Page 33 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 0B-2 MAINTENANCE AND LUBRICATION
Maintenance Schedule
Maintenance Schedule Under Normal Driving Conditions
NOTE:
This interval should be judged by odometer reading or months, whichever comes first.
This table includes service as scheduled up to 90,000 km (54,000 miles) mileage. Beyond 90,000 km
(54,000 miles), carry out the same services at the same intervals respectively.
IntervalKm (x 1,000) 15 30 45 60 75 90
Miles (x 1,000) 9 1827364554
Months 12 24 36 48 60 72
ENGINE
Drive belt V-belt I R I R I R
V-rib belt (Flat type)––I––R
Valve lash (clearance) –I–I–I
Engine oil and oil filter R R R R R R
Engine coolant––R––R
Exhaust system–I–I–I
IGNITION SYSTEM
✱Spark plugs When
unleaded
fuel is usedVehicle without
HO2SNickel spark
plug–R–R–R
Iridium spark
plug––R––R
Vehicle with
HO2SNickel spark
plug––R––R
Iridium spark
plug–––R––
When leaded fuel is used, refer to “Maintenance Recommended Under Severe Driving Condi-
tions” in this section.
FUEL SYSTEM
Air cleaner filter I I R I I R
Fuel lines and connections–I–I–I
Fuel filter Replace every 210,000 km (126,000 miles).
Fuel tank––I––I
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
Crankcase ventilation hoses and connections
(Vehicle without HO2S)––I––I
✱PCV valve Vehicle without HO2S––I––I
Vehicle with HO2S–––––I
✱Fuel evaporative emission
control systemVehicle without HO2S–I–I–I
Vehicle with HO2S–––––I
NOTE:
“R”: Replace or change
“I”: Inspect and correct, replace or lubricate if necessary
For Sweden, items with
✱
✱✱ ✱ (asterisk) should be performed by odometer reading only.
For spark plugs, replace every 50,000 km if the local law requires.
Nickel spark plug: BKR6E-11 (NGK) or K20PR-U11 (DENSO)
Iridium spark plug: IFR5E11 (NGK) or SK16PR-A11 (DENSO)
Page 116 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine STEERING, SUSPENSION, WHEELS AND TIRES 3-7
Radial Tire Lead
“Lead” is the deviation of the vehicle from a straight path on a level rod even with no pressure on the steering
wheel.
Lead is usually caused by:
1) Incorrect alignment.
2) Uneven brake adjustment.
3) Tire construction.
The way in which a tire is built can produce lead in a vehicle. An example of this is placement of the belt. Off
center belts on radial tires can cause the tire to develop a side force while rolling straight down the road. If one
side of the tire has a little larger diameter than the other, the tire will tend to roll to one side. This will develop a
side force which can produce vehicle lead.
The procedure in above figure (Lead Diagnosis) should be used to make sure that front alignment is not mis-
taken for tire lead.
1) Part of the lead diagnosis procedure is different from the proper tire rotation pattern currently in the owner
and service manuals. If a medium to high mileage tire is moved to the other side of the vehicle, be sure to
check that ride roughness has not developed.
2) Rear tires will not cause lead.
Vibration Diagnosis
Wheel unbalance causes most of the highway speed vibration problems. If a vibration remains after dynamic
balancing, its possible causes are as follows.
1) Tire runout.
2) Wheel runout.
3) Tire stiffness variation.
Measuring tire and/or wheel free runout will uncover only part of the problem. All three causes, known as loaded
radial runout, must be checked by using a Tire Problem Detector (TPD). If TPD is not available, alternative
method of substituting known good tire and wheel assemblies on the problem vehicle can be used, although it
takes a longer time.
