2006 INFINITI M35 air condition
[x] Cancel search: air conditionPage 3471 of 5621

GI-8
PRECAUTIONS
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
After installing plate clamps, apply force to them in the direction
of the arrow, tightening rubber hose equally all around.
Precautions for Engine OilsNAS0007E
Prolonged and repeated contact with used engine oil may cause skin cancer. Try to avoid direct skin contact
with used oil.
If skin contact is made, wash thoroughly with soap or hand cleaner as soon as possible.
HEALTH PROTECTION PRECAUTIONS
Avoid prolonged and repeated contact with oils, particularly used engine oils.
Wear protective clothing, including impervious gloves where practicable.
Do not put oily rags in pockets.
Avoid contaminating clothes, particularly underpants, with oil.
Heavily soiled clothing and oil-impregnated footwear should not be worn. Overalls must be cleaned regu-
larly.
First aid treatment should be obtained immediately for open cuts and wounds.
Use barrier creams, applying them before each work period, to help the removal of oil from the skin.
Wash with soap and water to ensure all oil is removed (skin cleansers and nail brushes will help). Prepa-
rations containing lanolin replace the natural skin oils which have been removed.
Do not use gasoline, kerosene, diesel fuel, gas oil, thinners or solvents for cleaning skin.
If skin disorders develop, obtain medical advice without delay.
Where practical, degrease components prior to handling.
Where there is a risk of eye contact, eye protection should be worn, for example, chemical goggles or face
shields; in addition an eye wash facility should be provided.
Precautions for Air Conditioning NAS0007F
Use an approved refrigerant recovery unit any time the air conditioning system must be discharged. Refer to
ATC/MTC section “HFC-134a (R-134a) Service Procedure”, “REFRIGERANT LINES” for specific instructions.
SMA022D
Page 3487 of 5621
GI-24
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
AbbreviationsNAS0007O
The following ABBREVIATIONS are used:
ABBREVIATION DESCRIPTION
A/C Air Conditioner
A/T Automatic Transaxle/Transmission
ATF Automatic Transmission Fluid
D
1Drive range 1st gear
D
2Drive range 2nd gear
D
3Drive range 3rd gear
D
4Drive range 4th gear
FR, RR Front, Rear
LH, RH Left-Hand, Right-Hand
M/T Manual Transaxle/Transmission
OD Overdrive
P/S Power Steering
SAE Society of Automotive Engineers, Inc.
SDS Service Data and Specifications
SST Special Service Tools
2WD 2-Wheel Drive
2
22nd range 2nd gear
2
12nd range 1st gear
1
21st range 2nd gear
1
11st range 1st gear
Page 3491 of 5621

GI-28
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
How to Perform Efficient Diagnosis for an Electrical IncidentNAS0007Q
WORK FLOW
INCIDENT SIMULATION TESTS
Introduction
Sometimes the symptom is not present when the vehicle is brought in for service. If possible, re-create the
conditions present at the time of the incident. Doing so may help avoid a No Trouble Found Diagnosis. The fol-
lowing section illustrates ways to simulate the conditions/environment under which the owner experiences an
electrical incident.
The section is broken into the six following topics:
Vehicle vibration
Heat sensitive
SGI838
STEP DESCRIPTION
STEP 1Get detailed information about the conditions and the environment when the incident occurred.
The following are key pieces of information required to make a good analysis:
WHATVehicle Model, Engine, Transmission/Transaxle and the System (i.e. Radio).
WHENDate, Time of Day, Weather Conditions, Frequency.
WHERERoad Conditions, Altitude and Traffic Situation.
HOWSystem Symptoms, Operating Conditions (Other Components Interaction).
Service History and if any After Market Accessories have been installed.
STEP 2Operate the system, road test if necessary.
Verify the parameter of the incident.
If the problem cannot be duplicated, refer to “Incident Simulation Tests”.
