2006 SUZUKI SWIFT rev limit
[x] Cancel search: rev limitPage 279 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Electrical Devices: 1C-7
Installation
Reverse removal procedure noting the following.
• Clean mating surfaces of ECT sensor and thermostat case.
• Check O-ring for damage and replace, if necessary.
• Tighten ECT sensor (1) to specified torque.
Tightening torque
ECT sensor (a): 15 N·m (1.5 kgf-m, 11.0 lb-ft)
• Connect connector to ECT sensor securely.
• Refill coolant referring to “Cooling System Flush and
Refill in Section 1F”.
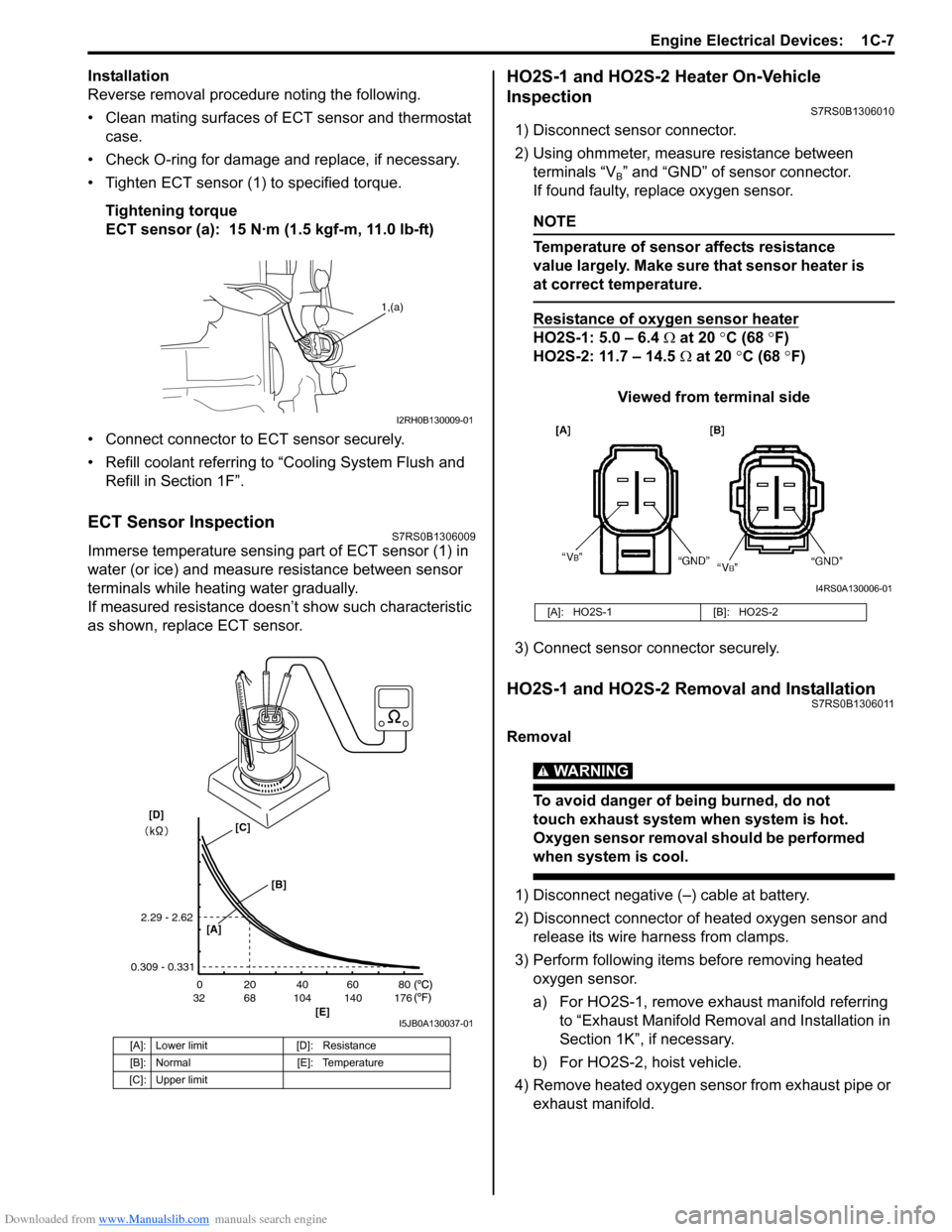
ECT Sensor InspectionS7RS0B1306009
Immerse temperature sensing part of ECT sensor (1) in
water (or ice) and measure resistance between sensor
terminals while heating water gradually.
If measured resistance doesn’t show such characteristic
as shown, replace ECT sensor.
HO2S-1 and HO2S-2 Heater On-Vehicle
Inspection
S7RS0B1306010
1) Disconnect sensor connector.
2) Using ohmmeter, measure resistance between terminals “V
B” and “GND” of sensor connector.
If found faulty, replace oxygen sensor.
NOTE
Temperature of sensor affects resistance
value largely. Make sure that sensor heater is
at correct temperature.
Resistance of oxygen sensor heater
HO2S-1: 5.0 – 6.4 Ω at 20 °C (68 °F)
HO2S-2: 11.7 – 14.5 Ω at 20 °C (68 °F)
Viewed from terminal side
3) Connect sensor co nnector securely.
HO2S-1 and HO2S-2 Removal and InstallationS7RS0B1306011
Removal
WARNING!
To avoid danger of being burned, do not
touch exhaust system when system is hot.
