Page 276 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine BRAKES 5-15
Fluid Pressure Test (If Equipped with LSPV)
Test procedure for LSPV assembly is as follows.
Before testing, confirm the following.
Fuel tank is filled with fuel fully.
Vehicle is equipped with spare tire, tools, jack and jack han-
dle.
1) Stop vehicle on level floor and place approximately about
140 kg (309 Ibs) weight on rear housing so that rear axle
weights 600 kg (1323 Ib).
Rear axle weight
“L” : 600 kg (1323 lb)
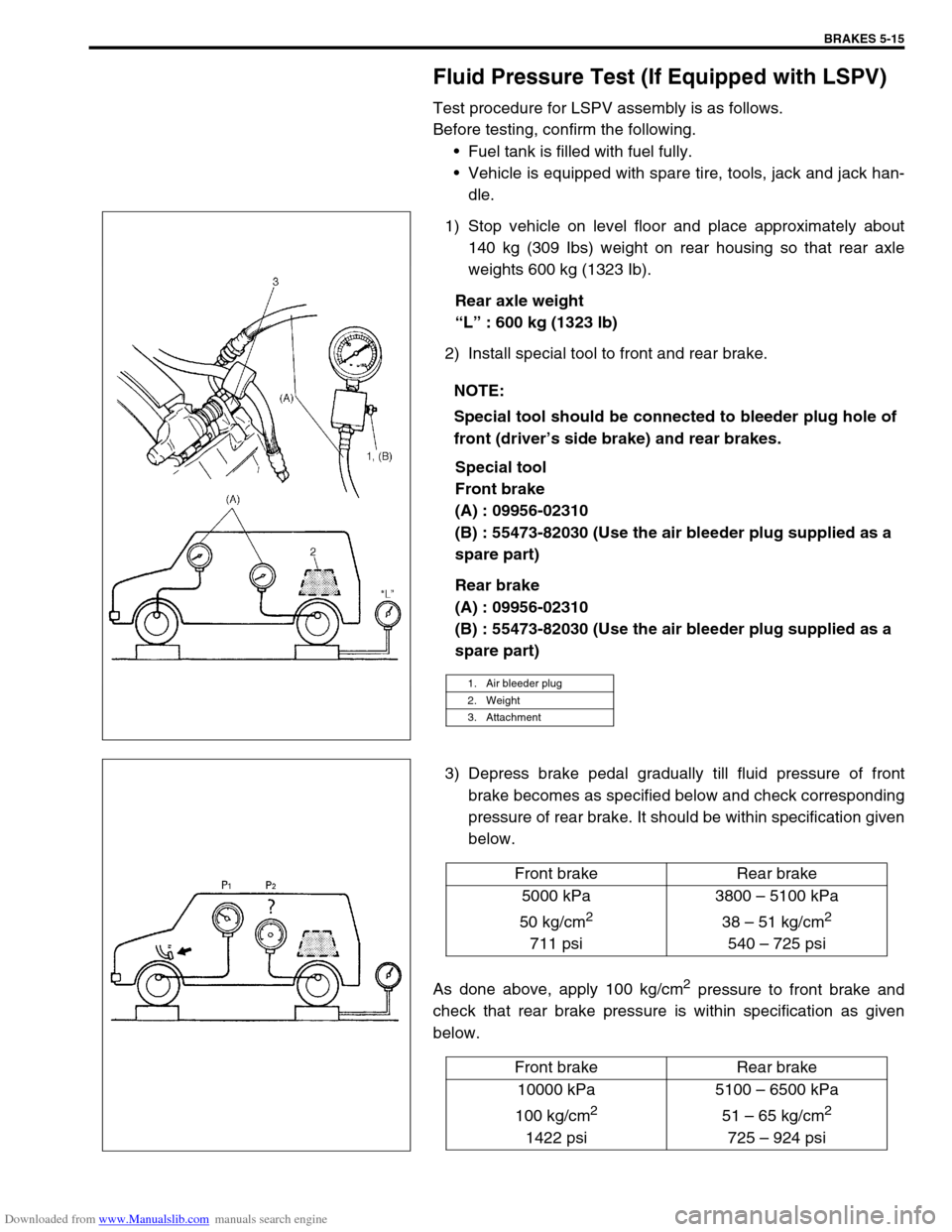
2) Install special tool to front and rear brake.