STEP 3Get the proper diagnosis materials together including:
Power Supply Routing
System Operation Descriptions
Applicable Service Manual Sections
Check for any Service Bulletins
Identify where to begin diagnosis based upon your knowledge of the system operation and the customer comments.
STEP 4Inspect the system for mechanical binding, loose connectors or wiring damage.
Determine which circuits and components are involved and diagnose using the Power Supply Routing and Harness
Layouts.
STEP 5 Repair or replace the incident circuit or component.
STEP 6Operate the system in all modes. Verify the system works properly under all conditions. Make sure you have not inad-
vertently created a new incident during your diagnosis or repair steps.
Page 3493 of 5621
GI-30
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
UNDER SEATING AREAS
An unclamped or loose harness can cause wiring to be pinched by seat components (such as slide guides)
during vehicle vibration. If the wiring runs under seating areas, inspect wire routing for possible damage or
pinching.
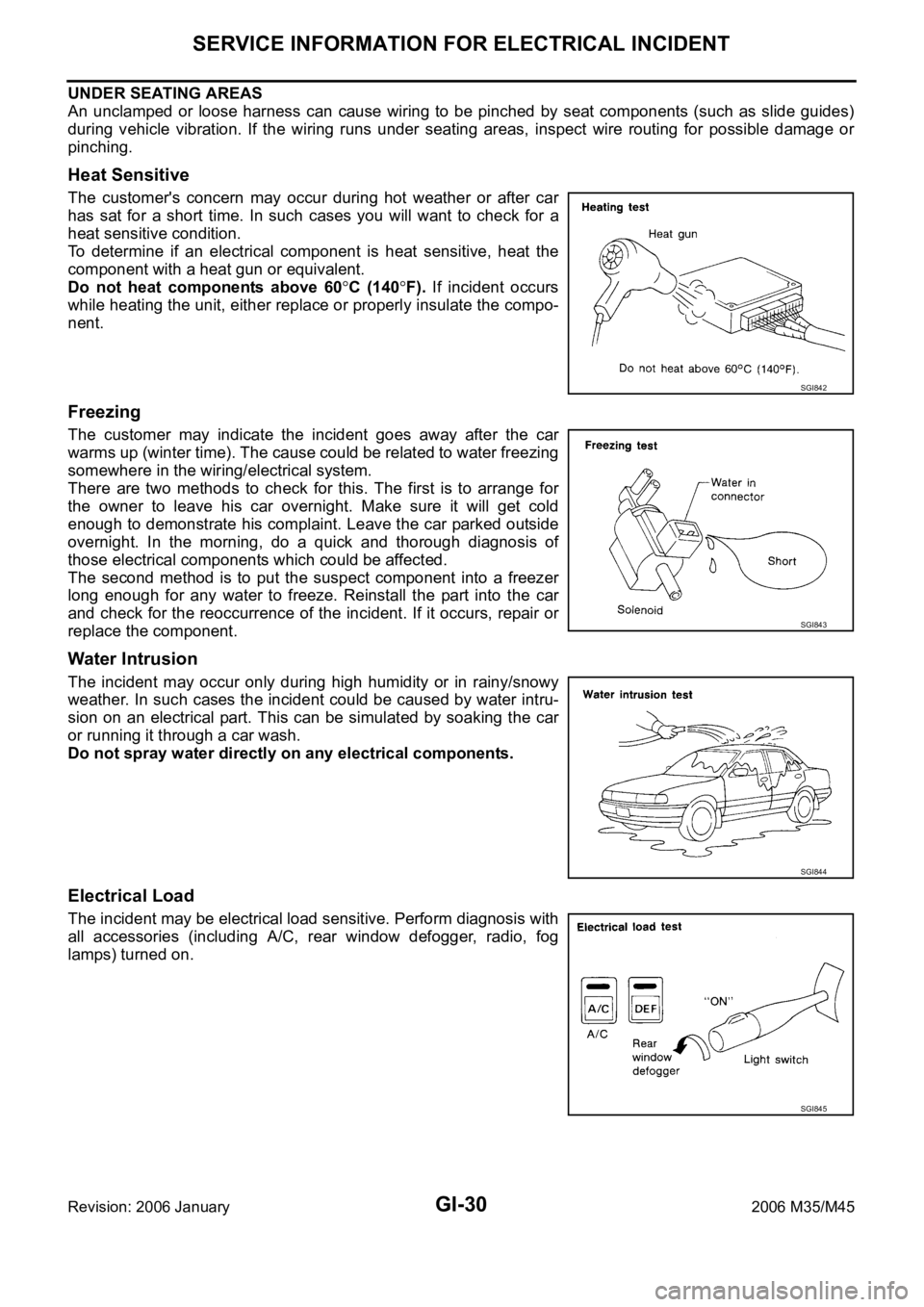
Heat Sensitive
The customer's concern may occur during hot weather or after car
has sat for a short time. In such cases you will want to check for a
heat sensitive condition.