Oxygen sensor removal should be performed
when system is cool.
1) Disconnect negative (–) cable at battery.
2) Disconnect connector of heated oxygen sensor and
release its wire harness from clamps.
3) Perform following items before removing heated oxygen sensor.
a) For HO2S-1, remove exhaust manifold referring to “Exhaust Manifold Remo val and Installation in
Section 1K”, if necessary.
b) For HO2S-2, hoist vehicle.
4) Remove heated oxygen sensor from exhaust pipe or exhaust manifold.
[A]: Lower limit [D]: Resistance
[B]: Normal [E]: Temperature
[C]: Upper limit
1,(a)
I2RH0B130009-01
20
0
68
32 104 140 176 40 60 80
[E]
2.29 - 2.62
0.309 - 0.331
[A]
[B]
[C][D]
I5JB0A130037-01
[A]: HO2S-1 [B]: HO2S-2
I4RS0A130006-01
Page 326 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-41 Engine Mechanical:
Valve head radial runout
Check each valve for radial runout with a dial gauge and
“V” block. To check runout, rotate valve slowly. If runout
exceeds its limit, replace valve.
Valve head radial runout
Limit: 0.08 mm (0.003 in.)
Seating contact width
Create contact pattern on each valve in the usual
manner, i.e., by giving uniform coat of marking
compound to valve seat and by rotatingly tapping seat
with valve head. Valve lapper (tool used in valve lapping)
must be used.
Pattern produced on seating face of valve must be a
continuous ring without any break, and the width of
pattern must be within specified range.
Standard seating width “a” revealed by contact
pattern on valve face
Intake and Exhaust: 1.0 – 1.4 mm (0.0389 – 0.0551
in.)Valve seat repair
A valve seat not producing
a uniform contact with its
valve or showing width of seating contact that is out of
specified range must be repaired by regrinding or by
cutting and regrinding and finished by lapping.
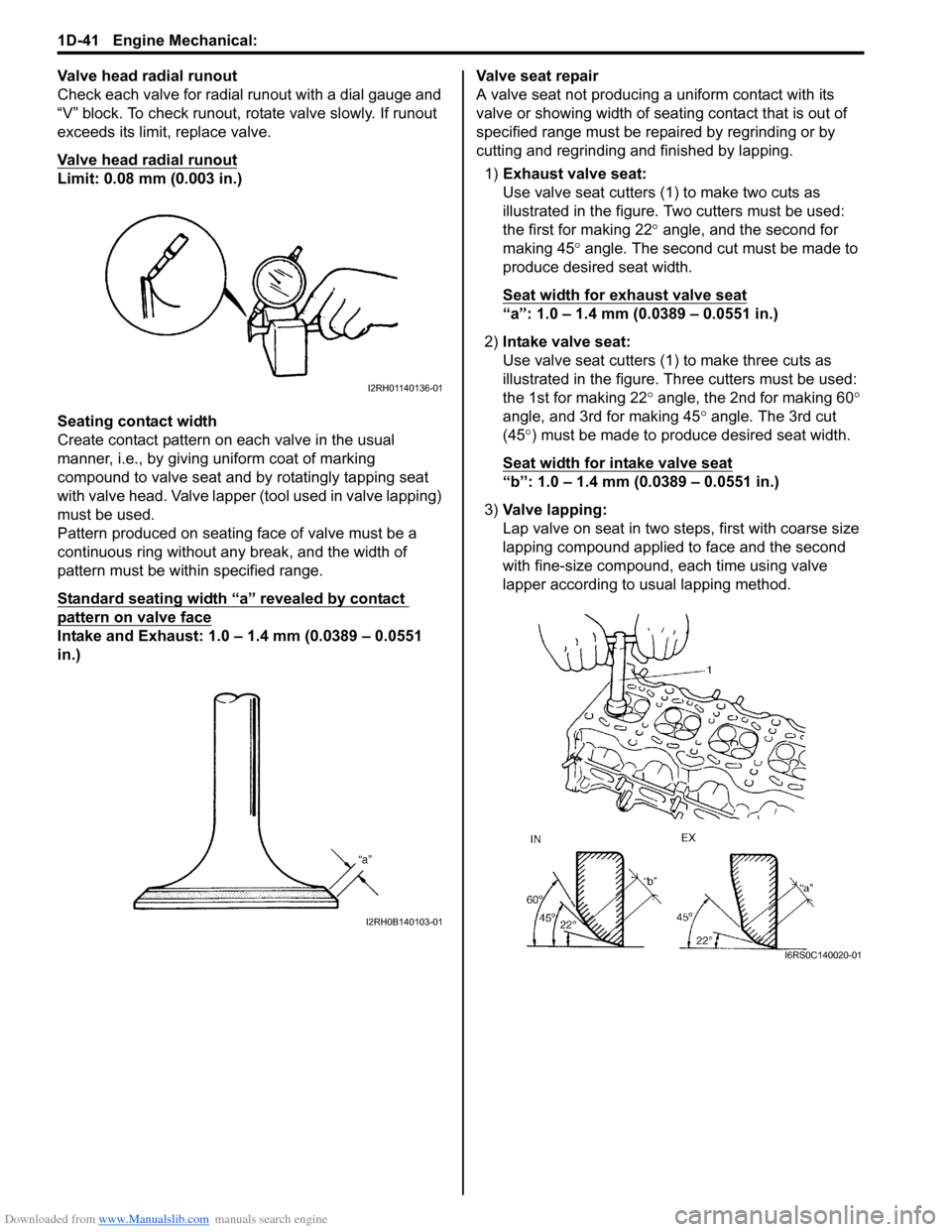
1) Exhaust valve seat:
Use valve seat cutters (1 ) to make two cuts as
illustrated in the figure. Two cutters must be used:
the first for making 22 ° angle, and the second for
making 45 ° angle. The second cut must be made to
produce desired seat width.
