2006 INFINITI M35 light
[x] Cancel search: lightPage 3614 of 5621
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER
GW-95
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
MA
B
GW
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
REPAIRING PROCEDURE
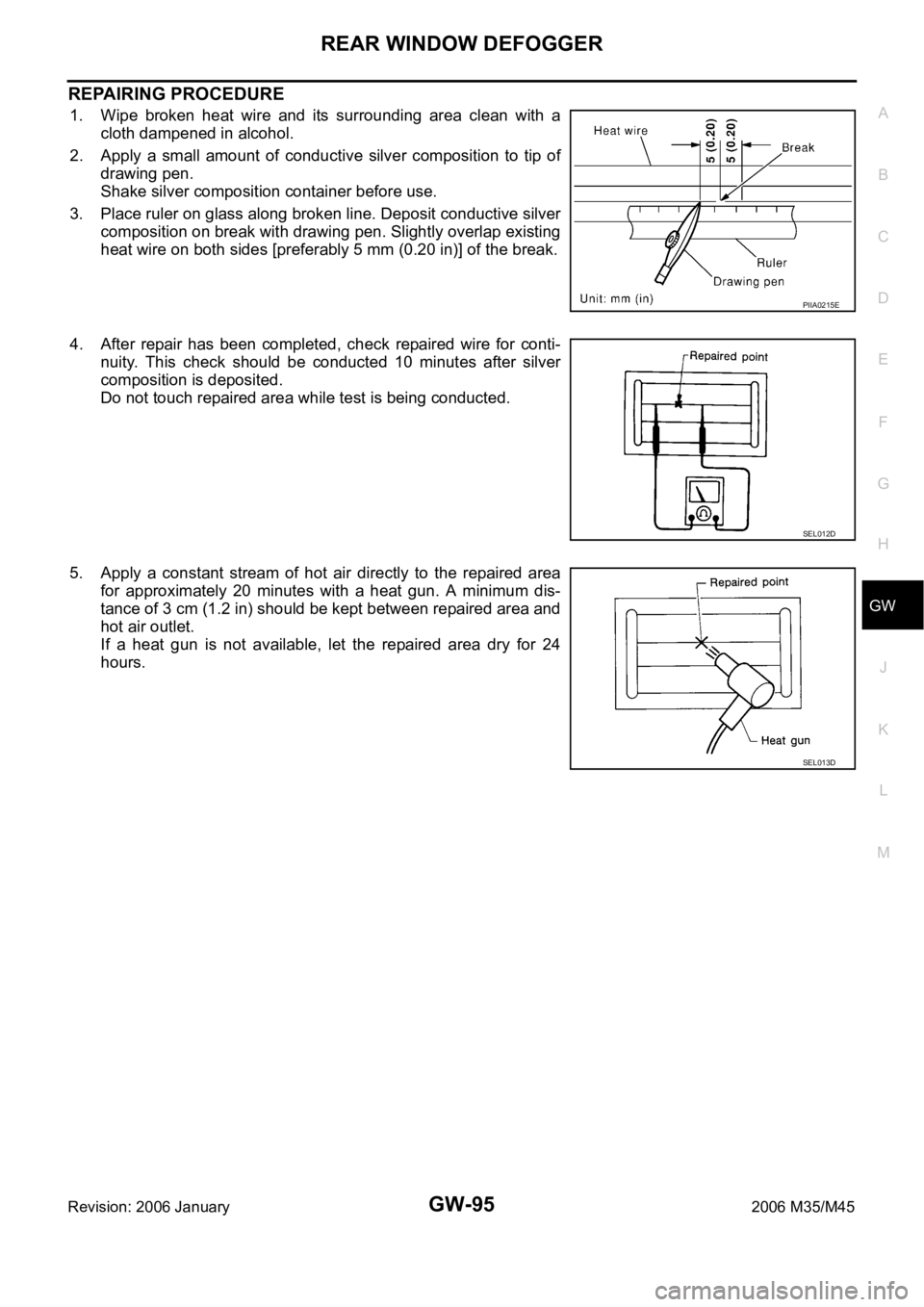
1. Wipe broken heat wire and its surrounding area clean with a
cloth dampened in alcohol.