To determine if an electrical component is heat sensitive, heat the
component with a heat gun or equivalent.
Do not heat components above 60
C (140F). If incident occurs
while heating the unit, either replace or properly insulate the compo-
nent.
Freezing
The customer may indicate the incident goes away after the car
warms up (winter time). The cause could be related to water freezing
somewhere in the wiring/electrical system.
There are two methods to check for this. The first is to arrange for
the owner to leave his car overnight. Make sure it will get cold
enough to demonstrate his complaint. Leave the car parked outside
overnight. In the morning, do a quick and thorough diagnosis of
those electrical components which could be affected.
The second method is to put the suspect component into a freezer
long enough for any water to freeze. Reinstall the part into the car
and check for the reoccurrence of the incident. If it occurs, repair or
replace the component.
Water Intrusion
The incident may occur only during high humidity or in rainy/snowy
weather. In such cases the incident could be caused by water intru-
sion on an electrical part. This can be simulated by soaking the car
or running it through a car wash.
Do not spray water directly on any electrical components.
Electrical Load
The incident may be electrical load sensitive. Perform diagnosis with
all accessories (including A/C, rear window defogger, radio, fog
lamps) turned on.
SGI842
SGI843
SGI844
SGI845
Page 3501 of 5621
GI-38
CONSULT-II CHECKING SYSTEM
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
CONSULT-II CHECKING SYSTEMPFP:00000
DescriptionNAS0007S
CONSULT-II is a hand-held type tester. When it is connected with a diagnostic connector equipped on the
vehicle side, it will communicate with the control unit equipped in the vehicle and then enable various
kinds of diagnostic tests.
Refer to “CONSULT-II Software Operation Manual” for more information.
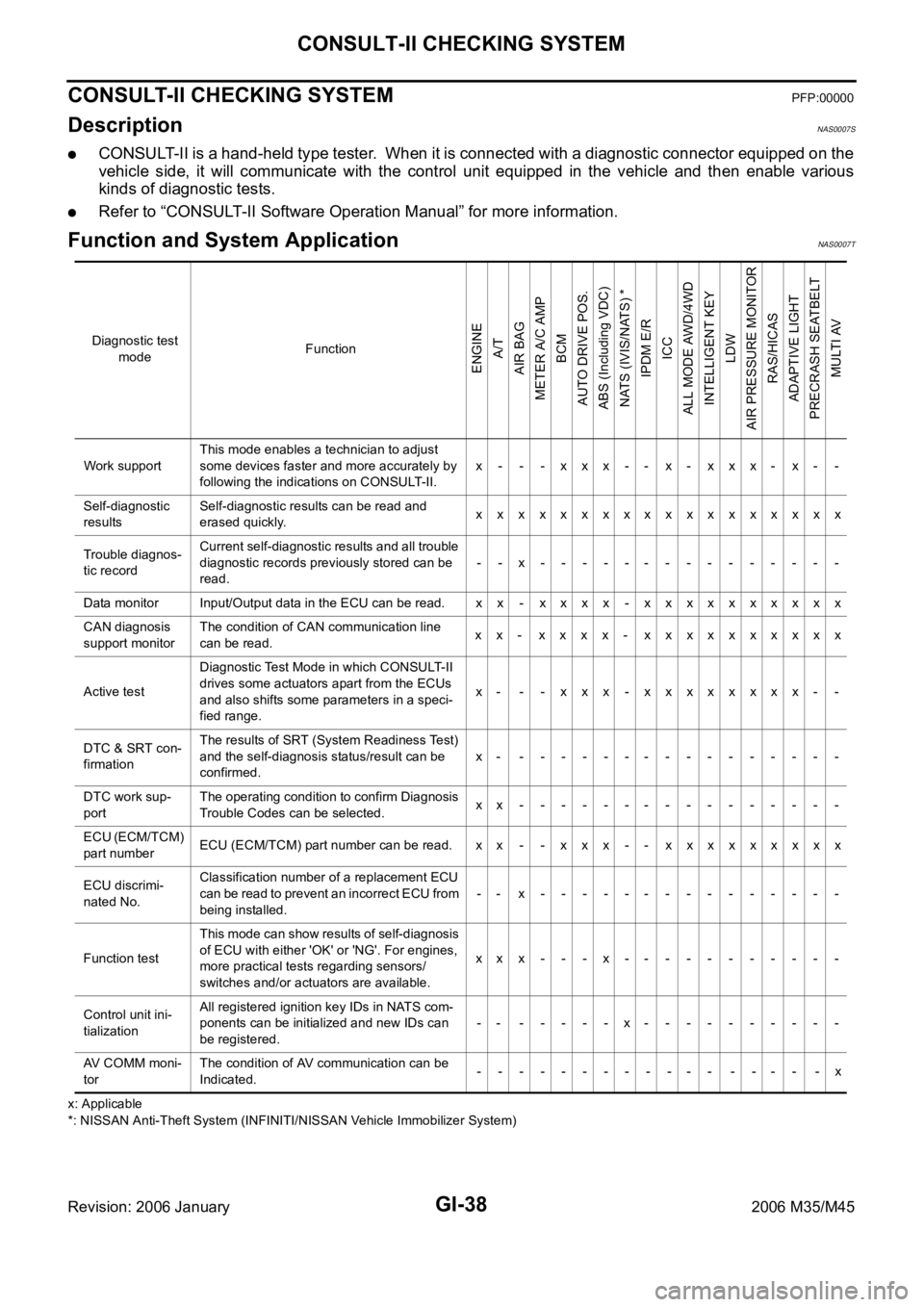
Function and System Application NAS0007T
x: Applicable
*: NISSAN Anti-Theft System (INFINITI/NISSAN Vehicle Immobilizer System) Diagnostic test
modeFunction
ENGINE
A/T
AIR BAG
METER A/C AMP
BCM
AUTO DRIVE POS.