Seat width for exhaust valve seat
“a”: 1.0 – 1.4 mm (0.0389 – 0.0551 in.)
2) Intake valve seat:
Use valve seat cutters (1) to make three cuts as
illustrated in the figure. Th ree cutters must be used:
the 1st for making 22 ° angle, the 2nd for making 60 °
angle, and 3rd for making 45 ° angle. The 3rd cut
(45 °) must be made to produce desired seat width.
Seat width for intake valve seat
“b”: 1.0 – 1.4 mm (0.0389 – 0.0551 in.)
3) Valve lapping:
Lap valve on seat in two steps, first with coarse size
lapping compound applied to face and the second
with fine-size compound, each time using valve
lapper according to usual lapping method.
I2RH01140136-01
I2RH0B140103-01
I6RS0C140020-01
Page 411 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Charging System: 1J-1
Engine
Charging System
General Description
Battery DescriptionS7RS0B1A01001
The battery has three major functions in the electrical
system.
• It is a source of electrical energy for cranking the engine.
• It acts as a voltage stabilizer for the electrical system.
• It can, for a limited time, provide energy when the electrical load exceeds the output of the generator.
Carrier and Hold-Down
The battery carrier should be in good condition so that it
will support the battery securely and keep it level. Before
installing the battery, the ba ttery carrier and hold-down
clamp should be clean and free from corrosion and
make certain there are no parts in carrier.
To prevent the battery from shaking in its carrier, the
hold-down bolts should be tight enough but not over-
tightened.
Electrolyte Freezing
The freezing point of electrolyte depends on its specific
gravity. Since freezing may ruin a battery, it should be
protected against freezing by keeping it in a fully
charged condition. If a battery is frozen accidentally, it
should not be charged until it is warmed.
Sulfation
If the battery is allowed to stand for a long period in
discharged condition, the lead sulfate becomes
converted into a hard, cryst alline substance, which will
not easily turn back to the active material again during
the subsequent recharging. “Sulfation” means the result
as well as the process of that reaction. Such a battery
can be revived by very slow charging and may be
restored to usable condition but its capacity is lower than
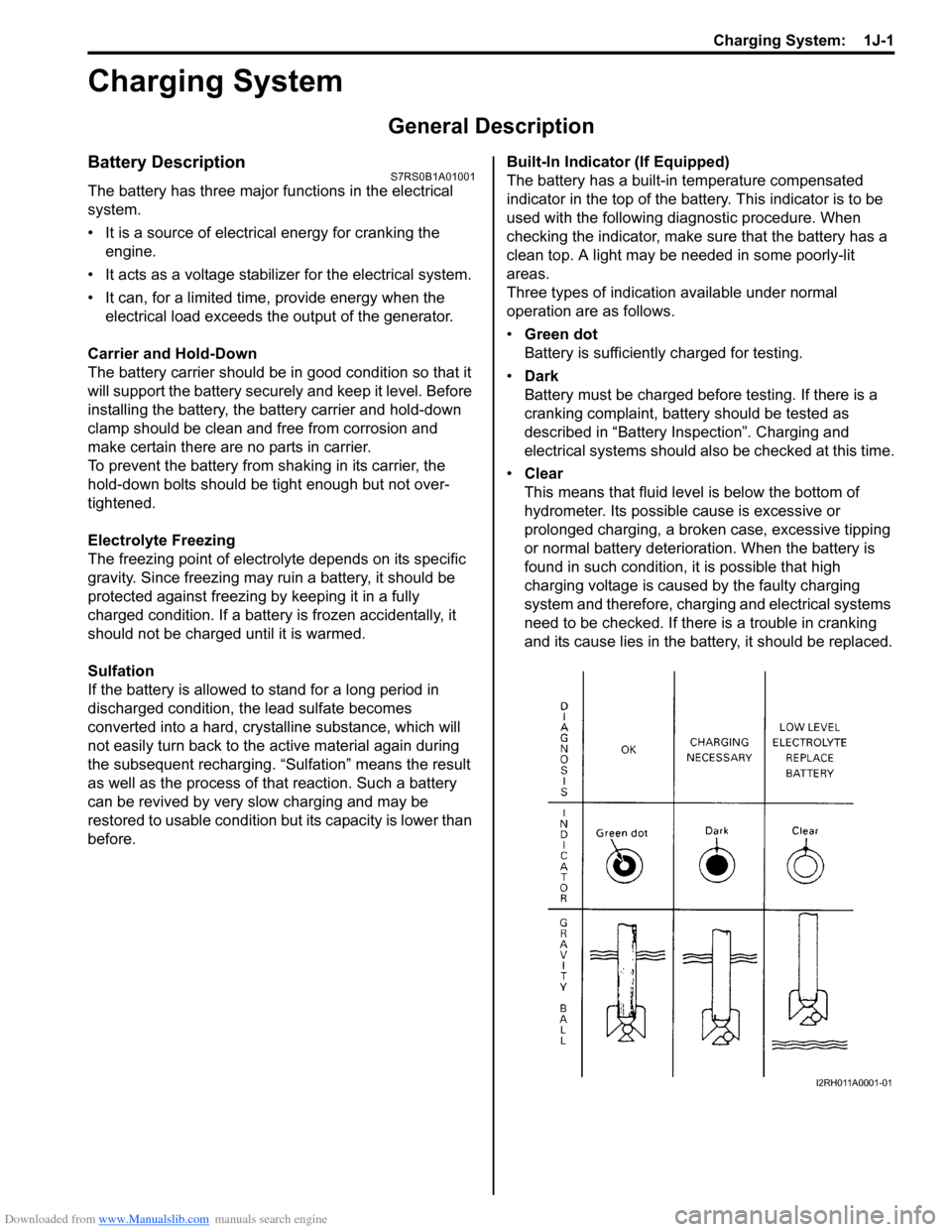
before. Built-In Indicator (If Equipped)
The battery has a built-in temperature compensated
indicator in the top of the battery. This indicator is to be
used with the following diagnostic procedure. When
checking the indicator, make sure that the battery has a
clean top. A light may be needed in some poorly-lit
areas.