Special tool
Front brake
(A) : 09956-02310
(B) : 55473-82030 (Use the air bleeder plug supplied as a
spare part)
Rear brake
(A) : 09956-02310
(B) : 55473-82030 (Use the air bleeder plug supplied as a
spare part)
3) Depress brake pedal gradually till fluid pressure of front
brake becomes as specified below and check corresponding
pressure of rear brake. It should be within specification given
below.
As done above, apply 100 kg/cm
2 pressure to front brake and
check that rear brake pressure is within specification as given
below.NOTE:
Special tool should be connected to bleeder plug hole of
front (driver’s side brake) and rear brakes.
1. Air bleeder plug
2. Weight
3. Attachment
Front brake Rear brake
5000 kPa
50 kg/cm
2
711 psi3800 – 5100 kPa
38 – 51 kg/cm
2
540 – 725 psi
Front brake Rear brake
10000 kPa
100 kg/cm
2
1422 psi5100 – 6500 kPa
51 – 65 kg/cm
2
725 – 924 psi
Page 277 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 5-16 BRAKES
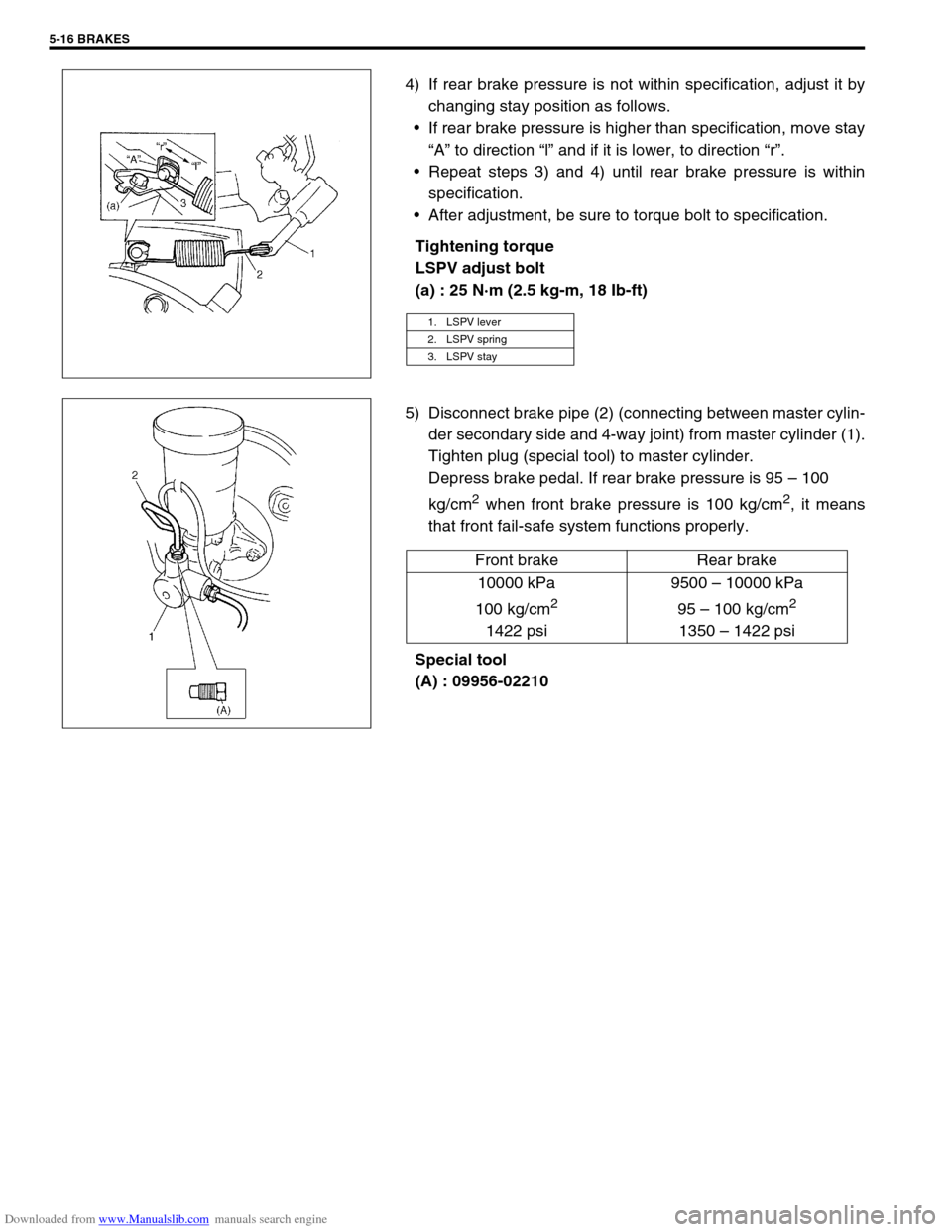
4) If rear brake pressure is not within specification, adjust it by
changing stay position as follows.