ABS (Including VDC)
NATS (IVIS/NATS) *
IPDM E/R
ICC
ALL MODE AWD/4WD
INTELLIGENT KEY
LDW
AIR PRESSURE MONITOR
RAS/HICAS
ADAPTIVE LIGHT
PRECRASH SEATBELT
MULTI AV
Work supportThis mode enables a technician to adjust
some devices faster and more accurately by
following the indications on CONSULT-II.x - - - xxx -- x- xxx- x- -
Self-diagnostic
resultsSelf-diagnostic results can be read and
erased quickly.xxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx
Trouble diagnos-
tic recordCurrent self-diagnostic results and all trouble
diagnostic records previously stored can be
read.--x---------------
Data monitor Input/Output data in the ECU can be read. x x - x x x x - x xxxxxxxxx
CAN diagnosis
support monitorThe condition of CAN communication line
can be read.xx- xxxx- xxxxxxxxxx
Active testDiagnostic Test Mode in which CONSULT-II
drives some actuators apart from the ECUs
and also shifts some parameters in a speci-
fied range.x- - - xxx -xxxxxxxx- -
DTC & SRT con-
firmationThe results of SRT (System Readiness Test)
and the self-diagnosis status/result can be
confirmed.x- ----------------
DTC work sup-
portThe operating condition to confirm Diagnosis
Trouble Codes can be selected.xx----------------
ECU (ECM/TCM)
part numberECU (ECM/TCM) part number can be read. xx - - xxx -- xxxxxxxxx
ECU discrimi-
nated No.Classification number of a replacement ECU
can be read to prevent an incorrect ECU from
being installed.-- x---------------
Function testThis mode can show results of self-diagnosis
of ECU with either 'OK' or 'NG'. For engines,
more practical tests regarding sensors/
switches and/or actuators are available.xxx---x-----------
Control unit ini-
tializationAll registered ignition key IDs in NATS com-
ponents can be initialized and new IDs can
be registered.-- -----x----------
AV COMM moni-
torThe condition of AV communication can be
Indicated.------------ ---- -x
Page 3513 of 5621
GI-50
IDENTIFICATION INFORMATION
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
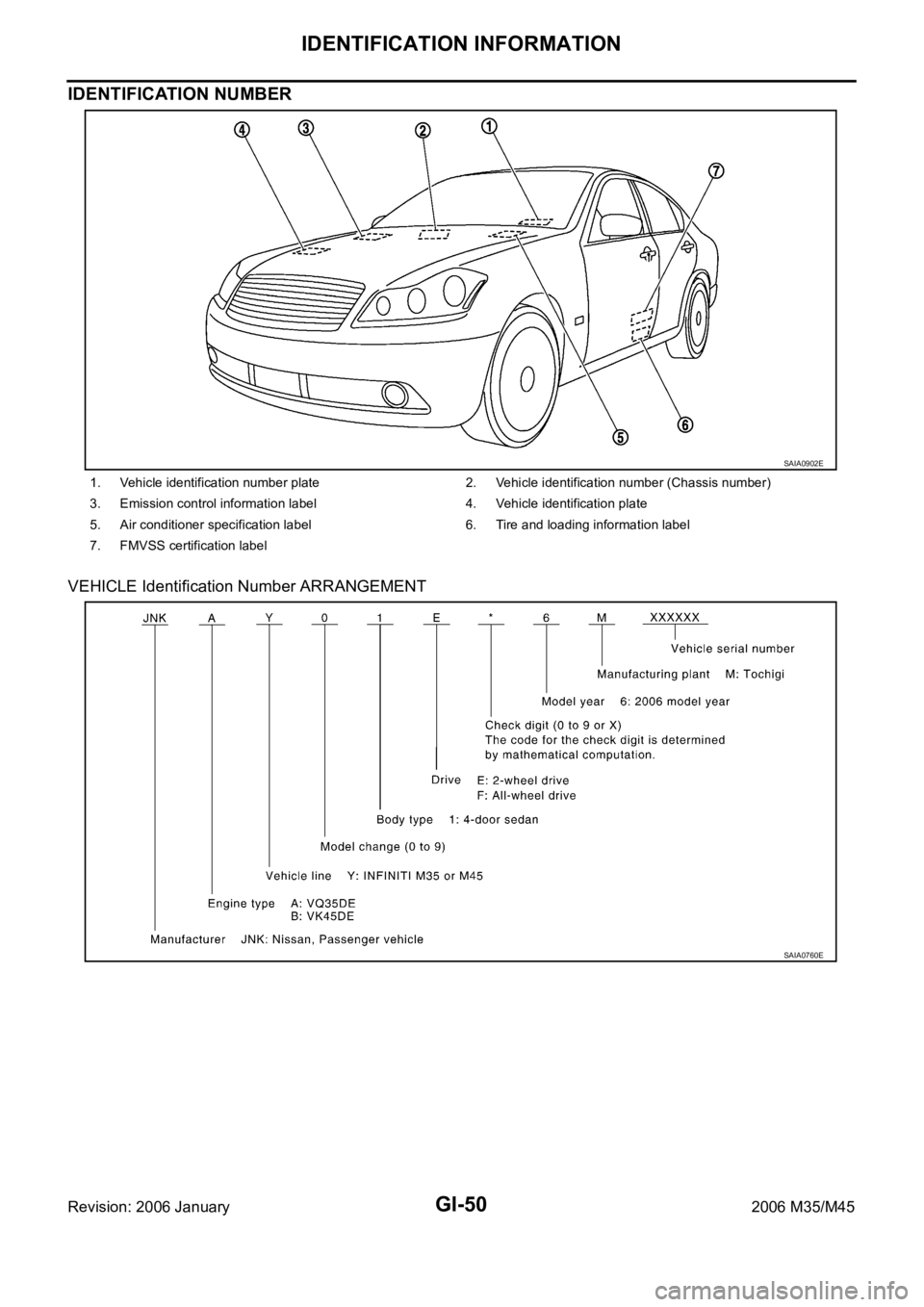
IDENTIFICATION NUMBER
VEHICLE Identification Number ARRANGEMENT
1. Vehicle identification number plate 2. Vehicle identification number (Chassis number)
3. Emission control information label 4. Vehicle identification plate
5. Air conditioner specification label 6. Tire and loading information label
7. FMVSS certification label
SAIA0902E
SAIA0760E
Page 3521 of 5621

GW-2Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45 SIDE WINDOW GLASS ............................................ 59
Removal and Installation ........................................ 59
REMOVAL ........................................................
... 59
INSTALLATION .................................................... 60
REAR WINDOW GLASS AND MOLDING ................ 61