Three types of indication available under normal
operation are as follows.
•
Green dot
Battery is sufficiently charged for testing.
• Dark
Battery must be charged before testing. If there is a
cranking complaint, battery should be tested as
described in “Battery Inspection”. Charging and
electrical systems should also be checked at this time.
• Clear
This means that fluid level is below the bottom of
hydrometer. Its possible cause is excessive or
prolonged charging, a broken case, excessive tipping
or normal battery deteriorat ion. When the battery is
found in such condition, it is possible that high
charging voltage is caused by the faulty charging
system and therefore, charging and electrical systems
need to be checked. If there is a trouble in cranking
and its cause lies in the battery, it should be replaced.
I2RH011A0001-01
Page 422 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1J-12 Charging System:
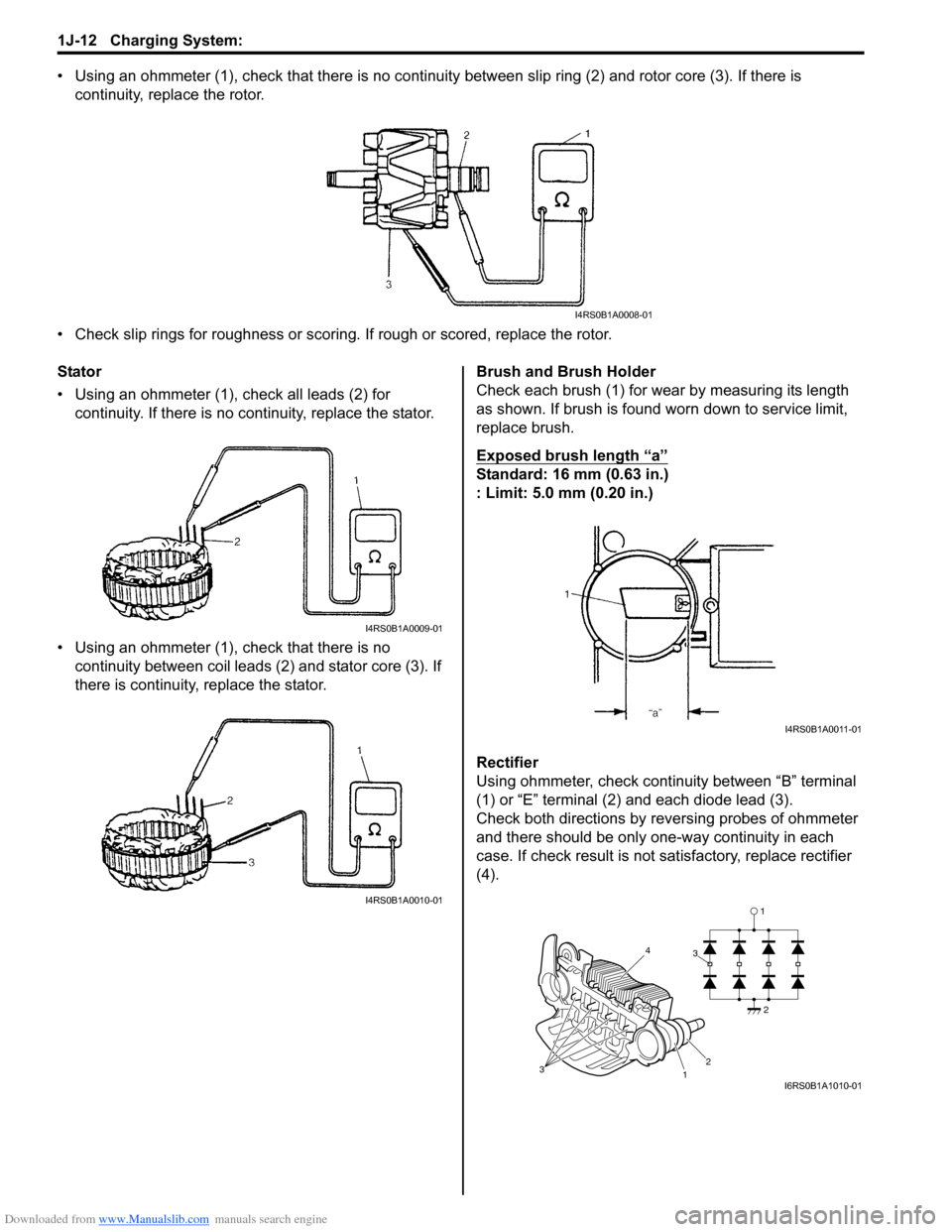
• Using an ohmmeter (1), check that there is no continuity between slip ring (2) and rotor core (3). If there is
continuity, replace the rotor.