2. Apply a small amount of conductive silver composition to tip of
drawing pen.
Shake silver composition container before use.
3. Place ruler on glass along broken line. Deposit conductive silver
composition on break with drawing pen. Slightly overlap existing
heat wire on both sides [preferably 5 mm (0.20 in)] of the break.
4. After repair has been completed, check repaired wire for conti-
nuity. This check should be conducted 10 minutes after silver
composition is deposited.
Do not touch repaired area while test is being conducted.
5. Apply a constant stream of hot air directly to the repaired area
for approximately 20 minutes with a heat gun. A minimum dis-
tance of 3 cm (1.2 in) should be kept between repaired area and
hot air outlet.
If a heat gun is not available, let the repaired area dry for 24
hours.
PIIA0215E
SEL012D
SEL013D
Page 3640 of 5621
DOOR MIRROR
GW-121
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
MA
B
GW
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
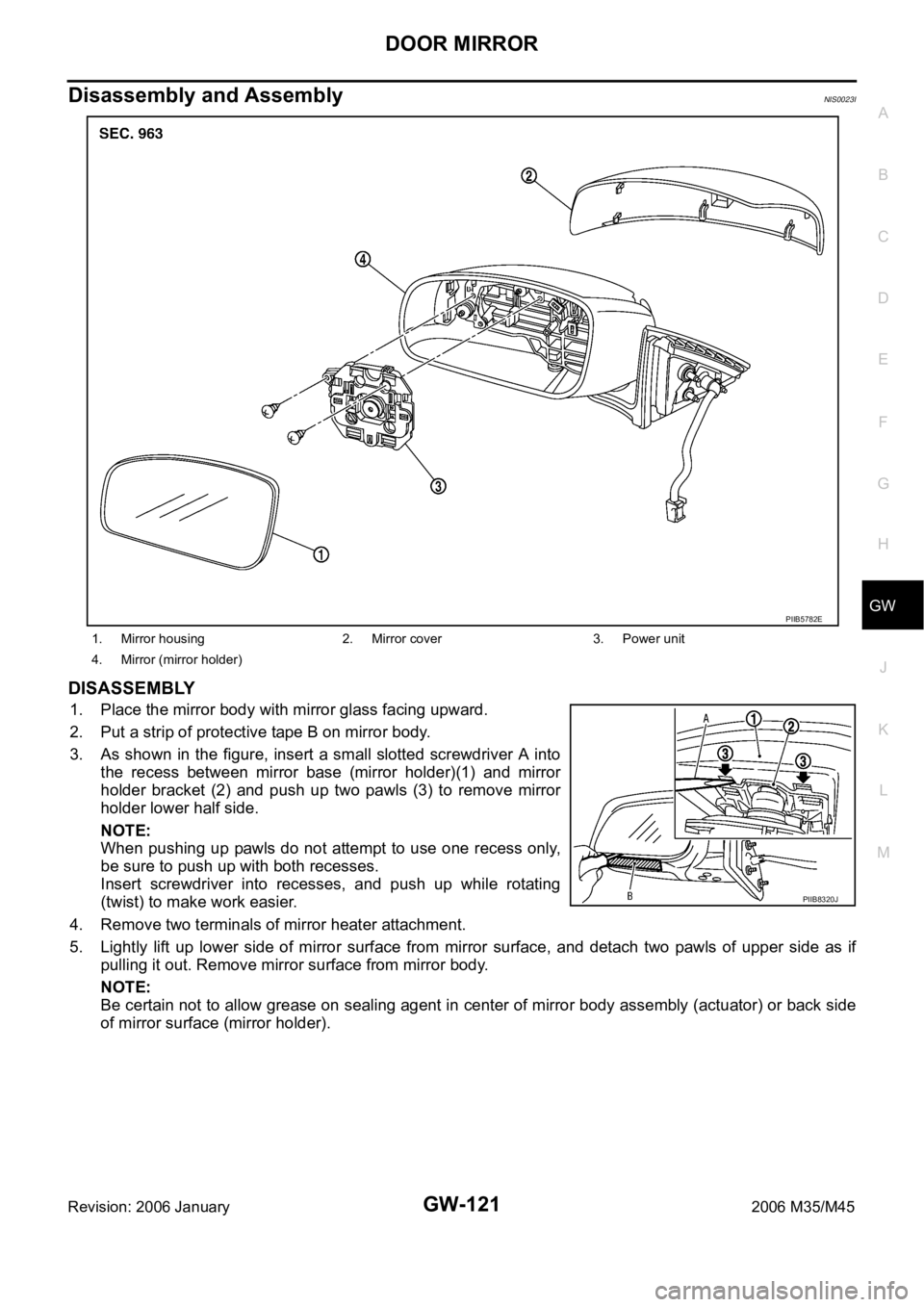
Disassembly and AssemblyNIS0023I
DISASSEMBLY
1. Place the mirror body with mirror glass facing upward.
2. Put a strip of protective tape B on mirror body.
3. As shown in the figure, insert a small slotted screwdriver A into
the recess between mirror base (mirror holder)(1) and mirror
holder bracket (2) and push up two pawls (3) to remove mirror
holder lower half side.
NOTE:
When pushing up pawls do not attempt to use one recess only,
be sure to push up with both recesses.
Insert screwdriver into recesses, and push up while rotating
(twist) to make work easier.
4. Remove two terminals of mirror heater attachment.
5. Lightly lift up lower side of mirror surface from mirror surface, and detach two pawls of upper side as if
pulling it out. Remove mirror surface from mirror body.
NOTE:
Be certain not to allow grease on sealing agent in center of mirror body assembly (actuator) or back side