If rear brake pressure is higher than specification, move stay
“A” to direction “l” and if it is lower, to direction “r”.
Repeat steps 3) and 4) until rear brake pressure is within
specification.
After adjustment, be sure to torque bolt to specification.
Tightening torque
LSPV adjust bolt
(a) : 25 N·m (2.5 kg-m, 18 Ib-ft)
5) Disconnect brake pipe (2) (connecting between master cylin-
der secondary side and 4-way joint) from master cylinder (1).
Tighten plug (special tool) to master cylinder.
Depress brake pedal. If rear brake pressure is 95 – 100
kg/cm
2 when front brake pressure is 100 kg/cm2, it means
that front fail-safe system functions properly.
Special tool
(A) : 09956-02210
1. LSPV lever
2. LSPV spring
3. LSPV stay
Front brake Rear brake
10000 kPa
100 kg/cm
2
1422 psi9500 – 10000 kPa
95 – 100 kg/cm
2
1350 – 1422 psi
Page 279 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 5-18 BRAKES
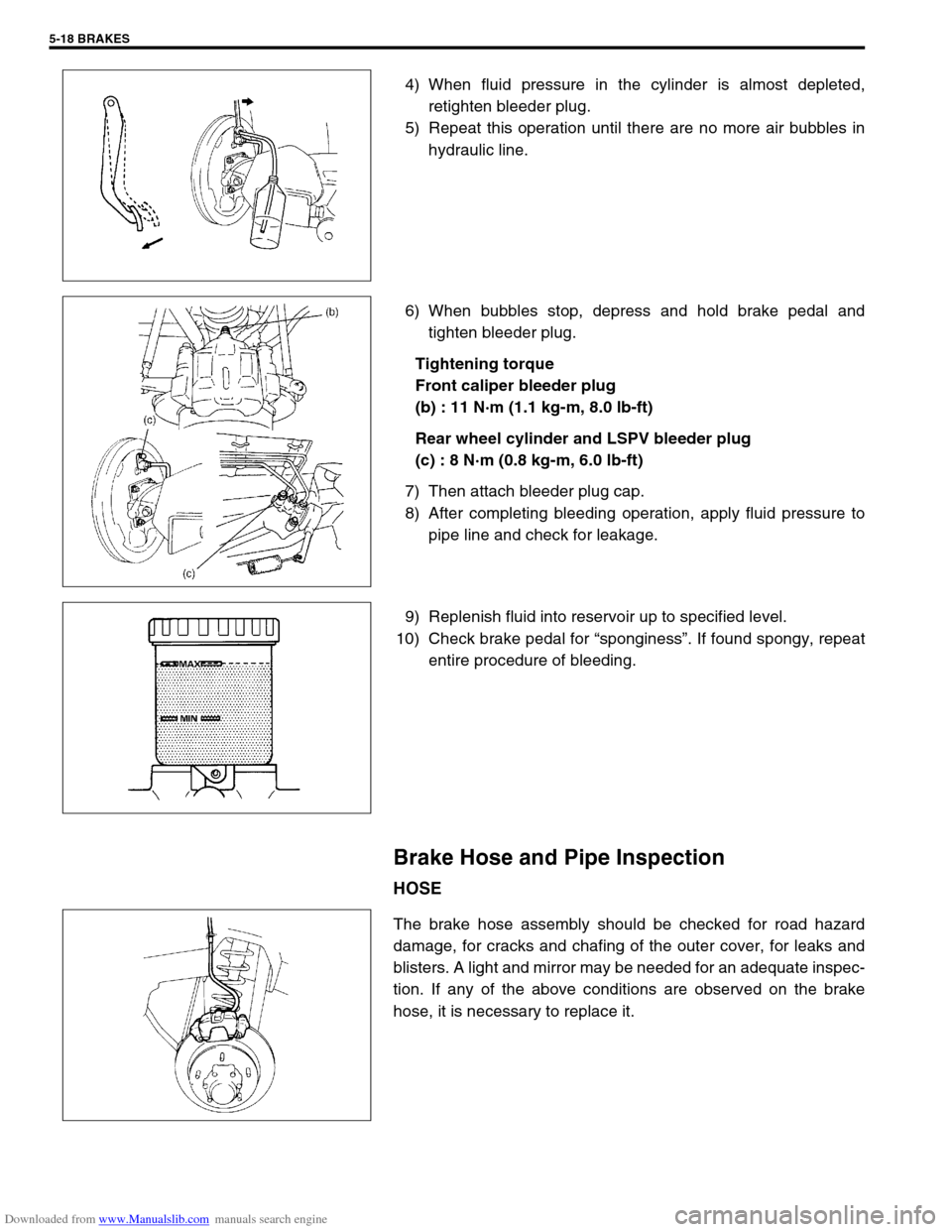
4) When fluid pressure in the cylinder is almost depleted,
retighten bleeder plug.
