2006 SUZUKI SX4 speed
[x] Cancel search: speedPage 386 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1G-9 Fuel System:
Fuel Injector On-Vehicle InspectionS6RW0D1706007
1) Using sound scope (1) or such, check operating
sound of injector (2) when engine is running or
cranking.
Cycle of operating sound should vary according to
engine speed.
If no sound or an unusual sound is heard, check
injector circuit (wire or coupler) or injector.
2) Disconnect connector (1) from injector, connect
ohmmeter between terminals of injector and check
resistance.
If resistance is out of reference value greatly,
replace.
Reference resistance of fuel injector
12.0 Ω at 20 °C, 68 °F
3) Connect connector to injector securely.
Fuel Injector Removal and InstallationS6RW0D1706008
WARNING!
Before starting the following procedure, be
sure to observe “Precautions on Fuel System
Service” in order to reduce the risk of fire and
personal injury.
Removal
1) Relieve fuel pressure according to “Fuel Pressure
Relief Procedure”.
2) Disconnect negative cable at battery.
3) Remove air cleaner case (1) and air suction hose
(2).
4) Disconnect fuel injector couplers.
5) Disconnect fuel feed hose (4) from fuel delivery pipe
(1).
6) Remove fuel delivery pipe bolts (2).
7) Remove fuel injector(s) (3).
I2RH0B170007-01
I2RH0B170008-01
1
2
I5RW0A140002-01
2
1
4
3
3
I5RW0A170010-01
Page 404 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1H-9 Ignition System:
2) Start engine and warm it up to normal operating
temperature.
3) Make sure that all of electrical loads except ignition
are switched off.
4) Check to be sure that idle speed is within
specification.
5) Fix ignition timing by using “Fixed Spark Control” of
“Engine / Active Test” mode on scan tool.
6) Set timing light (1) to high-tension cord for No.1
cylinder and check that ignition timing is within
specification.
Initial ignition timing
fixed with SUZUKI scan tool: 5 ± 3° BTDC (at
specified idle speed)
Ignition order
1 – 3 – 4 – 2
Special tool
(A): 09930–764207) If ignition timing is out of specification, check the
followings.
• CKP sensor
• CKP sensor plate
• TP sensor
• CMP sensor
• CMP sensor rotor tooth of camshaft
• Vehicle speed signal from ABS hydraulic unit /
control module
• Knock sensor
• Timing chain cover installation
8) After checking initial ignition timing, release ignition
timing fixation by using scan tool.
9) With engine idling (throttle opening at closed position
and vehicle stopped), check that ignition timing is
about 5° – 15° BTDC (Constant variation within a
few degrees from 5° – 15° BTDC indicates no
abnormality but proves operation of electronic timing
control system.) Also, check that increasing engine
speed advances ignition timing.
If the check results are not satisfactory, check CKP
sensor and ECM.
1, (A)10
0I3RB0A180004-01
Page 416 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1J-2 Charging System:
Care of battery
WARNING!
• Never expose battery to open flame or electric spark because of battery generate gas which is
flammable and explosive.
• Do not allow battery fluid to contact eyes, skin, fabrics, or painted surfaces as fluid is a corrosive
acid. Flush any contacted area with water immediately and thoroughly.
• Batteries should always be kept out of reach of children.
1) The battery is a very reliable component, but needs periodical attentions.
• Keep the battery carrier clean.
• Prevent rust formation on the terminal posts.
• Keep the electrolyte up to the upper level uniformly in all cells.
• When keeping battery on vehicle over a long period of time, follow instructions given below.
– Weekly, start the engine and run it until it reaches normal operating temperature with engine speed of 2000 to
3000 rpm. Make sure all electric switches are off before storing the vehicle.
– Recharge the battery twice a month to prevent it from discharging excessively. This is especially important
when ambient temperature is low.