of mirror surface (mirror holder).
1. Mirror housing 2. Mirror cover 3. Power unit
4. Mirror (mirror holder)
PIIB5782E
PIIB8320J
Page 3644 of 5621

IDX-3
A
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L B
IDX
ALPHABETICAL INDEX
Camshaft(VQ35DE) ........................................... EM-84
CAN .................................................................... DI-77
CAN - Wiring diagram ......... EC-174, EC-887, AT-106,
LAN-50
, LAN-91, LAN-132, LAN-179, LAN-226,
LAN-277
, LAN-323, LAN-369, LAN-419, LAN-469,
LAN-523
, LAN-566, LAN-609, LAN-658, LAN-707
CAN (Controller Area Network) ... SB-5, BL-26, BL-60,
BL-224
, GW-19, GW-75, GW-97, SE-16
CAN communication ........... EC-173, EC-176, EC-748,
EC-886
, EC-889, AT-32, AT-105, TF-13, TF-32, WT-12,
SB-5
, BL-26, BL-60, BL-224, GW-19, GW-75, GW-97,
SE-16
, WW-11
Canister-See EVAP canister ............... EC-42, EC-752
Center bearing assembly (propeller shaft) ........ PR-12
Center bearing disassembly (propeller shaft) .... PR-11
CHARGE - Wiring diagram ................................ SC-25
Charging system ................................................ SC-23
Chassis and body maintenance ........................ MA-29
CHIME - Wiring diagram ..................................... DI-64
CIGAR - Wiring diagram .................................. WW-49
Cigarette lighter ............................................... WW-49
Circuit breaker ................................................... PG-17
Clock ................................................................. DI-108
CLOCK - Wiring diagram .................................. DI-108
Closed loop control .............................. EC-32, EC-742
Closed loop control (Bank 1) ........... EC-509, EC-1236
Closed loop control (Bank 2) ........... EC-509, EC-1236
Collision diagnosis ........................................... SRS-50
Combination lamp, front, removal and installation ........