• Check slip rings for roughness or scoring. If rough or scored, replace the rotor.
Stator
• Using an ohmmeter (1), check all leads (2) for continuity. If there is no co ntinuity, replace the stator.
• Using an ohmmeter (1), check that there is no continuity between coil leads (2) and stator core (3). If
there is continuity, replace the stator. Brush and Brush Holder
Check each brush (1) for wear by measuring its length
as shown. If brush is found worn down to service limit,
replace brush.
Exposed brush length “a”
Standard: 16 mm (0.63 in.)
: Limit: 5.0 mm (0.20 in.)
Rectifier
Using ohmmeter, check continuity between “B” terminal
(1) or “E” terminal (2) and each diode lead (3).
Check both directions by reversing probes of ohmmeter
and there should be only one-way continuity in each
case. If check result is not satisfactory, replace rectifier
(4).
I4RS0B1A0008-01
I4RS0B1A0009-01
I4RS0B1A0010-01
I4RS0B1A0011-01
1
1
3 3
2
2
4
I6RS0B1A1010-01
Page 435 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Front Suspension: 2B-2
Front Wheel Alignment ConstructionS7RS0B2201002
Among factors for front wheel alignment, only toe setting
can be adjusted. Camber and caster are not adjustable.
Therefore, should camber or caster be out of
specification due to the damage caused by hazardous
road conditions or collision, whether the damage is in
body or in suspension should be determined and
damaged body should be repaired or damaged
suspension should be replaced.
Preliminary Checks Prior to Adjustment Front Wheel
Alignment
Steering and vibration complaints are not always the
result of improper wheel alignment. An additional item to
be checked is the possibility of tire lead due to worn or
improperly manufactured tires. “Lead” is the vehicle
deviation from a straight path on a level road without
hand pressure on the steering wheel. Refer to “Radial
Tire Lead / Pull Description in Section 2D” in order to
determine if the vehicle has a tire lead problem. Before
making any adjustment affecting wheel alignment, the
following checks and inspections should be made to
