors.
However, the circuit arrangement of the special tool’s
connectors is same as the one of the ECM
connectors. Therefore, measure circuit voltage and
resistance by identifying the terminal location subject
to the measurement.
Precautions of Electric Throttle Body System
Calibration
S6RW0D1100005
After performing one of works described below, it is
necessary to re-register the completely closed throttle
valve reference position stored in memory of ECM. (For
detailed information, refer to “Description of Electric
Throttle Body System Calibration”.) For the procedure to
register such data in ECM, refer to “Electric Throttle
Body System Calibration in Section 1C”.
• To shut off backup power of ECM for such purposes of
battery replacement or “DOME” fuse removal
• To erase DTCs P0122, P0123, P0222, P0223, P2101,
P2102, P2103, P2111, P2112, P2119 and/or P2135
• To replace ECM
• To replace throttle body and/or accelerator pedal
position (APP) sensor assembly
Page 54 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-4 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
Outline of troubleshooting
When there is a trouble with CAN, perform “Troubleshooting for Communication Error with Scan Tool Using CAN” and/
or “Troubleshooting for CAN-DTC”. Not using this procedure or performing troubleshooting in any other way may skip
some check points resulting in misdiagnosis or take a longer time than necessary.
1) Checking connector related to CAN
2) Checking CAN line
3) Checking each control module/sensor using “DTC check” or “Bus Check”
4) Checking power and ground connection of each control module/sensor
CAN-DTC
Even when DTC related to CAN (= CAN-DTC) as described below is detected, it is not possible to point out the
specific trouble point by CAN-DTC itself. Be sure to troubleshoot according to “Troubleshooting for CAN-DTC”.
CAN-DTC table
Communication with scan tool
• K line or CAN line is used for communication between each control module and scan tool.
Refer to “CAN schematic and routing diagram: ” to determine which line is used for communication between each
control module and scan tool.
• ECM and TCM use CAN line for communication with scan tool. Even if CAN has a trouble other than between DLC
and BCM, communication may also fail between scan tool and these control modules. In such case, perform
troubleshooting according to “Troubleshooting for Communication Error with Scan Tool Using CAN”.
• BCM, ABS control module and 4WD control module use K-line for communication with scan tool. Even if CAN has a
trouble, it is possible to communicate between scan tool and these control modules.
Bus check with SUZUKI scan tool
SUZUKI scan tool (SUZUKI-SDT) efficiently diagnoses a CAN bus malfunction by “Communication Bus Check” and
“Communication Malfunction DTC” under “Bus check”.
“Communication Bus Check” can display all control modules/sensors name communicated by CAN.
Also, “Communication Malfunction DTC” can display only CAN-DTC which is detected by the control modules (ECM
and TCM) communicating with scan tool using CAN line.
[A]: Non-Taiwan model [C]: CAN high line (RED) [E]: K-line
[B]: Taiwan model [D]: CAN low line (WHT)
No. Part Name Communication with scan tool Monitor of CAN-DTC
1. ABS control module K-line Not available
2. ECM CAN Available
3. TCM CAN Available
4. BCM K-line Available
5. Keyless start control module Not available Available
6. 4WD control module K-line Available
7. Combination meter Not available Not available
8. CAN junction connector — —
9. DLC — —
Detected Control Module CAN-DTC
ECM U0073/U0101/U0121/U0140/P1618
TCM U0073/U0100
BCM U0073/U0100/U0101/U0155/U1144
4WD control module U0073/U0100/U0121/U0155
Keyless start control module No.31/No.33
Page 58 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-8 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
For information about the following items, refer to “Euro
OBD model: ”.
• Warm-up cycle
• Driving cycle
• 2 driving cycle detection logic
• Pending DTC
Data Link Connector (DLC)S6RW0D1101011
NOTE
There are two types of OBD system
depending on the vehicle specification.
For identification, refer to “Precaution on On-
Board Diagnostic (OBD) System”.
DLC (1) is in compliance with SAE J1962 in the shape of
connector and pin assignment.
OBD CAN Hi line (6) and Low line (3) (CAN line of ISO
15765-4) are used for SUZUKI scan tool (SUZUKI-SDT)
(7) or CAN communication OBD generic scan tool to
communicate with ECM (included in immobilizer control)
and TCM (Transmission Control Module) (for A/T
model).
Engine and Emission Control System
Description
S6RW0D1101004
The engine and emission control system is divided into 4
major sub-systems: air intake system, fuel delivery
system, electronic control system and emission control
system.
Air intake system includes air cleaner, throttle body and
intake manifold.
Fuel delivery system includes fuel pump, delivery pipe,
etc.
Electronic control system includes ECM, various sensors
and controlled devices.