LT-76
Combination lamp, rear, removal and installation ........
LT-266
Combination meter ............................................... DI-5
COMPAS - Wiring diagram ............................... DI-106
Compass .......................................................... DI-105
Component Location (auto A/C) ...................... ATC-42
Compression pressure(VK45DE) .................... EM-233
Compression pressure(VQ35DE) .................... EM-101
Compressor special service tool ...................... ATC-16
Condenser ..................................................... ATC-165
Connecting rod bearing clearance(VK45DE) .. EM-273
Connecting rod bushing clearance .................. EM-142
Connecting rod bushing clearance(VK45DE) .. EM-268
Connecting rod(VK45DE) ................................ EM-268
Connecting rod(VQ35DE) ................................ EM-140
CONSULT-II Reference value (A/T) .................. AT-90
Control units (terminal arrangement) ............... PG-104
Control valve (A/T) ............................................. AT-38
Controller Area Network (CAN) ... SB-5, BL-26, BL-60,
BL-224
, GW-19, GW-75, GW-97, SE-16
Converter housing installation ............ AT-274, AT-277
COOL/F - Wiring diagram ................ EC-515, EC-1242
Coolant replacement(VQ35DE) ......................... MA-15
Cooling circuit (engine)(VK45DE) ...................... CO-38
Cooling circuit (engine)(VQ35DE) ....................... CO-9
Cooling fan motor ............ EC-524, EC-1249, EC-1250
Cooling fan(VK45DE) ........................................ CO-51
Cooling fan(VQ35DE) ........................................ CO-22
Cowl top ............................................................... EI-18
Cowl top cover .................................................... EI-18
Crankcase ventilation system - See Positive crankcase
ventilation ............................................. EC-51
, EC-761
Crankshaft position sensor (POS) ... EC-376, EC-1099
Crankshaft(VK45DE) ...................................... EM-250
Crankshaft(VQ35DE) ...................................... EM-140
Crash zone sensor .......................................... SRS-45
CUR/SE - Wiring diagram .. EC-539, EC-545, EC-551,
EC-557
, EC-1265, EC-1271, EC-1277, EC-1283
Cylinder block boring(VK45DE) ...................... EM-271
Cylinder block(VK45DE) ................................. EM-249
Cylinder block(VQ35DE) ................................. EM-123
Cylinder head bolt tightening(VK45DE) .......... EM-235
Cylinder head bolt tightening(VQ35DE) .......... EM-104
Cylinder head(VK45DE) ................................. EM-233
Cylinder head(VQ35DE) ................................. EM-101
D
D/LOCK - Wiring diagram .................................. BL-28
Daytime light system ........................................... LT-79
Daytime running light - See Daytime light system LT-79
DEF - Wiring diagram ............................ SB-7, SE-118
Diagnosis sensor unit ..................................... SRS-48
Diagnostic trouble code (DTC) for OBD system EC-16,
EC-58
, EC-726, EC-769
Direct clutch solenoid valve ............... AT-155, AT-157
Display and amp.assembly ............... ATC-53, ATC-66
Door glass ........................................... GW-63, GW-67
Door glass Fitting Adjustment(Front) ................ GW-66
Door glass Fitting Adjustment(Rear) ................. GW-70
Door lock .......................................................... BL-196
Door mirror ...................................................... GW-120
Door trim ............................................................. EI-34
Door, front ........................................... BL-190, GW-63
Door, rear ............................................ BL-190, GW-67
Drive belt inspection ......................................... MA-22
Drive belt inspection(VQ35DE) ......................... MA-14
Drive belt(VK45DE) ........................................ EM-174
Drive belt(VQ35DE) .......................................... EM-15
Drive shaft ......................................................... MA-38
Drive shaft (rear) ............................................... RAX-8
Driver air bag .................................................. SRS-38
DTRL - Wiring diagram ....................................... LT-84
Duct and grilles .............................................. ATC-144
E
ECM power supply EC-166
, EC-492, EC-879, EC-1211
ECM/PW - Wiring diagram ............... EC-493, EC-1212
ECTS - Wiring diagram ...................... EC-228, EC-950
Electric sunroof .................................................. RF-10
Electric throttle control actuator ........ EC-613, EC-624,
EC-1344
, EC-1356
Electric throttle control actuator (VK45DE) ..... EM-179
Electric throttle control actuator (VQ35DE) ....... EM-19
Electrical load signal circuit .............. EC-697, EC-1439
Electrical unit ................................................... PG-104
Electrical units location ...................................... PG-96
Page 3653 of 5621
IP-4
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSESPFP:00000
Work FlowNIS00259
CUSTOMER INTERVIEW
Interview the customer if possible, to determine the conditions that exist when the noise occurs. Use the Diag-
nostic Worksheet during the interview to document the facts and conditions when the noise occurs and any
customer's comments; refer to IP-8, "
Diagnostic Worksheet" . This information is necessary to duplicate the
conditions that exist when the noise occurs.