ensure correctness of alignment readings and alignment
adjustments:
• Check all tires for proper inflation pressures and approximately the same tread wear. • Check for loose of ball join
ts. Check tie-rod ends; if
excessive looseness is noted, it must be corrected
before adjusting.
• Check for run-out of wheels and tires.
• Check vehicle trim heights; if it is out of limit and a
correction is needed, it must be done before adjusting
toe.
• Check for loose of suspension control arms.
• Check for loose or missin g stabilizer bar attachments.
• Consideration must be given to excess loads, such as
tool boxes. If this excess load is normally carried in
vehicle, it should remain in vehicle during alignment
checks.
• Consider condition of equipment being used to check alignment and follow manufa cturer’s instructions.
• Regardless of equipment used to check alignment, vehicle must be placed on a level surface.
NOTE
To prevent possible incorrect reading of toe,
camber or caster, vehicle front and rear end
must be moved up and down a few times
before inspection.
Repair Instructions
Front Wheel Alignment Inspection and
Adjustment
S7RS0B2206001
Toe Inspection and Adjustment
Preparation for toe inspection and adjustment.
• Place vehicle in unloaded state on level surface.
• Set steering wheel in straight state.
• Check that inflation pressure of each tire is adjusted properly and wheel is free from deflection.
• Check that each suspension part is free from bend, dent, wear or damage in any other form.
• Check that ground clearance at the right and left is just about the same.
Inspection
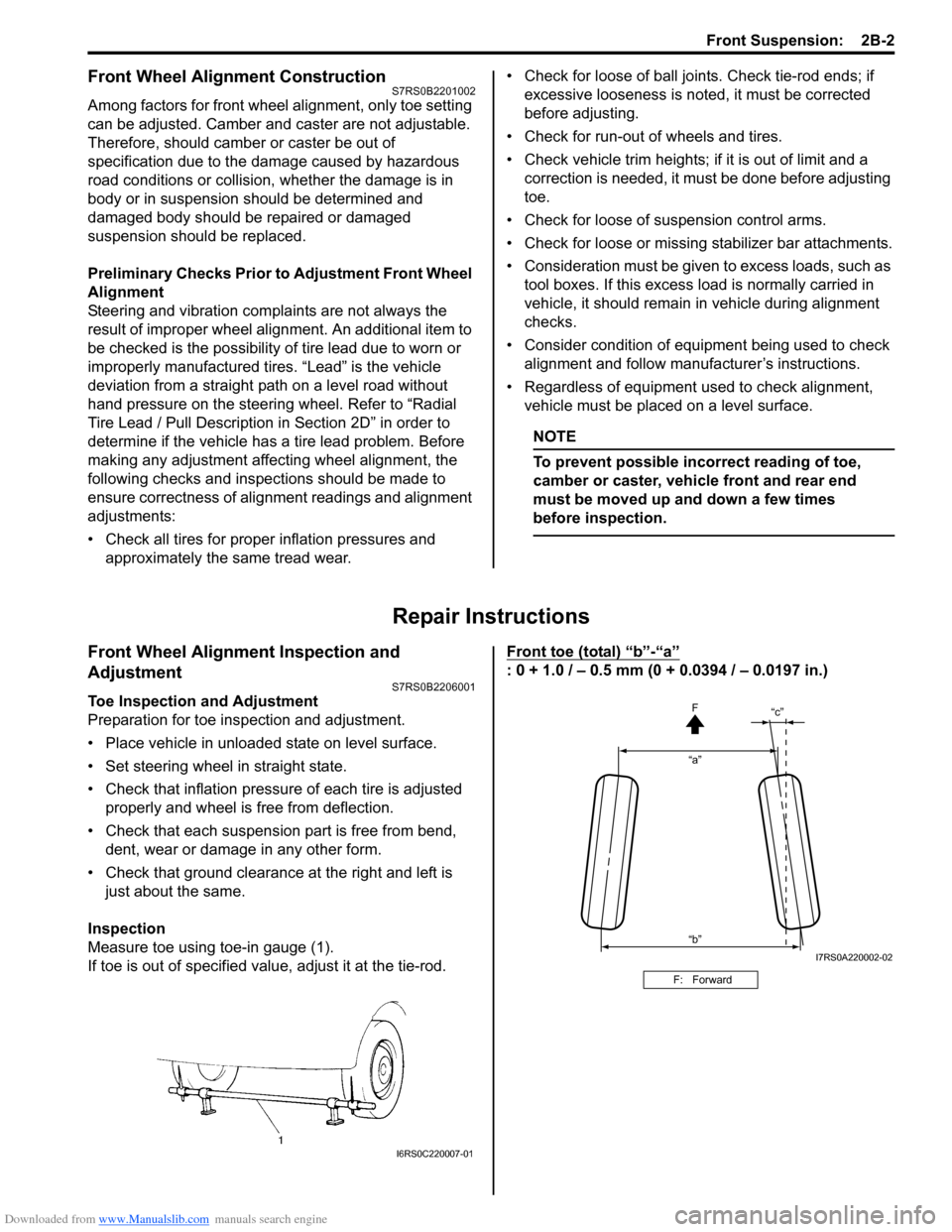
Measure toe using toe-in gauge (1).
If toe is out of specified value, adjust it at the tie-rod. Front toe (total) “b”-“a”
: 0 + 1.0 / – 0.5 mm (0 + 0.0394 / – 0.0197 in.)
I6RS0C220007-01
F: Forward
“a”
“c”
“b” F
I7RS0A220002-02
Page 465 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Rear Suspension: 2C-11
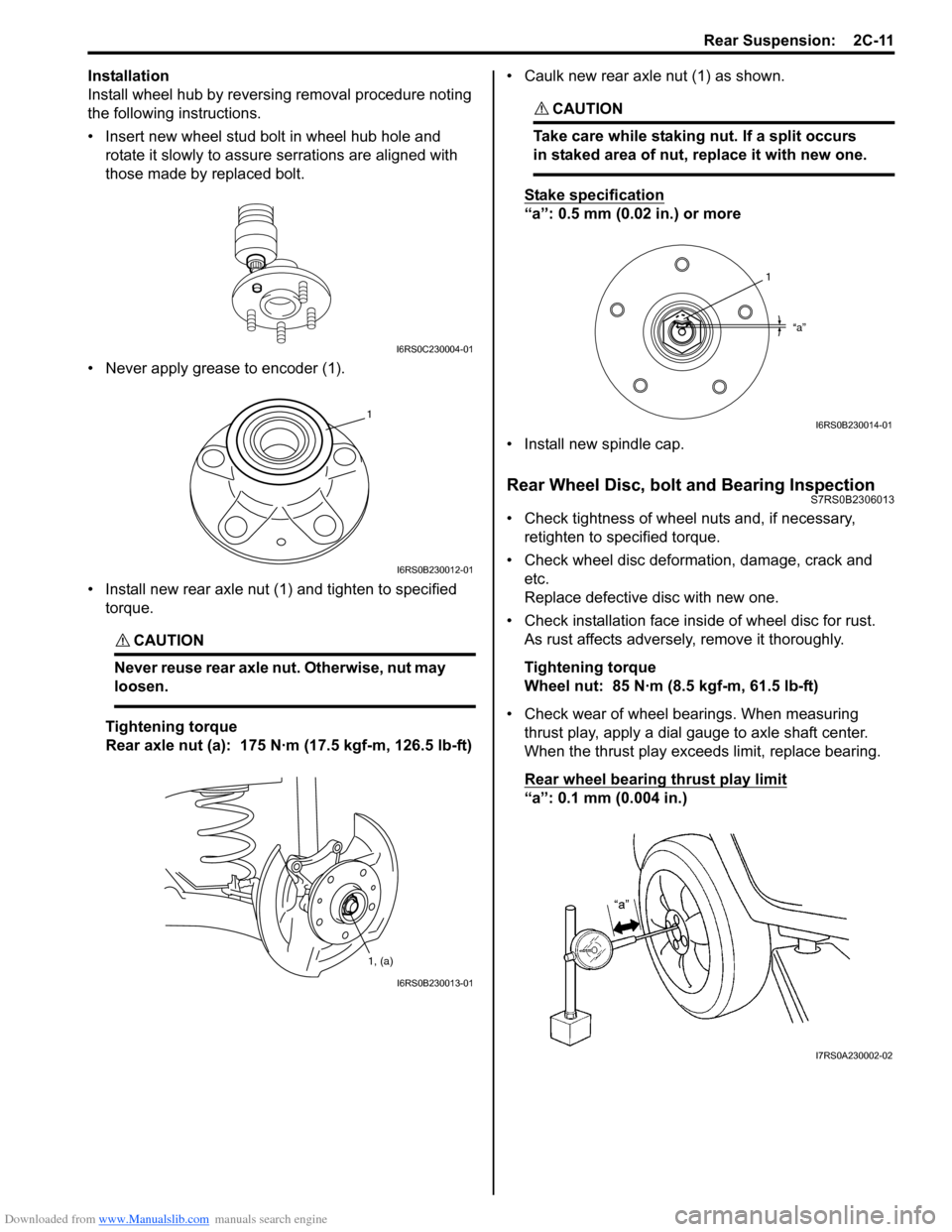
Installation
Install wheel hub by reversing removal procedure noting
the following instructions.