The battery discharges even when it is not used, while vehicles are being stored. Battery electrolyte can
freeze and battery case can crack at cold ambient condition if battery is not properly charged.
2) Keep the battery cable connections clean.
The cable connections, particularly at the positive (+) terminal post, tend to become corroded. The product of
corrosion, or rust, on the mating faces of conductors resists the flow of current.
Clean the terminals and fittings periodically to ensure good metal-to-metal contact, and grease the connections
after each cleaning to protect them against rusting.
3) Be always in the know as to the state of charge of the battery. The simplest way to tell the state of charge is to
carry out a hydrometer test. The hydrometer is an instrument for measuring the specific gravity (S.G.) of the
battery electrolyte. The S.G. of the electrolyte is indicative of the state of charge. Refer to “Battery Inspection”.
Page 418 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1J-4 Charging System:
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Battery InspectionS6RW0D1A04001
Common Causes of Failure
A battery is not designed to last indefinitely; however,
with proper care, it will provide many years of service. If
the battery performs satisfactorily during test buy fails to
operate properly for no apparent reason, the following
are some factors that may point to the cause of trouble:
• Accessories left on overnight or for an extended
period without the generator operating.
• Slow average driving speed for short periods.
• Electrical load exceeding generator output particularly
with addition of aftermarket equipment.
• Defects in charging system such as high resistance,
slipping drive belt, loose generator output terminal,
faulty generator or voltage regulator. Refer to
“Generator Symptom Diagnosis”.
• Battery abuse, including failure to keep battery cable
terminals clean and tight or loose battery hold down.
• Mechanical problems in electrical system such as
shorted or pinched wires.
Visual Inspection
Check for obvious damage, such as cracked or broken
case or cover, that could permit loss of electrolyte. If
obvious damage is noted, replace battery. Determine
cause of damage and correct as needed.
Generator Symptom DiagnosisS6RW0D1A04002
CAUTION!
• Do not mistake polarities of “IG” terminal
and “L” terminal.
• Do not create short circuit between “IG”
and “L” terminals. Always connect these
terminals through a lamp.
• Do not connect any load between “L” and
“E” terminals.
• When connecting charger or booster
battery to vehicle battery, refer to “Jump
Starting in Case of Emergency”.
Trouble in charging system will show up as one or more
of the following conditions:
1) Faulty indicator lamp operation.
2) An undercharged battery as evidenced by slow
cranking or indicator dark.
3) An overcharged battery as evidenced by excessive
spewing of electrolyte from vents.
Noise from generator may be caused by loose drive
pulley, loose mounting bolts, worn or dirty bearings,
defective diode, or defective stator.
B: Generator output (Battery terminal) IG: Ignition terminal
C: C terminal L: Lamp terminal
E: Ground FR: Field duty monitor
F: Field coil terminal
E FFRC
B
IG
L
I6RW0D1A0003-01
Page 427 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Charging System: 1J-13
Specifications
Charging System SpecificationsS6RW0D1A07003
Battery
NOTE
The battery used in each vehicle is one of the following two types, depending on specification.
Battery
: 46B24R (40.6AH/5HR), 55B24R (42.5AH/5HR) 12V
Generator
Tightening Torque SpecificationsS6RW0D1A07004
NOTE
The specified tightening torque is also described in the following.
“Generator Dismounting and Remounting”
“Generator Components”
Reference:
For the tightening torque of fastener not specified in this section, refer to “Fasteners Information in Section 0A”. Battery type 46B24R 55B24R
Rated capacity AH/5HR, 12 Volts 40.6 42.5
Electrolyte L (US / lmp pt.) — 2.8 (5.92 / 4.93)
Type 70 A type
Rated voltage 12 V
Nominal output 70 A
Permissible max. speed 18,000 r/min.
No-load speed 1020 r/min. (rpm)
Regulated voltage 14.2 – 14.8 V (Hi), 12.5 – 13.1 V (Lo)
Exposed brush length Standard: 10.5 mm (0.41 in.)