Removal and Installation ........................................ 61
REMOVAL ........................................................
... 61
INSTALLATION .................................................... 62
FRONT DOOR GLASS AND REGULATOR ............. 63
Removal and Installation ........................................ 63
DOOR GLASS ..................................................... 63
REGULATOR ASSEMBLY .................................. 64
Disassembly and Assembly .................................... 65
REGULATOR ASSEMBLY .................................. 65
Inspection after Installation ..................................... 65
SYSTEM INITIALIZATION ................................... 65
INSPECT THE FUNCTION OF THE ANTI-
PINCH SYSTEM. ................................................. 65
FITTING INSPECTION ........................................ 66
REAR DOOR GLASS AND REGULATOR ............... 67
Removal and Installation ........................................ 67
DOOR GLASS ..................................................... 67
REGULATOR ASSEMBLY .................................. 68
Disassembly and Assembly .................................... 70
REGULATOR ASSEMBLY .................................. 70
Inspection after Installation ..................................... 70
SYSTEM INITIALIZATION ................................... 70
INSPECT THE FUNCTION OF THE ANTI-
PINCH SYSTEM .................................................. 70
FITTING INSPECTION ........................................ 70
INSIDE MIRROR ....................................................... 71
Wiring Diagram –I/MIRR– ....................................... 71
Removal and Installation ........................................ 72
REMOVAL ........................................................
... 72
INSTALLATION .................................................... 72
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER .................................. 73
Component Parts and Harness Connector Location ... 73
System Description ................................................. 73
CAN Communication System Description .............. 75
CAN Communication Unit ....................................... 75
Schematic ............................................................... 76
Wiring Diagram — DEF — ..................................... 77
Terminal and Reference Value for BCM ................. 81
Terminal and Reference Value for IPDM E/R ......... 81
CONSULT-II Inspection Procedure ......................... 82
DATA MONITOR .................................................. 83
ACTIVE TEST ..................................................... 83
Work Flow ............................................................... 84Trouble Diagnoses Symptom Chart .....................