• Insert new wheel stud bolt in wheel hub hole and rotate it slowly to assure serrations are aligned with
those made by replaced bolt.
• Never apply grease to encoder (1).
• Install new rear axle nut (1) and tighten to specified torque.
CAUTION!
Never reuse rear axle nut. Otherwise, nut may
loosen.
Tightening torque
Rear axle nut (a): 175 N·m (17.5 kgf-m, 126.5 lb-ft) • Caulk new rear axle nut (1) as shown.
CAUTION!
Take care while staking nut. If a split occurs
in staked area of nut,
replace it with new one.
Stake specification
“a”: 0.5 mm (0.02 in.) or more
• Install new spindle cap.
Rear Wheel Disc, bolt and Bearing InspectionS7RS0B2306013
• Check tightness of wheel nuts and, if necessary, retighten to specified torque.
• Check wheel disc deformation, damage, crack and etc.
Replace defective disc with new one.
• Check installation face insi de of wheel disc for rust.
As rust affects adversely, remove it thoroughly.
Tightening torque
Wheel nut: 85 N·m (8.5 kgf-m, 61.5 lb-ft)
• Check wear of wheel bearings. When measuring thrust play, apply a dial gauge to axle shaft center.
When the thrust play exce eds limit, replace bearing.
Rear wheel bearing thrust play
limit
“a”: 0.1 mm (0.004 in.)
I6RS0C230004-01
1
I6RS0B230012-01
1, (a)
I6RS0B230013-01
1
“a”
I6RS0B230014-01
I7RS0A230002-02
Page 469 of 1496

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Wheels and Tires: 2D-2
Lower than recommended pressure can cause:
• Tire squeal on turns
• Hard Steering
• Rapid and uneven wear on the edges of the tread
• Tire rim bruises and rupture
• Tire cord breakage
• High tire temperature
• Reduced handling
• High fuel consumption
Replacement Tires
When replacement is necessary, the original equipment
type tire should be used. Refer to the Tire Placard.
Replacement tires should be of the same size, load
range and construction as those originally on the vehicle.
Use of any other size or type tire may affect ride,
handling, speedometer / odometer calibration, vehicle
ground clearance and tire or snow chain clearance to the
body and chassis.
It is recommended that new tires be installed in pairs on
the same axle. If necessary to replace only one tire, it
should be paired with the tire having the most tread, to
equalize braking traction.
WARNING!
Do not mix different types of tires on the
same vehicle such as radial, bias and bias-
belted tires except in emergencies, because
handling may be seriously affected and may
result in loss of control.
The metric term for tire infl ation pressure is the kilo
pascal (kPa). Tire pressures is usually printed in both
kPa and kgf/cm
2 on the “Tire Placard”.
Metric tire gauges are available from tool suppliers.
The chart, shown the table, converts commonly used
inflation pressures from kPa to kgf/cm
2 and psi.
Wheels DescriptionS7RS0B2401002
Wheel Maintenance
Wheel repairs that use welding, heating, or peening are
not approved. All damaged wheels should be replaced.
Replacement Wheels
Wheels must be replaced if they are bent, dented, have
excessive lateral or radial runout, air leak through welds,
have elongated bolt holes, if lug wheel bolts won’t stay
tight, or if they are heavily rusted. Wheels with greater
runout than shown in the following may cause
objectional vibrations.
Replacement wheels must be equivalent to the original
equipment wheels in load capacity, diameter, rim with
offset and mounting configuration. A wheel of improper
size or type may affect wheel and bearing life, brake
cooling, speedometer / odometer calibration, vehicle
ground clearance and tire clearance to body and
chassis.
How to Measure Wheel Runout
To measure the wheel runout, it is necessary to use an
accurate dial indicator. The tire may be on or off the
wheel. The wheel should be installed to the wheel
balancer of the like for proper measurement.
Take measurements of both lateral runout “a” and radial
runout “b” at both inside an d outside of the rim flange.
With the dial indicator set in place securely, turn the
wheel one full revolution slowly and record every reading
of the indicator.
When the measured runout exceeds the specification
and correction by the balancer adjustment is impossible,
replace the wheel. If the reading is affected by welding,
paint or scratch, it should be ignored.
Lateral runout limit “a”
: 0.3 mm (0.012 in.)