5) Repeat this operation until there are no more air bubbles in
hydraulic line.
6) When bubbles stop, depress and hold brake pedal and
tighten bleeder plug.
Tightening torque
Front caliper bleeder plug
(b) : 11 N·m (1.1 kg-m, 8.0 lb-ft)
Rear wheel cylinder and LSPV bleeder plug
(c) : 8 N·m (0.8 kg-m, 6.0 lb-ft)
7) Then attach bleeder plug cap.
8) After completing bleeding operation, apply fluid pressure to
pipe line and check for leakage.
9) Replenish fluid into reservoir up to specified level.
10) Check brake pedal for “sponginess”. If found spongy, repeat
entire procedure of bleeding.
Brake Hose and Pipe Inspection
HOSE
The brake hose assembly should be checked for road hazard
damage, for cracks and chafing of the outer cover, for leaks and
blisters. A light and mirror may be needed for an adequate inspec-
tion. If any of the above conditions are observed on the brake
hose, it is necessary to replace it.
Page 283 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 5-22 BRAKES
Caliper assembly
REMOVAL
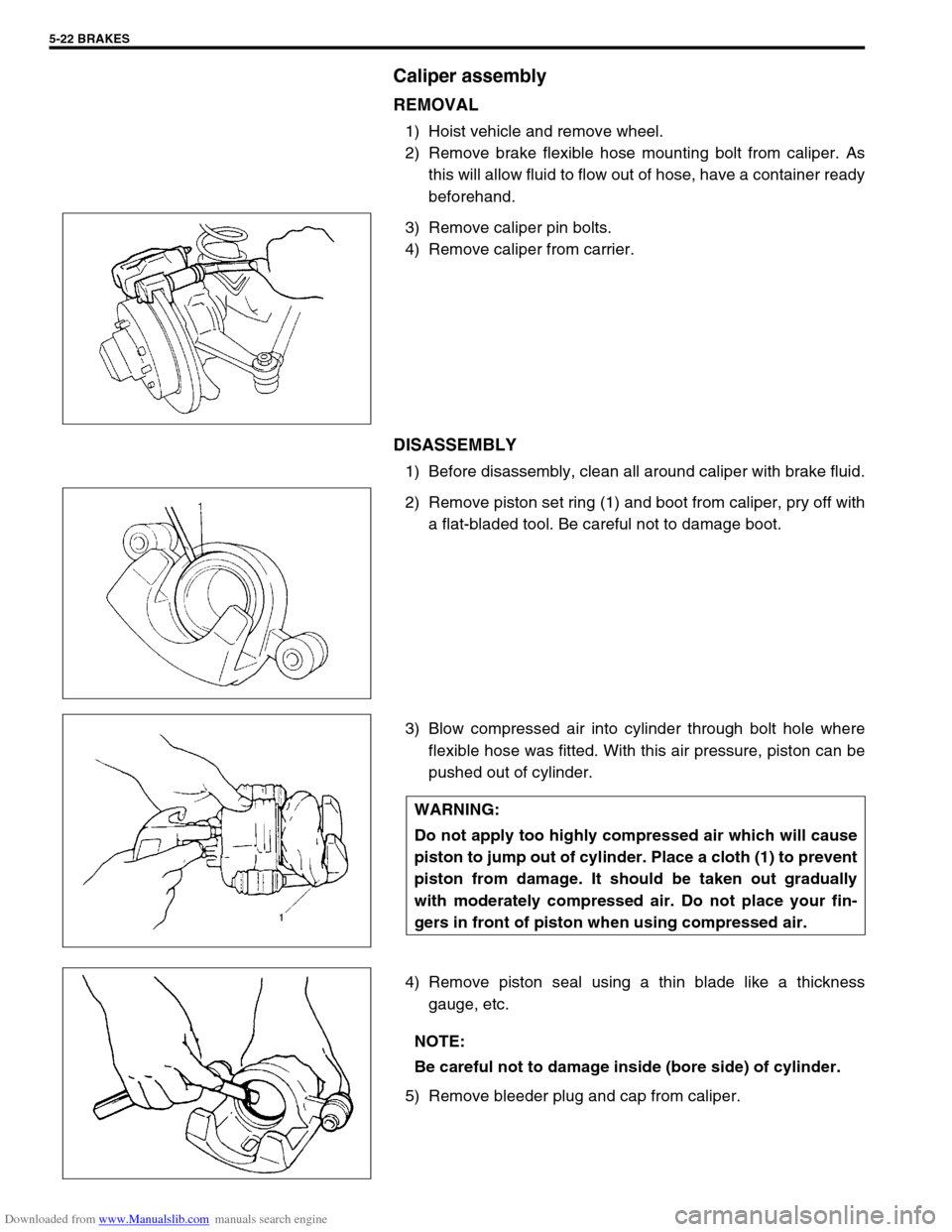
1) Hoist vehicle and remove wheel.