... 84
BCM Power Supply and Ground Circuit Check ...... 85
Rear Window Defogger Switch Circuit Check ......... 86
Rear Window Defogger Power Supply Circuit
Check ...................................................................... 86
Rear Window Defogger Circuit Check .................... 88
Door Mirror Defogger Power Supply Circuit Check ... 89
Driver Side Door Mirror Defogger Circuit Check ..... 91
Passenger Side Door Mirror Defogger Circuit Check
... 92
Filament Check ....................................................... 94
Filament Repair ....................................................... 94
REPAIR EQUIPMENT ......................................... 94
REPAIRING PROCEDURE ................................. 95
REVERSE INTERLOCK DOOR MIRROR SYSTEM ... 96
Component Parts and Harness Connector Location ... 96
System Description ................................................. 96
OPERATION CONDITIONS ................................ 96
MIRROR UNGLE MEMORY FUNCTION ............ 96
REVERSE INTERLOCK DOOR MIRROR SYS-
TEM OPERATION ............................................... 97
CAN Communication System Description .............. 97
CAN Communication Unit ....................................... 97
Schematic ............................................................... 98
Wiring Diagram —MIRROR— ................................ 99
Terminals and Reference Values for Automatic
Drive Positioner Control Unit .................................104
Terminals and Reference Values for Driver Seat
Control Unit ...........................................................105
CONSULT-II Function (AUTO DRIVE POS.) ........106
CONSULT-II INSPECTION PROCEDURE ........106
DATA MONITOR ................................................107
ACTIVE TEST ....................................................107
Work Flow .............................................................108
Symptom Chart .....................................................108
Check Changeover Switch Circuit ........................109
Check Mirror Switch Circuit Check ....................... 111
Check Mirror Motor Circuit Check .........................113
Check Mirror Sensor Circuit Check .......................116
Check A/T Control Device R Position Circuit ........119
DOOR MIRROR .......................................................120
Automatic Drive Positioner Interlocking Door Mirror .120
Removal and Installation .......................................120
REMOVAL ..........................................................120
INSTALLATION ..................................................120
Disassembly and Assembly ..................................121
DISASSEMBLY ..................................................121