Limit: 1.5 mm (0.05 in.)
Permissible ambient temperature –30 to 90 °C (–22 to 194 °F)
Polarity Negative ground
Rotation Clockwise viewed from pulley side
Fastening partTightening torque
Note
N⋅mkgf-mlb-ft
Generator bracket bolt 25 2.5 18.0�)
Generator pivot bolt 50 5.0 36.0�)
Generator adjusting bolt
Tighten 7.0 0.7 5.0by the specified
procedure. �)
Page 442 of 1556
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 2B-5 Front Suspension:
Front Strut Assembly Removal and InstallationS6RW0D2206003
CAUTION!
When rebound stopper and strut assembly
were removed, check strut support lower nut
for specified torque before installing strut
assembly.
Removal
1) Remove hood rear seal (1), and then remove cowl
top garnish (2) from vehicle.
NOTE
When servicing component parts of strut
assembly, beforehand loosen strut nut a little
before removing strut assembly. This will
make service work easier. Note that the nut
must not be removed at this point.
2) Hoist vehicle, allowing front suspension to hang free.
3) Remove wheel and disconnect stabilizer joint (1)
from strut bracket.
When loosening joint nut, hold stud with hexagon
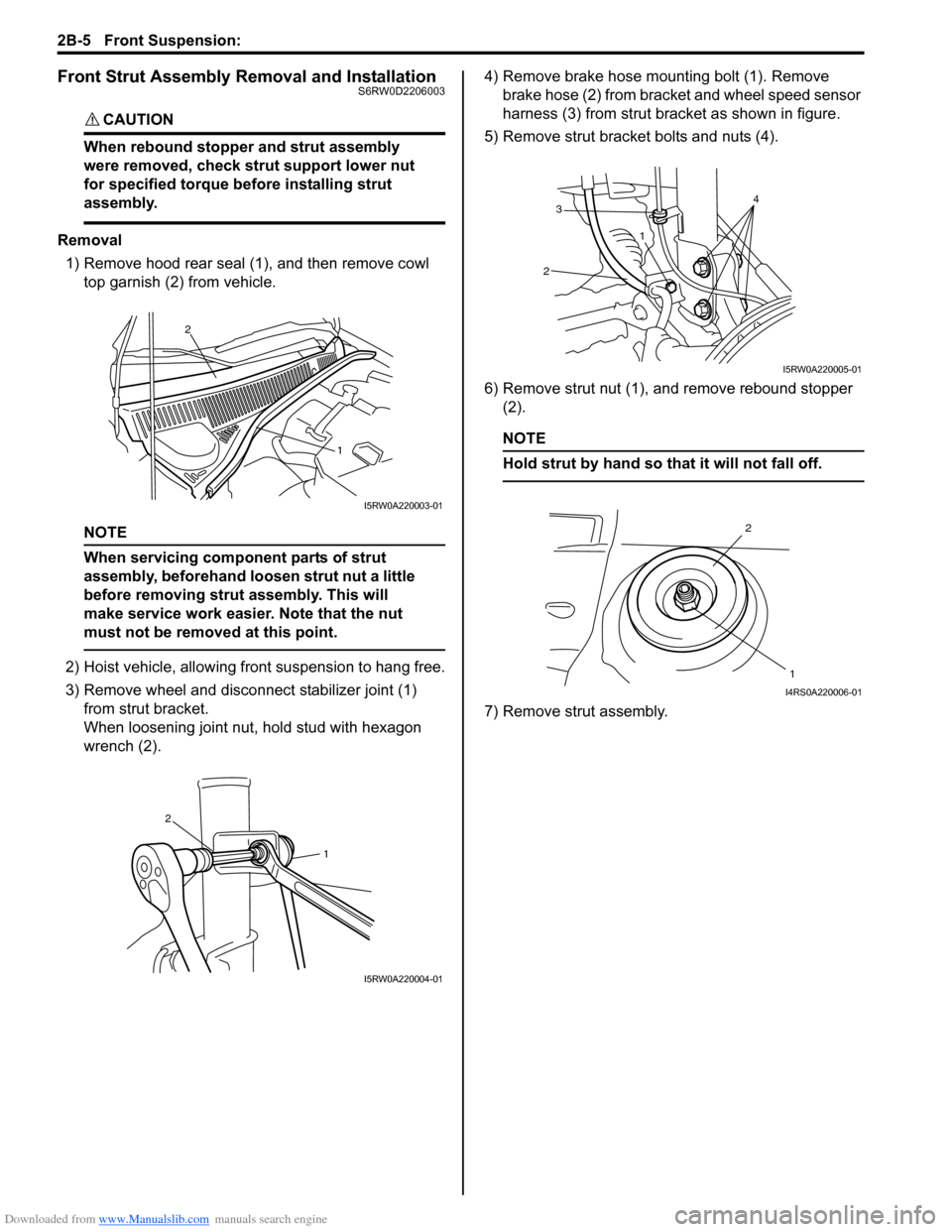
wrench (2).4) Remove brake hose mounting bolt (1). Remove
brake hose (2) from bracket and wheel speed sensor
harness (3) from strut bracket as shown in figure.
5) Remove strut bracket bolts and nuts (4).
6) Remove strut nut (1), and remove rebound stopper
(2).
NOTE
Hold strut by hand so that it will not fall off.
7) Remove strut assembly.
2
1
I5RW0A220003-01
1
2
I5RW0A220004-01
3
214
I5RW0A220005-01
2
1
I4RS0A220006-01
Page 443 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Front Suspension: 2B-6
Installation