2) Remove brake flexible hose mounting bolt from caliper. As
this will allow fluid to flow out of hose, have a container ready
beforehand.
3) Remove caliper pin bolts.
4) Remove caliper from carrier.
DISASSEMBLY
1) Before disassembly, clean all around caliper with brake fluid.
2) Remove piston set ring (1) and boot from caliper, pry off with
a flat-bladed tool. Be careful not to damage boot.
3) Blow compressed air into cylinder through bolt hole where
flexible hose was fitted. With this air pressure, piston can be
pushed out of cylinder.
4) Remove piston seal using a thin blade like a thickness
gauge, etc.
5) Remove bleeder plug and cap from caliper.
WARNING:
Do not apply too highly compressed air which will cause
piston to jump out of cylinder. Place a cloth (1) to prevent
piston from damage. It should be taken out gradually
with moderately compressed air. Do not place your fin-
gers in front of piston when using compressed air.
NOTE:
Be careful not to damage inside (bore side) of cylinder.
Page 299 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 5-38 BRAKES
INSTALLATION
1) Install master cylinder as shown and torque attaching nuts to
specification.
Tightening torque
Master cylinder nuts
(a) : 13 N·m (1.3 kg-m, 9.5 Ib-ft)
2) Attach hydraulic lines and torque flare nuts to specification.
Tightening torque
Brake pipe flare nuts
(b) : 16 N·m (1.6 kg-m, 12.0 lb-ft)
3) Connect reservoir lead wire.
4) Fill reservoir with specified brake fluid.
5) After installing, bleed air from system (refer to “Air Bleeding
of Brake System” in this section) and check brake pedal
height and play.
6) Perform brake test and check each installed part for fluid
leakage.
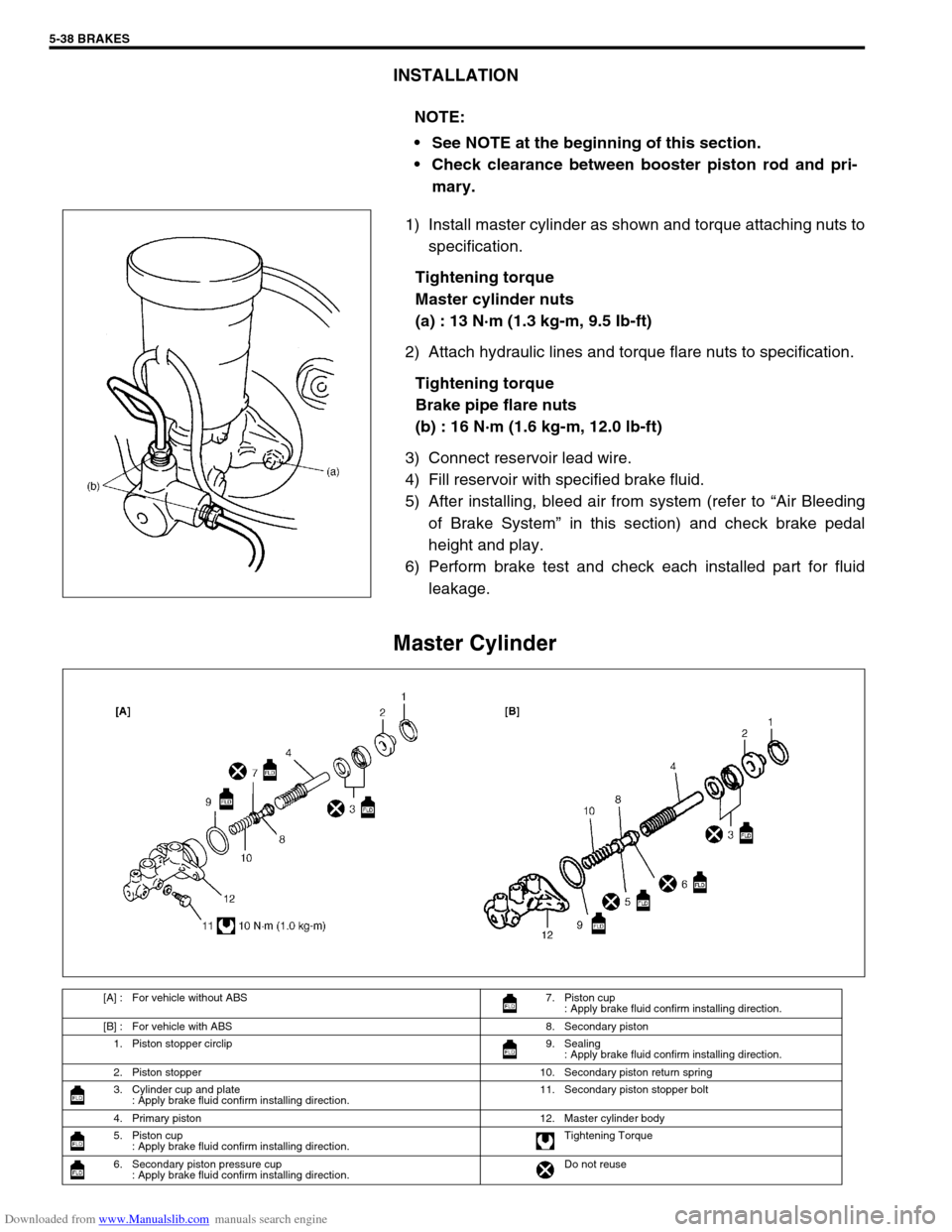
Master Cylinder
NOTE:
See NOTE at the beginning of this section.
Check clearance between booster piston rod and pri-
mary.
[A] : For vehicle without ABS 7. Piston cup
: Apply brake fluid confirm installing direction.
[B] : For vehicle with ABS 8. Secondary piston
1. Piston stopper circlip 9. Sealing
: Apply brake fluid confirm installing direction.
2. Piston stopper 10. Secondary piston return spring
3. Cylinder cup and plate
: Apply brake fluid confirm installing direction.11. Secondary piston stopper bolt
4. Primary piston 12. Master cylinder body
5. Piston cup
: Apply brake fluid confirm installing direction.Tightening Torque
6. Secondary piston pressure cup