ASSEMBLY ........................................................122
Page 3524 of 5621
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
GW-5
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
MA
B
GW
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSESPFP:00000
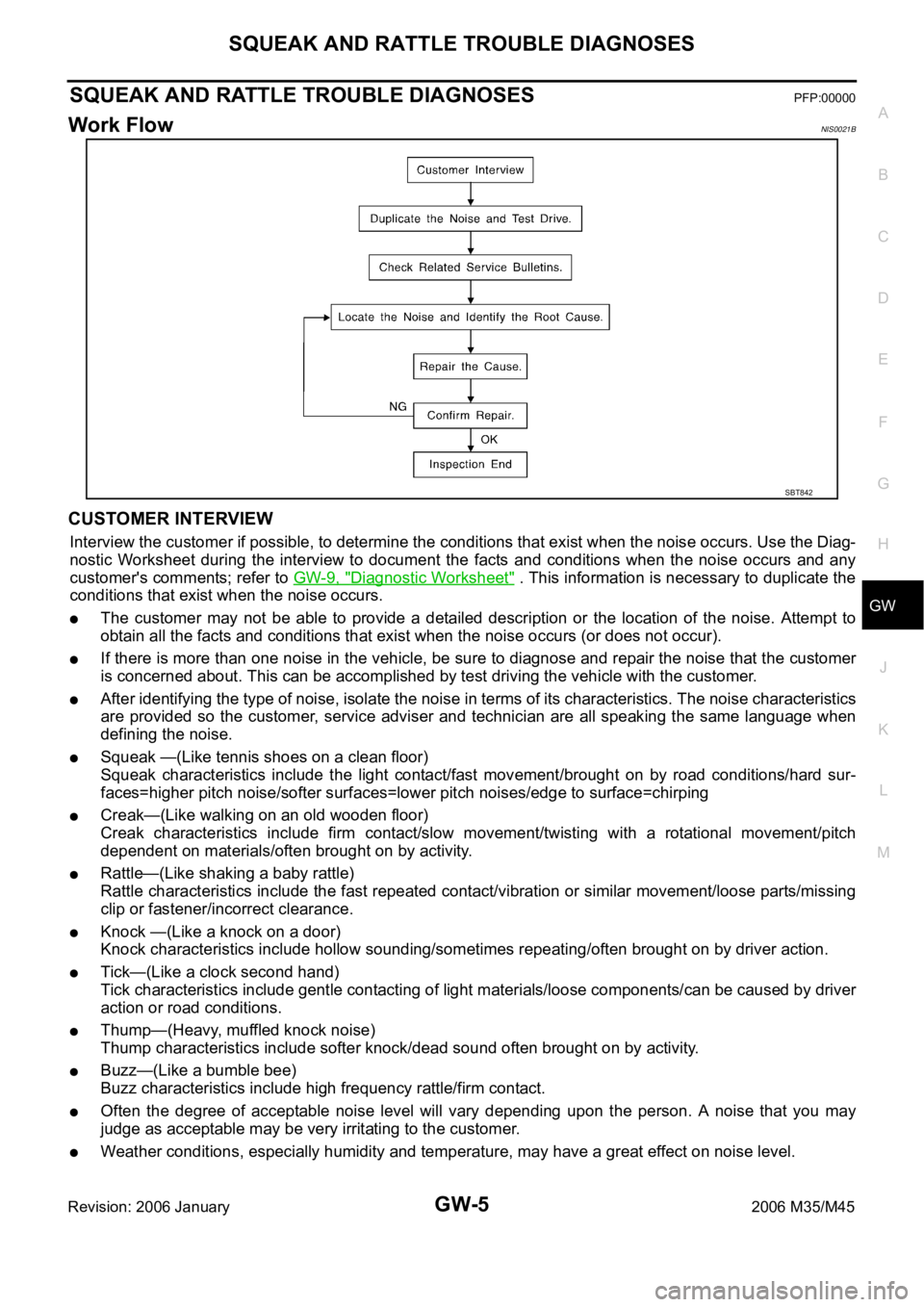
Work FlowNIS0021B
CUSTOMER INTERVIEW
Interview the customer if possible, to determine the conditions that exist when the noise occurs. Use the Diag-
nostic Worksheet during the interview to document the facts and conditions when the noise occurs and any
customer's comments; refer to GW-9, "
Diagnostic Worksheet" . This information is necessary to duplicate the
conditions that exist when the noise occurs.
The customer may not be able to provide a detailed description or the location of the noise. Attempt to
obtain all the facts and conditions that exist when the noise occurs (or does not occur).
If there is more than one noise in the vehicle, be sure to diagnose and repair the noise that the customer
is concerned about. This can be accomplished by test driving the vehicle with the customer.
After identifying the type of noise, isolate the noise in terms of its characteristics. The noise characteristics
are provided so the customer, service adviser and technician are all speaking the same language when
defining the noise.
Squeak —(Like tennis shoes on a clean floor)
Squeak characteristics include the light contact/fast movement/brought on by road conditions/hard sur-
faces=higher pitch noise/softer surfaces=lower pitch noises/edge to surface=chirping
Creak—(Like walking on an old wooden floor)
Creak characteristics include firm contact/slow movement/twisting with a rotational movement/pitch
dependent on materials/often brought on by activity.
Rattle—(Like shaking a baby rattle)
Rattle characteristics include the fast repeated contact/vibration or similar movement/loose parts/missing
clip or fastener/incorrect clearance.
Knock —(Like a knock on a door)
Knock characteristics include hollow sounding/sometimes repeating/often brought on by driver action.
Tick—(Like a clock second hand)
Tick characteristics include gentle contacting of light materials/loose components/can be caused by driver
action or road conditions.
Thump—(Heavy, muffled knock noise)
Thump characteristics include softer knock/dead sound often brought on by activity.
Buzz—(Like a bumble bee)
Buzz characteristics include high frequency rattle/firm contact.
Often the degree of acceptable noise level will vary depending upon the person. A noise that you may
judge as acceptable may be very irritating to the customer.
Weather conditions, especially humidity and temperature, may have a great effect on noise level.
SBT842