Install strut assembly by reversing removal procedure,
noting the following instructions.
• Insert bolts in such direction as shown in figure.
• Tighten all fasteners to specified torque.
Tightening torque
Strut bracket nut (a): 140 N·m (14.0 kgf-m, 101.5
lb-ft)
Brake hose mounting bolt (c): 26 N·m (2.6 kgf-m,
19.0 lb-ft)
Stabilizer joint nut (d): 50 N·m (5.0 kgf-m, 36.5 lb-
ft)
CAUTION!
Never reuse the removed strut bracket nut.
• Lower hoist and vehicle in unloaded condition, tighten
strut nut (b) to specified torque.
Tightening torque
Strut nut (b): 50 N·m (5.0 kgf-m, 36.5 lb-ft)
NOTE
Don’t twist brake hose and wheel speed
sensor harness when installing them.
• Tighten wheel nut to specified torque.
Tightening torque
Wheel nut: 85 N·m (8.5 kgf-m, 61.5 lb-ft)
• After installation, confirm front wheel alignment.
(b)
(a)
(c)
(d)
I5RW0A220006-01
Page 447 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Front Suspension: 2B-10
6) Pull out wheel hub (1) with special tools.
Special tool
(A): 09943–17912
(B): 09942–15511
CAUTION!
When wheel hub is removed, replace wheel
bearing with new one.
7) Disconnect tie-rod end (1) from steering knuckle (2)
with puller (3).
8) Remove wheel speed sensor (1) from knuckle.9) Loosen strut bracket nuts (1).
10) Remove ball joint bolt (4) and washer (3).
11) Remove strut bracket bolts (5) from strut bracket and
then steering knuckle (2).
12) Uncaulk and remove dust cover (1).
13) Remove circlip from knuckle.
14) Using hydraulic press (1) and special tool, remove
wheel bearing.
Special tool
(A): 09913–75510
(B): 09943–37910
I2RH01220028-01
1
2
3
1
I4RS0A220017-01
1
I5RW0A220013-01
F: Vehicle front
F
5
21
3
4
I7RW01220004-01
I2RH01220032-01
I5RW0A220014-01