The customer may not be able to provide a detailed description or the location of the noise. Attempt to
obtain all the facts and conditions that exist when the noise occurs (or does not occur).
If there is more than one noise in the vehicle, be sure to diagnose and repair the noise that the customer
is concerned about. This can be accomplished by test driving the vehicle with the customer.
After identifying the type of noise, isolate the noise in terms of its characteristics. The noise characteristics
are provided so the customer, service adviser and technician are all speaking the same language when
defining the noise.
Squeak —(Like tennis shoes on a clean floor)
Squeak characteristics include the light contact/fast movement/brought on by road conditions/hard sur-
faces=higher pitch noise/softer surfaces=lower pitch noises/edge to surface=chirping
Creak—(Like walking on an old wooden floor)
Creak characteristics include firm contact/slow movement/twisting with a rotational movement/pitch
dependent on materials/often brought on by activity.
Rattle—(Like shaking a baby rattle)
Rattle characteristics include the fast repeated contact/vibration or similar movement/loose parts/missing
clip or fastener/incorrect clearance.
Knock —(Like a knock on a door)
Knock characteristics include hollow sounding/sometimes repeating/often brought on by driver action.
Tick—(Like a clock second hand)
Tick characteristics include gentle contacting of light materials/loose components/can be caused by driver
action or road conditions.
Thump—(Heavy, muffled knock noise)
Thump characteristics include softer knock/dead sound often brought on by activity.
Buzz—(Like a bumble bee)
Buzz characteristics include high frequency rattle/firm contact.
Often the degree of acceptable noise level will vary depending upon the person. A noise that you may
judge as acceptable may be very irritating to the customer.
Weather conditions, especially humidity and temperature, may have a great effect on noise level.
SBT842
Page 3655 of 5621
IP-6
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
INSULATOR (Light foam block)
80845-71L00: 30 mm (1.18 in) thick, 30
50 mm (1.181.97 in)
FELT CLOTHTAPE
Used to insulate where movement does not occur. Ideal for instrument panel applications.
68370-4B000: 15
25 mm (0.590.98 in) pad/68239-13E00: 5 mm (0.20 in) wide tape roll
The following materials, not found in the kit, can also be used to repair squeaks and rattles.
UHMW (TEFLON) TAPE
Insulates where slight movement is present. Ideal for instrument panel applications.
SILICONE GREASE
Used in place of UHMW tape that will be visible or not fit. Will only last a few months.
SILICONE SPRAY
Use when grease cannot be applied.
DUCT TAPE
Use to eliminate movement.
CONFIRM THE REPAIR
Confirm that the cause of a noise is repaired by test driving the vehicle. Operate the vehicle under the same
conditions as when the noise originally occurred. Refer to the notes on the Diagnostic Worksheet.
Generic Squeak and Rattle TroubleshootingNIS0025A
Refer to Table of Contents for specific component removal and installation information.