Emission control system includes EGR, EVAP and PCV
system.
3. DLC
1
2 3
I5RW0C110001-01
2. B + (Unswitched vehicle battery positive)
4. ECM ground (Signal ground)
5. Vehicle body ground (Chassis ground)
2
45 6
1
9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
7
3
1I7RW01110092-01
Page 61 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-11
Air Intake System DescriptionS6RW0D1101006
The main components of the air intake system are air cleaner (1), air cleaner outlet hose (2), electric throttle body (3)
(for the details, refer to “Description of Electric Throttle Body System”.), and intake manifold (4).
The air (by the amount corresponding to throttle valve (5) opening and engine speed) is filtered by the air cleaner,
distributed by the intake, and finally drawn into each combustion chamber. Electric throttle body is not equipped with
IAC valve for idle speed control. Idle speed control is done by the throttle actuator (6) which opens/closes the throttle
valve. (For the details, refer to “Description of Electric Throttle Body System”.)
Description of Electric Throttle Body System CalibrationS6RW0D1101007
ECM calculates controlled opening of the throttle valve on the basis of the completely closed throttle valve position of
the electric throttle body system. The completely closed position data is saved in memory of ECM. However, the
completely closed position of the throttle valve of the electric throttle body system (signal voltage from throttle position
sensor when throttle is completely closed) differs one from the other depending on individual differences of the throttle
valve and throttle position sensor. As such individual differences must be taken into account for controlling the throttle
valve, it is necessary to register the completely closed throttle valve position data in ECM. When such data is
registered in ECM, it is saved in RAM (memory) of ECM and used as the base data for controlling the throttle valve.
This data is cleared, when any of the works described in “Precautions of Electric Throttle Body System Calibration” is
performed.
Also, after replacement of the throttle body and/or APP sensor assembly, the completely closed position data in
memory of ECM must be cleared once and a new one must be registered, or ECM cannot judge the complete closure
position properly.
For the procedure to register such data, refer to “Electric Throttle Body System Calibration in Section 1C”. (After the
completely closed position data is cleared, ECM, for the first time only, opens and closes the throttle valve for about 5
seconds after the ignition switch is turned ON position, for registration of the completely closed throttle valve position.
If the engine is started during this registration process, such symptom as “longer cranking time” or “slow rise of
revolution speed immediately after start-up” may occur. However, turning OFF the ignition switch once and restarting
will set correct registration.)
Description of Electric Throttle Body SystemS6RW0D1101009
The Electric Throttle Body System consists of electric throttle body assembly, accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor
assembly, ECM and throttle actuator control relay.
Among them, assembly components are as follows.
• Electric throttle body assembly: throttle valve, throttle actuator, 2 throttle position sensors