[A] : Tire out of round 1. Smooth road
[B] : Tire stiffness variation 2. Suspension movement (loaded runout)
[C] : Rim bent or out of round
Page 382 of 687
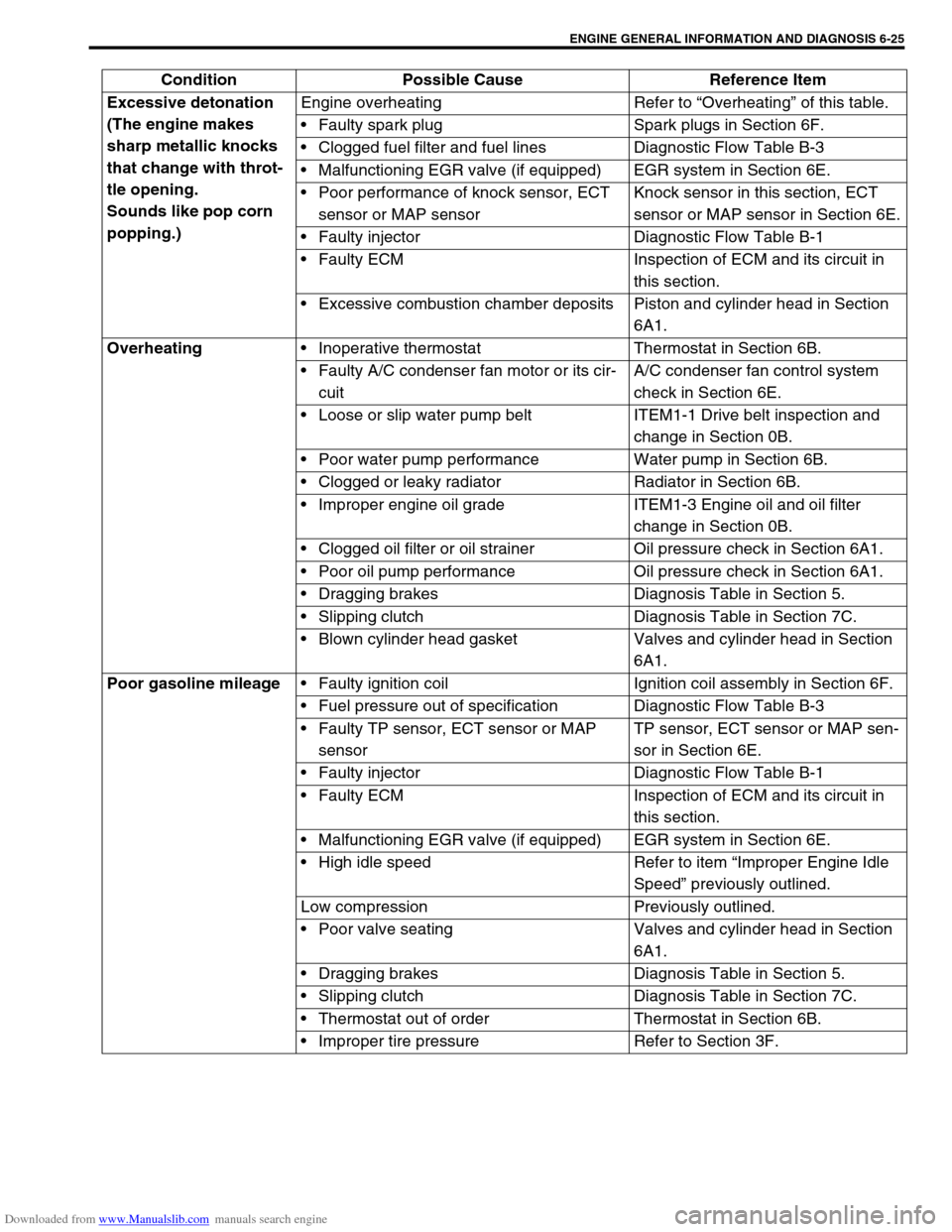
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-25
Excessive detonation
(The engine makes
sharp metallic knocks
that change with throt-
tle opening.
Sounds like pop corn
popping.)Engine overheating Refer to “Overheating” of this table.
Faulty spark plug Spark plugs in Section 6F.
Clogged fuel filter and fuel lines Diagnostic Flow Table B-3
Malfunctioning EGR valve (if equipped) EGR system in Section 6E.
Poor performance of knock sensor, ECT
sensor or MAP sensorKnock sensor in this section, ECT
sensor or MAP sensor in Section 6E.
Faulty injector Diagnostic Flow Table B-1
Faulty ECM Inspection of ECM and its circuit in
this section.
Excessive combustion chamber deposits Piston and cylinder head in Section
6A1.
Overheating
Inoperative thermostat Thermostat in Section 6B.
Faulty A/C condenser fan motor or its cir-
cuitA/C condenser fan control system
check in Section 6E.
Loose or slip water pump belt ITEM1-1 Drive belt inspection and
change in Section 0B.
Poor water pump performance Water pump in Section 6B.
Clogged or leaky radiator Radiator in Section 6B.
Improper engine oil grade ITEM1-3 Engine oil and oil filter
change in Section 0B.
Clogged oil filter or oil strainer Oil pressure check in Section 6A1.
Poor oil pump performance Oil pressure check in Section 6A1.
Dragging brakes Diagnosis Table in Section 5.
Slipping clutch Diagnosis Table in Section 7C.
Blown cylinder head gasket Valves and cylinder head in Section
6A1.
Poor gasoline mileage
Faulty ignition coil Ignition coil assembly in Section 6F.
Fuel pressure out of specification Diagnostic Flow Table B-3
Faulty TP sensor, ECT sensor or MAP
sensorTP sensor, ECT sensor or MAP sen-
sor in Section 6E.
Faulty injector Diagnostic Flow Table B-1
Faulty ECM Inspection of ECM and its circuit in
this section.
Malfunctioning EGR valve (if equipped) EGR system in Section 6E.
High idle speed Refer to item “Improper Engine Idle
Speed” previously outlined.
Low compression Previously outlined.
Poor valve seating Valves and cylinder head in Section
6A1.
Dragging brakes Diagnosis Table in Section 5.
Slipping clutch Diagnosis Table in Section 7C.
Thermostat out of order Thermostat in Section 6B.
Improper tire pressure Refer to Section 3F. Condition Possible Cause Reference Item