INSTRUMENT PANEL
Most incidents are caused by contact and movement between:
1. The cluster lid A and instrument panel
2. Acrylic lens and combination meter housing
3. Instrument panel to front pillar garnish
4. Instrument panel to windshield
5. Instrument panel mounting pins
6. Wiring harnesses behind the combination meter
7. A/C defroster duct and duct joint
These incidents can usually be located by tapping or moving the components to duplicate the noise or by
pressing on the components while driving to stop the noise. Most of these incidents can be repaired by apply-
ing felt cloth tape or silicon spray (in hard to reach areas). Urethane pads can be used to insulate wiring har-
ness.
CAUTION:
Do not use silicone spray to isolate a squeak or rattle. If you saturate the area with silicone, you will
not be able to recheck the repair.
CENTER CONSOLE
Components to pay attention to include:
1. Shifter assembly cover to finisher
2. A/C control unit and cluster lid C
3. Wiring harnesses behind audio and A/C control unit
The instrument panel repair and isolation procedures also apply to the center console.
DOORS
Pay attention to the:
1. Finisher and inner panel making a slapping noise
2. Inside handle escutcheon to door finisher
3. Wiring harnesses tapping
4. Door striker out of alignment causing a popping noise on starts and stops
Tapping or moving the components or pressing on them while driving to duplicate the conditions can isolate
many of these incidents. You can usually insulate the areas with felt cloth tape or insulator foam blocks from
the Nissan Squeak and Rattle Kit (J-43980) to repair the noise.
Page 3656 of 5621

SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
IP-7
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
MA
B
IP
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
TRUNK
Trunk noises are often caused by a loose jack or loose items put into the trunk by the owner.
In addition look for:
1. Trunk lid dumpers out of adjustment
2. Trunk lid striker out of adjustment
3. The trunk lid torsion bars knocking together
4. A loose license plate or bracket
Most of these incidents can be repaired by adjusting, securing or insulating the item(s) or component(s) caus-
ing the noise.
SUNROOF/HEADLINING
Noises in the sunroof/headlining area can often be traced to one of the following:
1. Sunroof lid, rail, linkage or seals making a rattle or light knocking noise
2. Sunvisor shaft shaking in the holder
3. Front or rear windshield touching headlining and squeaking
Again, pressing on the components to stop the noise while duplicating the conditions can isolate most of these
incidents. Repairs usually consist of insulating with felt cloth tape.
SEATS
When isolating seat noise it's important to note the position the seat is in and the load placed on the seat when
the noise is present. These conditions should be duplicated when verifying and isolating the cause of the
noise.
Cause of seat noise include:
1. Headrest rods and holder
2. A squeak between the seat pad cushion and frame
3. The rear seatback lock and bracket
These noises can be isolated by moving or pressing on the suspected components while duplicating the con-
ditions under which the noise occurs. Most of these incidents can be repaired by repositioning the component
or applying urethane tape to the contact area.
UNDERHOOD
Some interior noise may be caused by components under the hood or on the engine wall. The noise is then
transmitted into the passenger compartment.
Causes of transmitted underhood noise include:
1. Any component mounted to the engine wall
2. Components that pass through the engine wall
3. Engine wall mounts and connectors
4. Loose radiator mounting pins
5. Hood bumpers out of adjustment
6. Hood striker out of adjustment
These noises can be difficult to isolate since they cannot be reached from the interior of the vehicle. The best
method is to secure, move or insulate one component at a time and test drive the vehicle. Also, engine RPM
or load can be changed to isolate the noise. Repairs can usually be made by moving, adjusting, securing, or
insulating the component causing the noise.