• APP sensor assembly: Accelerator pedal, 2 accelerator position sensors
42
1
3
5
6
I5RW0A110006-02
Page 62 of 1556
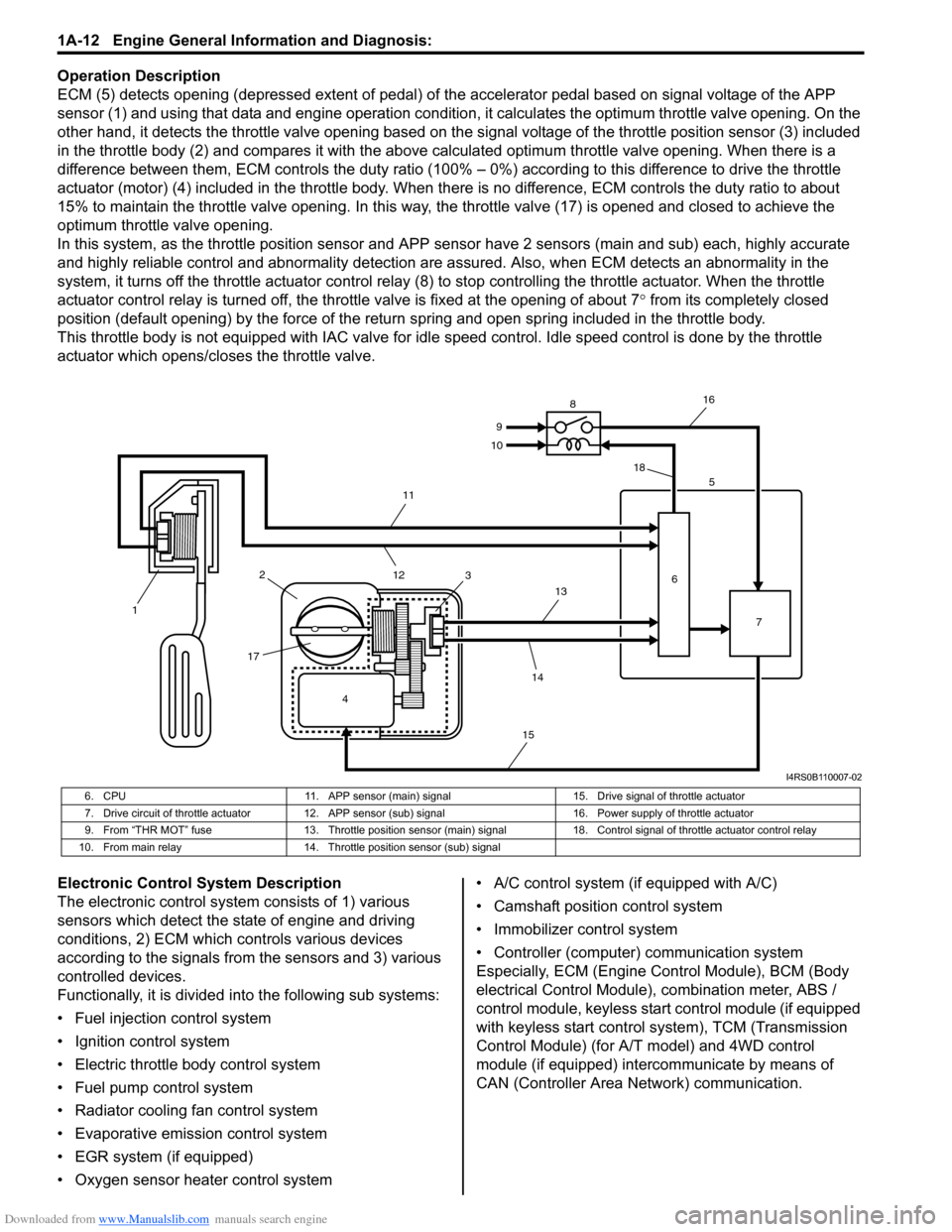
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1A-12 Engine General Information and Diagnosis:
Operation Description
ECM (5) detects opening (depressed extent of pedal) of the accelerator pedal based on signal voltage of the APP
sensor (1) and using that data and engine operation condition, it calculates the optimum throttle valve opening. On the
other hand, it detects the throttle valve opening based on the signal voltage of the throttle position sensor (3) included
in the throttle body (2) and compares it with the above calculated optimum throttle valve opening. When there is a
difference between them, ECM controls the duty ratio (100% – 0%) according to this difference to drive the throttle
actuator (motor) (4) included in the throttle body. When there is no difference, ECM controls the duty ratio to about
15% to maintain the throttle valve opening. In this way, the throttle valve (17) is opened and closed to achieve the
optimum throttle valve opening.
In this system, as the throttle position sensor and APP sensor have 2 sensors (main and sub) each, highly accurate
and highly reliable control and abnormality detection are assured. Also, when ECM detects an abnormality in the
system, it turns off the throttle actuator control relay (8) to stop controlling the throttle actuator. When the throttle
actuator control relay is turned off, the throttle valve is fixed at the opening of about 7° from its completely closed
position (default opening) by the force of the return spring and open spring included in the throttle body.
This throttle body is not equipped with IAC valve for idle speed control. Idle speed control is done by the throttle
actuator which opens/closes the throttle valve.
Electronic Control System Description
The electronic control system consists of 1) various
sensors which detect the state of engine and driving
conditions, 2) ECM which controls various devices
according to the signals from the sensors and 3) various
controlled devices.
Functionally, it is divided into the following sub systems:
• Fuel injection control system
• Ignition control system
• Electric throttle body control system
• Fuel pump control system
• Radiator cooling fan control system
• Evaporative emission control system
• EGR system (if equipped)
• Oxygen sensor heater control system• A/C control system (if equipped with A/C)
• Camshaft position control system
• Immobilizer control system
• Controller (computer) communication system
Especially, ECM (Engine Control Module), BCM (Body
electrical Control Module), combination meter, ABS /
control module, keyless start control module (if equipped
with keyless start control system), TCM (Transmission
Control Module) (for A/T model) and 4WD control
module (if equipped) intercommunicate by means of
CAN (Controller Area Network) communication.
4 12
1735
6
7 8
9
10
11
12
13
14
1516
18
I4RS0B110007-02
6. CPU 11. APP sensor (main) signal 15. Drive signal of throttle actuator
7. Drive circuit of throttle actuator 12. APP sensor (sub) signal 16. Power supply of throttle actuator
9. From “THR MOT” fuse 13. Throttle position sensor (main) signal 18. Control signal of throttle actuator control relay
10. From main relay 14. Throttle position sensor (sub) signal