Radial runout limit “b”
: 0.3 mm (0.012 in.)
kPa kgf/cm2psi
Conversion: 1 psi =
6.895 kPa 1 kgf/cm
2 =
98.066 kPa 160 1.6 23
180 1.8 26
200 2.0 29
220 2.2 32
240 2.4 35
260 2.6 38
280 2.8 41
300 3.0 44
I4RS0A240001-01
Page 518 of 1496
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 4B-2 Front Brakes:
Front Disc Brake Pad On-Vehicle InspectionS7RS0B4206002
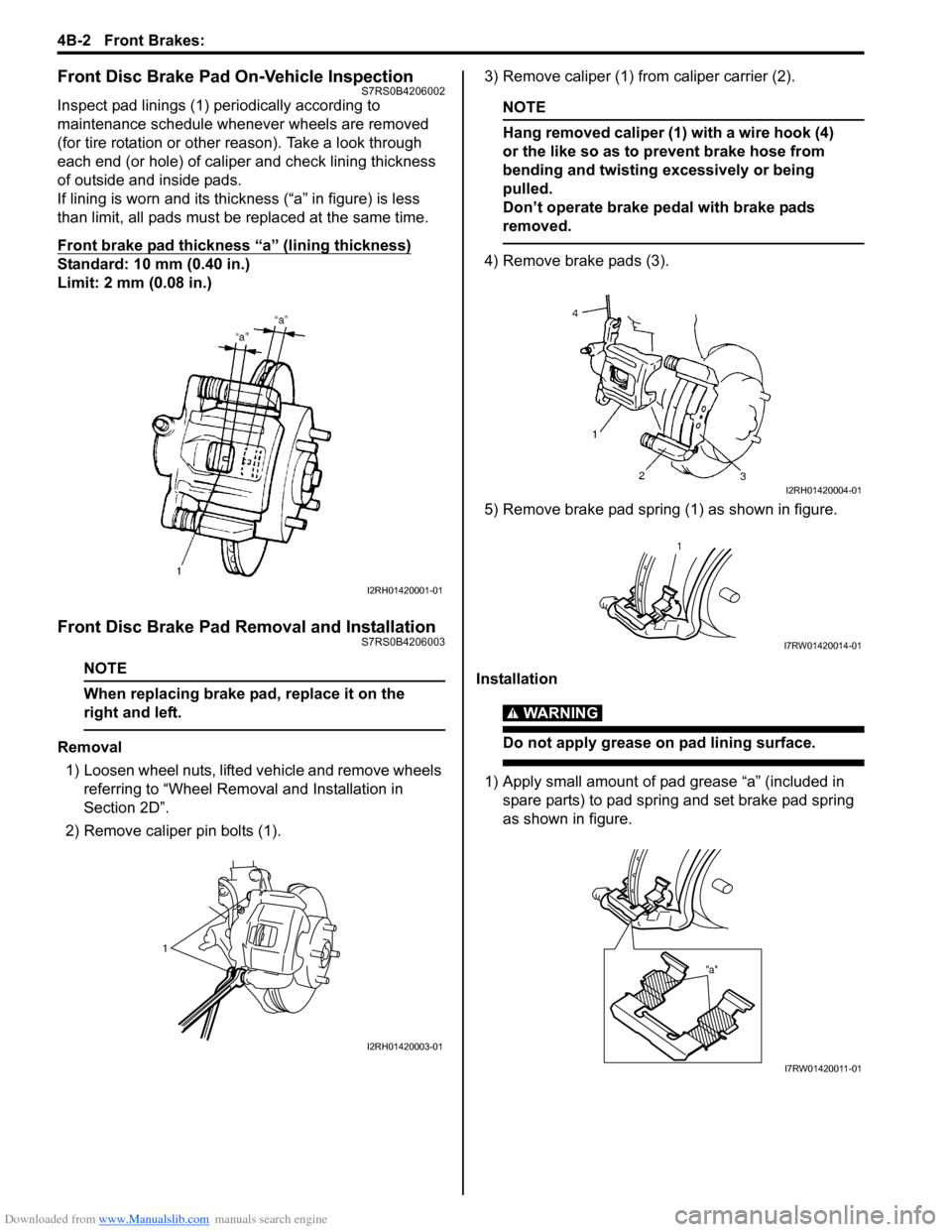
Inspect pad linings (1) periodically according to
maintenance schedule whenever wheels are removed
(for tire rotation or other reason). Take a look through
each end (or hole) of caliper and check lining thickness
of outside and inside pads.
If lining is worn and its thic kness (“a” in figure) is less
than limit, all pads must be replaced at the same time.
Front brake pad thickness “a” (lining thickness)
Standard: 10 mm (0.40 in.)
Limit: 2 mm (0.08 in.)
Front Disc Brake Pad Removal and InstallationS7RS0B4206003
NOTE
When replacing brake pad, replace it on the
right and left.
Removal
1) Loosen wheel nuts, lifted vehicle and remove wheels referring to “Wheel Remova l and Installation in
Section 2D”.
2) Remove caliper pin bolts (1). 3) Remove caliper (1) from caliper carrier (2).
NOTE
Hang removed caliper (1) with a wire hook (4)
or the like so as to prevent brake hose from
bending and twisting excessively or being
pulled.
Don’t operate brake pedal with brake pads
removed.
4) Remove brake pads (3).
5) Remove brake pad spring (1) as shown in figure.
Installation
WARNING!
Do not apply grease on pad lining surface.
1) Apply small amount of pad grease “a” (included in spare parts) to pad spring and set brake pad spring
as shown in figure.
I2RH01420001-01
1
I2RH01420003-01
I2RH01420004-01
1
I7RW01420014-01
"a"
I7RW01420011-01