Page 3691 of 5621
![INFINITI M35 2006 Factory Service Manual LAN-22
[CAN]
TROUBLE DIAGNOSES WORK FLOW
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
DESCRIPTION OF “CAN DIAG SUPPORT MNTR” SCREEN
FOR AFS CONTROL UNIT
Display Results (Present)
OK: Normal
UNKWN: The diag INFINITI M35 2006 Factory Service Manual LAN-22
[CAN]
TROUBLE DIAGNOSES WORK FLOW
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
DESCRIPTION OF “CAN DIAG SUPPORT MNTR” SCREEN
FOR AFS CONTROL UNIT
Display Results (Present)
OK: Normal
UNKWN: The diag](/manual-img/42/57023/w960_57023-3690.png)
LAN-22
[CAN]
TROUBLE DIAGNOSES WORK FLOW
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
DESCRIPTION OF “CAN DIAG SUPPORT MNTR” SCREEN
FOR AFS CONTROL UNIT
Display Results (Present)
OK: Normal
UNKWN: The diagnosed unit does not transmit or receive the applicable data normally.
–: There is no received unit or the unit is not in the condition that reception diagnosis is performed.
Display Results (Past)
OK: Normal
0: There is malfunction now.
1 ~ 39: Displays when it is normal at present and finds malfunction in the past. It increases like 012...3839 after returning to the
normal condition whenever IGN OFF
ON. If it is over 39, it is fixed to 39 until the self-diagnostic results are erased. It returns to 0
when malfunction is detected again in the process.
–: Undiagnosed
PKIB9800E
“SELECT SYSTEM”
screen“CAN DIAG SUPPORT
MNTR” screenDescription Present Past
ADAPTIVE LIGHTTRANSMIT DIAG Make sure of normal transmission. OK/UNKWN/–
OK/0/1~39/– ECM Make sure of normal reception from ECM. OK/UNKWN/–
METER/M&AMake sure of normal reception from unified
meter and A/C amp.OK/UNKWN/–
TCM Make sure of normal reception from TCM. OK/UNKWN/–
STRGMake sure of normal reception from steering
angle sensor. OK/UNKWN/–
IPDM E/R Make sure of normal reception from IPDM E/R. OK/UNKWN/–
Page 3703 of 5621
![INFINITI M35 2006 Factory Service Manual LAN-34
[CAN]
CAN COMMUNICATION
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
CAN COMMUNICATIONPFP:23710
System DescriptionNKS003XV
CAN (Controller Area Network) is a serial communication line for real time appli INFINITI M35 2006 Factory Service Manual LAN-34
[CAN]
CAN COMMUNICATION
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
CAN COMMUNICATIONPFP:23710
System DescriptionNKS003XV
CAN (Controller Area Network) is a serial communication line for real time appli](/manual-img/42/57023/w960_57023-3702.png)
LAN-34
[CAN]
CAN COMMUNICATION
Revision: 2006 January2006 M35/M45
CAN COMMUNICATIONPFP:23710
System DescriptionNKS003XV
CAN (Controller Area Network) is a serial communication line for real time application. It is an on-vehicle mul-
tiplex communication line with high data communication speed and excellent error detection ability. Many elec-
tronic control units are equipped onto a vehicle, and each control unit shares information and links with other
control units during operation (not independent). In CAN communication, control units are connected with 2
communication lines (CAN H line, CAN L line) allowing a high rate of information transmission with less wiring.
Each control unit transmits/receives data but selectively reads required data only.
CAN Communication UnitNKS003XW
Go to CAN system, when selecting your CAN system type from the following table.
: Applicable
SYSTEM DIAGRAM
Ty pe 1
Body typeSedan
Axle 2WD AWD
Engine VQ35DE/VK45DE VQ35DE
TransmissionA/T
Brake controlVDC
Navigation system
Pre-crash seat belt
Adaptive front-lighting system
ICC system
Lane departure warning
Rear active steer
CAN system type 12 3456789101112131415
CAN system trouble diagnosisLA
N-
48
LA
N-
89
LA
N-
130
LA
N-
177
LA
N-
224
LA
N-
275
LA
N-
321
LA
N-
367
LA
N-
417
LA
N-
467
LA
N-
521
LA
N-
564
LA
N-
607
LA
N-
656
LA
N-
705
PKIB8588E