: Apply brake fluid confirm installing direction.Do not reuse
Page 308 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine BRAKES 5-47
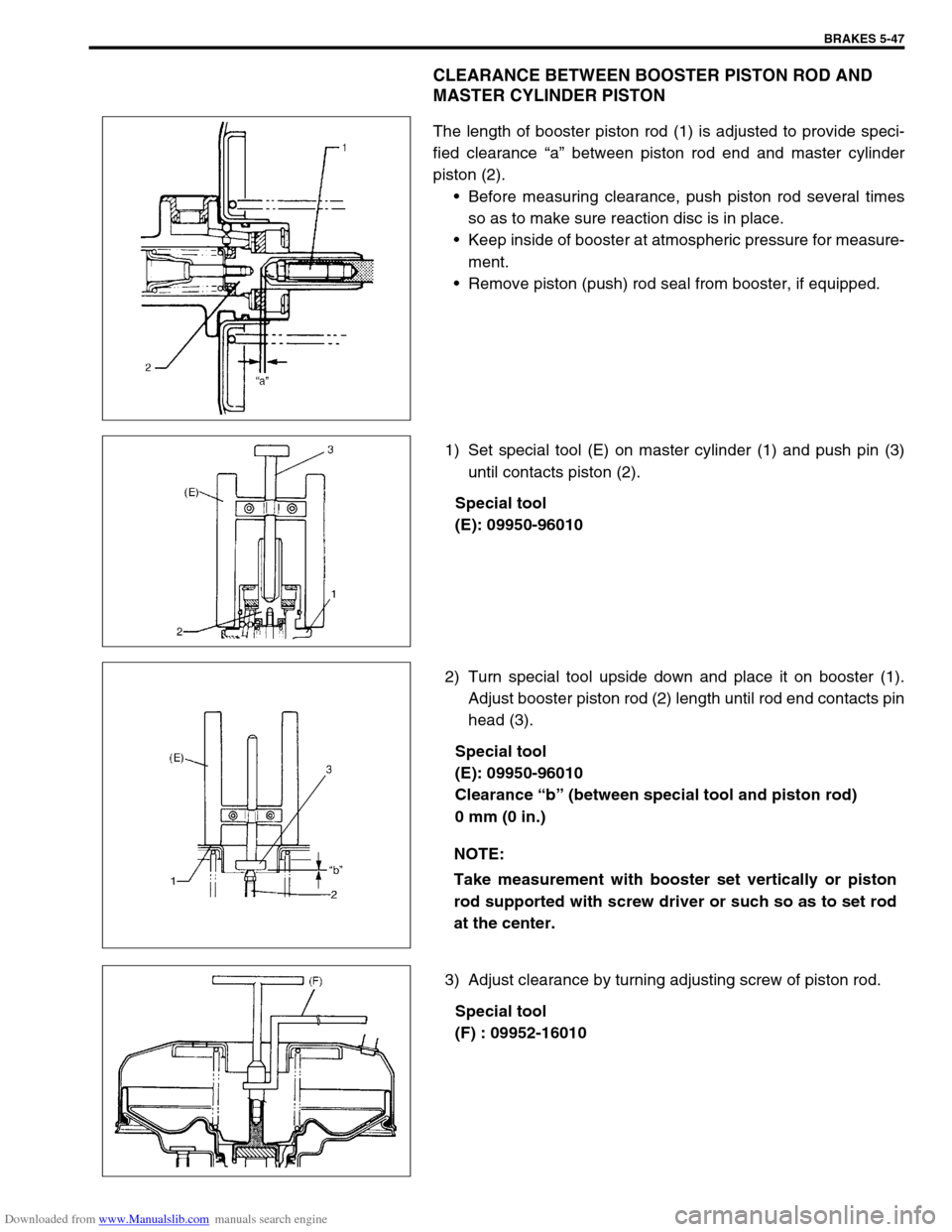
CLEARANCE BETWEEN BOOSTER PISTON ROD AND
MASTER CYLINDER PISTON
The length of booster piston rod (1) is adjusted to provide speci-
fied clearance “a” between piston rod end and master cylinder
piston (2).
Before measuring clearance, push piston rod several times
so as to make sure reaction disc is in place.
Keep inside of booster at atmospheric pressure for measure-
ment.
Remove piston (push) rod seal from booster, if equipped.
1) Set special tool (E) on master cylinder (1) and push pin (3)
until contacts piston (2).
Special tool
(E): 09950-96010
2) Turn special tool upside down and place it on booster (1).
Adjust booster piston rod (2) length until rod end contacts pin
head (3).
Special tool
(E): 09950-96010
Clearance “b” (between special tool and piston rod)
0 mm (0 in.)
3) Adjust clearance by turning adjusting screw of piston rod.
Special tool
(F) : 09952-16010
NOTE:
Take measurement with booster set vertically or piston
rod supported with screw driver or such so as to set rod
at the center.
Page 316 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine BRAKES 5-55
Special Tool
09900-20205 09900-20602 09900-20701 09956-02210
Micrometer (0 – 25 mm) Dial gauge (1/1000 mm) Magnetic stand Brake circuit plug
09922-85811 09942-15510 09943-35511 09950-78220
Connector pin remover Sliding hammer Brake drum remover
(Front wheel hub
remover)Flare nut wrench (10 mm)
09950-96010 09952-16010 09956-02310
Booster piston rod gauge Booster piston rod
adjusterFluid pressure gauge
Page 319 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 5E-2 ANTILOCK BRAKE SYSTEM (ABS)
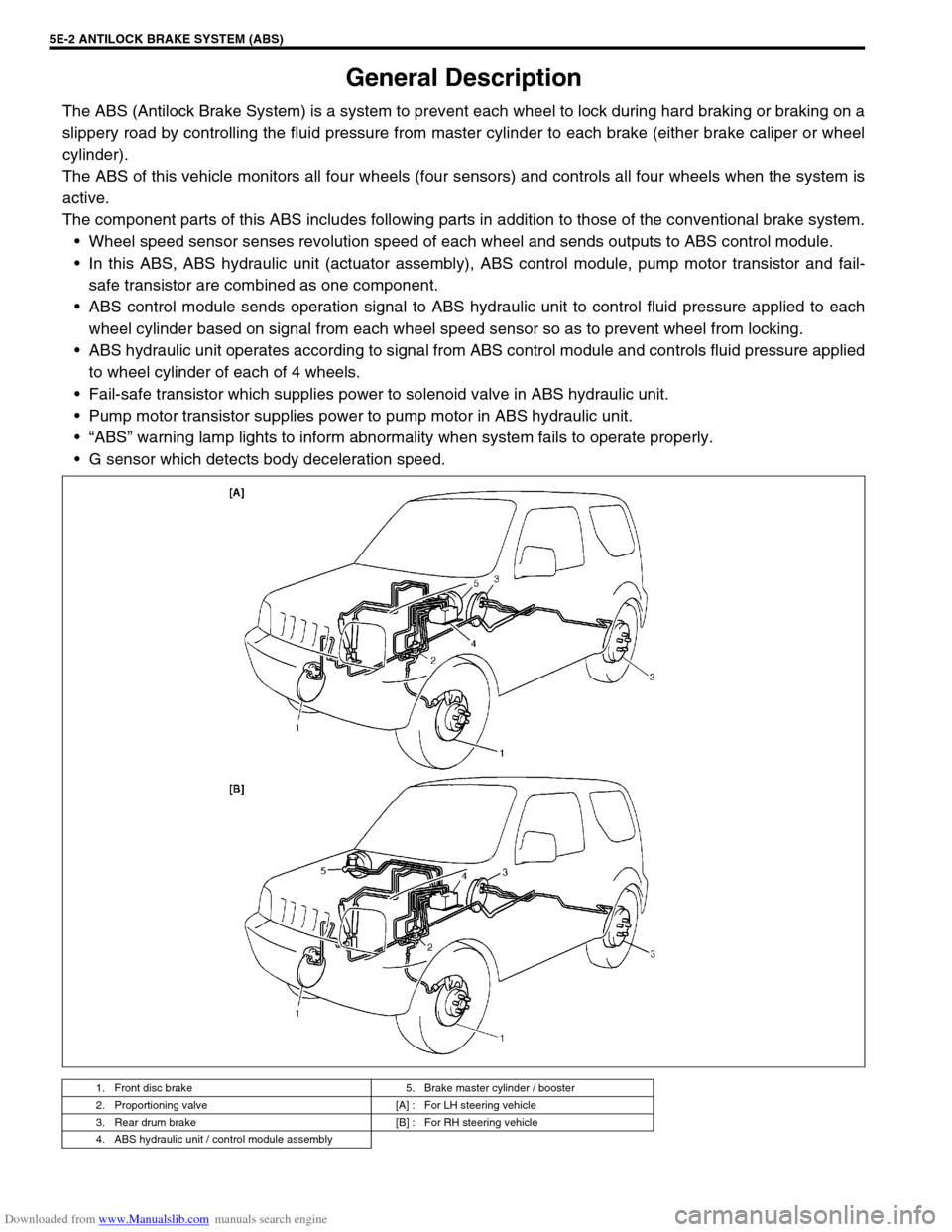
General Description
The ABS (Antilock Brake System) is a system to prevent each wheel to lock during hard braking or braking on a
slippery road by controlling the fluid pressure from master cylinder to each brake (either brake caliper or wheel
cylinder).
The ABS of this vehicle monitors all four wheels (four sensors) and controls all four wheels when the system is
active.
The component parts of this ABS includes following parts in addition to those of the conventional brake system.
Wheel speed sensor senses revolution speed of each wheel and sends outputs to ABS control module.
In this ABS, ABS hydraulic unit (actuator assembly), ABS control module, pump motor transistor and fail-
safe transistor are combined as one component.
ABS control module sends operation signal to ABS hydraulic unit to control fluid pressure applied to each
wheel cylinder based on signal from each wheel speed sensor so as to prevent wheel from locking.
ABS hydraulic unit operates according to signal from ABS control module and controls fluid pressure applied
to wheel cylinder of each of 4 wheels.
Fail-safe transistor which supplies power to solenoid valve in ABS hydraulic unit.
Pump motor transistor supplies power to pump motor in ABS hydraulic unit.
“ABS” warning lamp lights to inform abnormality when system fails to operate properly.
G sensor which detects body deceleration speed.
1. Front disc brake 5. Brake master cylinder / booster
2. Proportioning valve [A] : For LH steering vehicle
3. Rear drum brake [B] : For RH steering vehicle
4. ABS hydraulic unit / control module assembly